Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Astronomy Study Guide Answers
Загружено:
api-2406898820 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
1K просмотров2 страницыОригинальное название
astronomy study guide answers
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
1K просмотров2 страницыAstronomy Study Guide Answers
Загружено:
api-240689882Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
Name:_______________________________________________
Date:_____________________
Astronomy Study Guide
Test Date: 12/19/14
Textbook Pages: 4-37
ISN Pages: 38-58
Chapter 1 Section 1: Earth in Space
Key Terms: Astronomy, Axis, Rotation, Revolution, Orbit, Solstice, Equinox
1. How does Earth move in space?
The earth rotates on its axis and revolves around the sun.
2. What does rotation of Earth cause?
Earths rotation causes day and night.
3. What causes the cycle of seasons on Earth?
Earths seasons are caused by the tilt of Earths axis as it revolves around the sun.
4. What is true about the position of the sun in the sky during a solstice? Equinox?
During a solstice the suns direct light is farthest from the equator. During an equinox, the suns direct
light is pointed directly at the equator.
Chapter 1 Section 2: Gravity and Motion
Key Terms: Force, Gravity, Law of Universal Gravitation, Mass, Weight, Inertia, Newtons Laws of Motion
1. What determines the strength of the force of gravity between two objects?
Mass and Distance. The greater the mass the stronger the force of gravity. The farther the distance
between two objects the weaker the force of gravity.
2. What two factors combine to keep the moon and Earth in orbit? Explain how
Inertia and gravity work together to keep the moon and Earth in orbit. Inertia forces the planetary body
to move in a straight line, while tries to pull the planet inward. This causes the planetary body to move
on an angle at each point, causing an elliptical orbit.
3. What are Newtons three laws of motion? Be able to identify each.
1st Law An object in motion tends to stay in motion while an object at rest tends to stay at rest unless
acted on by an outside force.
2nd Law Force = Mass x Acceleration
3rd Law For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
4. What are Keplers Laws of Planetary Motion?
Planets orbit the sun in an elliptical shape
When a planet is closer to the sun it moves faster.
The farther a planet is from the sun, the greater the distance is must travel, the slower it moves, and
the longer it takes to travel around the sun.
Chapter 1 Section 3: Phases, Eclipses, and Tides
Key Terms: Phases, eclipse, solar eclipse, umbra, penumbra, lunar eclipse, tide, spring tide, neap tide
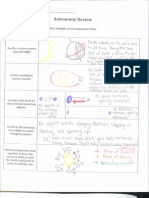
1. What causes the phases of the moon?
The moon looks different from Earth based on the amount of the sunlit side of the moon is visible.
2. Be able to identify the phases and order of phases.
3. What are solar and lunar eclipses?
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon blocks the light of the sun from reaching the Earth. A lunar eclipse
occurs when the Earth blocks the light of the sun from reaching the moon.
4. What causes the tides?
Tides are caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun on Earths water
5. How does the position of the Earth, Moon, and Sun affect the tides?
When the sun, moon, and Earth are in a line there are Spring Tides (the greatest difference between
High and Low Tides). When the sun and moon are at a right angle there are neap tides (the lowest
difference between High and Low Tides)
Chapter 1 Section 4: Earths Moon
Key Terms: Telescope, Maria, Craters, Meteoroids
1. What features are found on the moons surface?
Maria- Dark flat surfaces created by hardened lava flow
Craters Caused by the impact of meteroids
Highlands Mountain-like regions on the moon
2. What are some characteristics of the moon?
The moon is much less dense than Earth, and has a much lower mass. The lower mass causes the moon
to have very little gravity. Because there is little gravity, the moon does not have an atmosphere.
Without an atmosphere there are very drastic temperature changes on the moon. There is no liquid
water.
3. How did the moon form?
The moon formed because of a collision between ancient Earth and another planet. The debris formed a
ring around Earth, and then coalesced to create the moon.
Вам также может понравиться
- Astronomy Unit 3 Critical Thinking QuestionsДокумент3 страницыAstronomy Unit 3 Critical Thinking QuestionsDAKOTA FISHERОценок пока нет
- Monographin Phasesofthe Moonfor Grade 5Документ45 страницMonographin Phasesofthe Moonfor Grade 5Gerald GuevarraОценок пока нет
- U4 The Universe 2nd Grade Study GuideДокумент3 страницыU4 The Universe 2nd Grade Study GuideMaria EstradaОценок пока нет
- Astronomical Phenomena - EditedДокумент79 страницAstronomical Phenomena - EditedRIZALINA BATANОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9. Earth in The Solar SystemДокумент5 страницChapter 9. Earth in The Solar SystemAnmol TaurussОценок пока нет
- 14 Fun Facts About the Moon: A 15-Minute BookОт Everand14 Fun Facts About the Moon: A 15-Minute BookРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Exploring The Universe (English)Документ74 страницыExploring The Universe (English)YosieОценок пока нет
- Unit Iv: Earth and Space Activity: Prepared: Gracie Ann M. Dy Lohb - Eed 16 InstructorДокумент3 страницыUnit Iv: Earth and Space Activity: Prepared: Gracie Ann M. Dy Lohb - Eed 16 InstructorBianca Celine R. MirandaОценок пока нет
- 2223 Level M Physics - Outer SpaceДокумент178 страниц2223 Level M Physics - Outer Space-Bleh- WalkerОценок пока нет
- 1Документ2 страницы1mppsregistrarОценок пока нет
- Earth and The Solar System 220913 004914Документ50 страницEarth and The Solar System 220913 004914Bobfian WidjajaОценок пока нет
- Integrated Science I: M O D U L E 1 5Документ29 страницIntegrated Science I: M O D U L E 1 5Wilmae Grace ProvidoОценок пока нет
- Phy Topc 7 F4Документ9 страницPhy Topc 7 F4Kandrossy GlassОценок пока нет
- Module 15 PlanetsДокумент32 страницыModule 15 PlanetsJensen Ryan Lim100% (1)
- Unit 6 - The Earth and The Universe-RUBENДокумент13 страницUnit 6 - The Earth and The Universe-RUBENNico WlodarczykОценок пока нет
- Earth in Space-7th Grade Earth ScienceДокумент22 страницыEarth in Space-7th Grade Earth Scienceleojohn2Оценок пока нет
- Astronomy 1143 Final Exam Review Answers: What Is Science?Документ20 страницAstronomy 1143 Final Exam Review Answers: What Is Science?samsul bahriОценок пока нет
- Powerpoint Assignment 1 Edu 210Документ10 страницPowerpoint Assignment 1 Edu 210api-242428404Оценок пока нет
- 1 Eso GeographyДокумент3 страницы1 Eso GeographyEva Barreiro RománОценок пока нет
- Origin of The Solar System: Learning CompetenciesДокумент6 страницOrigin of The Solar System: Learning CompetenciesJIHAN BALASОценок пока нет
- The Earth in The Solar System GeographyДокумент12 страницThe Earth in The Solar System Geographydhwanil shahОценок пока нет
- Solar System Review Sheet KEYДокумент4 страницыSolar System Review Sheet KEYeumielsilvaОценок пока нет
- Examples of Astronomical PhenominaДокумент38 страницExamples of Astronomical PhenominaMary Rhodelyn Fermin100% (1)
- Lesson 20 Final Revised VersionДокумент11 страницLesson 20 Final Revised Versionidilsagal2021Оценок пока нет
- Earth Sci 11 - Astronomy Review Package - KEYДокумент4 страницыEarth Sci 11 - Astronomy Review Package - KEYdkrms DОценок пока нет
- 2 Space Systems (FINAL PART) Earth, Sun, MoonДокумент44 страницы2 Space Systems (FINAL PART) Earth, Sun, MoonKiki JoОценок пока нет
- Full Download Solar System 9th Edition Seeds Solutions ManualДокумент35 страницFull Download Solar System 9th Edition Seeds Solutions Manualcherlysulc100% (18)
- Concept Guide: Science Periodic 2Документ7 страницConcept Guide: Science Periodic 2api-270387817Оценок пока нет
- Social Studies Form 3Документ126 страницSocial Studies Form 3agyapong892Оценок пока нет
- MoonДокумент2 страницыMoonFaizahОценок пока нет
- Gravity (1) BEST OF ALL TIME ACPSДокумент5 страницGravity (1) BEST OF ALL TIME ACPSZawad IslamОценок пока нет
- Astronomy: Patterns in The Night SkyДокумент4 страницыAstronomy: Patterns in The Night SkyMa. Lucille AbarracosoОценок пока нет
- Earth's Place in SpaceДокумент11 страницEarth's Place in Spacerupalpatel0000Оценок пока нет
- Elementary AstronomyДокумент7 страницElementary AstronomyJoseph ManaseОценок пока нет
- UNIT 1 The Earth in The UniverseДокумент11 страницUNIT 1 The Earth in The UniverserosaronceroОценок пока нет
- SAP Pertemuan Ke 2Документ3 страницыSAP Pertemuan Ke 2Salsabila AnisaОценок пока нет
- ScienceДокумент23 страницыScienceJanice RomeroОценок пока нет
- 14 Fun Facts About the Galilean Moons of Jupiter: A 15-Minute Book, Educational VersionОт Everand14 Fun Facts About the Galilean Moons of Jupiter: A 15-Minute Book, Educational VersionОценок пока нет
- 14 Fun Facts About the Galilean Moons of Jupiter: A 15-Minute BookОт Everand14 Fun Facts About the Galilean Moons of Jupiter: A 15-Minute BookОценок пока нет
- Lesson 19 Final Revised VersionДокумент11 страницLesson 19 Final Revised Versionidilsagal2021Оценок пока нет
- Astronomy Powerpoint CHP 1Документ18 страницAstronomy Powerpoint CHP 1emailtotesttestОценок пока нет
- 14 Fun Facts About Mercury: A 15-Minute BookОт Everand14 Fun Facts About Mercury: A 15-Minute BookРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Science Guia de Estudio Primer GradoДокумент3 страницыScience Guia de Estudio Primer GradogenesisОценок пока нет
- The Sun: Educational Facts for Middle School Children About the Star of Our Solar SystemОт EverandThe Sun: Educational Facts for Middle School Children About the Star of Our Solar SystemОценок пока нет
- What Is Known About The MoonДокумент35 страницWhat Is Known About The MoonAbi Manahan-DoriaОценок пока нет
- Planetary Test Study GuideДокумент1 страницаPlanetary Test Study GuidestevekinneyОценок пока нет
- 5 - Lecture 8Документ23 страницы5 - Lecture 8aisha Al rifaiiОценок пока нет
- 350Документ36 страниц350kathleenjaneОценок пока нет
- Keplers LawsДокумент23 страницыKeplers LawsJhulia IlogonОценок пока нет
- Cheat Sheet For LIUДокумент1 страницаCheat Sheet For LIUNathan Korean KimОценок пока нет
- Solar System 9th Edition Seeds Solutions ManualДокумент25 страницSolar System 9th Edition Seeds Solutions ManualGregoryStricklandgtak100% (44)
- Eoy Review AnswersДокумент13 страницEoy Review Answersapi-240689882Оценок пока нет
- PH HomeworkДокумент1 страницаPH Homeworkapi-240689882Оценок пока нет
- Chem Study Guide Answer KeyДокумент4 страницыChem Study Guide Answer Keyapi-240689882100% (1)
- Light Study Guide AnswersДокумент2 страницыLight Study Guide Answersapi-240689882Оценок пока нет
- Light Study GuideДокумент1 страницаLight Study Guideapi-240689882Оценок пока нет
- Astronomy Review AnsweredДокумент3 страницыAstronomy Review Answeredapi-240689882Оценок пока нет
- Astronomy Study GuideДокумент1 страницаAstronomy Study Guideapi-240689882Оценок пока нет
- Climate Study Guide Answer Key 2014Документ2 страницыClimate Study Guide Answer Key 2014api-240689882Оценок пока нет
- Current Event ReflectionДокумент2 страницыCurrent Event Reflectionapi-240689882Оценок пока нет
- Climate Study Guide 2014Документ1 страницаClimate Study Guide 2014api-240689882Оценок пока нет
- Climate Regions Go CompleteДокумент2 страницыClimate Regions Go Completeapi-240689882Оценок пока нет
- Coriolli's Component of Acceleration ApparatusДокумент7 страницCoriolli's Component of Acceleration Apparatustinkusk24Оценок пока нет
- Mass-And-weight-worksheet (Nov. 3, 2023) - PHYSICS CLE ActivityДокумент1 страницаMass-And-weight-worksheet (Nov. 3, 2023) - PHYSICS CLE Activityskyty743Оценок пока нет
- Motion Graph Analysis WorksheetДокумент4 страницыMotion Graph Analysis WorksheetElias BlairОценок пока нет
- Newtonian Physics IДокумент97 страницNewtonian Physics IGanesh KumarОценок пока нет
- TESTДокумент5 страницTESTMelissa Favila Panaga100% (1)
- Pharma Screw FeedingДокумент8 страницPharma Screw FeedingrizwanОценок пока нет
- Section 1 General Information: CT Handbook - Book Page I Monday, October 17, 2005 4:03 PMДокумент98 страницSection 1 General Information: CT Handbook - Book Page I Monday, October 17, 2005 4:03 PMalexander almarioОценок пока нет
- Week 2: CIVE1187Документ58 страницWeek 2: CIVE1187Deepthi ReddyОценок пока нет
- Uniform Acceleration Problems With SolutionsДокумент9 страницUniform Acceleration Problems With SolutionsbingОценок пока нет
- Physics 10th Chapter 4thДокумент1 страницаPhysics 10th Chapter 4thNajm UllahОценок пока нет
- لقطة شاشة 2023-11-16 في 9.11.43 صДокумент35 страницلقطة شاشة 2023-11-16 في 9.11.43 ص5sr6xmsbsbОценок пока нет
- Length VectorsДокумент2 страницыLength VectorsAdri versouisseОценок пока нет
- Kimia Test 9Документ6 страницKimia Test 9bimskuyyОценок пока нет
- Shpenkov - Gravity2019Документ50 страницShpenkov - Gravity2019amthortuiОценок пока нет
- Elec P CДокумент31 страницаElec P CKria Vora100% (1)
- Exercises ArchimedesДокумент4 страницыExercises ArchimedesAnonymous UypCttW100% (2)
- Trio Test # 2 Questions Motion - Forces: 1. A. B. C. D. 2. A. B. C. D. 3. A. B. C. D. 4. A. B. C. DДокумент6 страницTrio Test # 2 Questions Motion - Forces: 1. A. B. C. D. 2. A. B. C. D. 3. A. B. C. D. 4. A. B. C. DPaulОценок пока нет
- Miles F. Osmaston - A Particle-Tied Aether: Indications of A Deeper Foundation For Physics and RelativityДокумент12 страницMiles F. Osmaston - A Particle-Tied Aether: Indications of A Deeper Foundation For Physics and RelativityKunma050Оценок пока нет
- The Daltons Atomic TheoryДокумент30 страницThe Daltons Atomic TheoryBianca Alcantara100% (1)
- A Net Force of 15 N Is Exerted On An Encyclopedia To Cause It To Accelerate at A Rate of 5 MДокумент5 страницA Net Force of 15 N Is Exerted On An Encyclopedia To Cause It To Accelerate at A Rate of 5 MAngie CondezaОценок пока нет
- Chapter05 Circular Motion SДокумент9 страницChapter05 Circular Motion SeltytanОценок пока нет
- HW 2Документ3 страницыHW 2JeeveshОценок пока нет
- Material BalanceДокумент14 страницMaterial BalanceManisha SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- Kinematics: Description of MotionДокумент30 страницKinematics: Description of MotionMind ControlОценок пока нет
- 5 - Pulleys and Systems PracticeДокумент3 страницы5 - Pulleys and Systems PracticeCalebОценок пока нет
- Newtons LawsДокумент8 страницNewtons LawsdenunderligeranОценок пока нет
- Motion in One DimensionДокумент58 страницMotion in One Dimensionismail mabroukОценок пока нет
- PHY130 Lab Report 2Документ7 страницPHY130 Lab Report 2Declan Gale Anak DellyОценок пока нет
- Practicum Report Basic Physics Swing Simple 1Документ7 страницPracticum Report Basic Physics Swing Simple 1ibnu KurniawanОценок пока нет