Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Cell Respiration and Fermentation Study Guide Cell Respiration
Загружено:
failures12Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cell Respiration and Fermentation Study Guide Cell Respiration
Загружено:
failures12Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Aaron Marcus
Cell Respiration and Fermentation
Study Guide
Cell
o
o
o
o
Respiration
C6H12O6+602=6CO2+6H20+32ATP
Raw materials= Glucose + Oxygen
Products= ATP, CO2, H2O
In both animals + plants
3 Stages of Cell Respiration
Glycolysis:
Anaerobic
Chemical reaction in cytoplasm
Break down glucose= 2 pyruvic acids
2 NADH produced
2 ATP molecules used + ATP molecules
produced= 2 Net ATP produced
Not very efficient
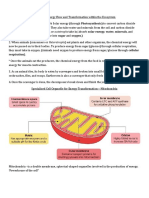
Krebs Cycle:
Aerobic
1 glucose= 2 turns of cycle
Takes place in mitochondria (Matrix)
6 NADH produced (per glucose)
2 FADH2 produced (per glucose)
Each turn= 1 ATP + 2 CO2 produced
Pass electrons to Electron Transport Chain
Electron Transport Chain (ETC):
Aerobic
Inner membrane of mitochondria
Electrons pass through chain + release ATP
32 ATP produced (or 34)
Oxygen+ final electron acceptor to form H2O
Fermentation
o Does NOT require Oxygen
Anaerobic
o Follows Glycolysis
All cells still utilize glycolysis
Glucose-> 2 pyruvates= 2 ATP (net gain)
Not a lot of energy
o Fermentation of Yeast, Bacteria
Pyruvate + NADH-> ethanol/alcohol + CO2+ NAD+
NAD+ is sent back to glycolyisis
Dead end process
Ethanol kills yeast cells= not reversible reaction
o Fermentation of Animals + some Fungi
Pyruvate + NADH<-> lactic acid+ NAD+
NAD+ sent back to glycolysis
Reversible process once O2 available
Lactate converted back to pyruvate by liver
If Oxygen is available the pyruvate will be sent to the
mitochondria for aerobic respiration
If Oxygen is not available= fermentation, anaerobic respiration
Materials and Products
o Glycolysis
Materials: Glucose, 2 ATP needed, 2 NAD+
Products: 2 Pyruvates, 4 ATP (2 net), 2 NADH
o Before Krebs cycle
Materials: 2 Pyruvates, Coenzyme A (CoA), 2NAD+
Products: 2 Acetyl CoA, 2NADH, 2CO2
o Krebs Cycle
Materials: 2 Acetyl CoA
Products: 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 4 CO2
o Electron Transport Chain
Materials: NADH, FADH2, O2
Products: 32-36 ATP, 2 H2O
Вам также может понравиться
- Lab 5 Alcoholic Fermentation in YeastДокумент15 страницLab 5 Alcoholic Fermentation in YeastFilipe GoncalvesОценок пока нет
- How Erythrocytes LiveДокумент21 страницаHow Erythrocytes LiveQuốc ViệtОценок пока нет
- 03 Glycolysis To Citric AcidДокумент9 страниц03 Glycolysis To Citric AcidAshley KrakowerОценок пока нет
- Powering The Cell-Cellular RespirationДокумент37 страницPowering The Cell-Cellular RespirationMarjorie VistaОценок пока нет
- Glycolysis & Kreb's CycleДокумент33 страницыGlycolysis & Kreb's CycleMapple Hernandez BelenОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9: Cellular RespirationДокумент36 страницChapter 9: Cellular RespirationMary GarciaОценок пока нет
- Topic 2 - 2012Документ151 страницаTopic 2 - 2012Messen OwОценок пока нет
- 20 3respiration 110923104133 Phpapp02Документ42 страницы20 3respiration 110923104133 Phpapp02Ira AgcaoiliОценок пока нет
- Carbon Dioxide and Convert These Into Sugar and Oxygen.) : Chapter 8: Fuels For LifeДокумент4 страницыCarbon Dioxide and Convert These Into Sugar and Oxygen.) : Chapter 8: Fuels For LifeSailor MehОценок пока нет
- Cellular Energy: Photosynthesis & RespirationДокумент12 страницCellular Energy: Photosynthesis & RespirationGobiОценок пока нет
- Cellular RespirationДокумент17 страницCellular Respirationapi-325274340Оценок пока нет
- Cellular Respiration: General Biology I Jose Amado Ds. TorredaДокумент22 страницыCellular Respiration: General Biology I Jose Amado Ds. TorredaDyames TVОценок пока нет
- BIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 8Документ12 страницBIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 8Noor JanahiОценок пока нет
- Cellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical Energy: 6H O + 6co + Energy C H O + 6OДокумент29 страницCellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical Energy: 6H O + 6co + Energy C H O + 6OlostgirlОценок пока нет
- Energy UtilizationДокумент29 страницEnergy UtilizationYudi SantosoОценок пока нет
- CH 7 Notes Cellular RespirationДокумент3 страницыCH 7 Notes Cellular RespirationCJ100% (1)
- BIO20 Cell Resp Teacher Notes 2020Документ39 страницBIO20 Cell Resp Teacher Notes 2020Shariq KhanОценок пока нет
- How Cells Harvest EnergyДокумент53 страницыHow Cells Harvest Energyjerry_brock_3Оценок пока нет
- Mitochondria Cellular RespirationДокумент65 страницMitochondria Cellular Respirationpotski413Оценок пока нет
- Cellular Respiration Notes - StudentДокумент3 страницыCellular Respiration Notes - StudentjoisbastaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 - Intermediary MetabolismДокумент53 страницыChapter 4 - Intermediary MetabolismBaxxОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7Документ19 страницChapter 7skywalkerОценок пока нет
- Cellular Respiration 1Документ28 страницCellular Respiration 1Maria Flor PabeloniaОценок пока нет
- Cellular RespirationДокумент31 страницаCellular Respirationyudi prakasaОценок пока нет
- CH 9 PPT Cellular RespirationДокумент47 страницCH 9 PPT Cellular RespirationJackie Swift FuntanillaОценок пока нет
- Cell RespiДокумент30 страницCell Respi11009911Оценок пока нет
- Summary of Cellular RespirationДокумент25 страницSummary of Cellular RespirationHeric ValdemoroОценок пока нет
- Aim 61Документ17 страницAim 61Tasneem MaruhomОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis & Respiration: By: James Grant & Aimee IrvinДокумент21 страницаPhotosynthesis & Respiration: By: James Grant & Aimee IrvindunklinjОценок пока нет
- Cell RespДокумент18 страницCell RespDebbie DulkoskiОценок пока нет
- Ap - Cellular Energetics - Cell RespirationДокумент22 страницыAp - Cellular Energetics - Cell Respirationapi-251015600100% (1)
- Cellular RespirationДокумент38 страницCellular RespirationItsYaBoiRZ YTОценок пока нет
- Cellular Respiration: Aerobic and Anaerobic MetabolismДокумент12 страницCellular Respiration: Aerobic and Anaerobic MetabolismIan Lusay OfendoreyesОценок пока нет
- ADP, ATP and Cellular RespirationДокумент30 страницADP, ATP and Cellular RespirationJillian Lao100% (2)
- Cellular RespirationДокумент14 страницCellular Respirationairish claineОценок пока нет
- Biological Oxidation. JP: Caloric Value of FoodДокумент13 страницBiological Oxidation. JP: Caloric Value of Foodsagar sagu100% (1)
- Energy & Respiration SimpliefiedДокумент6 страницEnergy & Respiration SimpliefiedEmrul HasanОценок пока нет
- Cellular Respiration Fermentation 2017 UPDATED Use For 2019Документ36 страницCellular Respiration Fermentation 2017 UPDATED Use For 2019aОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 BIO 1510Документ25 страницChapter 7 BIO 1510Chachi CОценок пока нет
- 10 Metabolisme MikrobiaДокумент51 страница10 Metabolisme MikrobiaHastomo Nur HidayatullohОценок пока нет
- Far Eastern University: Cellular Respiration: Glycolysis and Citric Acid CycleДокумент6 страницFar Eastern University: Cellular Respiration: Glycolysis and Citric Acid CycleAnne Nicole ZalamedaОценок пока нет
- 5 - Lab 5 - Alc Ferm in Yeast - F2009Документ15 страниц5 - Lab 5 - Alc Ferm in Yeast - F2009Odhiambo HenryОценок пока нет
- MR Jabbie GlycosisДокумент48 страницMR Jabbie Glycosisvandytommy308Оценок пока нет
- ADPATPand Cellular RespirationДокумент43 страницыADPATPand Cellular RespirationJessa CabusaoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 Notes: Cellular RespirationДокумент34 страницыChapter 9 Notes: Cellular RespirationJevon Freshness EllisОценок пока нет
- Cellular Respiration: Nelson Biology Pages 204 - 228Документ60 страницCellular Respiration: Nelson Biology Pages 204 - 228allie3d100% (14)
- Electron Transport Chain (ETC)Документ7 страницElectron Transport Chain (ETC)Jonathon JohnОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration SummaryДокумент5 страницPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Summarylady ann jimenezОценок пока нет
- BIOL223-Lab 6Документ35 страницBIOL223-Lab 6chicken friesОценок пока нет
- Chapter 14 Points To RememberДокумент6 страницChapter 14 Points To RememberSaksham YadavОценок пока нет
- Answer 2) : Cellular RespirationДокумент2 страницыAnswer 2) : Cellular RespirationNabeel ZahurОценок пока нет
- Ho10 Tca & EtsДокумент26 страницHo10 Tca & EtstresnowahyudienОценок пока нет
- Cellular Respiration STUDY GUIDEДокумент10 страницCellular Respiration STUDY GUIDEJee MascardoОценок пока нет
- Adenosine TriphosphateДокумент3 страницыAdenosine TriphosphateEvan Charl MoraledaОценок пока нет
- Students - Cellular-RespirationДокумент49 страницStudents - Cellular-RespirationechaОценок пока нет
- Cellular Respiration1Документ40 страницCellular Respiration1Danken Mathew P. TorresОценок пока нет
- Cellular Respiration: AP BiologyДокумент28 страницCellular Respiration: AP Biologynicole marquesesОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrate MetabolismДокумент83 страницыCarbohydrate Metabolismapi-3826907100% (5)
- 2 Glucose Is in Phase TwoДокумент6 страниц2 Glucose Is in Phase TwoLucas BuSheaОценок пока нет