Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Longrangeplansteddi
Загружено:
api-242288854Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Longrangeplansteddi
Загружено:
api-242288854Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
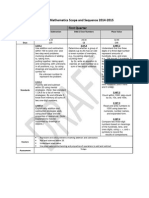
CCSS Mathematics Implementation Guide- Grade 2 (DRAFT)
2014-2015
First Nine Weeks
Pa
ci
ng
1st 9 Weeks
Big Ideas/Essential
Questions
1
0
D
a
ys
Mental strategies
and fact fluency help
solve addition and
subtraction problems
easily.
Standards
2.OA.2. Fluently add and subtract within
20 using mental strategies.2 By end of
Grade 2, know from memory all sums of
two one-digit numbers.
What are some
strategies you use to
solve addition and
subtraction
problems?
Why do we need to
be able to add or
subtract
quickly?
SMP
Resources
Assessment
Bolded standards indicate Power Standards.
Italicized standards indicate support
standards.
2.OA.1. Use addition and
subtraction within 100 to solve oneand two-step word problems
involving situations of adding to,
taking from, putting together, taking
apart, and comparing, with
unknowns in all positions, e.g., by
using drawings and equations with
a symbol for the unknown number
to represent the problem.
2.NBT.8. Mentally add 10 to a given
number mentally subtract 10 from a
given number.
2.NBT.9. Explain why addition and
subtraction strategies work, using
place value and the properties of
operations.
2, 7, 8
My Math Chapter(s): 1, 2
www.georgiastandards.org/Common
-Core/Pages/Math-K-5.aspx
Unit 2 and Unit 4
4, 5
2, 7, 8
www.illustrativemathematics.org/2
Building Toward Fluency
Hitting the Target
Common Assessment
(2.OA.1)
Student score will be
calculated as part of nine
weeks average.
www.engageny.org/resource/grade2-mathematics
Module 1 and Module 5
www.helpingwithmath.com
2, 3
Teacher-selected
assessments should be
administered throughout
the nine weeks.
Issued at conclusion of
nine weeks.
Assessment will be given
in lieu of instruction.
http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/grade_g_
2.html
http://www.k5mathteachingresources.com
Teacher may read the test
to the students.
CCSS Mathematics Implementation Guide- Grade 2 (DRAFT)
2014-2015
Pa
ci
ng
1st 9 Weeks
Big Ideas/Essential
Questions
1
0
D
a
ys
Skip counting follows
a number pattern
based on place value.
What do you notice
when you skip count
by 5s? By 10s? By
100s?
How can I prove that
a number is odd or
even?
5
D
a
ys
How can equal
groups help me add?
Standards
SMP
Resources
Bolded standards indicate Power Standards.
Italicized standards indicate support
standards.
2.NBT.2. Count within 1000; skip-count
by 5s, 10s, and 100s to record the results of
comparisons.
2.OA.3. Determine whether a group
of objects (up to 20) has an odd or
even number of members, e.g., by
pairing objects or counting them by
2s; write an equation to express an
even number as a sum of two equal
addends.
2.OA.4. Use addition to find the total
number of objects arranged in
rectangular arrays with up to 5 rows and
up to 5 columns; write an equation to
express the total as a sum of equal
addends.
2, 7, 8
My Math Chapter(s): 2, 5
www.georgiastandards.org/Common
-Core/Pages/Math-K-5.aspx
Unit 1 and Unit 6
www.illustrativemathematics.org/2
Red and Blue Tiles
Buttons Odd and Even
*possibly Saving Money 2
4 , 7, 8
My Math Chapter(s): 2
www.illustrativemathematics.org/2
Counting Dots in Arrays
Assessment
CCSS Mathematics Implementation Guide- Grade 2 (DRAFT)
2014-2015
Pa
ci
ng
1st 9 Weeks
Big Ideas/Essential
Questions
1
5
D
a
ys
Models can show
ones, tens, and
hundreds.
How many ways can
you show a three
digit number?
Standards
SMP
Resources
Bolded standards indicate Power Standards.
Italicized standards indicate support
standards.
2.NBT.1. Understand that the three digits
of a three-digit number represent amounts
of hundreds, tens, and ones; e.g., 706
equals 7 hundreds, 0 tens, and 6 ones.
Understand the following as special cases:
a. 100 can be thought of as a bundle
of ten tens called a hundred.
b. The numbers 100, 200, 300, 400,
500, 600, 700, 800, 900 refer to
one, two, three, four, five, six,
seven, eight, or nine hundreds (and
0 tens and 0 ones).
2.NBT.4. Compare two three-digit
numbers based on meanings of the
hundreds, tens, and ones digits,
using >, =, and < symbols to
record the results of comparisons.
2, 4, 8
My Math Chapter(s): 5
2, 4, 8
(2.NBT.1 and 2.NBT.4)
www.illustrativemathematics.org/2
Regrouping
Three composing/decomposing
problems
Bundling and Unbundling
Boxes and Cartons of Pencils
Party Favors
Etc.
2, 7
www.georgiastandards.org/Common
-Core/Pages/Math-K-5.aspx
Unit 1
www.engageny.org/resource/grade2-mathematics
Module 3
Assessment
CCSS Mathematics Implementation Guide- Grade 2 (DRAFT)
2014-2015
Pa
ci
ng
5
D
a
ys
1st 9 Weeks
Big Ideas/Essential
Questions
Models, numbers,
and number
sentences can show
numbers to 1,000.
The value of a digit
depends on its
position.
How many ways can
you show numbers to
1,000?
Why isnt a digit
always worth the
same?
Standards
SMP
Resources
Bolded standards indicate Power Standards.
Italicized standards indicate support
standards.
2.NBT.3. Read and write numbers to 1000
using base-ten numerals, number names,
and expanded form
2.NBT.1a. 100 can be thought of as
a bundle of ten tens called a
hundred.
2.NBT.1b The numbers 100, 200,
300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900
refer to one, two, three, four, five,
six, seven, eight, or nine hundreds
(and 0 tens and 0 ones)
2.NBT.4. Compare two three-digit
numbers based on meanings of the
hundreds, tens, and ones digits,
using >, =, and < symbols to
record the results of comparisons.
2, 4
My Math Chapter(s): 5
2, 4, 8
www.georgiastandards.org/Common
-Core/Pages/Math-K-5.aspx
Unit 1
2, 7
www.engageny.org/resource/grade2-mathematics
Module 3
www.illustrativemathematics.org/2
Looking at Numbers Every Which
Way
*See others listed above for previous
standard.
Second Nine Weeks
Assessment
CCSS Mathematics Implementation Guide- Grade 2 (DRAFT)
2014-2015
Pa
cin
g
2nd 9 Weeks
Standards
Big Ideas/Essential
Questions
Bolded standards indicate Power Standards.
Italicized standards indicate support
standards.
SMP
Resources
Assessment
CCSS Mathematics Implementation Guide- Grade 2 (DRAFT)
2014-2015
2
0
D
a
ys
Adding and
subtracting
sometimes requires
regrouping.
What are the steps to
add or subtract a 2
digit number?
2.NBT.5. Fluently add and subtract within
100 using strategies based on place value,
properties of operations, and/or the
relationship between addition and
subtraction.
How do you know
when you will need
to regroup?
2.OA.1. Use addition and
subtraction within 100 to solve oneand two-step word problems
involving situations of adding to,
taking from, putting together, taking
apart, and comparing, with
unknowns in all positions, e.g., by
using drawings and equations with
a symbol for the unknown number
to represent the problem
2.NBT.6. Add up to four two-digit
numbers using strategies based on
place value and properties of
operations.
2.NBT.8. Mentally add 10 or 100 to
a given number 100900, and
mentally subtract 10 or 100 from a
given number 100900.
2.NBT.9. Explain why addition
and subtraction strategies work,
using place value and the properties
of operations.1
2, 7
My Math Chapter(s): 3, 4
www.georgiastandards.org/Common
-Core/Pages/Math-K-5.aspx
Unit 2 and Unit 4
4, 5
(2NBT.5 and 2.OA.1)
www.illustrativemathematics.org/2
Saving Money 1, 2
Jamirs Penny Jar
(2.OA.1)
www.illustrativemathematics.org/2
A Pencil and a Sticker
(2NBT.6)
Toll Bridge Puzzle
2, 7
2, 7
3, 5, 7
www.georgiastandards.org/Common
-Core/Pages/Math-K-5.aspx
Unit 2
Teacher-selected
assessments should be
administered throughout
the nine weeks.
Common Assessment
Issued at
conclusion of nine
weeks
Student score will
be calculated as
part of nine weeks
average
Assessment will be
given in lieu of
instruction
Teacher will NOT
read assessment
UNLESS it is an
accommodation
for specific
students
CCSS Mathematics Implementation Guide- Grade 2 (DRAFT)
2014-2015
Pa
cin
g
2nd 9 Weeks
Standards
Big Ideas/Essential
Questions
Bolded standards indicate Power Standards.
Italicized standards indicate support
standards.
SMP
Resources
Assessment
CCSS Mathematics Implementation Guide- Grade 2 (DRAFT)
2014-2015
1
5
D
a
ys
Determine how and
when to use addition
or subtraction to
solve word problems.
What strategy did
you use to solve the
word problem?
Why does it work?
2.OA.1 Represent and solve problems
involving addition and subtraction.
2.OA.1. Use addition and
subtraction within 100 to solve oneand two-step word problems
involving situations of adding to,
taking from, putting together, taking
apart, and comparing, with
unknowns in all positions, e.g., by
using drawings and equations with
a symbol for the unknown number
to represent the problem.
4, 5
My Math Chapter(s): 1-4 and
throughout text
www.georgiastandards.org/Common
-Core/Pages/Math-K-5.aspx
Unit 2
www.engageny.org/resource/grade2-mathematics
Module 4
www.illustrativemathematics.org/2
A Pencil and a Sticker
Saving Money 2
CCSS Mathematics Implementation Guide- Grade 2 (DRAFT)
2014-2015
1
0
D
a
ys
Students use a
variety of addition
and subtraction
strategies to solve a
number sentence.
Can you solve an
addition or
subtraction math
sentence using at
least two different
ways?
2.NBT.7. Add and subtract within 1000,
using concrete models or drawings and
strategies based on place value, properties
of operations, and/or the relationship
between addition and subtraction; relate
the strategy to a written method.
Understand that in adding or subtracting
three-digit numbers, one adds or subtracts
hundreds and hundreds, tens and tens,
ones and ones; and sometimes it is
necessary to compose or decompose tens
or hundreds.
2, 4, 7
www.georgiastandards.org/Common
-Core/Pages/Math-K-5.aspx
Units 2 and 4
www.engageny.org/resource/grade2-mathematics
Module 5
www.illustrativemathematics.org/2
2.OA.2. Fluently add and subtract
within 20 using mental strategies.2
By end of Grade 2, know from
memory all sums of two one-digit
numbers.
2.NBT.9. Explain why addition and
subtraction strategies work, using
place value and the properties of
operations.1
My Math Chapter(s): 6, 7
2, 7, 8
How Many Days Until Summer
Vacation?
Many Ways to do Addition 2
2, 7, 8
Useful Links:
www.helpingwithmath.com
http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/grade_g_
2.html
http://www.k5mathteachingresources.com
CCSS Mathematics Implementation Guide- Grade 2 (DRAFT)
2014-2015
Mathematics 1st Nine Weeks:
Days:
Day 1-Day 10
Objectives:
Students will use mental strategies and fact fluency to help them
solve addition and subtraction problems easily. (2.OA.2)
Essential Questions: What are some strategies you use to solve
addition and subtraction problems? Why do we need to be able
to add or subtract quickly?
Day 11-Day 21
Students will use skip counting to follow a number pattern based
on place value. (2.NBT.2)
Essential Questions: What do you notice when you skip count by
5s? By 10s? By 100s? How can I prove that a number is odd or
even?
Day 22-26
Students will use equal groups to help them add. (2.OA.4)
Essential Questions: How can equal groups help me add?
CCSS Mathematics Implementation Guide- Grade 2 (DRAFT)
2014-2015
Day 27-42
Students will use models to show ones, tens, and hundreds.
(2.NBT.1)
Essential Questions: How many ways can you show a three-digit
number?
Day 43-47
Students will use models, numbers, and number sentences to
demonstrate numbers to 1,000 showing that the value of a digit
depends on its position. (2.NBT.3)
Essential Questions: How many ways can you show numbers to
1,000? Why isnt a digit always worth the same?
Reflection: (Scope and Sequence)
During the first nine weeks, I decided to introduce Numbers and Operations in Base Ten. I chose to introduce this topic first because
it gives the students a strong foundation before they begin other chapters. In numbers and operations, students work on sums and
differences with whole numbers, skip counting, and place value. These topics are mandatory for mastering upcoming topics later
introduced in math. During the first nine weeks, students need a review from the previous year, so its important to put the review
chapters at the beginning of the unit. During the second nine weeks students are focusing on Operations and Algebraic Thinking. Its
very important that students have mastered the earlier math concepts in order for them to fully understand the new concepts.
Students are working more on regrouping when adding and subtracting during the second nine weeks, whereas during the first nine
weeks students were still adding and subtracting using basic strategies such as number lines, ten frames, etc. During the third nine
weeks students are introduced to Geometry. In Geometry, students are focusing on reasoning with shapes and their attributes.
During the fourth nine weeks, students are introduced to Measurement and Data. In Measurement and Data, students are focusing
on measuring and estimating lengths in standard units, relating addition and subtraction to length, working with time and money,
CCSS Mathematics Implementation Guide- Grade 2 (DRAFT)
2014-2015
and representing and interpreting data. In my opinion, measurement and data skills come much easier to students than numbers
and operations do. I chose to teach these concepts at the end of the year, since students will begin becoming very anxious for
summer vacation. The four performance goals were taught in a sequential order because they each build on one another.
Вам также может понравиться
- 7th Grade Math Team Lesson Plan Aug 11 - 18 2014Документ5 страниц7th Grade Math Team Lesson Plan Aug 11 - 18 2014conyersmiddleschool_7thgradeОценок пока нет
- Interim Assessment Design ProcessДокумент3 страницыInterim Assessment Design ProcesslmagstadtОценок пока нет
- 5th Common Core EngageNYДокумент385 страниц5th Common Core EngageNYLaurelОценок пока нет
- Student Learning Objective - Teacher: Content Area: Mathematics Grade Level: Gr. 1 Objective StatementДокумент3 страницыStudent Learning Objective - Teacher: Content Area: Mathematics Grade Level: Gr. 1 Objective StatementRoopaliSharmaОценок пока нет
- Math g2 m5 Full ModuleДокумент312 страницMath g2 m5 Full ModuleRivka Share100% (1)
- Grade 2 Doc FinalДокумент50 страницGrade 2 Doc Finalapi-32541207Оценок пока нет
- EnVision CC To CCSSM Grade 1Документ4 страницыEnVision CC To CCSSM Grade 1Ram YennamОценок пока нет
- Set1 - Gr9 2012 ExemplarДокумент28 страницSet1 - Gr9 2012 ExemplarHuấn LêОценок пока нет
- Math g2 m5 Full Module PDFДокумент312 страницMath g2 m5 Full Module PDFSonu KumarОценок пока нет
- 0607 Y10 SyДокумент25 страниц0607 Y10 SytajudОценок пока нет
- Grade 1 Doc FinalДокумент75 страницGrade 1 Doc Finalapi-32541207Оценок пока нет
- STEP Standard 2 TemplateДокумент2 страницыSTEP Standard 2 TemplateCharon HolmesОценок пока нет
- How To Read The Grade Level Standards: Number and Operations in Base Ten 3.NbtДокумент4 страницыHow To Read The Grade Level Standards: Number and Operations in Base Ten 3.NbtmohammadОценок пока нет
- Maths Introduction Igcse Extended 3 YrsДокумент9 страницMaths Introduction Igcse Extended 3 YrsYenny TigaОценок пока нет
- Mayugher For TerДокумент19 страницMayugher For Terhhfg hjggОценок пока нет
- Item Bank Maths Class 10 by Fastest Education YtДокумент231 страницаItem Bank Maths Class 10 by Fastest Education YtSuhani GosainОценок пока нет
- Math Lesson Plan For WikiДокумент3 страницыMath Lesson Plan For WikimexitravОценок пока нет
- First Quarter and 2nd Quarter Scope and Sequence MathДокумент2 страницыFirst Quarter and 2nd Quarter Scope and Sequence Mathapi-234156613Оценок пока нет
- 2 Nyc Scopeandsequence 5-130606Документ3 страницы2 Nyc Scopeandsequence 5-130606api-351301306Оценок пока нет
- MIDTERM Module in Industrial Math 8Документ66 страницMIDTERM Module in Industrial Math 8kervin oñОценок пока нет
- Math 7 Commom Core Syllabus 2014-2015Документ8 страницMath 7 Commom Core Syllabus 2014-2015api-261815606Оценок пока нет
- Common Core State Standards: A Crosswalk To The Michigan Grade Level Content ExpectationsДокумент12 страницCommon Core State Standards: A Crosswalk To The Michigan Grade Level Content ExpectationslchamblessОценок пока нет
- Reveal Math Grade 2 Curriculum GuideДокумент13 страницReveal Math Grade 2 Curriculum GuideGhada NabilОценок пока нет
- 2012-2013 Quarter 1 - 5th Grade Math RubricДокумент4 страницы2012-2013 Quarter 1 - 5th Grade Math Rubricnelly_marlina02100% (1)
- Rubrics PDFДокумент21 страницаRubrics PDFallanОценок пока нет
- AZ Math Standards For Grade 1Документ6 страницAZ Math Standards For Grade 1shawnsblog100% (2)
- Alignment To Content Standards MathДокумент67 страницAlignment To Content Standards Mathapi-324382335Оценок пока нет
- Parent Overview Addition Subtraction 2 10 14Документ2 страницыParent Overview Addition Subtraction 2 10 14api-266271266Оценок пока нет
- Math Fluency Activities for K–2 Teachers: Fun Classroom Games That Teach Basic Math Facts, Promote Number Sense, and Create Engaging and Meaningful PracticeОт EverandMath Fluency Activities for K–2 Teachers: Fun Classroom Games That Teach Basic Math Facts, Promote Number Sense, and Create Engaging and Meaningful PracticeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Grade 7 Unit 1 Performance Task StudentДокумент4 страницыGrade 7 Unit 1 Performance Task StudentKclyn Carniyan TagayunОценок пока нет
- 2nd Grade Pacing Plan 2013-14Документ9 страниц2nd Grade Pacing Plan 2013-14api-237255436Оценок пока нет
- Common Core State Standards: A Crosswalk To The Michigan Grade Level Content ExpectationsДокумент15 страницCommon Core State Standards: A Crosswalk To The Michigan Grade Level Content ExpectationslchamblessОценок пока нет
- Math g2 m4 Full ModuleДокумент405 страницMath g2 m4 Full ModuleHirenkumar ShahОценок пока нет
- Math 7 Unit 2 OverviewДокумент2 страницыMath 7 Unit 2 Overviewapi-314307886Оценок пока нет
- Unit StandardsДокумент7 страницUnit Standardsapi-284886534Оценок пока нет
- g2 Mathematics Florida StandardsДокумент5 страницg2 Mathematics Florida Standardsapi-290541111Оценок пока нет
- GSAT Mathematics Revision ToolkitДокумент35 страницGSAT Mathematics Revision Toolkitdwayne dixonОценок пока нет
- March 8, 2023Документ32 страницыMarch 8, 2023Rosales Joseph M.100% (1)
- Step TemplateДокумент24 страницыStep Templateapi-533069806Оценок пока нет
- g1 Mathematics Florida StandardsДокумент5 страницg1 Mathematics Florida Standardsapi-290541111Оценок пока нет
- Task 4 - Part G - Math Assessment CommetaryДокумент10 страницTask 4 - Part G - Math Assessment Commetaryapi-242291532100% (2)
- Tech Trends Lesson PlanДокумент5 страницTech Trends Lesson PlantonyagrantОценок пока нет
- REVISION 3 Sem 2 Methods With Calculator Unit 3-4 2016Документ21 страницаREVISION 3 Sem 2 Methods With Calculator Unit 3-4 2016TonyОценок пока нет
- Year 6 t1 Unit 3 Mathematics TermДокумент6 страницYear 6 t1 Unit 3 Mathematics Termapi-267136654Оценок пока нет
- ECON+1274 1248 Project 2023Документ4 страницыECON+1274 1248 Project 2023kdoll 29Оценок пока нет
- Lab Manual On ADDBMS 29-11-2023Документ28 страницLab Manual On ADDBMS 29-11-2023madhura.rahalkarОценок пока нет
- Tws 6Документ4 страницыTws 6api-242288854Оценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan For Social StudiesДокумент3 страницыLesson Plan For Social Studiesapi-242288854Оценок пока нет
- Student Teaching Lesson 1Документ4 страницыStudent Teaching Lesson 1api-242288854Оценок пока нет
- Weebly Tws 9Документ3 страницыWeebly Tws 9api-242288854Оценок пока нет
- Tws 3Документ3 страницыTws 3api-242288854Оценок пока нет
- Pitch and Volume LP 3rd GradeДокумент3 страницыPitch and Volume LP 3rd Gradeapi-242288854Оценок пока нет
- Weebly Lesson 4 429Документ5 страницWeebly Lesson 4 429api-242288854Оценок пока нет
- Mathlessondividing 2Документ3 страницыMathlessondividing 2api-242288854Оценок пока нет
- Weebly Lesson 1 429Документ4 страницыWeebly Lesson 1 429api-242288854Оценок пока нет
- Science Lesson 2educ 329Документ4 страницыScience Lesson 2educ 329api-242288854Оценок пока нет
- Conductor Vs Insulator Sciencelessonplan2Документ3 страницыConductor Vs Insulator Sciencelessonplan2api-242288854Оценок пока нет
- Holland Party GameFINAL1 PDFДокумент6 страницHolland Party GameFINAL1 PDFAnonymous pHooz5aH6VОценок пока нет
- Philippine Psychometricians Licensure Exam RevieweДокумент1 страницаPhilippine Psychometricians Licensure Exam RevieweKristelle Mae C. Azucenas0% (1)
- Anthropology Chapter 2 AДокумент17 страницAnthropology Chapter 2 AHafiz SaadОценок пока нет
- Why The Sea Is SaltДокумент3 страницыWhy The Sea Is SaltVictor CiobanОценок пока нет
- Rath'S Lectures: Longevity Related Notes On Vimsottari DasaДокумент5 страницRath'S Lectures: Longevity Related Notes On Vimsottari DasasudhinnnОценок пока нет
- Anglicanism QuestionsДокумент36 страницAnglicanism QuestionsspringsdanielconceptОценок пока нет
- 2009FallCatalog PDFДокумент57 страниц2009FallCatalog PDFMarta LugarovОценок пока нет
- Sample Opposition To Motion To Alter or Amend Judgment in United States District CourtДокумент3 страницыSample Opposition To Motion To Alter or Amend Judgment in United States District CourtStan BurmanОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Biostatistics KMPK 2023Документ46 страницIntroduction To Biostatistics KMPK 2023ciciОценок пока нет
- SD OverviewДокумент85 страницSD OverviewSamatha GantaОценок пока нет
- Waterfront Development Goals and ObjectivesДокумент2 страницыWaterfront Development Goals and ObjectivesShruthi Thakkar100% (1)
- Diplomatic Quarter New Marriott Hotel & Executive ApartmentsДокумент1 страницаDiplomatic Quarter New Marriott Hotel & Executive Apartmentsconsultnadeem70Оценок пока нет
- Top Websites Ranking - Most Visited Websites in May 2023 - SimilarwebДокумент3 страницыTop Websites Ranking - Most Visited Websites in May 2023 - SimilarwebmullahОценок пока нет
- Oral Abstract PresentationДокумент16 страницOral Abstract Presentationapi-537063152Оценок пока нет
- Individual Assignment: Prepared By: Tigist WoldesenbetДокумент12 страницIndividual Assignment: Prepared By: Tigist WoldesenbetRobel YacobОценок пока нет
- Story of Their Lives: Lived Experiences of Parents of Children With Special Needs Amidst The PandemicДокумент15 страницStory of Their Lives: Lived Experiences of Parents of Children With Special Needs Amidst The PandemicPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalОценок пока нет
- De Villa vs. Court of AppealsДокумент1 страницаDe Villa vs. Court of AppealsValerie Aileen AnceroОценок пока нет
- Adult Consensual SpankingДокумент21 страницаAdult Consensual Spankingswl156% (9)
- Rules and IBA Suggestions On Disciplinary ProceedingsДокумент16 страницRules and IBA Suggestions On Disciplinary Proceedingshimadri_bhattacharje100% (1)
- Persephone by Julia Donaldson: (A Meadow. Enters Persephone, Picking The Petals of A Daisy.)Документ10 страницPersephone by Julia Donaldson: (A Meadow. Enters Persephone, Picking The Petals of A Daisy.)Dobler Liliana100% (1)
- Exercise On Relative ClausesДокумент5 страницExercise On Relative ClausesSAmuel QuinteroОценок пока нет
- Imam Muhammad Baqir (As) BioДокумент5 страницImam Muhammad Baqir (As) BioFatema AbbasОценок пока нет
- Case StudyДокумент3 страницыCase StudyAnqi Liu50% (2)
- What Is Art?Документ14 страницWhat Is Art?Sarvenaaz QaffariОценок пока нет
- Subject: Animal Breeding and Genetics - II Course Code: ABG-301Документ2 страницыSubject: Animal Breeding and Genetics - II Course Code: ABG-301Hamid Ali AfridiОценок пока нет
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2019: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in English Language (4EB1) Paper 01RДокумент19 страницMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2019: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in English Language (4EB1) Paper 01RNairit100% (1)
- PPH CasestudyДокумент45 страницPPH CasestudyRona Mae PangilinanОценок пока нет
- Contents:: Project ProgressДокумент22 страницыContents:: Project ProgressJosé VicenteОценок пока нет
- Grunig J, Grunig L. Public Relations in Strategic Management and Strategic Management of Public RelationsДокумент20 страницGrunig J, Grunig L. Public Relations in Strategic Management and Strategic Management of Public RelationsjuanОценок пока нет
- A Week in My CountryДокумент2 страницыA Week in My CountryAQhuewulland Youngprincess HokageNarutoОценок пока нет