Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
6 Sound at Work
Загружено:
api-200253170Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
6 Sound at Work
Загружено:
api-200253170Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Public
c Schools
s North Co
oast RTO
O 90162
M
MEM20
105 Cerrtificate II in Eng
gineering
g
Unit 2
W
WHS
Prin
nciples & Safety
Theo
ory Module No
oise @ Work
W
Unit of compete
ency:
M13014A
A Apply
y princip
ples of
MEM
occu
upationa
al healtth and safety
s
in
n the
work
k enviro
onment
MEM
M11011B
B Underrtake manual
m
hand
dling
____________________
____________________________________________
Student Naame: ______
N O I S E
I N
T H E
W O R K P L A C E
What is sound?
Sound is caused by the vibration of air particles like waves in the sea.
Noise is unwanted sound. Many workplaces are very noisy and this can
affect your hearing over a long period of time.
Workplace Health and Safety Training Resource Kit
97
N O I S E
I N
T H E
W O R K P L A C E
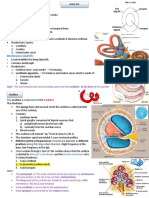
The ear... how does it work?
The ear has three main sections - outer, middle and inner ear.
Label the diagrams to show:
1 outer ear
5 inner ear
2 ear drum
6 cochlea
3 bones
7 hairs
4 middle ear
8 auditory nerve
Cochlea of a person with
normal hearing
Workplace Health and Safety Training Resource Kit
Cochlea of a person with
severe hearing loss
98
N O I S E
I N
T H E
W O R K P L A C E
The ear... how does it work?
When sound waves enter the ear they strike the eardrum making it vibrate. The
vibration is passed on to three bones in the middle ear which vibrate the fluid in
the cochlea. The tiny hair cells in the cochlea pick up the movement from the
fluid and change it into electrical impulses for the brain.
The thousands of hair cells in the cochlea are like grass on a lawn. If the traffic
on the lawn increases the grass is flattened. If the traffic stops for a while, the
grass stands up again. However, if the traffic remains heavy, the grass will remain
flat and will die off.
Too much noise will have the same effect on the ear.
When sound waves enter the ear they strike the eardrum
making it vibrate.
Workplace Health and Safety Training Resource Kit
99
N O I S E
I N
T H E
W O R K P L A C E
Measuring noise
Sound intensity is measured in units called Decibels (dB). The following
diagrams give examples of common noises and their decibel values from
low to high. The chart below shows the noise levels produced by various
noise sources.
Effect on
people
Sound
Sound
level in dB source
a lot of damage
140
Jet Engine
130
Rivet Hammer
120
damaging
110
Chain saw
100
Sheet-metal workshop
90
80
irritating
Workplace Health and Safety Training Resource Kit
Pain threshold
General standard in Australia for eight hours
Heavy traffic
70
60
Normal conversation
50
Low conversation
40
Quiet radio music
30
Whispering
20
Quiet urban room
10
Rustling leaves
Hearing threshold
100
N O I S E
I N
T H E
W O R K P L A C E
If the sound level increases
by three dB then the sound
intensity doubles.
For example:
83dB is double the sound intensity of 80dB and can cause twice as much
damage to your hearing.
if 80dB
if 83dB
if 86dB
if 89dB
Workplace Health and Safety Training Resource Kit
101
N O I S E
I N
T H E
W O R K P L A C E
Measuring sound...
Intensity
Frequency
Exposure time
measured in
decibels (dB)
from low,
such as thunder
above 85dB for a
short time only
to high,
such as a chainsaw
Hearing loss
If you have a hearing problem it can be either permanent or temporary
hearing loss. You will probably not hear the higher frequency sounds.
Measuring noise at work
Noise is measured at work using a noise meter. It is important to measure
the intensity and the frequency. This is done using a scale called decibels (dB).
A worker should not be continuously exposed to a noise level above
85 decibels.
What happens if the noise level is too high?
Workplace Health and Safety Training Resource Kit
102
N O I S E
I N
T H E
W O R K P L A C E
What happens if the noise level
is measured and it is too high?
Remember... the different ways of controlling hazards.
Noise is a hazard so it is a problem to be solved like any other potential
danger at work.
1. Isolate or enclose the sound
Eliminate or substitute.
2. Use engineering to change the machine
Engineering controls.
3. Use job rotation
Administrative controls.
4. Use hearing protection
Personal protective equipment.
Workplace Health and Safety Training Resource Kit
103
N O I S E
I N
T H E
W O R K P L A C E
Foundry case study
A foundry used air jets in its dye-casting plant to clean the finished castings.
Each casting was cleaned by blasts from six air jets and this produced noise
levels of more than 108 decibels in peak periods.
Is a noise level of 108 decibels (dB) a workplace hazard?
What could they do to reduce the noise level?
Which of the five control measures did you choose?
high velocity air movement
and poorly designed nozzles
expose workers to
excessive noise levels
Workplace Health and Safety Training Resource Kit
104
N O I S E
I N
T H E
W O R K P L A C E
Possible solutions...
to the foundry noise problem
1. Isolate the noise problem
by separating the worker from the air jets area.
Eliminate
2. Change the machine using engineering
by replacing the nozzles on each air jet.
Engineering control
3. Use job rotation
by moving workers through different jobs so they do not spend all day
in the dye-casting plant.
Administrative control
4. Use hearing protection
by wearing ear muffs when working in the dye-casting plant.
Personal protective equipment
Workplace Health and Safety Training Resource Kit
105
N O I S E
I N
T H E
W O R K P L A C E
Activity
In small groups think of a noise problem in your workplace.
Try to come up with a solution by working through the four levels of control.
Workplace Health and Safety Training Resource Kit
106
N O I S E
I N
T H E
W O R K P L A C E
Safety tips...
avoiding noise problems
What can you do to help yourself and others?
Close doors designed to reduce noise.
Report any noise problems with machines.
Make sure you know how to correctly use your ear protectors.
Have your hearing checked by a doctor.
Workplace Health and Safety Training Resource Kit
107
N O I S E
I N
T H E
W O R K P L A C E
Listening activity
When Frank finishes work on the assembly line he usually has a ringing in
his ears. He also has a headache and is tired and irritable.
During the tea break he often sits on his own and reads the newspaper
because he has difficulty hearing people talk in a group and often
misunderstands what is being said.
At home his family complain he has the TV on too loudly.
His wife says he is becoming anti-social and rarely wants to go out with
their friends. Frank just feels stressed.
What is the effect of excessive noise on Frank's life?
What other effects happen if you lose your hearing?
Workplace Health and Safety Training Resource Kit
108
N O I S E
I N
T H E
W O R K P L A C E
Noise in the workplace...
key words
English
First language
sound
noise
irritating
threshold
intensity
frequency
exposed
excessive
measuring
Workplace Health and Safety Training Resource Kit
109
N O I S E
I N
T H E
W O R K P L A C E
Developing your writing skills
Write out the key words breaking them into syllables.
Example:
s o
n d
(1)
noise
irritating
threshold
intensity
frequency
exposed
excessive
measuring
Workplace Health and Safety Training Resource Kit
110
N O I S E
I N
T H E
W O R K P L A C E
Developing your writing skills
How many more words can you find that belong to the same word family?
Example: sound... (soundless, soundlessly, soundly, unsound)
noise
irritating
intensity
frequency
excessive
measuring
Workplace Health and Safety Training Resource Kit
111
N O I S E
I N
T H E
W O R K P L A C E
Can you find the following
words in the grid?
The first word has been done for you...
threshold
exposed
fluid
sound
intensity
impulses
irritating
noise
decibels
ear
bones
Workplace Health and Safety Training Resource Kit
112
Вам также может понравиться
- So,You Want To Be An Audio Engineer: A Complete Beginners Guide For Selecting Audio GearОт EverandSo,You Want To Be An Audio Engineer: A Complete Beginners Guide For Selecting Audio GearРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Environmental Health and Safety University of TennesseeДокумент54 страницыEnvironmental Health and Safety University of TennesseeEm WaОценок пока нет
- Resume About NoiseДокумент5 страницResume About NoiseElsa MutiaraОценок пока нет
- 3 Osha NoiseДокумент7 страниц3 Osha NoiseAlaa AllamОценок пока нет
- Hearing Conservation Training: Environmental Health and Safety Wake Forest UniversityДокумент53 страницыHearing Conservation Training: Environmental Health and Safety Wake Forest UniversityBirendra ShekhawatОценок пока нет
- Perdida Auditiva en El TrabajoДокумент16 страницPerdida Auditiva en El TrabajoFernando Arauz JustinianoОценок пока нет
- Hearing Conservation Training: Environmental Health and Safety University of TennesseeДокумент54 страницыHearing Conservation Training: Environmental Health and Safety University of TennesseeMG NandanОценок пока нет
- Environmental Health and Safety University of TennesseeДокумент63 страницыEnvironmental Health and Safety University of Tennesseeimran_istОценок пока нет
- Listen Up. Hea Ring Damage IS Permanent. P Rotect Your E ArsДокумент8 страницListen Up. Hea Ring Damage IS Permanent. P Rotect Your E Arspanca_xpОценок пока нет
- 8 Osha NoiseДокумент7 страниц8 Osha Noiseosama1928100% (1)
- Health and Safety Measuring Assessment Reports For EettecДокумент9 страницHealth and Safety Measuring Assessment Reports For Eettecasif_2kiОценок пока нет
- STC 5 - Group 13 - 4 A - Summary - Physical and Psychological Hazards and ControlДокумент13 страницSTC 5 - Group 13 - 4 A - Summary - Physical and Psychological Hazards and ControlVincent Ronin SerratoОценок пока нет
- Industrial Engineering and Management: NoiseДокумент12 страницIndustrial Engineering and Management: NoiseRami AbdelaalОценок пока нет
- HSE Professionals - Noise (Hearing Protection)Документ5 страницHSE Professionals - Noise (Hearing Protection)walidОценок пока нет
- Hearing Conservation Education v3Документ34 страницыHearing Conservation Education v3Frank CraftОценок пока нет
- Noise HazardДокумент20 страницNoise HazardRicky jhonsОценок пока нет
- NoiseДокумент88 страницNoiseManal OtОценок пока нет
- Noise ExposureДокумент20 страницNoise Exposureapi-270822363Оценок пока нет
- Noise (Hearing Protection)Документ9 страницNoise (Hearing Protection)Ansar AliОценок пока нет
- Noise and Hearing LossДокумент18 страницNoise and Hearing LossAnthonyОценок пока нет
- Occupationalnoiseexposure 170513025451Документ39 страницOccupationalnoiseexposure 170513025451H. Leyva100% (1)
- IGC 2 Element 8Документ74 страницыIGC 2 Element 8Fahad Maqsood100% (4)
- Carpenter Sid WebДокумент16 страницCarpenter Sid WebmichelleОценок пока нет
- Noise Exposure at Work: Hearing Loss Prevention Rule (Noise) WAC 296-817Документ48 страницNoise Exposure at Work: Hearing Loss Prevention Rule (Noise) WAC 296-817Gunnie PandherОценок пока нет
- Permissible Exposure TimeДокумент4 страницыPermissible Exposure TimecartarОценок пока нет
- MMIS 103 (Autosaved) (Repaired)Документ104 страницыMMIS 103 (Autosaved) (Repaired)dhruv singhОценок пока нет
- Noise at Work - A Guide For Health and Safety RepresentativesДокумент6 страницNoise at Work - A Guide For Health and Safety RepresentativesIrdam JonoОценок пока нет
- NoisebasicsДокумент6 страницNoisebasicsligin11112192Оценок пока нет
- Noise: Training GuideДокумент5 страницNoise: Training GuideSaddem HadfiОценок пока нет
- Noise in The Workplace: What You Should KnowДокумент20 страницNoise in The Workplace: What You Should KnowMumtaz AliОценок пока нет
- Noise and The Worker - 1st Ed - June 1963Документ13 страницNoise and The Worker - 1st Ed - June 1963dogmatooth100% (2)
- Noise and VibrationДокумент5 страницNoise and VibrationermankurОценок пока нет
- Preliminary: I. BackgroundДокумент7 страницPreliminary: I. BackgroundIntan R SОценок пока нет
- IE558 - Chapter 22Документ40 страницIE558 - Chapter 22h8wvk5y22zОценок пока нет
- NEBOSH - IG1 - Element - 5 NewДокумент40 страницNEBOSH - IG1 - Element - 5 NewAnil100% (1)
- Biggest Noise at Work Mistakes EbookДокумент24 страницыBiggest Noise at Work Mistakes EbookAbbas HussainОценок пока нет
- Global Manufacturing Training: SAF-111 Noise HazardsДокумент53 страницыGlobal Manufacturing Training: SAF-111 Noise HazardsZaid Tariq AlabiryОценок пока нет
- Multiple Activity Chart: Group - 1Документ27 страницMultiple Activity Chart: Group - 1VaanazhaganОценок пока нет
- Construction Noise Hearing Loss 30 Minute Presentation FinalДокумент31 страницаConstruction Noise Hearing Loss 30 Minute Presentation FinalIlyas khokharОценок пока нет
- Occupational Nosie Exposure and Hearing Loss PreventionДокумент26 страницOccupational Nosie Exposure and Hearing Loss Preventionpradip13123Оценок пока нет
- Noise at WorkДокумент20 страницNoise at WorkAlaa Eldin MohamedОценок пока нет
- WSNZ 1311 Construction Machinery Fact Sheet v5Документ4 страницыWSNZ 1311 Construction Machinery Fact Sheet v5Gemunu WeerethungaОценок пока нет
- Hearing ConservationДокумент22 страницыHearing ConservationMuhammed Mohsin100% (1)
- Ergonomics 1 Laboratory: By: Maria Lourdes H. ParceroДокумент4 страницыErgonomics 1 Laboratory: By: Maria Lourdes H. ParceroKian Russel LinsanganОценок пока нет
- Unit 7.1, Introduction To NoiseДокумент3 страницыUnit 7.1, Introduction To NoiseSangharsh RathoreОценок пока нет
- Occupational Noise-Induced Hearing Loss in Auto Part Factory Workers in Welding Units in ThailandДокумент8 страницOccupational Noise-Induced Hearing Loss in Auto Part Factory Workers in Welding Units in ThailandPratiwi UmbohОценок пока нет
- Noise & Hearing ConservationДокумент24 страницыNoise & Hearing Conservationc_k_tinОценок пока нет
- Noise PollutionДокумент34 страницыNoise PollutionFast ReinОценок пока нет
- Anthropometry of External Auditory Canal by Non-Contactable MeasurementДокумент6 страницAnthropometry of External Auditory Canal by Non-Contactable MeasurementMusdah MMОценок пока нет
- Headset Safety Resource Kit: A Resource Guide For Call Centre Employees and Health and Safety DelegatesДокумент16 страницHeadset Safety Resource Kit: A Resource Guide For Call Centre Employees and Health and Safety DelegatesxrashexОценок пока нет
- Noise Exposure at Work: Hearing Loss Prevention Rule (Noise) WAC 296-817Документ47 страницNoise Exposure at Work: Hearing Loss Prevention Rule (Noise) WAC 296-817RAMSHA RAMSHA100% (2)
- HEALTH 6 - Module 4Документ2 страницыHEALTH 6 - Module 4Lemuel MoradaОценок пока нет
- Industrial Noise ControlДокумент5 страницIndustrial Noise ControlVelpandian ManiОценок пока нет
- Noise at Workplaces in The Call CenterДокумент12 страницNoise at Workplaces in The Call CenterYAIОценок пока нет
- Safety - Lecture 5Документ33 страницыSafety - Lecture 5Tamer MohamedОценок пока нет
- DM-PH&SD-P4-TG10 - (Guidelines For Personal Protective Equipment-Hearing Protection) PDFДокумент3 страницыDM-PH&SD-P4-TG10 - (Guidelines For Personal Protective Equipment-Hearing Protection) PDFdemie figueroaОценок пока нет
- Hearing Protection: Demonstrate Explain DangersДокумент1 страницаHearing Protection: Demonstrate Explain DangersSkariah MathewsОценок пока нет
- Safety Bulletin (Occupational Noise)Документ2 страницыSafety Bulletin (Occupational Noise)ManZooR Ul HassaNОценок пока нет
- Noise Level Measurement PRELAB: #01 Group 5Документ7 страницNoise Level Measurement PRELAB: #01 Group 5louryОценок пока нет
- Noise HazardsДокумент27 страницNoise HazardsZainorin Ali0% (1)
- Year 12 Completed Workbooks t2 2015Документ4 страницыYear 12 Completed Workbooks t2 2015api-200253170Оценок пока нет
- Engo ResultsДокумент5 страницEngo Resultsapi-200253170Оценок пока нет
- Mem10105 Certificate I in Engineering May2015Документ9 страницMem10105 Certificate I in Engineering May2015api-200253170Оценок пока нет
- Folding ToolboxДокумент5 страницFolding Toolboxapi-200253170Оценок пока нет
- Manual Production - Sheet Production Student TaskДокумент5 страницManual Production - Sheet Production Student Taskapi-200253170Оценок пока нет
- Bar ClampДокумент19 страницBar Clampapi-200253170Оценок пока нет
- Manual Production - Sheet Production Student TaskДокумент5 страницManual Production - Sheet Production Student Taskapi-200253170Оценок пока нет
- Electronicsbook 2015Документ23 страницыElectronicsbook 2015api-200253170Оценок пока нет
- 25 Facts About The Great Pyramid of GizaДокумент3 страницы25 Facts About The Great Pyramid of Gizaapi-200253170Оценок пока нет
- Yr 9 Engineering 2015 Intro Challenge 1 StudentsДокумент2 страницыYr 9 Engineering 2015 Intro Challenge 1 Studentsapi-200253170Оценок пока нет
- Esis Approved Equipment Industrial Arts TechnologyДокумент2 страницыEsis Approved Equipment Industrial Arts Technologyapi-200253170Оценок пока нет
- Why Do and What Is ArtДокумент20 страницWhy Do and What Is Artapi-2002531700% (1)
- Art ExpectationsДокумент6 страницArt Expectationsapi-200253170Оценок пока нет
- 1-Continuity IndДокумент1 страница1-Continuity Indapi-200253170Оценок пока нет
- Work Health and Safety Student TaskДокумент17 страницWork Health and Safety Student Taskapi-200253170Оценок пока нет
- Year 11 Completed Workbooks t4 2014Документ2 страницыYear 11 Completed Workbooks t4 2014api-200253170Оценок пока нет
- Design ModsДокумент1 страницаDesign Modsapi-200253170Оценок пока нет
- Listening Answer5 JLMTДокумент14 страницListening Answer5 JLMTQuangОценок пока нет
- Nervous System - Summary NotesДокумент9 страницNervous System - Summary NotesHarshОценок пока нет
- Science Form 2 Chapter 1Документ9 страницScience Form 2 Chapter 1Lim Cj100% (2)
- Thesis - The Importance of Sound Design & Its Affect On Perception - JR DrakeДокумент48 страницThesis - The Importance of Sound Design & Its Affect On Perception - JR DrakedoeditОценок пока нет
- ENT For Entrance Exams - S. Buchiraja PDFДокумент442 страницыENT For Entrance Exams - S. Buchiraja PDFBharat G90% (20)
- Navajo Medicine Man Remedy For Hearing Loss PDFДокумент44 страницыNavajo Medicine Man Remedy For Hearing Loss PDFgerald nacinopaОценок пока нет
- Special Senses Eye and EarДокумент60 страницSpecial Senses Eye and EarTosinОценок пока нет
- Nanoparticle Based Drug Delivery in The Inner Ear Current Challenges Limitations and OpportunitiesДокумент10 страницNanoparticle Based Drug Delivery in The Inner Ear Current Challenges Limitations and OpportunitiesRana Sabouni TabariОценок пока нет
- The Ear. The Helix. The External Auditory Canal and Tympanic Membrane. Air and Bone JoiningДокумент40 страницThe Ear. The Helix. The External Auditory Canal and Tympanic Membrane. Air and Bone JoiningHarshit BhardwajОценок пока нет
- Auditory Evoked Potentials - AEPs - Underlying PrinciplesДокумент19 страницAuditory Evoked Potentials - AEPs - Underlying PrinciplesMansi SinghОценок пока нет
- Cristobal 2008Документ8 страницCristobal 2008Rendra SyaniОценок пока нет
- Sensory Process and PerceptionДокумент58 страницSensory Process and Perceptiondrkadiyala2Оценок пока нет
- Knowledge Organiser: Properties of Waves Sound Waves HearingДокумент1 страницаKnowledge Organiser: Properties of Waves Sound Waves HearingLuisGamesОценок пока нет
- Chapter 12 The Sense Organs Anatomy and Physiology of Eye Ear Skin Tongue NoseДокумент7 страницChapter 12 The Sense Organs Anatomy and Physiology of Eye Ear Skin Tongue NoseSanketraje JadhavОценок пока нет
- The Special SensesДокумент95 страницThe Special SensesRuchieОценок пока нет
- Psychology: (8th Edition) David MyersДокумент88 страницPsychology: (8th Edition) David MyersAdesh Nidhi TiwaryОценок пока нет
- Ent Notes For PGДокумент12 страницEnt Notes For PGSHAKEEL1991Оценок пока нет
- Physiology MnemonicsДокумент7 страницPhysiology MnemonicsplaincircleОценок пока нет
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 9Th Edition Sherwood Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFДокумент33 страницыHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems 9Th Edition Sherwood Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFcleopatrabanhft1vh7100% (10)
- Music Education To Train Hearing Abilities in Children With Cochlear ImplantsДокумент8 страницMusic Education To Train Hearing Abilities in Children With Cochlear ImplantsYopi YupiiОценок пока нет
- Psych 1xx3 Quiz Stuff MehДокумент28 страницPsych 1xx3 Quiz Stuff MehminiОценок пока нет
- ANAPHY Lec Session #11 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Документ11 страницANAPHY Lec Session #11 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaОценок пока нет
- 24 Inner Ear Anatomy, Emberyology, Drugs Ototoxicity (Done)Документ24 страницы24 Inner Ear Anatomy, Emberyology, Drugs Ototoxicity (Done)osamaeОценок пока нет
- NCLEX Exam Ear Disorders and CareДокумент8 страницNCLEX Exam Ear Disorders and CareHeather ClemonsОценок пока нет
- Coombe, Suzanne - MAUD ThesisДокумент134 страницыCoombe, Suzanne - MAUD ThesisasprillaОценок пока нет
- Topss Sensation PerceptionДокумент46 страницTopss Sensation PerceptionDaisy RodriguezОценок пока нет
- ENT Hodder Arnold PDFДокумент176 страницENT Hodder Arnold PDFAkbar LimpoОценок пока нет
- 040 Human Performance & Limitations - V2+v3 - 31OUT09Документ166 страниц040 Human Performance & Limitations - V2+v3 - 31OUT09kest32100% (1)
- Physiology of HearingДокумент3 страницыPhysiology of HearingKC RajagopalОценок пока нет