Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
416 Gas Turbine Engineering Handbook: 4.0 40 60 FSX-414 IN-738 Stress
Загружено:
oquintero99Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
416 Gas Turbine Engineering Handbook: 4.0 40 60 FSX-414 IN-738 Stress
Загружено:
oquintero99Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
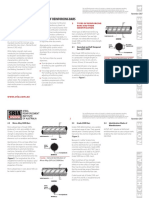
416
Gas Turbine Engineering Handbook
40
3.0
FSX-414
IN-738
GTD-222
2.0
Kg/cm 10
Stress
4.0
KSI
60
U-500
N-155
1.0
10
Temp,
100,000 Hrs
Life
GTD-111
Blades
Nozzles
500
600
1000
800
700
C
1400
1200
1600
F
40
42
46
48
50
44
Larson - Miller Parameter
3
PLM = T (20 + log t) 10
Figure 11-4. Larson-Miller parameter for various types of blades.
Ductility is erratic in its behavior and is not always repeatableeven under
laboratory conditions. Ductility of a metal is affected by the grain size,
the specimen shape, and the techniques used for manufacturing. A fracture
that results from elongation can be of two types: brittle or ductile, depending
on the alloy. A brittle fracture is intergranular with little or no elongation. A
ductile fracture is trangranular and typical of normal ductile tensile fracture.
Turbine blade alloys tend to indicate low ductility at operating temperatures.
As a result, surface notches are initiated by erosion or corrosion, and then
cracks are propagated rapidly.
Cyclic Fatigue
All materials would fail at a certain load if cycled over a large amount of
cycles. A very common type of failure, which blades in turbines undergo is
known as ``high cycle fatigue.'' This type of failure is caused when the blade is
subjected repeatedly to an unsteady load. Most materials under these alternating loads would fail in about 107 cycles, assuming that the resonance
frequency for a given blade is 103 Hz. This would tend to mean that the
material would fail within 104 seconds, about 2.8 hours, if the blade was
subjected to an alternating force, which would excite the blade resonance
frequency. This type of failure would be depicted by a chevron
type of markings on the failed surface, near the trailing edge of the blade.
Вам также может понравиться
- Cor-Ten - Weather & Corrosion Resistant SteelДокумент5 страницCor-Ten - Weather & Corrosion Resistant SteelAnjan DeyОценок пока нет
- SAW Wire / Flux: Typical Chemical Composition of Rod (WT%) Product FeaturesДокумент4 страницыSAW Wire / Flux: Typical Chemical Composition of Rod (WT%) Product Featuresehsan.mОценок пока нет
- Technical Data 3CR12Документ15 страницTechnical Data 3CR12rudiskw456Оценок пока нет
- Tata Steel Cutting Edges GuideДокумент2 страницыTata Steel Cutting Edges GuideKen SmithОценок пока нет
- UR35NДокумент4 страницыUR35NricardodelatorreОценок пока нет
- X5CrNiCuNb 16-41.4542Документ2 страницыX5CrNiCuNb 16-41.4542nuesteОценок пока нет
- Dillimax 690: High Strength Fine Grained Structural Steel Quenched and TemperedДокумент4 страницыDillimax 690: High Strength Fine Grained Structural Steel Quenched and TemperedBui Chi TamОценок пока нет
- Steel Casting Handbook Supplement 8 - High Alloy Data Sheets - Corrosion SeriesДокумент93 страницыSteel Casting Handbook Supplement 8 - High Alloy Data Sheets - Corrosion SeriesjosemiguelzuОценок пока нет
- Corten Steel Data SheetДокумент3 страницыCorten Steel Data SheetNur Hasanudin0% (1)
- SS 1.4122Документ2 страницыSS 1.4122Bipin Sadasivan100% (2)
- UR45 NPlusДокумент4 страницыUR45 NPlusMaiara Lima PereiraОценок пока нет
- Nitro Nic 50 BookДокумент18 страницNitro Nic 50 Booka100acomОценок пока нет
- Al6XN AlloyДокумент10 страницAl6XN AlloyTommaso Di GiamberardinoОценок пока нет
- Datasheet-Sandvik-Springflex-En-V2021-09-23 08 - 09 Version 1Документ8 страницDatasheet-Sandvik-Springflex-En-V2021-09-23 08 - 09 Version 1aceinsteinОценок пока нет
- .Au-Aluminium Alloy 3003Документ5 страниц.Au-Aluminium Alloy 3003ali alhamilОценок пока нет
- FSW of Aluminum MMC 6092-17.5%SiCpДокумент22 страницыFSW of Aluminum MMC 6092-17.5%SiCpSanthosh Kumar KodhandapaniОценок пока нет
- Physical Properties of SteelДокумент1 страницаPhysical Properties of SteelBigfoot2018Оценок пока нет
- Material PropertiesДокумент16 страницMaterial PropertiesMadan Kulkarni100% (1)
- Nirosta 4104: Krupp EdelstahlprofileДокумент2 страницыNirosta 4104: Krupp EdelstahlprofileLuis MayorgaОценок пока нет
- DH 1232NSДокумент1 страницаDH 1232NSGopiNathОценок пока нет
- Metrode Cryogenic ER316 B-38Документ5 страницMetrode Cryogenic ER316 B-38Claudia MmsОценок пока нет
- Recom. de Soldadura XARДокумент4 страницыRecom. de Soldadura XARelias667Оценок пока нет
- Print Web-2Документ2 страницыPrint Web-2aries andhikaОценок пока нет
- Series: PR13 /PR13 /PR13Документ8 страницSeries: PR13 /PR13 /PR13machineCanОценок пока нет
- Partie 3Документ34 страницыPartie 3vincent.guilbault7894Оценок пока нет
- VOKSEL Power CablesДокумент33 страницыVOKSEL Power CablesAbyssus TntОценок пока нет
- SM-70EN MIG Welding WireДокумент30 страницSM-70EN MIG Welding WireErick Quan LunaОценок пока нет
- 1 4021 PDFДокумент2 страницы1 4021 PDFSarah FitzgeraldОценок пока нет
- K48-50 Carbon Film ResistorsДокумент3 страницыK48-50 Carbon Film ResistorseminuscloudОценок пока нет
- CS310AДокумент4 страницыCS310Arabacet2923Оценок пока нет
- Guia Practica Eleccion AporteДокумент26 страницGuia Practica Eleccion AporteNegrito RosarinoОценок пока нет
- Monel K500 PDFДокумент6 страницMonel K500 PDFOZAIRTRADELINKОценок пока нет
- Metrode 410NiMo B-11Документ4 страницыMetrode 410NiMo B-11Claudia MmsОценок пока нет
- Fluoride Basic Welding Flux UV 420 TTR / UV 420 TTR-WДокумент1 страницаFluoride Basic Welding Flux UV 420 TTR / UV 420 TTR-WKaushal GandhiОценок пока нет
- Offshore Structural Plate Fabrication GuideДокумент8 страницOffshore Structural Plate Fabrication Guidedaniel_c_popa3357Оценок пока нет
- Unbrako Catalog FastenerДокумент26 страницUnbrako Catalog Fastenerdesign_rajeev100% (1)
- Properties and Welding Procedure For Grade 91 Alloy Steel: Siddharth Pant and Swati BhardwajДокумент6 страницProperties and Welding Procedure For Grade 91 Alloy Steel: Siddharth Pant and Swati BhardwajArvind ShuklaОценок пока нет
- Plate: Any Sizes Not Listed in This Section Can Be Available Upon RequestДокумент22 страницыPlate: Any Sizes Not Listed in This Section Can Be Available Upon RequestTonyRiverosBecerraОценок пока нет
- SS 409M WeldingДокумент12 страницSS 409M WeldingwentropremОценок пока нет
- 3 PH LT Sq. Cage IMДокумент7 страниц3 PH LT Sq. Cage IMAnanda DuttaОценок пока нет
- Graphitization, temper embrittlement and other forms of damageДокумент12 страницGraphitization, temper embrittlement and other forms of damagemajid100% (1)
- AVESTA How To Weld Duplex SteelДокумент20 страницAVESTA How To Weld Duplex SteelGMacella100% (1)
- Carbon Steel Bars Cold FinishedДокумент18 страницCarbon Steel Bars Cold FinishedjaytronizerОценок пока нет
- Welding and ReinforcementДокумент9 страницWelding and ReinforcementScottBuchholzОценок пока нет
- Llautó M38 CuZn37Документ2 страницыLlautó M38 CuZn37Josep TanuОценок пока нет
- Fluxes For Welding and SurfacingДокумент4 страницыFluxes For Welding and SurfacingVăn Trường LêОценок пока нет
- Kaiser Aluminum Shapes Soft Alloy PDFДокумент18 страницKaiser Aluminum Shapes Soft Alloy PDFgerrzen64Оценок пока нет
- Metrode Welding Duplex & Superduplex Stainless SteelsДокумент18 страницMetrode Welding Duplex & Superduplex Stainless SteelsClaudia Mms50% (2)
- Tested Per MIL-R-46163 or ASTM D5363Документ4 страницыTested Per MIL-R-46163 or ASTM D5363rowatersОценок пока нет
- 78 PDFДокумент1 страница78 PDFGogo PОценок пока нет
- Midalloy ER70S-2Документ1 страницаMidalloy ER70S-2nasirfahimОценок пока нет
- Welding Craft Practice: Oxy-Acetylene Gas Welding and Related StudiesОт EverandWelding Craft Practice: Oxy-Acetylene Gas Welding and Related StudiesОценок пока нет
- Weld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesОт EverandWeld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- Automation and Robotisation in Welding and Allied Processes: Proceedings of the International Conference Held at Strasbourg, France, 2-3 September 1985, under the Auspices of the International Institute of WeldingОт EverandAutomation and Robotisation in Welding and Allied Processes: Proceedings of the International Conference Held at Strasbourg, France, 2-3 September 1985, under the Auspices of the International Institute of WeldingP D BoydОценок пока нет
- Welding the Inconel 718 Superalloy: Reduction of Micro-segregation and Laves PhasesОт EverandWelding the Inconel 718 Superalloy: Reduction of Micro-segregation and Laves PhasesОценок пока нет
- Ceramic Materials for Energy Applications V: A Collection of Papers Presented at the 39th International Conference on Advanced Ceramics and CompositesОт EverandCeramic Materials for Energy Applications V: A Collection of Papers Presented at the 39th International Conference on Advanced Ceramics and CompositesJosef MatyášОценок пока нет
- Babbitt as a Bearing Material GuideДокумент16 страницBabbitt as a Bearing Material Guideoquintero99Оценок пока нет
- Dream Theater - 11 - 12 RiderДокумент20 страницDream Theater - 11 - 12 RiderEmilio Satti Popelka100% (1)
- Aircraft GT Blade and Vane Repair - TMSДокумент10 страницAircraft GT Blade and Vane Repair - TMSoquintero99Оценок пока нет
- NickelAlloysandStainlessSteelsforElevatedTemperatureService WeldabilityConsiderations 14053Документ16 страницNickelAlloysandStainlessSteelsforElevatedTemperatureService WeldabilityConsiderations 14053oquintero99Оценок пока нет
- NAVEDTRA 14111 - Gas Turbine Systems SupervisorДокумент128 страницNAVEDTRA 14111 - Gas Turbine Systems SupervisorfriendlysniperОценок пока нет
- Nickel Based Superalloy Welding Practices For Industrial Gas Turbine ApplicationsДокумент15 страницNickel Based Superalloy Welding Practices For Industrial Gas Turbine Applicationsoquintero99Оценок пока нет
- How to turn $20k into $26 million in 12 yearsДокумент28 страницHow to turn $20k into $26 million in 12 yearsLukman AididОценок пока нет
- Understanding DecarburizationДокумент6 страницUnderstanding Decarburizationoquintero990% (1)
- Chem Comp at Ability Chart Cat Pumps)Документ15 страницChem Comp at Ability Chart Cat Pumps)paulortsОценок пока нет
- A Study of Casting Characteristics For Die Cast Aluminum Alloy-Anwar HussainДокумент23 страницыA Study of Casting Characteristics For Die Cast Aluminum Alloy-Anwar Hussainoquintero99100% (2)
- Selective Management of Selected Gas Turbine EnginesДокумент53 страницыSelective Management of Selected Gas Turbine Enginesoquintero99Оценок пока нет
- Power Plant Inspection, Repair and Testing Gas TurbineДокумент30 страницPower Plant Inspection, Repair and Testing Gas Turbineoquintero99100% (2)
- Microstructural Degradation of Boiler Tubes Long Term High TemperatureДокумент69 страницMicrostructural Degradation of Boiler Tubes Long Term High Temperatureoquintero99Оценок пока нет
- Diffusion Welding of Nickel AlloysДокумент4 страницыDiffusion Welding of Nickel Alloysoquintero99Оценок пока нет
- Sea Water ChemistryДокумент63 страницыSea Water ChemistryVijay KumarОценок пока нет
- Major Ion Composition of SeawaterДокумент2 страницыMajor Ion Composition of Seawateroquintero99Оценок пока нет
- Mirhosseinimst 29-12-1513 Effects Partial SolutionДокумент6 страницMirhosseinimst 29-12-1513 Effects Partial Solutionoquintero99Оценок пока нет
- Failure Analysis Fundamental CausesДокумент12 страницFailure Analysis Fundamental Causesoquintero99Оценок пока нет
- Parr Stress Crack Corrosion InfoДокумент8 страницParr Stress Crack Corrosion InfoBangkit Rachmat HilcaОценок пока нет
- Railway TechnicalДокумент440 страницRailway TechnicalFrancisco Abraham Baeza92% (13)
- Gas Turbine Vehicles - Chrysler CorporationДокумент45 страницGas Turbine Vehicles - Chrysler Corporationoquintero99Оценок пока нет
- FN01476 1213 Mounting Application GuideДокумент12 страницFN01476 1213 Mounting Application Guideoquintero99Оценок пока нет
- Sulphide Scavengers in Oil and Gas Industry - A ReviewДокумент8 страницSulphide Scavengers in Oil and Gas Industry - A ReviewMartín Diego MastandreaОценок пока нет
- Heat Treatment ProcessingДокумент16 страницHeat Treatment Processingoquintero99Оценок пока нет
- Advanced Gas Turbine Concept, Design and Evaluation Methodolody. Preliminary Desigh of Highly Loaded LP GT Aircraft Engine - 2007Документ6 страницAdvanced Gas Turbine Concept, Design and Evaluation Methodolody. Preliminary Desigh of Highly Loaded LP GT Aircraft Engine - 2007oquintero99Оценок пока нет
- The Ultimate Guitar Rig Building GuideДокумент32 страницыThe Ultimate Guitar Rig Building Guideoquintero99100% (1)
- Characterization Glasses and CeramicsДокумент4 страницыCharacterization Glasses and Ceramicsoquintero99Оценок пока нет
- Dke672 ch7Документ38 страницDke672 ch7thotalnОценок пока нет
- Turbine Engine Hot Section PrognosticsДокумент9 страницTurbine Engine Hot Section PrognosticsD ARUL KUMARESANОценок пока нет