Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Cell-Structure-And-Organization-Mark-Schemes-For-Practical-Skills-And Discussion-Questions
Загружено:
api-268670530Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cell-Structure-And-Organization-Mark-Schemes-For-Practical-Skills-And Discussion-Questions
Загружено:
api-268670530Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
B
r
i
l
l
i
a
n
t
B
i
o
l
o
g
y
S
t
u
d
e
n
t
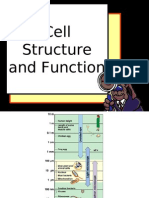
Cell Structure
& Organization
Biology Practical Skills
BrilliantBiologyStudent.weebly.com
General Guidelines
Specific Guidelines
Drawing
Wet Mount Preparation
Use of Light Microscope
Calcualtion of Magnification
Manipulation
& Measurement
Model Anwers Provided
Discussion
Questions
BrilliantBiologyStudent.weebly.com
DRAWING
TOPIC: CELL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION
AIM: To draw an animal/plant cell as seen under a light microscope
SKILL CRITERIA MARK
Drawing
Clarity
1. Clean, continuous lines of even thickness
2. No shading or unnecessary details ( some hatching is acceptable)
3. Large/Reasonable size
4. Two-dimensional
Labelling Lines
1. Neat, drawn with a ruler
2. Lines do not cross each other
3. Lines touch structures ( no arrowheads)
4. Adequate space for labelling on right
Labels/Annotations
1. All in lower case print script
2. Correctly labelled structures ( 2 all; 1- most)
3. Labels are spelled correctly (2-all; 1-most)
Accuracy
1. Structures are typical of specimen
2. Proportions are reasonable
Title
In uppercase printscript in a standard position e.g. below the drawing
Includes
o Orientation
o Name of the specimen ( and Classification)
o Stain used ( if any)
o Magnification
At the end of the title rounded up 1 d.p.
Reasonable/correctly calculated
4
4
5
2
3
Total 18
SPECIFIC GUIDELINES
The mark scheme above is a general mark scheme. For this practical in
which cell diagrams are drawn
Labels/Annotate
Animal or plant cells: cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm
Plant cell only: Cell wall, chloroplast, vacuole
Note any stained structures in annotations
Title
View: DRAWN UNDER A LIGHT MICROSCOPE
Magnification X ( magnification of eye piece * magnification of
objective lens) ; usually at 200 X magnification or more
Accuracy
One complete cell is adequate
Include parts of neighbouring cells to show relationship
BrilliantBiologyStudent.weebly.com
MEASUREMENT & MANIPULATION
SKILL
TOPIC: CELL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION
AIM: To examine animal/plant cell as seen under a light microscope
Manipulation
Measurement
Wet Mount Preparation
1. Places a small drop of relevant fluid/stain with a teat dropper
2. Lowers cover slip slowly with forceps/needle and at an angle; very
few bubbles
3. Removes excess fluid on or near coverslip with absorbent paper
4. Holds slides at the edges
Set-up and Use of Light Microscope
Care before Use
1. Carries microscope using arm, supports the base and places gently
on the bench
2. Uses lens tissue to clean lenses; does not touch with fingers
3. Turns on microscope after ensuring illumination is on minimum setting;
Adjusts the lamp setting to ~2/3 maximum
Use/Focusing the Specimen
4. Select a low-powered objective lens
5. Places the slide on the stage, with the specimen over the light; adjust
with clips
6. Low-powered objective lens
uses coarse and then fine controls
7. High-powered objective lens
checks first that the distance between the stage and lens is
adequate
uses fine controls only
Care after Use
8. Removes slide only after turning back to lowest magnification and
lowering the stage
9. Cleans stage - if necessary, cleans eyepiece with lens tissue,
10. Sets illumination at minimum and unplugs power cable, winding
around the stand, below the stage
11. Replaces dust cover, once light sources have cooled
Calculates object magnification as a product of the magnifications of the
ocular and objective lenses
4
3
5
4
2
Total 18
BrilliantBiologyStudent.weebly.com
LAB QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
1. State the function/s of any 3 visible organelles/structures (3)
Cell Wall
Provides mechanical support and maintains turgor by preventing osmotic bursting of
the cell
Cell Surface Membrane
Selectively permeable barrier which controls the exchange of substances between
the cell and its environment
Cytoplasm
Aqueous medium in which organelles and other structures are suspended. Site of most
cellular reactions
Nucleus
Contains DNA - the molecule of inheritance and controls all the activity of the cells
Chloroplast (plant cells only)
Site of photosynthesis. (May contain starch granules stain violet with iodine)
Vacuole ( large vacuoles in plant cells are easily visualized)
Sac which serves as storage for various substances. In plants the vacuole contains cell
sap sugars, mineral salts, organic acids, etc.
2. Name 3 organelles which are visible at higher resolution (electron microscopy) but are not visible
under the light microscope. (3)
Endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, centriole, lysosome
3. What is the significance of placing a drop of iodine/methylene blue/name of vital stain on the slide?
(2)
Biological structures are mostly transparent so need to be stained to create contrast and
increase visibility. Iodine/methylene blue is used to stain cells and is an example of a vital stain
(stains which are non-toxic to living tissue at low concentrations).
4. Why must the cover-slip be lowered slowly and at an angle? (1)
This technique reduces the formation of air bubbles between the cover slip and the specimen.
Air bubbles distort images and hinder observation of the specimen.
5. What is the purpose of a cover slip?(2)
The cover slip protects the objectives lens from stains, water, oils (for oil immersion) and dirt. It
also prevents the specimen from drying out, and undergoing structural changes/deterioration as
it becomes crenated (animal cell) or plasmolyzed (plant cell).
Вам также может понравиться
- Collins Book 1 PDF FreeДокумент214 страницCollins Book 1 PDF FreeSơnSơnОценок пока нет
- Topic 9 Plant Biology IB Biology 9.2 Transport in The Phloem of Plants Nature of Science: Developments in Scientific Research Follow Improvements in Apparatus: ExperimentalДокумент4 страницыTopic 9 Plant Biology IB Biology 9.2 Transport in The Phloem of Plants Nature of Science: Developments in Scientific Research Follow Improvements in Apparatus: ExperimentalMoahmed Mahmoud IB15A 363KAGYОценок пока нет
- Cambridge Science Worksheet 8Документ13 страницCambridge Science Worksheet 8ozmanОценок пока нет
- Osmosis Diffusion Lab-1Документ7 страницOsmosis Diffusion Lab-1api-1658690000% (1)
- Photosynthesis Chapter 8 30616 PDFДокумент24 страницыPhotosynthesis Chapter 8 30616 PDFGilberto Ragnar NodarseОценок пока нет
- Water Potential Word ProblemsДокумент1 страницаWater Potential Word Problemsapi-524061079Оценок пока нет
- Cell Structure and FunctionДокумент41 страницаCell Structure and FunctionAhkyluzLaniaz100% (1)
- IGCSE Biology Course PlanДокумент7 страницIGCSE Biology Course PlaneeappleОценок пока нет
- Grade 11 12 Science CurrДокумент264 страницыGrade 11 12 Science Currapi-301141568Оценок пока нет
- 4th Grade: ScienceДокумент9 страниц4th Grade: Scienceapi-355029044Оценок пока нет
- Ib Biology Syllabus-NewДокумент20 страницIb Biology Syllabus-NewVishnu SharmaОценок пока нет
- Biology A2 Snab CourseworkДокумент120 страницBiology A2 Snab CourseworkIshwarya SivakumarОценок пока нет
- Disease of The Nervous System AssignmentДокумент3 страницыDisease of The Nervous System Assignmentapi-290895709100% (1)
- 3.2 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins WORDДокумент6 страниц3.2 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins WORDCaitlin Barrett100% (1)
- Practice Questions Topic 1.4 IB BiologyДокумент12 страницPractice Questions Topic 1.4 IB BiologySamantha DAIROОценок пока нет
- AP Biology Syllabus 2009-2010Документ10 страницAP Biology Syllabus 2009-2010yulianaholicОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 TestДокумент5 страницUnit 1 Testapi-485795043Оценок пока нет
- Concepts of BiologyДокумент35 страницConcepts of Biologyamir khanОценок пока нет
- Formative Assessment BiologyДокумент2 страницыFormative Assessment Biologyroosita damayantiОценок пока нет
- Prokaryotic Cells: Cell Membrane Cell Wall Capsule Pili Plasmid Flagella Nucleoid Region Ribosomes CytoplasmДокумент3 страницыProkaryotic Cells: Cell Membrane Cell Wall Capsule Pili Plasmid Flagella Nucleoid Region Ribosomes CytoplasmErvin WilliamsОценок пока нет
- COAS Biology 1 Chapter 1Документ23 страницыCOAS Biology 1 Chapter 1Daniel Conway100% (1)
- IB BIOLOGY SL TOPIC 3 Nucleic Acids & Proteins and Chemical Elements & WaterДокумент13 страницIB BIOLOGY SL TOPIC 3 Nucleic Acids & Proteins and Chemical Elements & WaterweeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11 Review PacketДокумент17 страницChapter 11 Review PacketLalisampt.20% (1)
- Biology Unit PlanДокумент10 страницBiology Unit Planapi-246097943Оценок пока нет
- Unit 4 Revision Notes SNAB Topics 5 & 6 A2Документ38 страницUnit 4 Revision Notes SNAB Topics 5 & 6 A2Olivia Panterka Vainilla100% (2)
- BiologyДокумент76 страницBiologycabdifataxОценок пока нет
- Cell SurfaceДокумент3 страницыCell SurfaceNabindra RuwaliОценок пока нет
- C 1 1 2025 Topic Test MsДокумент4 страницыC 1 1 2025 Topic Test MsRawanMazen SharifОценок пока нет
- Questions IBДокумент7 страницQuestions IBJohn OsborneОценок пока нет
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells WorksheetsДокумент17 страниц1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells WorksheetsZaigham ZiaОценок пока нет
- H2 Biology - Notes On Genetics of BacteriaДокумент10 страницH2 Biology - Notes On Genetics of BacteriaSefLRho0% (1)
- TOPIC 3 CELL AND NUCLEAR DIVISION My Notes 2020Документ20 страницTOPIC 3 CELL AND NUCLEAR DIVISION My Notes 2020reeОценок пока нет
- New Syllabus Questions Part OneДокумент19 страницNew Syllabus Questions Part OneKhaled Dabour100% (1)
- Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis PDFДокумент50 страницCell Division Mitosis Meiosis PDFRozel EncarnacionОценок пока нет
- IB Biology Photosynthesis IAДокумент12 страницIB Biology Photosynthesis IAAshwinОценок пока нет
- New World International School Biology Igcse Notes Chapter - 1Документ15 страницNew World International School Biology Igcse Notes Chapter - 1Noor Samir100% (1)
- Study Guide Questions StudentДокумент4 страницыStudy Guide Questions Studentapi-299996815Оценок пока нет
- Revision Biology Midyear Exam 2011 - Stage 1 SACEДокумент2 страницыRevision Biology Midyear Exam 2011 - Stage 1 SACENhi HinОценок пока нет
- Summary Notes - Topic 6 Microbiology, Immunity and Forensics - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelДокумент11 страницSummary Notes - Topic 6 Microbiology, Immunity and Forensics - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelsalmaОценок пока нет
- As Level BiologyДокумент18 страницAs Level BiologyAasiya SultanaОценок пока нет
- Characteristics and Classification of Living Organisms: IGCSE Biology (O610) WorkbookДокумент14 страницCharacteristics and Classification of Living Organisms: IGCSE Biology (O610) WorkbookDr-Qussai ZuriegatОценок пока нет
- MCQs of Plant TransportationДокумент5 страницMCQs of Plant Transportationprofessor zulfi100% (2)
- Teaching Scheme - A2 ConceptДокумент7 страницTeaching Scheme - A2 Conceptaby251188Оценок пока нет
- 3-1 Cell Cycle ActivityДокумент3 страницы3-1 Cell Cycle Activityanon_374314835Оценок пока нет
- Question Bank in Biology Class XIIДокумент64 страницыQuestion Bank in Biology Class XIIaleena'Оценок пока нет
- Corkscrew Swamp Field Trip ReportДокумент7 страницCorkscrew Swamp Field Trip ReportKarolina Terra100% (1)
- Respiration and Excretion Chapter 16 TestДокумент4 страницыRespiration and Excretion Chapter 16 TestAnonymous KgU0Oh3Оценок пока нет
- Biology Worksheets - XIIДокумент188 страницBiology Worksheets - XIIlatishabasilОценок пока нет
- Topic 5 MsДокумент22 страницыTopic 5 Msbody fayezОценок пока нет
- Enzymes (AS Level Bio)Документ23 страницыEnzymes (AS Level Bio)DrMufaddal RampurwalaОценок пока нет
- 3 Enzymes Paper 2 - N-MQДокумент67 страниц3 Enzymes Paper 2 - N-MQMostafa AmerОценок пока нет
- Final Bioa 2015Документ10 страницFinal Bioa 2015api-237801056100% (1)
- Homework 7 J23.Документ15 страницHomework 7 J23.mauoshaОценок пока нет
- JujuScientific ProblemДокумент50 страницJujuScientific ProblemJuan LunaОценок пока нет
- 6bi04 Mark Scheme Edexcel A2 BiologyДокумент18 страниц6bi04 Mark Scheme Edexcel A2 BiologySumana MalekОценок пока нет
- iGCSE-revision-mindmaps-new-specification-double-award ANSWERS Year 10 ModДокумент25 страницiGCSE-revision-mindmaps-new-specification-double-award ANSWERS Year 10 Modlily wongОценок пока нет
- Science Strategies to Increase Student Learning and Motivation in Biology and Life Science Grades 7 Through 12От EverandScience Strategies to Increase Student Learning and Motivation in Biology and Life Science Grades 7 Through 12Оценок пока нет
- Hyundai HL780-3AДокумент636 страницHyundai HL780-3AAnonymous yjK3peI740% (5)
- Emkarate RL 32H: Material Safety Data Sheet Date Revised: Feb, 2008Документ6 страницEmkarate RL 32H: Material Safety Data Sheet Date Revised: Feb, 2008angelo collaОценок пока нет
- University of Santo Tomas: Williamson Ether Synthesis: Preparation of PhenacetinДокумент4 страницыUniversity of Santo Tomas: Williamson Ether Synthesis: Preparation of PhenacetinMarilou MagdalagaОценок пока нет
- Chem Final Notes UsydДокумент5 страницChem Final Notes UsydRobs0% (1)
- AMPCO 18 SandДокумент1 страницаAMPCO 18 SandS BHATTACHARYYAОценок пока нет
- Water Quality - Vocabulary - : British Standard Bs Iso 6107-3:1993 BS 6068-1.3: 1993Документ13 страницWater Quality - Vocabulary - : British Standard Bs Iso 6107-3:1993 BS 6068-1.3: 1993Thomas ValoОценок пока нет
- TUGAS STHE - Achri Isnan Khamil - Kelas A - 191910401008 SalinanДокумент13 страницTUGAS STHE - Achri Isnan Khamil - Kelas A - 191910401008 SalinanAditya Haswarna PutraОценок пока нет
- ASTM D7393-07 (2012) Standard Practice For Indicating Oil in AbrasivesДокумент2 страницыASTM D7393-07 (2012) Standard Practice For Indicating Oil in Abrasivesalexander zuritaОценок пока нет
- Preparation of Tin TetraiodideДокумент2 страницыPreparation of Tin Tetraiodidestudent_4_evaОценок пока нет
- Point Source Nonpoint Source PollutionДокумент2 страницыPoint Source Nonpoint Source PollutionHwangMiyoungОценок пока нет
- Thurmalox 8200 Painting SpecificationДокумент2 страницыThurmalox 8200 Painting SpecificationFreddy Carl FredricksenОценок пока нет
- Automated Sorting of Polymer Flakes Fluorescence Labeling and Development of A Measurement System PrototypeДокумент12 страницAutomated Sorting of Polymer Flakes Fluorescence Labeling and Development of A Measurement System PrototypeSəkinə ƏliyevaОценок пока нет
- Magnum CV and Magnum IT Valves Installation InstructionsДокумент86 страницMagnum CV and Magnum IT Valves Installation InstructionsWattsОценок пока нет
- 131 - 1.9.1.2-95MXC - UltraHardДокумент4 страницы131 - 1.9.1.2-95MXC - UltraHardJSH100Оценок пока нет
- Valve StandardsДокумент15 страницValve StandardsabduОценок пока нет
- Design of Steel StructureДокумент16 страницDesign of Steel StructureRajarshi ChakrabortyОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Equilibrium WorksheetДокумент5 страницChemistry Equilibrium WorksheetMarkОценок пока нет
- Water Supply Sanitary Eng PDFДокумент5 страницWater Supply Sanitary Eng PDFReddy NaveenОценок пока нет
- Media Search - SEBU6400 - Cat Gas Engine Lubricant SOSДокумент4 страницыMedia Search - SEBU6400 - Cat Gas Engine Lubricant SOSThepowerОценок пока нет
- Jack WelchДокумент5 страницJack Welchapi-314805892Оценок пока нет
- Primary ClarifierДокумент26 страницPrimary ClarifierDavid Charles Meissner100% (3)
- Predicting Production Performance of A Field With Complex Reservoir Heterogeneities Undergoing Water Injection - A Case Study of A Niger-Delta FieldДокумент14 страницPredicting Production Performance of A Field With Complex Reservoir Heterogeneities Undergoing Water Injection - A Case Study of A Niger-Delta FieldnoorОценок пока нет
- Varshini KO-Araviind SДокумент178 страницVarshini KO-Araviind SDhaksha AnieshОценок пока нет
- ReviewerДокумент7 страницReviewerAriel Mark Pilotin50% (2)
- The Pneumatics Installation GuideДокумент186 страницThe Pneumatics Installation GuideHAMIT100% (1)
- NJ Mpje PDFДокумент168 страницNJ Mpje PDFPatrick Mata100% (3)
- People VS PascuaДокумент11 страницPeople VS PascuaShiena Lou B. Amodia-RabacalОценок пока нет
- Refineries: Application Focus: HydroprocessingДокумент4 страницыRefineries: Application Focus: HydroprocessingmudrikaОценок пока нет
- 2023 o Level Chemistry SyllabusДокумент56 страниц2023 o Level Chemistry SyllabusFooxОценок пока нет