Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Atiral Fib
Загружено:
api-2684054710 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
91 просмотров15 страницОригинальное название
atiral fib
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
91 просмотров15 страницAtiral Fib
Загружено:
api-268405471Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 15
Atrial fibrillation
By: Kaytlyn Stephens, Mariette Armitstead, and Tonia Nielsen
What is a dysrhythmia?
A cardiac dysrhythmia is an abnormal heart beat: the rhythm may
be irregular in its pacing or the heart rate may be low or high.
Some dysrhythmias are potentially life threatening while other
dysrhythmias (such as sinus arrhythmia) and normal.
Supraventricular Dysrhythmias
Dysrhythmias that originate in the atria are termed
supraventricular dysrhythmias (supraventricular means above the
ventricles). These dysrhythmias include:
Atrial flutter
Atrial fibrillation
Paroxysmal Supraventricular tachycardia
Premature Atrial Contractions(PAC)
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
Ventricular Dysrhythmias
Ventricular dysrhythmias begin in the ventricles
and include:
Ventricular fibrillation
Ventricular Tachycardia
Premature ventricular contractions
Long QT syndrome
Dysthymias
Tachycardia is a fast (over 100 beats per minute) heart rhythm.
Tachycardia's can originate in the atria or ventricles.
Bradycardia is a slow (under 60 beats per minute) heart rhythm.
Sinus bradycardia
Conduction Block
Sick Sinus Syndrome
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (also called AFib or AF) is a quivering or irregular
heartbeat (arrhythmia) that can lead to blood clots, stroke, heart
failure and other heart-related complications.
Pathophysiology
Caused by atrial fibrosis, and lost of atrial muscle mass.
The regular impulses produced by the sinus node to provide
rhythmic contraction of the heart are overwhelmed by the rapid
randomly generated electrical discharges produced by larger areas
of triggering atrial tissue.
The atria is not quadrated with the ventricles
Etiology
Abnormalities or damage to the heart's structure are the most common cause of
atrial fibrillation. Possible causes of atrial fibrillation include:
High blood pressure
Mitral regurg, Mitral stenosis
Hypoxia
Heart attacks
Coronary artery disease
Abnormal heart valves
Heart defects you're born with (congenital)
An overactive thyroid gland or other metabolic imbalance
Exposure to stimulants, such as medications, caffeine or tobacco, or to alcohol
Previous heart surgery
Viral infections
Risk Factors
Age
Heart disease
Chronic Disease
such as thyroid problems, sleep apnea, metabolic syndrome, diabetes,
chronic kidney disease or lung disease
High blood pressure
especially if it's not well-controlled with lifestyle changes or medication
Drinking alcohol
Obesity
Family history
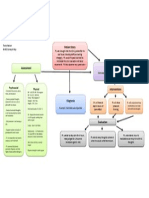
Nursing Diagnosis
What are some nursing diagnosis
for a patient with A-Fib?
Nursing Diagnosis
Decreased Cardiac Output R/T Alterations in rate, rhythm,
electrical conduction AEB decrease BP, chest pain, Irregular
HR, pale and dyspnea.
Goal: increase cardiac output
Interventions:
Continuously monitor EKG.
Assess and document vitals and physical symptoms every 30 minutes
Supplemental O2.
Be prepared for cardioversion.
Outcome: Patient will have increased cardiac output
Nursing Diagnosis
Decreased cardiac output R/T alteration in heart rate and rhythm
AEB irregular heart rate and BP 96/50.
Goals: Pt. will maintain BP within normal limits. Pt. will have
regular cardiac rhythm.
Interventions:
Administer medications as prescribed and assess the effects of the
medications to see if helping the cardiac rhythm to be normal
Outcome: Patient maintains normal BP and has regular rhythem
Nursing Diagnosis
Anxiety RT Atrial fibrillation AEB pt statements of anxiety,
restlessness, diaphoresis, increased BP, and tachycardia
Goal: Pt will have reduced anxiety
Intervention:
Orient client to environment, equipment, medications, and routine.
Outcome: Pt was oriented to environment, equipment,
medications, and routine.
Patient Education
Explain why they are on an anticoagulant drug
They are an increased risk for stroke because of the clotting in the heart
Heart Rate control is very important.
Medications such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and digitalis can be used to
help slow conduction of electrical impulses over the AV node to maintain a heart rate less
than 80 beats per minute at rest.
Know S/S of an episode of A-Fib
Palpitations, which are sensations of a racing, uncomfortable, irregular heartbeat or a
flip-flopping in your chest
Weakness
Reduced ability to exercise
Fatigue
Lightheadedness
Dizziness
Confusion
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Patient Education
Cardio version
cardioversion is a medical procedure done to restore a normal heart rhythm
for people who have certain heart rhythm disorders such as atrial
fibrillation.
If A-Fib as lasted longer than 48 hours
It is most often done by sending electric shocks to your heart through
electrodes placed on your chest (electrical cardioversion). Occasionally,
your doctor may perform cardioversion using only medications to restore
your heart's rhythm.
Вам также может понравиться
- Bmed Concept MapДокумент1 страницаBmed Concept Mapapi-268405471Оценок пока нет
- Caring PaperДокумент4 страницыCaring Paperapi-268405471Оценок пока нет
- Ebp AssignmentДокумент1 страницаEbp Assignmentapi-268405471Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Process vs. Critical Thinking: Which Is Best For Clinical Judgment? Tonia Nielsen Dixie State UniversityДокумент5 страницNursing Process vs. Critical Thinking: Which Is Best For Clinical Judgment? Tonia Nielsen Dixie State Universityapi-268405471Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Philosophy PaperДокумент6 страницNursing Philosophy Paperapi-268405471Оценок пока нет
- Nursing ResumeДокумент2 страницыNursing Resumeapi-268405471Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Cover LetterДокумент1 страницаNursing Cover Letterapi-268405471Оценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- MfA Leadership ExperienceДокумент49 страницMfA Leadership ExperienceAlex MoralesОценок пока нет
- Amy L. Lansky - Impossible Cure - The Promise of HomeopathyДокумент295 страницAmy L. Lansky - Impossible Cure - The Promise of Homeopathybjjman88% (17)
- CSR Activities by TATAДокумент13 страницCSR Activities by TATAMegha VaruОценок пока нет
- Umbar - Performance Task 7Документ3 страницыUmbar - Performance Task 7Bella CiaoОценок пока нет
- Catalogo Baby MarketДокумент53 страницыCatalogo Baby Marketmiguel quispeОценок пока нет
- Estimation of Blood GlucoseДокумент3 страницыEstimation of Blood Glucosepodcast gazalОценок пока нет
- Rule On Adoption AM NO. 02-6-02-SCДокумент16 страницRule On Adoption AM NO. 02-6-02-SCAnathea Cadagat100% (1)
- AishwaryaДокумент52 страницыAishwaryamohitОценок пока нет
- Job Application LetterДокумент12 страницJob Application LetterIcha Aisah100% (3)
- HB2704IДокумент6 страницHB2704IJENNIFER WEISERОценок пока нет
- The Varsity 39Документ254 страницыThe Varsity 39cosmin_bloju8997Оценок пока нет
- CDCS French Forein MinistryДокумент36 страницCDCS French Forein MinistryZakaria ABBIOUIОценок пока нет
- Final Sheet MotalityДокумент69 страницFinal Sheet MotalityAshima GabgotraОценок пока нет
- Im9 2002 PDFДокумент89 страницIm9 2002 PDFV1QT0RОценок пока нет
- Hong Kong Dental Journal - Volume 2 - Number 2 - YuLeungДокумент1 страницаHong Kong Dental Journal - Volume 2 - Number 2 - YuLeungFebySiampaОценок пока нет
- Group 2 - Up-Fa1-Stem11-19 - Chapter IiДокумент7 страницGroup 2 - Up-Fa1-Stem11-19 - Chapter IijamesrusselОценок пока нет
- Ch5 PDFДокумент35 страницCh5 PDFsandeepОценок пока нет
- Annual Leave Policy of University of YorkДокумент15 страницAnnual Leave Policy of University of YorkJohn Son100% (1)
- Lse Su Gym: Membership Application FormДокумент2 страницыLse Su Gym: Membership Application Formgregorioalejandro05Оценок пока нет
- 7th Edition NRP Brings Big Changes For NRP Instructors: Instructor UpdateДокумент12 страниц7th Edition NRP Brings Big Changes For NRP Instructors: Instructor UpdateJoev SaquinОценок пока нет
- Group 3 Oral Bioavailability EditedДокумент10 страницGroup 3 Oral Bioavailability EditedBaguma MichaelОценок пока нет
- Kinds of Blood. Differences Between Men and WomenДокумент11 страницKinds of Blood. Differences Between Men and WomenTiagoSantosОценок пока нет
- ApproachPerformance 01 PDFДокумент6 страницApproachPerformance 01 PDFAdam MazurekОценок пока нет
- Maslow TheoryДокумент10 страницMaslow Theoryraza20100% (1)
- StoryДокумент6 страницStoryGerard NicholasОценок пока нет
- Predictive Models Receiver-Operating Characteristic Analysis For Evaluating Diagnostic Tests andДокумент5 страницPredictive Models Receiver-Operating Characteristic Analysis For Evaluating Diagnostic Tests andLucila Figueroa GalloОценок пока нет
- Brasso Metal Polish v1.3 D8340649 PDFДокумент10 страницBrasso Metal Polish v1.3 D8340649 PDFNia PuanОценок пока нет
- Fetal Mummification in CowsДокумент22 страницыFetal Mummification in CowsTahseen AlamОценок пока нет
- H. Pylori IgA ELISA Package InsertДокумент2 страницыH. Pylori IgA ELISA Package Inserttalha saleemОценок пока нет
- Summary of Wind Turbine Accident Data To 31 December 2016Документ6 страницSummary of Wind Turbine Accident Data To 31 December 2016أحمد دعبسОценок пока нет