Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Grade 2 Module 5 Family Letter
Загружено:
api-2712838900 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
90 просмотров2 страницыОригинальное название
grade 2 module 5 family letter
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
90 просмотров2 страницыGrade 2 Module 5 Family Letter
Загружено:
api-271283890Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
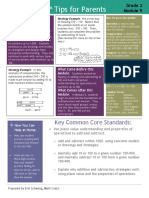
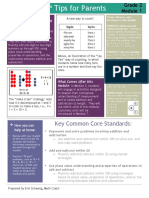
Eureka Math Tips for Parents
Addition and Subtraction
Parents
Within 1,000 with Word
Problems to 100
In this module, students build upon
all their previous work with place
value. They extend their work with
addition and subtraction algorithms
to numbers up to 1,000. Students
continue to use drawings and models
to strengthen and deepen their
conceptual understanding. They also
continue to work with various types
of word problems with numbers up to
100.
Strategy Example: In this
example of compensation, the
subtraction problem 514 290 is
made much simpler by adding 10 to
both numbers before solving:
Strategy Example: the arrow way
of showing 570 110. Notice that
the solution builds on an easier
problem first: 570 100. Then,
students can complete the problem
by subtracting 10 more.
(See reverse for more on the arrow
way.)
Help your student
practice counting both
backward and forward
by 10s and 100s.
Given any two- or
three-digit number,
help your student
practice finding 10
more or 10 less, and/or
100 more or 100 less
Algorithm: a step-by-step
procedure to solve a particular
type of problem
Compensation: a simplifying
strategy where students add or
subtract the same amount to or
from both numbers to create an
equivalent but easier problem,
e.g., 610-290 = 620-300 = 320
Decompose: to break 1 larger
unit into 10 smaller units
What Came Before this
Module: Students worked on
fluency in adding and subtracting to
100 and built conceptual
understanding for operations on
numbers up to 200.
begin to examine the foundations of
multiplication and division. They
learn about equal groups, arrays,
and the idea that numbers other
than 1, 10, and 100 can be
units/groups.
Help at Home:
New Terms in this Module:
Compose: to make 1 larger unit
from 10 smaller units
What Comes After this
Module: In Module 6, students
+ How You Can
Grade 2
Module 5
New groups below: show
newly composed units on the
line below the appropriate
place in the addition algorithm
Simplifying strategy: e.g., to
solve 299 + 6, think
299 + 1 + 5 = 300 + 5 = 305
Familiar Terms:
Addend
Addition
Bundle
Difference
Equation
Number bond
Place value
Rename
Subtraction
Tape diagram
Total
Unbundle
Units of ones, tens, hundreds
Key Common Core Standards:
Use place value understanding and properties of
operations to add and subtract.
o Add and subtract within 1000, using concrete models
or drawings and strategies.
o Mentally add 10 or 100 to a given number 100900,
and mentally subtract 10 or 100 from a given number
100900.
o Explain why addition and subtraction strategies work,
using place value and the properties of operations.
than the number.
Prepared by Erin Schweng, Math Coach
Eureka Math, A Story of Units
Grade 2
Module 5
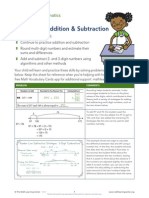
Spotlight on Math
Strategies:
This is an example of how one might add 590 + 240 using the
arrow way. Notice that 240 has been decomposed, or chunked,
into 10 + 30 + 200 in order to make the adding easier.
This is a simple subtraction example of 780 390. In this case,
390 has been decomposed into 300, 80, and 10.
The Arrow Way
Students will
frequently use this
strategy in this
module of A Story
of Units.
The arrow way is a strategy for both addition and subtraction
that is heavily featured in this module.
At first glance, arrow notation, or the arrow way of doing mathematical operations, may seem
complicated. However, it is a very helpful method, and it is actually very similar to what many of
us have naturally learned to do mentally while adding and subtracting.
The arrow way involves chunking a number into more manageable mental pieces in order to add or
subtract. Students use numbers that they have become confident working with, such as 100 and 10, in
order to simplify the problem. They record their mathematical thinking as an expression with arrows
in between the numbers to show the chunks of numbers that they are working with as they go.
This method is just one of several that students will be encouraged to use throughout this module.
By employing various models and strategies, students deepen their facility with the mathematics they
are learning and eventually build a tool kit of strategies to choose from as math becomes more
complex throughout the elementary grades.
Sample Problem from Module 5:
(Example taken from Module 5, Lesson 9)
The table to the right represents the
halftime score at a basketball game.
The red team scored 19 points in the second half.
The yellow team scored 13 points in the second half.
a. Who won the game?
b. By how much did that team win?
For more information visit commoncore.org
This problem gives students
many options for solving. They
can choose from the strategies
they have learned in this module
to do the addition and
subtraction necessary to solve
the problem.
Вам также может понравиться
- Graduated Difficulty Tiered Lesson Plan RegroupingДокумент3 страницыGraduated Difficulty Tiered Lesson Plan Regroupingapi-317478721Оценок пока нет
- Math g2 m5 Full ModuleДокумент312 страницMath g2 m5 Full ModuleRivka Share100% (1)
- Miaa 360 Intervention PBLДокумент5 страницMiaa 360 Intervention PBLapi-268936515Оценок пока нет
- Graduated Difficulty Lesson - BosseДокумент3 страницыGraduated Difficulty Lesson - Bosseapi-252935769Оценок пока нет
- Adding Two 2-Digit Numbers With Regrouping Lesson PlanДокумент3 страницыAdding Two 2-Digit Numbers With Regrouping Lesson Planapi-283422107100% (2)
- Eureka Math-Tips For Parents-Grade 2 Module 3Документ2 страницыEureka Math-Tips For Parents-Grade 2 Module 3api-271283890Оценок пока нет
- Motion in 2 DДокумент12 страницMotion in 2 DVenesia Ayu Dewanti0% (1)
- B M O B M O: Ritish Athematical Lympiad Ritish Athematical LympiadДокумент65 страницB M O B M O: Ritish Athematical Lympiad Ritish Athematical LympiadeduhubОценок пока нет
- Motoman ManualДокумент16 страницMotoman ManualvalentincaciorОценок пока нет
- Solved According To Your Preferences Do The Following Pairs of ProductsДокумент1 страницаSolved According To Your Preferences Do The Following Pairs of ProductsM Bilal SaleemОценок пока нет
- 1.2 History and Scope of Fluid Mechanics: Chapter 1 IntroductionДокумент2 страницы1.2 History and Scope of Fluid Mechanics: Chapter 1 IntroductionFelipe Rocco EspinozaОценок пока нет
- G11 Physics Extreme Series BookДокумент435 страницG11 Physics Extreme Series BookHabtamu Worku100% (2)
- Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 5 Parent Tip SheetДокумент2 страницыEureka Math Grade 2 Module 5 Parent Tip Sheetapi-324573119Оценок пока нет
- Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 5 Parent Tip Sheet 1Документ2 страницыEureka Math Grade 2 Module 5 Parent Tip Sheet 1api-236750381Оценок пока нет
- Kaedah Algoritma PenambahanДокумент7 страницKaedah Algoritma PenambahanHasniza Abd HamidОценок пока нет
- Day 2 Lesson PlanДокумент1 страницаDay 2 Lesson Planapi-490230700Оценок пока нет
- Math g2 m5 Full ModuleДокумент275 страницMath g2 m5 Full Modulemadhu63Оценок пока нет
- Math Lab Grade 3 Module 1a pdf1Документ18 страницMath Lab Grade 3 Module 1a pdf1api-276903925Оценок пока нет
- Lesson: Addition of Three Digit Numbers Using Base Ten Blocks and Expanded Notation Grade: 2 MA FrameworksДокумент3 страницыLesson: Addition of Three Digit Numbers Using Base Ten Blocks and Expanded Notation Grade: 2 MA Frameworksapi-310204339100% (1)
- Unit Day 3Документ6 страницUnit Day 3api-284886534Оценок пока нет
- Three Digit Addition Strategies Review 2Документ6 страницThree Digit Addition Strategies Review 2RiriОценок пока нет
- Grade 2 Unit 4 ParentletterДокумент3 страницыGrade 2 Unit 4 Parentletterapi-294044622Оценок пока нет
- Tech Trends Lesson PlanДокумент5 страницTech Trends Lesson PlantonyagrantОценок пока нет
- Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 1 Tips For ParentsДокумент2 страницыEureka Math Grade 1 Module 1 Tips For Parentsapi-270945269100% (1)
- Winter Observation Lesson PlanДокумент2 страницыWinter Observation Lesson Planapi-304782077Оценок пока нет
- Vels and Ac Mathematics Lesson Plan Start and Jump NumbersДокумент7 страницVels and Ac Mathematics Lesson Plan Start and Jump Numbersapi-221544422Оценок пока нет
- Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 1 Parent Tip Sheet 092415Документ2 страницыEureka Math Grade 2 Module 1 Parent Tip Sheet 092415api-324573119Оценок пока нет
- Grade 3, Unit Two: Place Value Structures & Multi-Digit ComputationДокумент2 страницыGrade 3, Unit Two: Place Value Structures & Multi-Digit ComputationMeganMaynardОценок пока нет
- Tiered Lesson Regrouping Graduated DifficultyДокумент3 страницыTiered Lesson Regrouping Graduated Difficultyapi-315872239Оценок пока нет
- IMB Lesson Plan: Activity Description of Activities and Setting TimeДокумент6 страницIMB Lesson Plan: Activity Description of Activities and Setting Timeapi-453481434Оценок пока нет
- Unit 3Документ4 страницыUnit 3api-260708970Оценок пока нет
- Aims Esp LessonДокумент11 страницAims Esp Lessonapi-302577842Оценок пока нет
- Bridges 3rd Grade Unit 3Документ2 страницыBridges 3rd Grade Unit 3api-289263859100% (1)
- Number Sense: Subject Area: Math Grade Level: Grade 6 Length of Unit: 3 MonthsДокумент15 страницNumber Sense: Subject Area: Math Grade Level: Grade 6 Length of Unit: 3 Monthsapi-273179753Оценок пока нет
- Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 15 (B)Документ18 страницMathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 15 (B)ALJEM TUBIGONОценок пока нет
- Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 3 Chapter 9 Multiples and Problem Solving - Big Ideas Math AnswersДокумент1 страницаBig Ideas Math Answers Grade 3 Chapter 9 Multiples and Problem Solving - Big Ideas Math Answersjetrex15Оценок пока нет
- Teaching Children To Calculate MentallyДокумент75 страницTeaching Children To Calculate Mentallyapi-110727701Оценок пока нет
- Math g2 m1 Full ModuleДокумент128 страницMath g2 m1 Full ModuleRivka ShareОценок пока нет
- Addition of IntegersДокумент6 страницAddition of IntegersCyrene Joy BermidoОценок пока нет
- Fractions Decimals and Percentages Teaching IdeasДокумент2 страницыFractions Decimals and Percentages Teaching IdeasRajkumar GulatiОценок пока нет
- Year 6 t1 Unit 3 Mathematics TermДокумент6 страницYear 6 t1 Unit 3 Mathematics Termapi-267136654Оценок пока нет
- My Homework Lesson 1 Subtract MentallyДокумент7 страницMy Homework Lesson 1 Subtract Mentallyffutcfrmg100% (1)
- New LP TemplateДокумент10 страницNew LP TemplateTasia Starling ScruggsОценок пока нет
- Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 2 Tips For ParentsДокумент2 страницыEureka Math Grade 5 Module 2 Tips For Parentsapi-327422647Оценок пока нет
- LessonplanmathДокумент5 страницLessonplanmathapi-698817165Оценок пока нет
- Unit 2: Family Letter: Estimation and CalculationДокумент4 страницыUnit 2: Family Letter: Estimation and Calculationapi-196928388Оценок пока нет
- Unit StandardsДокумент7 страницUnit Standardsapi-284886534Оценок пока нет
- CSC Techniques in Numerical Reasoning TestДокумент3 страницыCSC Techniques in Numerical Reasoning TestMay Ann GervacioОценок пока нет
- Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 1 Parent Tip SheetДокумент2 страницыEureka Math Grade 2 Module 1 Parent Tip Sheetapi-522113163Оценок пока нет
- Key Principles of CalculationДокумент12 страницKey Principles of Calculationapi-194991201Оценок пока нет
- Primary 1 Chapter 6 Add and Subtract Up To 100: Learning OutcomesДокумент38 страницPrimary 1 Chapter 6 Add and Subtract Up To 100: Learning OutcomesSu Myat NoeОценок пока нет
- Student A: Mia Grade: 2 Date Interviewed: 27/03/2013: Domain Assigned Growth PointДокумент9 страницStudent A: Mia Grade: 2 Date Interviewed: 27/03/2013: Domain Assigned Growth Pointapi-285941433Оценок пока нет
- Math UnitplanДокумент5 страницMath Unitplanapi-252035669Оценок пока нет
- Long Lesson Plan For 2 Observed Lessons: Addition Equality VariablesДокумент2 страницыLong Lesson Plan For 2 Observed Lessons: Addition Equality Variablesapi-243870961Оценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan-KiahaVictorianoДокумент6 страницLesson Plan-KiahaVictorianoVICTORIANO PAQUIULОценок пока нет
- LESSON PLAN IN GRADE 7 - Copy...........................................................................Документ4 страницыLESSON PLAN IN GRADE 7 - Copy...........................................................................Kimberly JoyОценок пока нет
- Mental Math StrategiesДокумент3 страницыMental Math StrategiesEric SloanОценок пока нет
- Educ 420 Lesson Plan 3 Two-Digit Addition With RegroupingДокумент2 страницыEduc 420 Lesson Plan 3 Two-Digit Addition With Regroupingapi-302683612Оценок пока нет
- Math g2 m4 Full ModuleДокумент405 страницMath g2 m4 Full ModuleHirenkumar ShahОценок пока нет
- KS3 Maths Level Up!: Recovery GuidanceДокумент20 страницKS3 Maths Level Up!: Recovery Guidancedadajee420Оценок пока нет
- Thinking Strategies For Basic Facts (: Tutorial Week 3)Документ25 страницThinking Strategies For Basic Facts (: Tutorial Week 3)Sara ChanОценок пока нет
- Math LP Feb 23-27, 2015Документ9 страницMath LP Feb 23-27, 2015Tasia Starling ScruggsОценок пока нет
- Interactivewhiteboardactivity AgatlinДокумент3 страницыInteractivewhiteboardactivity Agatlinapi-284767326Оценок пока нет
- Lesson BДокумент2 страницыLesson Bapi-312641906Оценок пока нет
- Unit OverviewДокумент4 страницыUnit Overviewapi-242316638Оценок пока нет
- Math Fluency Activities for K–2 Teachers: Fun Classroom Games That Teach Basic Math Facts, Promote Number Sense, and Create Engaging and Meaningful PracticeОт EverandMath Fluency Activities for K–2 Teachers: Fun Classroom Games That Teach Basic Math Facts, Promote Number Sense, and Create Engaging and Meaningful PracticeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- First Grade Policies and ProceduresДокумент4 страницыFirst Grade Policies and Proceduresapi-271283890Оценок пока нет
- October NewsletterДокумент2 страницыOctober Newsletterapi-271283890Оценок пока нет
- Eureka Math-Tips For Parents-Grade 2 Module 4Документ2 страницыEureka Math-Tips For Parents-Grade 2 Module 4api-271283890Оценок пока нет
- Experiment 2: Plane and Spherical MirrorsДокумент13 страницExperiment 2: Plane and Spherical MirrorsJason DemdamОценок пока нет
- 8 2 Angle Bisectors of TrianglesДокумент8 страниц8 2 Angle Bisectors of Trianglesapi-332361871Оценок пока нет
- Modeling and Simulation of Surface Roughness: Rajendra M. PatrikarДокумент8 страницModeling and Simulation of Surface Roughness: Rajendra M. PatrikarMEHDI FARROKHIОценок пока нет
- Measures of Central Tendency and Measures of VariabilityДокумент41 страницаMeasures of Central Tendency and Measures of VariabilityJoshua Kim Tabiolo Escalona100% (1)
- K Air Conditioning M1Документ82 страницыK Air Conditioning M1bhalchandrapatilОценок пока нет
- Imaths Topics and Victorian Curriculum MatchДокумент16 страницImaths Topics and Victorian Curriculum MatchfazalОценок пока нет
- DS Lecture 5Документ29 страницDS Lecture 5CH HASEEB AMJADОценок пока нет
- Python SyllabusДокумент6 страницPython SyllabusVenkat KancherlaОценок пока нет
- M257 316 2012 Lecture 20Документ6 страницM257 316 2012 Lecture 20salmanОценок пока нет
- Geometrical Formulation of Quantum MechanicsДокумент41 страницаGeometrical Formulation of Quantum Mechanicskipikos45Оценок пока нет
- Customer Satisfaction On Service Quality in Private Commercial Banking Sector in BangladeshДокумент11 страницCustomer Satisfaction On Service Quality in Private Commercial Banking Sector in BangladeshUmar KhanОценок пока нет
- Prediction of Airline Ticket Price: Motivation Models DiagnosticsДокумент1 страницаPrediction of Airline Ticket Price: Motivation Models DiagnosticsQa SimОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 Aerodynamic VariablesДокумент19 страницLecture 1 Aerodynamic VariablessaintanddevilОценок пока нет
- Petro Peru PDFДокумент137 страницPetro Peru PDFLuiz Cabello100% (1)
- SYMBOL Characters and GlyphsДокумент8 страницSYMBOL Characters and GlyphssabitavabiОценок пока нет
- Toc Unit IIIДокумент14 страницToc Unit IIIanilostaОценок пока нет
- Structured Mathematical Modeling of Industrial BoiДокумент22 страницыStructured Mathematical Modeling of Industrial BoiAndrey CaroОценок пока нет
- Spectral DilationДокумент20 страницSpectral DilationEsteban ZuluagaОценок пока нет
- M&M Analysis KC SharedДокумент103 страницыM&M Analysis KC SharedDebanjan MukherjeeОценок пока нет
- Cbse Practical/Project Schedule: Class-Xi/Xii Mode S.NO. TopicДокумент26 страницCbse Practical/Project Schedule: Class-Xi/Xii Mode S.NO. TopicGrand PlayerОценок пока нет
- Physics Paper-1: Marks:60 Time 3 HrsДокумент1 страницаPhysics Paper-1: Marks:60 Time 3 HrsÇybêrkïñg SumerОценок пока нет
- HubbleДокумент2 страницыHubbleAlam AhmedОценок пока нет
- Asm1 Programming 1st Nguyenthiminhnguyet Bh00468Документ38 страницAsm1 Programming 1st Nguyenthiminhnguyet Bh00468Nguyệt MinhОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 - Differential EquationsДокумент33 страницыChapter 6 - Differential Equationsdiktatorimhotep8800Оценок пока нет