Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Energy Analysis of Ideal Rankine Cycle: Thermodynamics - II
Загружено:
samhameed20 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
5 просмотров11 страницThe document discusses the ideal Rankine cycle, which involves four main components: a turbine, condenser, pump, and boiler. It analyzes the energy transfers and balances within each component, assuming they are control volumes at steady state. The document also covers performance parameters for the Rankine cycle such as thermal efficiency and heat rate, defined as the heat input required to generate 1 kWh of electricity. An example problem is presented to demonstrate the calculations.
Исходное описание:
thrermodynamics
Оригинальное название
Lec 2_Ch 10
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe document discusses the ideal Rankine cycle, which involves four main components: a turbine, condenser, pump, and boiler. It analyzes the energy transfers and balances within each component, assuming they are control volumes at steady state. The document also covers performance parameters for the Rankine cycle such as thermal efficiency and heat rate, defined as the heat input required to generate 1 kWh of electricity. An example problem is presented to demonstrate the calculations.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
5 просмотров11 страницEnergy Analysis of Ideal Rankine Cycle: Thermodynamics - II
Загружено:
samhameed2The document discusses the ideal Rankine cycle, which involves four main components: a turbine, condenser, pump, and boiler. It analyzes the energy transfers and balances within each component, assuming they are control volumes at steady state. The document also covers performance parameters for the Rankine cycle such as thermal efficiency and heat rate, defined as the heat input required to generate 1 kWh of electricity. An example problem is presented to demonstrate the calculations.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 11
Thermodynamics - II
Lecture 2
Energy Analysis of Ideal Rankine
Cycle (Ch-10)
Zia Ud Din
Evaluating Ideal Rankine Cycle:
Principal Work and Heat Transfers:
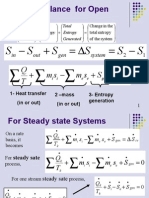
TURBINE: It involves one-inlet, one-exit CV at steady state.
Applying the energy rate balance (Q = 0 for turbine)
Evaluating Ideal Rankine Cycle:
Principal Work and Heat Transfers:
CONDENSER: It involves one-inlet, one-exit CV at steady state.
Applying the energy rate balance (W = 0 for condenser)
Evaluating Ideal Rankine Cycle:
Principal Work and Heat Transfers:
PUMP: It involves one-inlet, one-exit CV at steady state. Applying
the energy rate balance (Q = 0 for pump)
Evaluating Ideal Rankine Cycle:
Principal Work and Heat Transfers:
BOILER:
It involves one-inlet, one-exit CV at steady state.
Applying the energy rate balance (W = 0 for boiler)
Evaluating Ideal Rankine Cycle:
Performance Parameters:
Thermal Efficiency:
Evaluating Ideal Rankine Cycle:
Performance Parameters:
Thermal Efficiency/ Heat Rate:
The efficiency of power plants in the U.S. is often expressed in
terms of heat rate, which is the amount of heat supplied, in Btus,
to generate 1 kWh of electricity.
Back Work Ratio:
Ratio of the pump work input to the work developed by the turbine
Example 10-1
Example 10-1
Example 10-1
10
Example 10-1
11
Вам также может понравиться
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2От EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Оценок пока нет
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1От EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Рейтинг: 2.5 из 5 звезд2.5/5 (3)
- EntropyДокумент46 страницEntropyAnonymous UqsAfi100% (1)
- Analysis of Engineering Cycles: Power, Refrigerating and Gas Liquefaction PlantОт EverandAnalysis of Engineering Cycles: Power, Refrigerating and Gas Liquefaction PlantОценок пока нет
- Chap 1 - Steam Power PlantДокумент60 страницChap 1 - Steam Power PlantMuhammad Qusyairi100% (2)
- Thermodynamics 2 Rankine CycleДокумент207 страницThermodynamics 2 Rankine CycleRyan TegioОценок пока нет
- Ch1 - Steam Power PlantsДокумент43 страницыCh1 - Steam Power PlantsShiau Fen100% (1)
- Rankine Cycle PDFДокумент41 страницаRankine Cycle PDFAlmeghalawy83% (12)
- Heat Pump - Refrigeration and LiquefactionДокумент72 страницыHeat Pump - Refrigeration and LiquefactionhananОценок пока нет
- Coal Fired Power Plants: Background Thermodynamics and IntroductionДокумент43 страницыCoal Fired Power Plants: Background Thermodynamics and IntroductionDurgesh SharmaОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics 2 - Rankine CycleДокумент207 страницThermodynamics 2 - Rankine CycleStudentAssistant200981% (31)
- Thermodynamics 2 Rankine CycleДокумент214 страницThermodynamics 2 Rankine CycleDebbie Diane MarananОценок пока нет
- Ch1 - Steam Power PlantsДокумент44 страницыCh1 - Steam Power PlantsSyahir LokhmanОценок пока нет
- Ideal Regenerative Rankine Cycle - Closed Feedwater Heaters: Thermodynamics - IIДокумент10 страницIdeal Regenerative Rankine Cycle - Closed Feedwater Heaters: Thermodynamics - IIsamhameed2Оценок пока нет
- Lec 15 16 - CH 9 BRAYTON TurbineДокумент17 страницLec 15 16 - CH 9 BRAYTON Turbinesamhameed2100% (1)
- Steam Power Plants (System)Документ58 страницSteam Power Plants (System)Hafzal Gani100% (1)
- ThermodynamicsДокумент26 страницThermodynamicsManikanta Reddy100% (1)
- Rankine Cycle: Figures From Cengel and Boles, Thermodynamics, An Engineering Approach, 6 Ed., Mcgraw Hill, 2008Документ17 страницRankine Cycle: Figures From Cengel and Boles, Thermodynamics, An Engineering Approach, 6 Ed., Mcgraw Hill, 2008JunaldiОценок пока нет
- Rankine Cycle: Figures From Cengel and Boles, Thermodynamics, An Engineering Approach, 6 Ed., Mcgraw Hill, 2008Документ17 страницRankine Cycle: Figures From Cengel and Boles, Thermodynamics, An Engineering Approach, 6 Ed., Mcgraw Hill, 2008Gerald GregorioОценок пока нет
- Ch.2.Regenerative Rankine Cycle With Closed Feed Water HeaterДокумент55 страницCh.2.Regenerative Rankine Cycle With Closed Feed Water Heaterlayanalfar0Оценок пока нет
- Lecture-02-Thermal Power PlantДокумент21 страницаLecture-02-Thermal Power PlantTahir DedefoОценок пока нет
- PTG EnginesДокумент62 страницыPTG Enginesnona wayne dela peñaОценок пока нет
- Module 5: Vapour and Refrigeration Cycles: Dr. Feroskhan M Associate Professor, SMECДокумент63 страницыModule 5: Vapour and Refrigeration Cycles: Dr. Feroskhan M Associate Professor, SMECAgilan ChellaramОценок пока нет
- Faculty of Engineering: TutorialДокумент13 страницFaculty of Engineering: TutorialDavid ChikuseОценок пока нет
- Rankine CycleДокумент17 страницRankine CycleM.ThirunavukkarasuОценок пока нет
- Gas Power Cycles: Cengel & BolesДокумент18 страницGas Power Cycles: Cengel & BoleskishoremarОценок пока нет
- Lecture-02-Thermal Power PlantДокумент21 страницаLecture-02-Thermal Power PlantGetu TadesseОценок пока нет
- 4 Air Standared Cycles PDFДокумент75 страниц4 Air Standared Cycles PDFAli ZameerОценок пока нет
- Lecture 02 Thermal Power PlantДокумент21 страницаLecture 02 Thermal Power PlantGetu TadesseОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Steam Turbine - Rankine CycleДокумент41 страницаChapter 2 - Steam Turbine - Rankine CycleAnthony AbourahalОценок пока нет
- Heat Engines, Entropy and The Second Law of ThermodynamicsДокумент70 страницHeat Engines, Entropy and The Second Law of Thermodynamicsraj_mishra108Оценок пока нет
- Vapor Power CyclesДокумент48 страницVapor Power CyclesJames WankerОценок пока нет
- Termodinamica ch05Документ19 страницTermodinamica ch05Rebeca AlmeidaОценок пока нет
- IV. Second Law of ThermodynamicsДокумент48 страницIV. Second Law of ThermodynamicsBORASCA EZEKIELОценок пока нет
- Thermo 2 OELДокумент8 страницThermo 2 OELHamza SohailОценок пока нет
- Chapter Two: Vapor Power CyclesДокумент72 страницыChapter Two: Vapor Power CyclesAnything You Could ImagineОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics Chapter 2 Lec1Документ8 страницThermodynamics Chapter 2 Lec1ahmadalsaiahОценок пока нет
- The Rankine Cycle: Ideal Cycle Problems To SolveДокумент12 страницThe Rankine Cycle: Ideal Cycle Problems To Solveأحمد صلاح الدينОценок пока нет
- Uteg College The Second LawДокумент32 страницыUteg College The Second Lawjaqm75Оценок пока нет
- Further Thermodynamics Steam Turbine PlantsДокумент38 страницFurther Thermodynamics Steam Turbine Plantsamdan srlОценок пока нет
- 1 Second LowДокумент22 страницы1 Second LowMohammedОценок пока нет
- DSPPC 1Документ26 страницDSPPC 1Crystal WoodsОценок пока нет
- Ch1 - Steam Power PlantsДокумент44 страницыCh1 - Steam Power Plantsaminjoe93100% (1)
- WK 4 TR2019 - ICE TheoryДокумент72 страницыWK 4 TR2019 - ICE TheoryHoàng LongОценок пока нет
- DMX9208 Lecture08 S2 V0 2021Документ54 страницыDMX9208 Lecture08 S2 V0 2021Sampath WeeratungeОценок пока нет
- Heat Engine 1Документ37 страницHeat Engine 1rakeshbalgoОценок пока нет
- Power Generation Cycles Vapor Power Generation The Rankine CycleДокумент20 страницPower Generation Cycles Vapor Power Generation The Rankine Cyclematto najijОценок пока нет
- Chapter 10 CompleteДокумент48 страницChapter 10 CompleteKamil Rasheed SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- 01-Steam Power Plant 26 OctДокумент64 страницы01-Steam Power Plant 26 OcthuusenaliОценок пока нет
- Chương 22Документ28 страницChương 22phuongtienhiep05Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 2.1 - The Rankine Cycle PDFДокумент21 страницаLesson 2.1 - The Rankine Cycle PDFBilly JhunОценок пока нет
- Air Standard CycleДокумент28 страницAir Standard CycleStalan JonathanОценок пока нет
- Power Production & RefrigerationДокумент30 страницPower Production & RefrigerationVina Dwita100% (1)
- 01-NORA - Steam Power PlantДокумент51 страница01-NORA - Steam Power PlantmasrizaОценок пока нет
- Vapor Power Cycles Lecture 1Документ23 страницыVapor Power Cycles Lecture 1Albert Shesman100% (1)
- Thermo 2Документ23 страницыThermo 2SHek Hxni100% (1)
- Madanapalle Institute of Technology & Science (UGC Autonomous) Department of Mechanical EngineeringДокумент11 страницMadanapalle Institute of Technology & Science (UGC Autonomous) Department of Mechanical EngineeringHarsha DadanaОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics Problem Based Learning Group Report. Rankine CycleДокумент17 страницThermodynamics Problem Based Learning Group Report. Rankine CycleRafael DamarОценок пока нет
- Heat Engines: by Aneetta .S. Vayattattil Xi - AДокумент23 страницыHeat Engines: by Aneetta .S. Vayattattil Xi - ALaly ThundathilОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Rankine Cycle and Its Utility in Thermal Power Plant - A Theoretical ApproachДокумент7 страницAnalysis of Rankine Cycle and Its Utility in Thermal Power Plant - A Theoretical ApproachAnonymous sG3iVImJОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2.1c - The Rankine Cycle 3 PDFДокумент19 страницLesson 2.1c - The Rankine Cycle 3 PDFBilly JhunОценок пока нет
- Lec 20 - CH 9 Jet EngineДокумент12 страницLec 20 - CH 9 Jet Enginesamhameed2100% (1)
- Lec 19 - CH 9 Reheat+ Intercooling+regenrativeДокумент12 страницLec 19 - CH 9 Reheat+ Intercooling+regenrativesamhameed2Оценок пока нет
- Lec 18 - CH 9 Reheat+regenrativeДокумент7 страницLec 18 - CH 9 Reheat+regenrativesamhameed2Оценок пока нет
- Lec 21 22 - CH 13Документ21 страницаLec 21 22 - CH 13samhameed2Оценок пока нет
- Lec 17 - CH 9 BRAYTON RegenrationДокумент7 страницLec 17 - CH 9 BRAYTON Regenrationsamhameed2Оценок пока нет
- Lec 14 - CH 9 Strling and ErricsonДокумент3 страницыLec 14 - CH 9 Strling and Erricsonsamhameed2Оценок пока нет
- Evaluating Air-Standard Otto Cycle For Spark Ignition EnginesДокумент14 страницEvaluating Air-Standard Otto Cycle For Spark Ignition Enginessamhameed2Оценок пока нет
- Entropy Change of An Ideal Gas: Approximate Analysis (Constant Specific Heats) Exact Analysis (Variable Specific Heats)Документ10 страницEntropy Change of An Ideal Gas: Approximate Analysis (Constant Specific Heats) Exact Analysis (Variable Specific Heats)samhameed2Оценок пока нет
- Evaluating Air-Standard Diesel Cycle For Compression Ignition EnginesДокумент13 страницEvaluating Air-Standard Diesel Cycle For Compression Ignition Enginessamhameed2Оценок пока нет
- Energy Analysis of Real Rankine Cycle: Thermodynamics - IIДокумент8 страницEnergy Analysis of Real Rankine Cycle: Thermodynamics - IIsamhameed2Оценок пока нет
- Lec 13 - CH 9 Duel CycleДокумент8 страницLec 13 - CH 9 Duel Cyclesamhameed2Оценок пока нет
- Lec 9 - CH 9Документ13 страницLec 9 - CH 9samhameed2Оценок пока нет
- Cogeneration Combined Power Cycles: Thermodynamics - IIДокумент8 страницCogeneration Combined Power Cycles: Thermodynamics - IIsamhameed2100% (1)
- Improving Performance of Rankine Cycle: Thermodynamics - IIДокумент9 страницImproving Performance of Rankine Cycle: Thermodynamics - IIsamhameed2Оценок пока нет
- Ideal Reheat Rankine Cycle: Thermodynamics - IIДокумент9 страницIdeal Reheat Rankine Cycle: Thermodynamics - IIsamhameed2Оценок пока нет
- Ideal Regenerative Rankine Cycle - Open Feedwater Heaters: Thermodynamics - IIДокумент10 страницIdeal Regenerative Rankine Cycle - Open Feedwater Heaters: Thermodynamics - IIsamhameed2Оценок пока нет
- Vapor Power Cycles Ideal Rankine Cycle: Thermodynamics - IIДокумент10 страницVapor Power Cycles Ideal Rankine Cycle: Thermodynamics - IIsamhameed2100% (1)
- Lab Report: Subject Dynamics and Control (Lab)Документ4 страницыLab Report: Subject Dynamics and Control (Lab)samhameed2Оценок пока нет