Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Metacenter of Floating Bodies
Загружено:
BLLL0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
105 просмотров4 страницыThe document discusses the stability of bodies floating in fluids. It states that a body is neutrally buoyant and will remain at rest if its weight to volume ratio equals the specific weight of the surrounding fluid. Small particles can be used to track fluid flows. A submarine achieves different buoyancy levels by pumping water into or out of ballast tanks. A floating body may be statically unstable if it can overturn from a small disturbance. Engineers must design floating bodies to avoid instability. The document outlines how to calculate static stability by determining the restoring moment when a body is tilted - if the metacenter point is above the center of mass, the body is stable, and if below, it is unstable.
Исходное описание:
Fluid Mechanics
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe document discusses the stability of bodies floating in fluids. It states that a body is neutrally buoyant and will remain at rest if its weight to volume ratio equals the specific weight of the surrounding fluid. Small particles can be used to track fluid flows. A submarine achieves different buoyancy levels by pumping water into or out of ballast tanks. A floating body may be statically unstable if it can overturn from a small disturbance. Engineers must design floating bodies to avoid instability. The document outlines how to calculate static stability by determining the restoring moment when a body is tilted - if the metacenter point is above the center of mass, the body is stable, and if below, it is unstable.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
105 просмотров4 страницыMetacenter of Floating Bodies
Загружено:
BLLLThe document discusses the stability of bodies floating in fluids. It states that a body is neutrally buoyant and will remain at rest if its weight to volume ratio equals the specific weight of the surrounding fluid. Small particles can be used to track fluid flows. A submarine achieves different buoyancy levels by pumping water into or out of ballast tanks. A floating body may be statically unstable if it can overturn from a small disturbance. Engineers must design floating bodies to avoid instability. The document outlines how to calculate static stability by determining the restoring moment when a body is tilted - if the metacenter point is above the center of mass, the body is stable, and if below, it is unstable.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 4
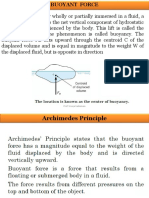
STABILITY
A body immersed in a fluid of specific
weight
If ratio of its weight and volume =
specific weight of fluid
Neutrally buoyant
Remain at rest at any point where it
is immersed
Small particles - used in flow
visualization
For example Swallow float used to
track ocean currents
A submarine achieves positive,
neutral or negative buoyancy by
pumping water in or out of its ballast
tanks
A floating body may be statically
unstable in the position in which it is
floating
Will overturn at the first opportunity
e.g. pencil balanced on its point
The least disturbance will cause it to
seek another equilibrium position
Engineers must design to avoid floating
instability
How?
Disturb the body by a slight amount
mathematically
See whether the body develops a
RESTORING MOMENT to return to its
original position.
Application in naval architecture
Outline of basic principle of static
stability calculation:
1. Calculate basic floating position
Fb = (displaced volume) = floating
body weight
Compute bodys center of mass (C)
and center of buoyancy (B)
2. Tilt the body by a small angle
and establish new water line.
Calculate the new position B of the
center of buoyancy. Draw a vertical
line upward from B to intersect line
of symmetry at a point M, called the
metacenter, which is independent
of for small angles
3. If point M is above G, that is the
metacentric height MG is positive, a
restoring moment is present and
the original position is STABLE. If M
is below G (negative MG), the body
is UNSTABLE and will overturn when
disturbed.
Calculation of the metacenter M of the floating
body shown in (a).
Tilt the body a small angle
(b) B moves far out (point M above G denotes
stability)
(c) B moves slightly (point M below G denotes
instability)
Вам также может понравиться
- Unit 5 Buoyancy and StabilityДокумент6 страницUnit 5 Buoyancy and StabilityMOJALEFA JACOB MOLEFIОценок пока нет
- Floatation and BuoyancyДокумент7 страницFloatation and BuoyancyDAVID CHEGEОценок пока нет
- Fluid MechanicsДокумент11 страницFluid Mechanicshamza khanОценок пока нет
- Archimedes' Principle: Figure 1. Two Views of A Body Immersed in A LiquidДокумент14 страницArchimedes' Principle: Figure 1. Two Views of A Body Immersed in A LiquidJohn GaviolaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3.4 - Measurement of The Stability of Floating BodiesДокумент11 страницChapter 3.4 - Measurement of The Stability of Floating BodiesErnesto LimОценок пока нет
- Buoyancy and StabilityДокумент12 страницBuoyancy and StabilityZac IriberriОценок пока нет
- Metacentric Height of Ship ModelДокумент4 страницыMetacentric Height of Ship ModelmitulkindОценок пока нет
- Buoyancy and Stability of Floating Bodies PDFДокумент15 страницBuoyancy and Stability of Floating Bodies PDFSalah HasonaОценок пока нет
- Lecture-4-Fluid StaticsДокумент26 страницLecture-4-Fluid StaticsCh ZainОценок пока нет
- Buoyance and FlotationДокумент8 страницBuoyance and FlotationT J Construction LimitedОценок пока нет
- Lect.9.FM-I. BuoyancyДокумент5 страницLect.9.FM-I. BuoyancyHassan ZahidОценок пока нет
- Stability of Floating BodiesДокумент12 страницStability of Floating BodieskierОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics: Statical Stability of Submerged Bodies ObjectivesДокумент6 страницFluid Mechanics: Statical Stability of Submerged Bodies ObjectivesRey VicencioОценок пока нет
- FM Unit 2 2Документ9 страницFM Unit 2 2Prem T RajuОценок пока нет
- Stability of Completely Submerged BodiesДокумент5 страницStability of Completely Submerged BodiesK'roll Azham AvearОценок пока нет
- Bouyancy AND Flotation: Engr. Clainie Gay LabisteДокумент43 страницыBouyancy AND Flotation: Engr. Clainie Gay LabisteAngel LoricaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 BuoyancyДокумент9 страницChapter 4 BuoyancyRavindu Jayalath100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics Lesson 3Документ5 страницFluid Mechanics Lesson 3livchatousОценок пока нет
- Experiment No - 3metacentric HeightДокумент22 страницыExperiment No - 3metacentric HeightWHfamilyОценок пока нет
- Lecture 4 Fluid StaticsДокумент21 страницаLecture 4 Fluid StaticsRIZWAN KHANОценок пока нет
- 4 Buoyancy 2023 W6&W7Документ60 страниц4 Buoyancy 2023 W6&W7saramelissa1192Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Buoyancy StabilityДокумент18 страницChapter 2 Buoyancy StabilitykohОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics Fluid Statics BuoyancyДокумент9 страницFluid Mechanics Fluid Statics BuoyancyJey MidayОценок пока нет
- Stability of Floating BodiesДокумент2 страницыStability of Floating BodiesMarc Dared CagaoanОценок пока нет
- Stability of A Floating Body!Документ18 страницStability of A Floating Body!M. ShayanОценок пока нет
- Damage Control TrainingДокумент179 страницDamage Control TrainingMD100% (1)
- Bouyancy Bouyancy: Week 4Документ15 страницBouyancy Bouyancy: Week 4CHIBUIKE UDENTAОценок пока нет
- Lecture - Week 3Документ15 страницLecture - Week 3johnОценок пока нет
- Metacentric HeightДокумент4 страницыMetacentric Heightkriap95Оценок пока нет
- Notes Lecture 4 Fluid StaticsДокумент23 страницыNotes Lecture 4 Fluid StaticsTarunОценок пока нет
- Reference Material I 12-Aug-2019 MEE1004 UNIT2 C2Документ27 страницReference Material I 12-Aug-2019 MEE1004 UNIT2 C2Mukul Ganwal 18BME0628Оценок пока нет
- Buoyancy and FloatationДокумент21 страницаBuoyancy and FloatationAhmad RazaОценок пока нет
- Fluid PresentationДокумент30 страницFluid Presentationmohammedhesham3002Оценок пока нет
- The Laws of Buoyancy and Initial Stability: Şekil 5.1. Forces Acting On A Displacement VesselДокумент7 страницThe Laws of Buoyancy and Initial Stability: Şekil 5.1. Forces Acting On A Displacement VesselRahul Phadake100% (1)
- Buoyancy and FloatationДокумент27 страницBuoyancy and FloatationProf. Avinash Mahale85% (13)
- Buoyancy and Floatation: Bhivarabai Sawant College of Engineering & Research Narhe, Pune-41Документ27 страницBuoyancy and Floatation: Bhivarabai Sawant College of Engineering & Research Narhe, Pune-41Ofosu Anim100% (1)
- Group 4 Nav Arch Ka LNG DiДокумент10 страницGroup 4 Nav Arch Ka LNG DimarpelОценок пока нет
- LX7 - Metacentric HeightДокумент8 страницLX7 - Metacentric Heightsweet mondayОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ47 страницChapter 2Philimond SegieОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 Part 2Документ20 страницLecture 2 Part 2Flamboyant RobertОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 PDFДокумент16 страницUnit 2 PDFveerendraОценок пока нет
- Lecture 4 Fluid StaticsДокумент23 страницыLecture 4 Fluid StaticsHistoric MemeОценок пока нет
- Yaba College of Technology: Civil Engineering Department Fluid Mechanics (Cec107) Lecturer: Olayinka Ojewunmi (Wk3)Документ6 страницYaba College of Technology: Civil Engineering Department Fluid Mechanics (Cec107) Lecturer: Olayinka Ojewunmi (Wk3)Abdulsabur AdenijiОценок пока нет
- HandoutTransverse Statical StabilityДокумент6 страницHandoutTransverse Statical StabilitySamОценок пока нет
- Cec 107Документ7 страницCec 107Micheal FiverrОценок пока нет
- Week 7 List 1 1 1Документ11 страницWeek 7 List 1 1 1MJ CabacabaОценок пока нет
- Experiment (2) : Metacentric Height of Floating Bodies: Hydraulics Lab (ECIV 3122) Islamic University - Gaza (IUG)Документ8 страницExperiment (2) : Metacentric Height of Floating Bodies: Hydraulics Lab (ECIV 3122) Islamic University - Gaza (IUG)G Sri SoumyaОценок пока нет
- Buoyancyandfloatation 150316030756 Conversion Gate01 PDFДокумент21 страницаBuoyancyandfloatation 150316030756 Conversion Gate01 PDFSomnath SwamyОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of StabilityДокумент17 страницFundamentals of StabilityJoemar de la Peña50% (2)
- GP3 Mass, Inertia, C.GДокумент3 страницыGP3 Mass, Inertia, C.GKatlo MokgethiОценок пока нет
- What Makes A Boat Float ?Документ20 страницWhat Makes A Boat Float ?Roxy MansОценок пока нет
- Buoyancy and StabilityДокумент56 страницBuoyancy and StabilityJuan Sebastian Varela SanabriaОценок пока нет
- Metacentro de Un FlotadorДокумент5 страницMetacentro de Un FlotadorEmerson RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Lecture 6 - Buoyancy, Flotation and Stability PDFДокумент34 страницыLecture 6 - Buoyancy, Flotation and Stability PDFLendo PosaraОценок пока нет
- Stabilitas KapalДокумент65 страницStabilitas KapaltutengОценок пока нет
- Winsem2016-17 Mee1004 Eth 4844 Rm004 Unit Iib-Buoyancy & FloatationДокумент9 страницWinsem2016-17 Mee1004 Eth 4844 Rm004 Unit Iib-Buoyancy & FloatationorionОценок пока нет
- Topic 2.2Документ35 страницTopic 2.2Naqib KamarozamanОценок пока нет
- Lathe Graphics: Exploring Visual Manipulation in Lathe Graphics through Computer VisionОт EverandLathe Graphics: Exploring Visual Manipulation in Lathe Graphics through Computer VisionОценок пока нет