Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Tabla EDO Orden 1
Загружено:
José Antonio Pelegrina CalventeИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Tabla EDO Orden 1
Загружено:
José Antonio Pelegrina CalventeАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
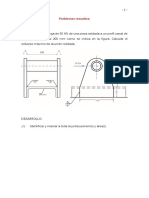
TIPO DE ECUACION
Separables
METODO
DE RESOLUCION
Z
Z
dy
= g(x) dx + C
h(y)
dy
= g(x)h(y)
dx
dy
= f (Ax + By + C)
dx
M (x, y) dx + N (x, y) dy = 0
Homog
eneas
con M y N funciones homogeneas del mismo grado
Coeficientes
lineales
M (x, y) dx + N (x, y) dy = 0
con
M (x, y) = a1 x + b1 y + c1
N (x, y) = a2 x + b2 y + c2
Lineales
Bernoulli
Exactas
dy
+ P (x)y = f (x)
dx
dy
+ P (x)y = f (x)y n
dx
M (x, y) dx + N (x, y) dy = 0
@M
@N
(x, y) =
(x, y)
@y
@x
M (x, y) dx + N (x, y) dy = 0
@M
@N
donde
(x, y) 6=
(x, y)
@y
@x
donde
Exactas por
factor
integrante
Cambio de variable: u = Ax + By + C
Se obtiene una ecuacion separable.
OBSERVACIONES
Realizar un cambio de variable:
y = ux ) dy = u dx + x du
No olvidar C.
No olvidar soluciones constantes
dadas por los ceros de h.
No olvidar deshacer el cambio
de variable.
No olvidar deshacer el cambio
de variable.
x = vy ) dx = v dy + y dv
Se obtiene una ecuacion separable
dy
Si las rectas son paralelas )
= f (Ax + By + C)
dx
Si las rectas se cortan en (h, k), cambio de variable:
x=u+h
) ecuacion homog
enea
y =v+k
R
Factor integrante: (x) = exp
P (x) dx
h
i
d
E.D. )
(x)y = (x)f (x)
dx
Cambio de variable: u = y 1 n
Se obtiene una ecuacion lineal
Dependiendo de la forma de M y N
Solucion f (x, y) = C donde f cumple
Integrar respecto a una variable y
@f
@f
(x, y) = M (x, y),
(x, y) = N (x, y)
@x
@y
Buscar factor integrante = (z(x, y)) con z(x, y) conocida:
i
@h
@h i
E.D. debe ser exacta )
M =
N
@y
@x
Resolver la ecuacion exacta E.D.
es m
as beneficioso un cambio u otro.
No olvidar deshacer cambios
de variable.
No olvidar C.
No olvidar despejar y.
n 6= 0, 1. No olvidar deshacer
el cambio de variable.
derivar el resultado respecto a la otra.
Se obtiene una ecuaci
on diferencial
ordinaria para en la variable z.
Comprobar que E.D. es exacta.
Вам также может понравиться
- Calculo Diferencial - CANEK - UAM - CompressedДокумент544 страницыCalculo Diferencial - CANEK - UAM - Compressedcosmofloyd100% (4)
- 5.3 Integrales Iteradas, Dobles y Triples.Документ11 страниц5.3 Integrales Iteradas, Dobles y Triples.Juan Mcfly Badillo60% (5)
- Solucionario de Dennis G Zill - Ecuaciones DiferencialesДокумент86 страницSolucionario de Dennis G Zill - Ecuaciones DiferencialesArianaLexyPadillaMondocorreОценок пока нет
- Derivada Parcial-DireccionalДокумент30 страницDerivada Parcial-Direccionalluis kanaОценок пока нет
- Ecuaciones Diferenciales ExactasДокумент4 страницыEcuaciones Diferenciales Exactasjoserami7073370100% (6)
- Aplicacion de Derivadas en La Ingenieria MecatronicaДокумент6 страницAplicacion de Derivadas en La Ingenieria MecatronicaLucy LucyОценок пока нет
- Serie de Ejercicios Resueltos de Cálculo Integral PDFДокумент20 страницSerie de Ejercicios Resueltos de Cálculo Integral PDFCarlos TapiaОценок пока нет
- Matematicai PDFДокумент11 страницMatematicai PDFLuis GarcíaОценок пока нет
- Libro de Ejercicios Resueltos - Ecuaciones Diferenciales PDFДокумент141 страницаLibro de Ejercicios Resueltos - Ecuaciones Diferenciales PDFKroonik100% (3)
- Introduccion Al Calculo DiferencialДокумент310 страницIntroduccion Al Calculo DiferencialMiguel Angel Amaya100% (2)
- 2da ExposicionДокумент5 страниц2da ExposicionAlejandro Fuel67% (3)
- Solucionario Matematicas 3Документ253 страницыSolucionario Matematicas 3Victoria gomez100% (2)
- Ecuaciones DiferencialesДокумент14 страницEcuaciones DiferencialesbraulioОценок пока нет
- Ejercicios ElectromagnetismoДокумент70 страницEjercicios ElectromagnetismoFrancisco Henriquez100% (1)
- Álgebra - Ingeniería Mecánica - UC3 - Ecuaciones LinealesДокумент4 страницыÁlgebra - Ingeniería Mecánica - UC3 - Ecuaciones LinealesJosé Manuel Sánchez0% (1)
- 1.1 Ecuaciones ParamétricasДокумент10 страниц1.1 Ecuaciones ParamétricasStalin Paul Rodriguez Leon100% (1)
- CALCULO VECTORIAL Problemas Res - Karen PaoДокумент232 страницыCALCULO VECTORIAL Problemas Res - Karen Paoantosega80% (5)
- Guía ETS Cálculo Vectorial 2012Документ7 страницGuía ETS Cálculo Vectorial 2012origen123Оценок пока нет
- Solucionario de Dennis G Zill - Ecuaciones DiferencialesДокумент86 страницSolucionario de Dennis G Zill - Ecuaciones DiferencialesAlí A. Cabrera SolisОценок пока нет
- Calculo Vectorial Unidad 5Документ30 страницCalculo Vectorial Unidad 5Gerardo Luk67% (3)
- La Ecuación de Cauchy-EulerДокумент5 страницLa Ecuación de Cauchy-EulerCarolina SernaОценок пока нет
- Calculo Larson-Hostetler 6 Ed V1 PDFДокумент898 страницCalculo Larson-Hostetler 6 Ed V1 PDFSaul Almonte100% (1)
- El Método de Integración Por PartesДокумент16 страницEl Método de Integración Por PartesWilfrido ToMartОценок пока нет
- Ecuación Diferencial ExactaДокумент4 страницыEcuación Diferencial ExactaGiancarlo ParedesОценок пока нет
- Ecuaciones ParamétricasДокумент7 страницEcuaciones ParamétricasKassandra Von Kaulitz Trmpr0% (1)
- Grupo Simétrico S4 - AbstractДокумент8 страницGrupo Simétrico S4 - AbstractLeonardo García100% (1)
- 3 Integración Por Cambio de VariableДокумент20 страниц3 Integración Por Cambio de VariableAnonymous s8aG0pОценок пока нет
- Integrales No Elementales PDFДокумент9 страницIntegrales No Elementales PDFJuan OcañaОценок пока нет
- Soluciones Por SustituciónДокумент8 страницSoluciones Por SustituciónGerson Villa GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Formulario Ecuaciones DiferencialesДокумент14 страницFormulario Ecuaciones Diferencialesramm_ÁlvarezОценок пока нет
- Formulario de Series InfinitasДокумент4 страницыFormulario de Series InfinitasacomillaОценок пока нет
- Curvas Planas Graficadas en Coordenadas Polares. Aplicaciones de Vectores INVДокумент7 страницCurvas Planas Graficadas en Coordenadas Polares. Aplicaciones de Vectores INVMartin Bojan KarkicОценок пока нет
- Funciones de Varias VariablesING - Jesus CLAROSДокумент10 страницFunciones de Varias VariablesING - Jesus CLAROSMgonzalez93Оценок пока нет
- Aplicaciones de La IntegralДокумент3 страницыAplicaciones de La IntegralLuis Angel Briones JuárezОценок пока нет
- Ada 2 DTДокумент4 страницыAda 2 DTAlejandro Cardeña BenitezОценок пока нет
- Problemario Calculo VectorialДокумент11 страницProblemario Calculo VectorialBerenis JeronimoОценок пока нет
- Integral Por PartesДокумент18 страницIntegral Por PartesGus Chavez50% (2)
- Cortaduras de DedekindДокумент3 страницыCortaduras de DedekindPascual Emilio Molina100% (1)
- Conduccion de Calor en Una Placa RectangularДокумент3 страницыConduccion de Calor en Una Placa RectangularPepi VerónОценок пока нет
- Formulario de Metodos de Integracion e Integral DefinidaДокумент2 страницыFormulario de Metodos de Integracion e Integral Definidabernardsanz100% (2)
- Larson 3 SolucionarioДокумент358 страницLarson 3 Solucionariodashoneman74% (23)
- Ecuaciones DiferencialesДокумент30 страницEcuaciones DiferencialesRonald FloresОценок пока нет
- Ecuacion y Valor Caracteristico de Una MatrizДокумент2 страницыEcuacion y Valor Caracteristico de Una MatrizDavid P100% (1)
- Calculo I Ing Carlos Walsh 1 PDFДокумент266 страницCalculo I Ing Carlos Walsh 1 PDFRaúl González80% (5)
- Metodos Numericos para IngenieriaДокумент69 страницMetodos Numericos para Ingenieriajose david100% (10)
- Ecuaciones Diferenciales Con MapleДокумент10 страницEcuaciones Diferenciales Con Maple130quinterosОценок пока нет
- Formulario Mate 3Документ4 страницыFormulario Mate 3Luis Miguel Mendoza GarciaОценок пока нет
- Ecuaciones 1Документ37 страницEcuaciones 1Dean ParkОценок пока нет
- Trayectorias OrtogonalesДокумент28 страницTrayectorias OrtogonalesCristian Mirso Torrez Sanchez100% (1)
- Formulas Ecuaciones Diferenciales (By Carrascal)Документ11 страницFormulas Ecuaciones Diferenciales (By Carrascal)Iñaki100% (5)
- Ecuaciones DiferencialesДокумент29 страницEcuaciones Diferencialescecyalvarez47Оценок пока нет
- Formulario de Ecuaciones Diferenciales OrdinariasДокумент7 страницFormulario de Ecuaciones Diferenciales OrdinariasZamty JmОценок пока нет
- Tabla E.diferencialesДокумент3 страницыTabla E.diferencialesCapebeta100% (1)
- FORMULARIOДокумент4 страницыFORMULARIOYeni Mariana Can BeОценок пока нет
- Ecuaciones DiferencialesДокумент41 страницаEcuaciones DiferencialesOrlando AlcaОценок пока нет
- Ecuacion Diferencial LinealДокумент4 страницыEcuacion Diferencial LinealJavier AlzateОценок пока нет
- FI15 C3 Form Ec DifДокумент28 страницFI15 C3 Form Ec DifKashitokatatemoОценок пока нет
- Taller Global 1.4 Ecuaciones Diferenciales 2021-2Документ2 страницыTaller Global 1.4 Ecuaciones Diferenciales 2021-2Anais GivovichОценок пока нет
- Resumen Calculo I II IIIДокумент20 страницResumen Calculo I II IIIJorge Ortega ArriagadaОценок пока нет
- Tablas de Tiro Obús 105-14Документ474 страницыTablas de Tiro Obús 105-14José Antonio Pelegrina CalventeОценок пока нет
- Tema 02Документ63 страницыTema 02José Antonio Pelegrina CalventeОценок пока нет
- Coleccion ExamenesДокумент15 страницColeccion ExamenesJosé Antonio Pelegrina CalventeОценок пока нет
- Listado Por Orden Reinos OlvidadosДокумент4 страницыListado Por Orden Reinos OlvidadosJosé Antonio Pelegrina Calvente100% (1)
- Biomateriales Monografia EvolucionДокумент9 страницBiomateriales Monografia EvolucionIsa Cerdá RiveraОценок пока нет
- Sistema de Acumulación de CostosДокумент8 страницSistema de Acumulación de CostosVeronica DazaОценок пока нет
- Productividad Fabrica Nacional Calzado Curtiduria Zamora S.AДокумент5 страницProductividad Fabrica Nacional Calzado Curtiduria Zamora S.ADiana Marcela Sanchez PerezОценок пока нет
- Problemas ResueltosДокумент10 страницProblemas ResueltosRomarioОценок пока нет
- Tarea GRHДокумент2 страницыTarea GRHAdrian Tello OrellanaОценок пока нет
- Cómo Se Pagan Las Vacaciones No Disfrutadas en MéxicoДокумент6 страницCómo Se Pagan Las Vacaciones No Disfrutadas en MéxicoAnne GaleanaОценок пока нет
- RESPONSABILIDAD SOCIAL y ETICA EMPRESARIAL - ROBBINS COULTERДокумент33 страницыRESPONSABILIDAD SOCIAL y ETICA EMPRESARIAL - ROBBINS COULTERBlanca FernandezОценок пока нет
- Artículo de Tesis - Paola 2022Документ10 страницArtículo de Tesis - Paola 2022SegundoОценок пока нет
- Principio de OrganizaciónДокумент4 страницыPrincipio de OrganizaciónMichelle CamayoОценок пока нет
- Ficha de Notificacion SisvesoДокумент2 страницыFicha de Notificacion SisvesoJohanna VargasОценок пока нет
- Tema 14.la Improvisación en El Lenguaje MusicalДокумент26 страницTema 14.la Improvisación en El Lenguaje MusicalMarta FernándezОценок пока нет
- La Pobre AnastasiaДокумент22 страницыLa Pobre AnastasiaAnita Pérez0% (1)
- Instructivo 2023-1 MAE Economia FIN Nov2021Документ10 страницInstructivo 2023-1 MAE Economia FIN Nov2021Eliana AlvarezОценок пока нет
- BitácoraДокумент15 страницBitácorajfegioteamriton3Оценок пока нет
- Coevaluacion Del Estudiante Por InterlocutorДокумент1 страницаCoevaluacion Del Estudiante Por InterlocutorKelly DuranОценок пока нет
- Hace Mucho TiempoДокумент2 страницыHace Mucho TiempoMaria Ignacia Van De Wyngard GillmoreОценок пока нет
- BIP Julyette Paulin Gómez Vera 3Документ8 страницBIP Julyette Paulin Gómez Vera 3julianaОценок пока нет
- Elaboracion de Leche de Soya (Mezcla en Polvo A Base de Proteina de Soya)Документ19 страницElaboracion de Leche de Soya (Mezcla en Polvo A Base de Proteina de Soya)Valentina VanegasОценок пока нет
- Estudio de Calidad Croquetas para PerrosДокумент23 страницыEstudio de Calidad Croquetas para PerrosIsidro MuñizОценок пока нет
- Yo Composto en Casa, en La Escuela y en Mi ComunidadДокумент2 страницыYo Composto en Casa, en La Escuela y en Mi ComunidadPalestrante Maria Dolores Fortes AlvesОценок пока нет
- Tarea 6.1 - Cuadro Comparativo Entre El Período Barroco, Clásico, Romántico y Contemporaneo, Esteban Tabora Castro - #21411330.Документ15 страницTarea 6.1 - Cuadro Comparativo Entre El Período Barroco, Clásico, Romántico y Contemporaneo, Esteban Tabora Castro - #21411330.Marshall LoackwoodОценок пока нет
- Taller Incoterms PDFДокумент2 страницыTaller Incoterms PDFSandra BerdugoОценок пока нет
- Cuestionario Cap 5Документ3 страницыCuestionario Cap 5Jacome MonserrathОценок пока нет
- Ejercicios Placa BaseДокумент5 страницEjercicios Placa BaseJugador FelizОценок пока нет
- Funciones de Varias Variables AvanzadoДокумент10 страницFunciones de Varias Variables AvanzadoJulio PillacaОценок пока нет
- Instrucciones Discurso Fin de AñoДокумент2 страницыInstrucciones Discurso Fin de AñopettitaeОценок пока нет
- Examen 2 Sistemas de Ecuaciones de Primer GradoДокумент4 страницыExamen 2 Sistemas de Ecuaciones de Primer GradoErnesto Laguna gonzalezОценок пока нет
- Gran Manifiesto Gnostico 1971 PDFДокумент16 страницGran Manifiesto Gnostico 1971 PDFHardy Enrique Pennekamp CantillanaОценок пока нет
- FISICA II Taller1 CondensadoresДокумент1 страницаFISICA II Taller1 CondensadoresFabian Molina CarvajalОценок пока нет
- Digital Business PDFДокумент56 страницDigital Business PDFAngélica LozadaОценок пока нет