Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Irfanmir Step 1 Uw Notes
Загружено:
Manisanthosh KumarАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Irfanmir Step 1 Uw Notes
Загружено:
Manisanthosh KumarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Femoral nerve damage -- loss of knee jerk reflex
* Common peroneal nerve courses from the lateral neck of the fibula -- foot drop (due to inability to dorsiflex the foot)
* Tibial nerve damage --- inability to planter flex the foot.
* Duodenum is the main site of dietary lipid digestion vs. Jejunum is the main site of dietary lipid absorption (so does the all fat soluble vit)
* Coronary sinus collect the blood from coronary veins, it locate in the posterior surface of the heart and drain directly into the left atrium.
* Isthmus of the horse shoe kidney (1 in 500 autopsies) lies ant to the aorta and inferior venacava and post to the inferior mesentric artery.
* Body iron content is regulated by proximal intestinal epithelium vs. body iron stores are present in bone marrow macrophages.
* Hemolysis increases the iron absorption regardless of body iron level (dec or inc).
* particles < 2m capable to reach the terminal bronchioles and clear by macrophages vs. particles > 2.5 - 10m trap into trachea and bronchi & cleared by
mucociliary action
* Thoracocentesis should be performed above 7th rib in mid clavicular line, along 9th rid in mid axillary line, 11th rib along post scapular line or paravertebral
line.
* Morphine inc K+ efflux in the post synaptic neuron (via G - protein coupled activation of potassium channel) to to block pain.
* tPA is good if used in first 6 hrs of MI. it is contraindicated in bleeding problem of any cause and cerebral stroke with in 1 yr and BP > 110/180.
tPA induced blood flow restoration may result into Benign arrhythmia which usually subsides with out any harmful effect.
* Bone specific Alkaline phosphatase reflects Osteoblastic activity VS. Titrate - Resistant Acid Phosphatase, Urinary Hydroxyproline, Urinary
Deoxypyridinoline reflects Osteoclastic activity . (Urinary DeoxyPyridinoline is most reliable among three).
* Elevated Serum FSH level confirms Menopause, Although LH is also elevated but it is a later and less prominent phenomenon.
* Retroperitoneal space includes -1. Major vessels, Abdominal aorta, Inferior vena cava and there branches.
2. Pancreas except tail, Kidney adrenal gland.
3. Hollow organ (part 2, 3 & portion of part 4 of duodenum, Ascending and descending colon, rectum, ureter, bladder.
4. Vertebral column and pelvic muscle.
* Tachyphylaxis is term used to describe decreased drug responsiveness with repeated administration.
* The combination of two drugs is equal to the sum of effects expected from individual drugs, the effect is called additive, vs. when the combined effect
exceed the sum of the individual drug effect, the interaction is called synergistic. For example The response of Cortisol combined with Nor EN is not
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
considered additive or Synergistic because cortisol alone does not have any significant effect on vascular activity.
Instead Cortisol has Permissive effect by increasing the transcription of several genes which may increase the responsiveness of catecholamine.
* Metabolic effect alter the drug metabolism by increasing or decreasing the P 450 cytochrome oxidase thus effecting drugs Pharmacokinetics and
pharmacodynamics
* Injury to the posterior urethra is associated with pelvic fracture with resultant inability to void despite full bladder (High riding prostate on rectal exam ).
* Injury to Anterior urethra is most often caused by Urinary tract trauma like in saddle injury in which perineum is struck forcefully on the cross bar of bicycle,
fence. Pt shows inability to void in spite full bladder, blood at urethral meatus, urine extravasate into superficial perineal space of penis, scrotum & ant
abdominal wall, The hematoma is called Butterfly - Like because it does not extend to thigh and superficial perineal fascia.
* Majority of Gastric ulcer occur at the lesser curvature, at the border between acid secreting and gastrin secreting mucosa.
* Left and Right Gastric arteries run along the lesser curvature and are likely to be damage in gastric ulcer in that region.
* Gastroduodenal artery lies along the post wall of the duodenal bulb and is likely to be eroded by posterior duodenal ulcer.
* Superior Mesentric artery (SMA) syndrome occur when transverse portion of the duodenum is entrap b/w SMA and aorta because of decrease
Aortomesentric Angle either due to diminish mesentric fat or pronounced lordosis. It produces sign of duodenal obstruction.
* Most of the blood supply to the heart occur in diastole that is why duration & length of diastole is a critical factor in determining coronary blood flow.
* PTH Inc bone resorption by acting as osteoclast indirectly. It isOsteoblast that have PTH receptors which when stimulated cause osteoblast to produce
RANK - Ligand and Monocyte colony stimulating factor. These two factors stimulate osteoclast precursor to differentiate into bone resorbing mature
osteoclast with resultant Inc in serum Ca++. PTH Inc renal Ca++ absorption & dec serum Phosphate by losing in urine.
* Failure of ovulation can be treated with Menotropin (human menopausal gonadotropin) which act like FSH and cause dominant follicle formation , ovulation
is than induced by large dose of hCG which stimulate LH surge.
* T - tubule are invagination of the sarcolemma (plasma mem) that extend into the muscle fiber. They transmit depolarization signals to the sarcoplasmic
reticulum and trigger Ca++ release. The uniform distribution of T- tubule ensure coordinated contraction of all myofibrils.
* Beside causing contraction in skeletal muscle Ca++ also activates myophosphorylase (muscle phosphorylase) to cause break down of glycogen and
release Glucose -1- ph.
Remember Muscle glycogen store do not contribute blood glucose level during fasting.
* DNR (do not resuscitate) include 3 key element. 1. No intubations or mechanical ventilation, 2. No defibrillation, 3. No IV drug to acutely treat the terminal
rhythem. Pt may additionally specify wishes such as desire of not to be fed by artificial means.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Femoral Hernia are inferior to the Inguinal ligament lateral to the pubic tubercle, and medial to the Femoral vein. Manifest as the bulge to the upper high
which enlarges with straining ( valsalva maneuver ). Incarceration (constriction of hernial sac) and Strangulation are common complication of femoral hernia.
* Inferior Epigastric vein is located laterally to Direct Inguinal hernia VS. inferior epigastric vein locate medially in Indirect Inguinal hernia. They contribute
the lateral border of Hesselbach triangle.
* Of 5 major facilitative glucose transporters only GLUT4 is responsive to Insulin. Which present predominantly muscles and adipose tissue.
GLUT4 is normally sequestered in cytoplasm but with insulin action it moves to the plasma mem which allows glucose to move down to the conc in the cell.
In the absence of insulin muscle and adipose tissue are impermeable to glucose. VS. All other GLUT receptors are always present on the plasma mem to
transport glucose
* Profuse diarrhea and vomiting cause sever hypovolemia and subsequent dec renal plasma flow. hypovolemia stimulate renin secretion with resultant ATII
production. ATII constrict the Efferent arterioles which inc hydrostatic P in Glomerular capillaries and maintain GFR. Due to this compensatory mechanism
dec is GFR is less pronounced than dec in RPF (Renal Plasma Flow) which result in Inc FF (filtration fraction) because FF = GFR/RPF. ( which in
hypovolemic case is FF = GFR / RPF )
* Amphetamine and Cocaine is most commonly associated with Violent behavior. Hallucinogen are LCD & Phencyclidine (PCP or angels dust).
Belligerence (war like aggressive hostile condition) and Psychomotor agitation tend to be more common with PCP than with LCD.
* It is Ethical to except gift from pt if those gifts are not beyond the means of physician or pt, if the gift is not made with the intention of secure preferential tx,
if the gift does not place the pt or family in financial hardship, and if the pt is not demented. Gift can contribute to positive doctor pt relationship. declining gift
may make pt feel awkward as gift giving is common in many cultures.
* There are only 4 situations where disclosure of pt information without the consent is allowable.
1. When child elder and spousal abuse is suspected.
2. When pt has sustained gunshot and stabbing injury.
2. When pt is diagnosed with reportable communicable dis 3. When pt is threatens to kill or harm some one else .
* Marijuana stimulate cannabinoid receptor and cause mild euphoria, laughing behavior, slowed reflexes, dizziness, impaired coordination, and short term
memory loss. Rapid heart rate and conjunctival reddening are two immediate physical symptom of marijuana use. It remain in system and can be detected
up to 30 days after use.
* Pyridoxal phosphate is necessary cofactor in the synthesis of - aminolevulenic acid (which is elevated in case of lead poisoning).
* Biotin acts as a CO2 carrier on the surface of the carboxylase enz (like acetyl CoA Carboxylase, Pyruvate Carboxylase, Propionyl Carboxylase, etc). All
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
these enzymes play a role in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. for eg. in gluconeogenesis, for instance pyruvate carboxylase (and therefore Biotin) is
necessary for the conversion of pyruvate to Oxaloacetate, in Biotin deficient the level of pyruvate rise and convert to lactic acid instead, metabolic acidosis
result.
* Hypoxia induced Lactic acidosis due to low pyruvate dehydrogenase (TCA cycle) and high activity of Lactate dehydrogenase.
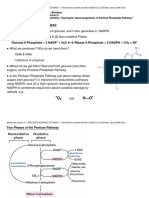
* NADPH is a reduced form of NADP. When glucose is metabolized via HMP shunt. NADPH is produced which is used as a reducing equivalent in cytosol
rather than as a source of energy for ATP synthesis in Electron transport chain. HMP shunt is also responsible for the production of ribose - 5 - phosphate for
the synthesis of nucleotide. From 1 molecule of Glucose HMP shunt produce 5 carbon sugar, 2 molecule of NADPH & CO2. The HMP shunt consist of two
types of reaction Oxidative (irreversible) and nonoxidative ( Reversible).
* Active form of Pantothenic acid is coenz A which bind to Oxaloacetate to form citrate and succinyl CoA in the first step of TCA cycle.
* The Oxidative reaction of HMP produced NADPH as an electron donor which is necessary in cholesterol and Fatty acid synthesis.
* Glucose 6 ph dehydrogenase def is common X linked disorder of HMP pathway which result into hemolytic anemia due to oxidative stress.
* Erythrocyte use HMP shunt generate Large amount of NADPH to maintain reduced state of glutathione by the action of glutathione reductase, this is
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
reduced state of glutathione which protect erythrocyte from oxidative damage (from drugs or oxidizing environmental toxins). HMP shunt is the only major
pathway that generate NADPH in erythrocyte, any defect in this pathway results in poor protection of RBC from free radical, Hydrogen peroxide or other
oxidant stress.
* Peroxisomal Dis (rare inborn error) characterized by either absent or nonfunctional peroxisomes. Very long fatty acid cannot undergo mitochondrial beta
oxidation instead metabolized with in peroxisomes. these dis commonly lead to improper CNS myelination.
* Aldolase reductase convert Glucose into sorbitol which cannot cross cell mem and trap inside the cell if the enz Sorbitol dehydrogenase is absent which
convert sorbitol into fructose. This pathway is imp in seminal vesicle because sperm use fructose as their primary energy source. Tissue like Lens, retina
Schwann cell, kidney have much lower activity of Sorbitol dehydrogenase which cause sorbitol to accumulate inside the cell specially in hyperglycemic
situation which results into Inc osmotic P inside the cell and facilitate water influx and injury and cause Retinopathy and neuropathy or cataract in DM.
* Galactosemia can result from and of 3 enz (see above). Galactose 1 ph Uridyl transferase def is the common most and cause classic glactosemia which
characterized by vomiting, lethargy, failure to thrive, soon after breast feeding is begun. It shows Impaired liver function, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis
and aminoaciduria. Dietary restriction of lactose results in improvement of symptoms.
* Secondary Lactase def can occur after viral gastroenteritis or dis that disturb intestinal epithelium. It cause abdominal distention, flatulence and diarrhea
after lactose ingestion.
* Elastin Plasticity and ability to recoil upon release of tension is caused by desmosine cross linking b/w 4 different lysine residue on 4 different elastin chain.
this cross linking is accomplished by the action of lysyl hydroxylase.
* Thyroid hormone alter gene transcription by binding to the receptor located inside the nucleus. Receptors for Glucocorticoids, mineracorticoids, androgens,
and estrogen are initially present in the cytoplasm than they migrate to the nucleus once activated.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Regulation of insulin secretion.-- First Glucose enter in beta cell by facilitate diffusion via glucose transporter2 (GLUT2), after entering beta cell glucose go
under oxidative metabolism through glycolysis which produce pyruvate. Pyruvate than enter TCA cycle and generate ATP with resultant high ATP to ADP
ratio. Than ATP binds to regulatory subunit of Potassium (KATP) channels to block efflux of K+ which cause Beta cell to depolarize. Depolarize beta cell than
open voltage dependant Ca++ channel with resultant inc IC Ca++ and release of Insulin. Remember defect in closing of KATP channel results into type II
Diabetes, and sulfonylurea bind directly to regulatory subunit of KATP channel causing them to close.
* In beta cell of pancreas 1st enz in glycolytic pathway is Glucokinase where as in other tissue it is Hexokinase.
* Glucokinase convert Glucose to Glucose 6 ph. Glucokinase is less sensitive to allosteric inhibition by its product Glucose 6 ph and serve as a major glucose
sensor for beta cell. Glucose to Glucose 6 ph conversion by glukinase is crucial and rate limiting thats why once metabolized to Glucose 6 ph results into
rapid metabolism to pyruvate and TCA cycle.
* Inactivating mutation of enz Glucokinase can results in mild hyperglycemia that can be exacerbate by pregnancy.
* Protein kinase is primarily responsible for IC effect of G protein / adenylate cyclase second messenger. (eg TSH, glucagon, PTH, adrenergic receptor)
* Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) convert pyruvate to Acetyl CoA in the presence of O2 (During Aerobic Metabolism). where as during Anaerobic metabolism
or PDH def pyruvate is converted to lactate by enz Lactate dehydrogenase with resultant metabolic acidosis.
* In Pyruvate dehydrogenase def ketogenic diet is recommended. AA catabolism following removal of Amine group result in the formation intermediate that
are either glucogenic (producing intermediated of TCA cycle) or ketogenic (producing acetoacetate or its precursor) or both. for eg. phenylalanine, isoleusine,
tryptophan. Leusine and lysine (essential AA) are purely ketogenic.
* In Inactivated state corisol receptor lies in association heat shock protein with in the cytoplasm. when cortisol binds heat shock protein is liberated and
receptor hormone complex mobilize to nucleus for transcription. Cortisol inc the transcription of enz involve in gluconeogenesis (from fat and protein
substrate)
that is why cause lipolysis and proteolysis.
* EN and Glucagon inc gylogenolysis. where as GH Gluconeogenesis by increasing lipolysis.
* Glycine is the most abundant AA in Collagen molecule (every 3rd AA).
* Vit K assistance pf Glutamine residue is essential for some clotting factor production.
* Sucrose (disaccharides) ------------ Fructose + Glucose
Lactose (disaccharides) ------------ Galactose + Glucose
Maltose (disaccharides) ------------ Glucose + Glucose
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Aldolase B metabolize fructose its def cause fructose intolerance, hypoglycemia with fructose ingestion. Sucrose and fructose should be removed form diet.
* Thiamine serves as a cofactor with transketolase, Ketaoglutarate dehydrogenase, pyruvate dehydrogenase. Pt with thiamine def (alcoholic) should be
administered thiamine first than glucose to prevent neurologic complication of Wernicks encephalopathy which is characterized by acute confusion,
opthalmoplegia, ataxia.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
USMLE WORLD NOTES
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* The symptoms dysphagia, spooning of nail (Koilonychia) are more sp for Iron def Anemia. Dysphagia is often cause by formation of esophageal web and is
described as Plummer Vinson Kelly $. Clinical features common to all types of anemia are Dec Hg, Malaise, Fatigue, dec exercise capacity, and CHF.
* Niacin B3 can be synthesized endogenously by tryptophan. Its def cause Pellagra Dermatitis, diarrhea, dementia.
* In deoxygenated state (low O2) Hemoglobin S (HbS) tend to aggregates, reduces Cell mem flexibility and promoting sickling. Low PH and Inc 2,3 DPH
also promote sickling.
* Pyruvate kinase def cause hemolytic anemia due to failure of glycolysis (dec ATP) in RBC splenic hypertrophy due to Inc removal of RBC form
circulation.
* Insulin act via Tyrosine kinase 2nd messenger sys which activate protein phosphatase which further modulate the activity of enzymes in metabolic pathway
regulated by insulin. Insulin stimulate synthesis of Glycogen, Fatty acid, & nucleic acid.
* Hydrolysis of protein is achieved by Pepsin and trypsin these enz is secreted in inactivated form as pepsinogen and trypsinogen from stomach and
pancreas respectively. Trypsin in turn activate other proteolytic enzymes (chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase, elastase). Activation of trypsinogen to trypsin is
achieved by enteropeptidase (enterokinase) release for brush border of duodenum, its def cause diarrhea growth retardation and hypoprotienemia. On other
hand pepsinogen release from chief cell in stomach low PH activate it to pepsin where it digest protein than Inc PH of duodenum will inactivate it
(achlorhydria inhibit pepsinogen activation to pepsin)
* - Oxidation, of fatty acid, TCA cycle, Part of urea cycle (Carbamoyl phosphate synthatase 1 and Ornithine transcarbamoylase) and pyruvate carboxylation
all occur exclusively in mitochondria.
vs.
Transketolase is an enz of HMP shunt . Both HMP pathway and its enz are localize to cytoplasm.
*
*
*
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Procollagen is synthesized in ER of cells like fibroblast, this molecule is than released in extracellular (EC) space by transport through Golgi apparatus
and converted into collagen by procollagen peptidase by cleaving water soluble non - helical N and C - terminal portion. Collagen monomers covalently
crosslinked each other by enz Lysyl oxidase. Defective cleavage yield more soluble collagen which can not crosslink properly and result into joint laxity, loose
skin easy bruisability in Ehler Donlos $.
* Hydroxylation of proline and lysine residues in the collagen precursor occur in RER and requires Vit C as a Cofactor. Terminal peptide cleavage and
collagen fibril cross linking occur in EC space, as describe above.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
10
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Metabolism of fructose involves Fructokinase, Aldolase B and triokinase. Def of fructokinase cause Essential fructosuria (ARD). Urine Dipstick utilizes
glucose oxidase to determine the presence of glucose in urine and will not test positive if Fructose or galactose is present (as in fructosuria). Unlike fructose
intolerance and Classic galactosemia, essential fructosuria is benign disorder.
* Aldolase def cause hereditary fructose intolerance which result into vomiting, hypoglycemia 20 - 30 min after fructose ingestion. Infant present with failure
to thrive, hepatomegaly and cirrhosis.
* Dietary fructose is phosphorylated in the liver to F - 1 - P and is metabolized fast because it bypasses PFK - 1, the rate limiting enz of glycolysis. Other
sugar enters glycolysis before this rate limiting enz (PFK - 1) therefore metabolize slowly.
* Wernicks $ (ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, confusion) characterized by Foci of hemorrhage and necrosis in mamillary bodies and periaqueductal gray matter due
to thiamine B1 def in alcoholics.
* Thiamine B1 is cofactor for Pyruvate dehydrogenase (convert pyruvate into acetyl CoA), Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (TCA Cycle), Transketolase (enz
of HMP shunt convert Pentose to glyceraldehyde 3P (PNMT) which is an intermediary of glycolysis). CNS is the most frequent organ affected by thiamine B1
def.
* Conversion of Nor EN to EN occurs mostly in adrenal medulla by enz Phenyl ethanolamine -N- methyltransferase. Cortisol Inc the expression of gene and
transcription of this enz, because venous drainage of adrenal cortex goes through the adrenal medulla and conc of cortex is very high in adrenal medulla.
Normal adrenal medulla catecholamine is approx 80% EN and 20% nor EN (4:1 ratio). This heavy EN ratio is due to +ve effect of cortisol on PNMT enz.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
11
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* RBC do not have mitochondria or nucleus thats why it acquire energy through glycolysis and HMP shunt. Glycolysis provides energy for survival and HMP
shunt provides reducing agent NADPH to protect from oxidant injury. In 1st Oxidative portion of HMP Shunt convert G -6- Ph is converted to 6
Phosphogluconolactone and One molecule of NADPH This reaction is catalyze by G -6- Ph dehydrogenase (imp enz) it is rate limiting enz of HMP shunt. In
2nd Oxidative portion of HMP produce 2nd molecule of NADPH. Remember Oxidative reactions are reversible and Non oxidative reactions are irreversible.
* In RBC partial reduction of molecular O2 produces Hydrogen peroxide which is detoxified by glutathione peroxidase. Glutathione is Oxidized by this
reaction and its reduced form is regenerated by enz Glutathione reductase which uses NADPH (produced by HMP shunt) as an electron donor. Def of
Glutathione peroxidase or def of NAPH due to any Defect in HMP shunt Inc the susceptibility of RBC to oxidative damage.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------* G6PD def is a defect in HMP Shunt that impairs glutathione reduction due to failure to produce NADPH. Glutathione reductase def cause similar effect.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
12
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* In gluconeogenesis pyruvate cannot be converted directly back to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) because pyruvate kinase is unidirectional enz. Conversion
of pyruvate to PEP requires 2 mitochondrial enz Pyruvate carboxylase and PEP carboxikinase. For Gluconeogenesis to proceed the OAA produced by
Pyruvate carboxylase need to be transported to the cytosol where OAA is converted to PEP by PEP carboxykinase. Mitochondrial OAA can be transport to
cytosol via 3 pathways 1. conversion of PEP as indicated above 2. Transamination of aspartate 3. reduction to malate. (later 2 transport directly to cytosol.
* GTP synthesized in the succinyl CoA thiokinase (synthatase) is used as a source of energy for decarboxylation of OAA to PEP by PEP carboxykinase in
gluconeogenesis. (After over night fasting gluconeogenesis is the main source of energy)
* Acetyl CoA is an imp allosteric activator of Gluconeogenesis that acts by increasing the activity of Pyruvate Carboxylase.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
13
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Glycogenolysis provides immediate energy for strenuous muscle contraction, myophosphorylase def lead to failure of glycogenolysis produce clinical
manifestation of dec excersize tolerance, myoglobinuria, and muscle pain with activity.
* Acid maltase ( 1,4 Glucosidase) def cause Pompe dis which results into glycogen accumulation with in lysosomes. Clinical manifestation include
hepatomegaly, cardiomagaly, macroglossia, hypotonia, and mental retardation in its severe form.
* Debranching enz def cause Cori dis which results into incomplete glycogen degradation ( 1,6 glucosidic branch can not degraded) and dextrin like
material accumulation in cytosol of hepatocytes. Pt with Cori dis present with hypoglycemia, hypertriglyseridemia, lactic acidosis and hepatomegaly
* HbS contain valine in place of glutamic acid in 6th position of beta subunit. This promotes hydrophobic interaction among hemoglobin molecules and
resultant polymerization of HbS distortion of RBC.
* Under anaerobic condition, NADH transfer protons to pyruvate to form lactate and to regenerate NAD+. NAD+ is required to form glyceraldehyde -3- ph
from 1-3 biphosphoglycerate in glycolysis.
* In normal fetal development the ureter are fully canalized before the metanephros begin to produce urine which occur 8 - 10 week of gestation. Inadequate
recanalization of ureteropelvic junction (junction b/w kidney and ureter) is most common cause of fetal hydronephrosis.
* Failure of vetilline duct (omphalomesentric duct) to obliterate results into Enterocyst and Meckels diverticulum.
* Urachus is the remnant of Allantois that connect the bladder with the yolk sac. Failure of urachus to obliterate by birth results into Patent urachus which
presents as urine discharge from umbilicus.
* Failure of thyroid gland to migrate cause Lingual thyroid, Clinical feature are hypothyroidism, lethargy, feeding problem, constipation, macroglossia,
umbilical hernia, large fontanels, dry skin, hypothermia, prolong jaundice. (could be the only thyroid tissue present in neonate, caution with surgery)
* Eg of Defective migration -- Failure of GnRH secreting neuron to migrate form the olfactory lobes to the hypothalamus may lead to Kallmann's $. Failure of
testes to migrate from there intra abdominal location cause Cryptorchidism.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
14
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Apoptosis is responsible of no of endocrine disease for eg DM type I where beta cell undergo apoptosis.
* Echocardiogram show aorta lying ant to and to the right of the pulmonary artery is Dx of transposition of great arteries which cause by failure of
aorticopulmonary septum to spiral during the septation of the truncus arteriosus. It produces life threatening cyanosis at birth.
* Failure of Differentiation cause syndactyly (fused digits).
* Failure of proliferation cause unilateral aplasia of fibula.
* Failure of Apoptosis autoimmune disease due to persistence of autoreactive cells.
* Failure of obliteration cause brachial cleft cyst
* Failure of migration cause Hirschsprung dis (failure of migration of the neural crest cells that form the colonic ganglion cell.).
* Both maternal and fetal cortisol helps to accelerate fetal lung maturation by stimulating surfactant production.
* Elevated AFP suggests neural tube defect like spinabifida.
* Imperforated anus most commonly occur in associattion with urogenital tract anomaly, or with fistula with other organ.
* Craniopharyngioma (calcified cystic tumor) arise form the remnant of Rathke's pouch. it commonly cause headache, growth failure, bitemporal
hemianopsia.
* Hydrocele and indirect inguinal hernia caused by incomplete obliteration of the process vaginalis. Hydrocele occurs when there is connection b/w scrotum
and abdominal cavity allows the leakage of fluid where as hernia occurs when the opening allows the protrusion of abdominal organ along the inguinal canal.
* Polyhydramnios -- dec fetal swallowing or Inc fetal urination. causes are GI obstruction , intestinal atresia , anencephaly.
* Abnormal migration of ventral pancreatic bud leads to the formation of annular pancreas which encircles the descending part of the duodenum and may
lead to symptoms of duodenal obstruction in neonate.
* Dorsal pancreatic bud form the major pancreatic tissue (body, tail and most of head) where as Ventral pancreatic bud form inferior/ posterior portion of the
head and major pancreatic duct. Failure of dorsal and ventral pancreatic bud to fuse together lead to Pancreas Divisium in which two pancreatic duct open
into the duodenum.
* Failure of neuropores to fuse results into Neural tube defect. It lead to persistent communication b/w spinal canal and amniotic fluid. Leakage of AFP and
acetylcholinestrase occur. Valproate Inc the risk because it inhibit intestinal folic acid absorption and is teratogenic.
* Meckels diverticulum is remnant of Omphalomesentric (vitelline) duct. It is connected to the ileum and located 2 feet proximal to the iliocecal valve. It often
contains ectopic gastric mucosa that ulcerates and causes malena with RLQ pain. M diverticulum is true diverticulm and contains all parts of the intestinal
wall. It also can produce intussusceptions with colicky pain current jelly stool. (current jelly stool look like strawberry jam)
* Triple test is used to determine AFP, hCG, and Estriol level b/w 16 -18 week of gestation.
AFP is synthesize by fetal liver, GI tract, and yolk sac early in gestation. maternal AFP level Increases with gestational age. Most common cause of Inc AFP
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
15
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
is Dating error, other reason are Neural tube defect, multiple gestation. Remember Down $ is associated with dec AFP level.
Estriol level reflects both placental and fetal function. dec level of estriol suggests placental insufficiency.
hCG is synthesized by trophoblast. Inc level is associated with multiple gestation, Hydatidiform mole and choriocarcinoma.
* Intestinal malrotation in early fetal life manifest as intestinal obstruction (due to compression by the adhesive band) and midgut volvulus (intestinal ischemia
due to twisting around the blood vessel.
* Hirschsprung dis always affect the rectum and anus because neural crest cell migrate caudally. Sigmoid colon is involve 75 %.
* Both Chromaffin cell of Adrenal medulla and Parafollicular cell (C- Cell) of the thyroid originate from neural crest. Common germ line mutation in neural
crest can cause tumor in both adrenal medulla and thyroid gland. this phenomenon seen in MEN2a and MEN2b
MEN1 --- Tumor of parathyroid , pancreas and pituitary.
MEN2a -- Medullary carcinoma of thyroid , pheochromocytoma, parathyroid tumor.
MEN2b -- Medullary carcinoma of thyroid, pheochromocytoma , mucosal neuroma.
* Ant abdominal wall is formed by the closure of 4 folds. Cephalic, two lateral and two caudal. Failure of any one of the fold results into
Cephalic fold failure --------- sternal defect
Two laterals fold failure ---- Omphalocele
Caudal fold Failure ---------- Extrophy of bladder and cloaca.
* Bilious vomiting after 1st 24 hrs of life is a sign of intestinal obstruction below the part of duodenum.
* Jejunal, ileal and colonic atresia are not caused by abnormal fetal development (not congenital anomaly), instead they are due to diminish intestinal
perfusion with resultant ischemia of a bowel segment and obliteration of lumen and obstruction. The ileum is most commonly affected. If major vessel is
occluded like superior mesentric artery than area of necrosis will be large and appear as an apple peel.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
16
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* MG is associated with abnormality of the thymus (thymoma , thymic hyperplasia)
* Early onset of Alzheimers dis is associated with 3 gene mutation -- APP (ch21). presenilin1 and presenilin2. Late onset of Alzheimers is associated with
Apolipoprotein E4 genotype.
* Mutation in CFTR gene product causes defective post translational folding and glycosylation which results into degradation of protein before it reaches the
cell surface.
* Both sporadic and familial (von hippel lindau dis) renal cell carcinoma have deletion of ch 3p.
* Fragile X $ (X linked disorder) is common cause of mental retardation in males. It manifest as dysmorphic facial features like large jaw, large protruding ear
and macroorchidism.
* Male with delayed puberty with anosmia is consistent with Kallmann's $. Which results from failure of GnRH secreting neuron to migrate from olfactory
placode to their normal anatomic location in the hypothalamus. (due to mutation in KAL-1 gene or the FGF receptor gene which codes for protein require for
this migration)
* Alteration of gene expression in Huntington is believed to occur due to hypermethylation pf histone. Hypermethylated histone binds DNA results into
distruption of synthesis of some neurotrophic protein.
* Mitochondrial dis affect both male and female with equal frequency (100%). The variability of severity occurs due to random distribution of mitochondria
during mitosis among daughter cells. As a result some cell contain mostly damage mtDNA and some mostly normal mtDNA this mixture of two type are
called heteroplasmy and is responsible of clinical variability of mitochondrial dis. Imp mitochondrial $ are as follow
1. Leber hereditary optic neuropathy leads to bilateral vision loss.
2. Myoclonic epilepsy manifest myoclonic seizures, myopathy associated with excersize. Biopsy shows irregular shaped Ragged red fibers.
3. Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy with lactic acidosis and stroke like episodes.
* Genetic imprinting is a selective inactivation of paternal or maternal alleles. this phenomenon explains the difference in clinical presentation of Prader willi
and Angleman syndrome.
* Anticipation refers to increase in severity of genetic disorder in subsequent generation eg are Huntington dis and fragile X $.
* Variable expressivity refer to the difference of severity of Autosomal dominant disorder for eg pt with Marfan $ may have only tall stature but other will
manifest as tall stature, dilated aortic root, lens dislocation.
* Renal Angiomyolipoma is a benign tumor composed of blood vessels, smooth muscle and fat can be diagnosed by abdominal CT scan because density of
fat is less than water. Renal angiomyolipoma is associated with tuberous sclerosis a condition that cause hamartoma in brain, cardiac rhabdomyomas, facial
angiofibromas, hypopigmented leaf shape patches of skin (see below)
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
17
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Xeroderma pigmentosum results fro DNA excisional repair. The dis is characterized by Inc sensitivity to UV radiation. High incidence of malignancy.
* Retinoblastoma gene (Rb gene) regulates cell cycle, abnormality cause loss of ability of cell to arrest in G1 phase. mutation associated with
Retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma.
* ras codes for G - protein that regulates signal transduction. abnormality cause unregulated cell division, inhibited apoptosis, and dec cell adhesion.
* Abnormality of gene responsible for DNA mismatch repair are found in pt with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNCCP or Lynch $). these pts has
high risk of other cancer too.
* In Klinefelters $ ( 47XXY, hypogonadism, small firm testes, gynecomastia, elongated limb, mild mental retardation) the seminiferous tubules are
progressively destroyed and hyalinized causing testis to be small and firm which further cause low testosterone and inhibin level and erectile dysfunction and
infertility. Because of low testosterone and Inhibin LH and FSH are elevated. Hypogonadism cause epiphyseal fusion to be delayed hence elongated limbs.
Klinefelters $ occur due to nondisjunction of sex ch during mitotic division in either parent.
* Achondroplasia (Autosomal Dominant Disorder) occurs in 50% of offspring of effected parents.
* About 25% of offsrings are affected in Autosomal recessive disorder, if both parents carry the defective gene.
* About X linked disorder approx 50% offspring will have disorder if female parent is affected and for affected male all of his daughter will be affected and non
of the son will be affected.
* Deletion of long arm of ch 22 results into Facial and palatal malformation and also can cause Digeorge $.
* Pick bodies are eosinophillic intarcytoplasmic inclusion found in the cortical neuron in pick dis where as lewy bodies are round eosinophillic
intracytoplasmic inclusion that contain neurofilament seen in neuron of substantia nigra in parkinson dis.
* Spongiform transformation is characteristic of Cruetzfeldt - Jacob dis which results into rapidly progressive dementia and myoclonic jerks.
* Negri bodies are round eosinophillic inclusion (contain rabies virus) seen in cytoplasm of hippocampus & cerebellar perkinji cell in pt with rabies.
* Psamomma bodies are laminar calcification found in # of tumor like meningioma, papillary thyroid carcinoma.
* Neurofirillary tangles are form due to Beta amyloid protein which develop in Alzheimers dis. Gene for beta amyloid protein is located on ch 21 this is why pt
with down $ likely to develop Alzheimers by age 40.
* Diminish femoral pulse compared to brachial pulse results form coarctation of aorta. Turner $ is associated with Coarctation of aorta.
* Down $ -- associated with cushion defect (Ostium premium ASD, regurgitant atrioventricular valve)
* Digeorge $ -- associated with Tetralogy of fallot and interrupted aortic arch.
* Friedreich's ataxia -- associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
* Marfan $ -- associated with cystic medial necrosis of aorta.
* Tuberous sclerosis -- associated with valvular obstruction due to cardiac rhabdomyoma.
* Friedreich's Ataxia (ARD) caused by degeneration of post column, spinocerebellar tract and loss of sensory cells of dorsal root ganglia in 5 - 15 yrs age of
children. It manifest as wide based gait, difficulty maintaining balance, loss of position and vibration sensation, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, arrhythmia,
CHF, skeletal abnormalities (kyphoscoliosis, pes caves, hammer toes) and DM (10%).
* MHC Class I molecules present either self Ag, tumor Ag or Ag synthesized by the cell due to viral infection; this pathway of Ag presentation is called
endogenous pathway. Protein in the cytoplasm are degraded by proteosome and than transported into RER where they are loaded onto MHC Class I
molecule and subsequently routed to the cell surface via Glogi apparatus. Remember MHC Class I never go through lysosomes.
* MHC Class II is expressed on Ag presenting cells (APC) like B cell, macrophages, langerhan cells, dendritic cells etc. This Ag is taken into the APC by
phagocytosis or endocytosis and is loaded onto MHC Class II with in the acidified endosomes, and MHC Class II protein - complex is than expressed on the
cell surface for subsequent interaction with T lymphocytes. Failure to acidified lysosomes would lead to deficient expression of MHC Class II bound to foreign
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
18
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
Ag with resultant lack of interaction b/w APCs and T cells.
* Staphylococcus scalded skin $ (SSSS) is caused by staph that produce Exfoliatin exotoxin. Nikolisky sign (skin slip of with gentle pressure), epidermal
necrolysis, fever & pain with skin rash is present. SSSS is more common in infants & young children & is frequently not fatal unless skin is secondarily
infected.
* Process of apoptosis is separated into initiation phase and execution phase. The proapoptotic protein allow for the Inc permeability of mitochondria, which
results in the release of caspase - activating subs like cytochrome c and initiation phase begin; During initiation phase, Protein - hydrolyzing caspases are
activated. In Execution phase these caspases bring about the cell death by cleaving cellular protein and activating DNAses.
* Bruton agammaglobinemia is X linked immunodeficiency resulting in absence of B cells with resultant absence of germinal center and paralymphoid
follicles in lymph node. Remember T cells number and function are intact so the paracortical zone of the lymph node is normal (populated by T cells and
dendritic cells).
* Hyperacute rejection (type II hypersensitivity) is mediated by performed recipient Ab against Ag on the host organ. eg ABO mismatch. This form of rejection
often diagnosed intraoperatively due to immediate mottling of the organ.
* Immune complex mediated damage (type III hypersensitivity) AgAb complex circulating in the blood binds to tissue such as vessels wall, glomerular
basement mem with resultant release of chemotactic mediator and finally cause tissue damage. eg are SLE, serum sickness, mem glomerulonephritis.
* Progressive rise in serum creatinine over a period of month in kidney transplant pt who has not had hyperacute or acute graft rejection (with in 10 day) is
most likely due to chronic rejection. Chronic rejection results from injury to graft vascular endothelium predominantly in cortical arteries which further results
into obliterative intimal smooth muscle hypertrophy and fibrosis.
* IgA consist of two Ig monomers, J chain & secretory component. IgA is abundant in tears, saliva, mucous, & colostrum (provide passive immunity after
birth)
* Contact dermatitis, granulomatous inflammation, tuberculin skin test and candida extract skin reaction all are egs of delayed type hypersensitivity reaction
which involve TH 1 lymphocytes that release interferon - gamma to cause recruitment and stimulation of macrophages.
* B lymphocytes are major effectors cell in humoral immunity because they synthesize and secret Ig. involve in Type I, II, III hypersensitivity reaction.
* Ataxia talengiectasia (ARD) manifest by early cerebellar ataxia (cerebral atrophy) and delayed abnormal dilatation of capillaries (telangiectasia). pt also
manifest with repeated sinopulmonary infection. ATM gene mutation is involve gene is responsible for DNA break repair. High risk of cancer is associated
due to inefficient DNA repair. (pt is hypersensitive to X rays.).
* Eosinophils provide defense against parasite via Ig E by releasing major basic protein and enzymes that damage Ab bound parasite without using
complements, this mechanism is called Ab dependant cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). On other hand Eosinophil contain histaminase which degrade histamine
thus regulate the type I hypersensitivity reaction. It also facilitate inflammation by releasing leukotriens and peroxidases.
* RA is autoimmune dis triggered by unknown Ag. Cartilage serves as autoantigens that activate CD4 T Cells, which in turn stimulate B cells to secrete IgM
against the Fc component of IgG (Rheumatoid factor)
* Classical compliment cascade begins with binding of C1 complement component to either two molecule of IgG or to two molecule of IgM, since IgM
circulate in pentameric form it is much better activator of complement system. The C1 binds to the Fc region of heavy Ig chain in the region near the hinge
point.
Point A and B is hypervariable region of the Fab (Ag binding fragment) also called complementary - determining region of the Ab because their structure
determine what complementary portion of Ag will bound to Ab.
* Sever combined immunodeficiency most commonly results from autosomal recessive deficiency of adenosine deaminase (enz remove excessive
deaminase) with resultant accumulation of adenosine in lymphocytes leading to cell death. Tx in research is retroviral vector to infect pt stem cell with the
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
19
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
gene coding for adenosine deaminase.
* The Fas receptor (FasR) is the most intensely studied death receptor. Its aliases include CD95, Apo-1, and tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily,
member 6 (TNFRSf6). The gene is situated on chromosome 10 in humans
* Wiscott - Aldrich $ consist of triad of eczema, thrombocytopenia and combined B and T lymphocyte def.
* Sarcoidosis is a dis of disordered immune regulation. Immunologic abnormalities include intraalveolar and interstitial accumulation of CD4 T Cells resulting
in high CD4 : CD8 ratio (from 5 : 1 to 20 :1). vs. In hypersensitivity pneumonitis the ratio is significantly decreased and also in Aids pt with pneumonia.
* Leukocyte Adhesion def (ARD) results from absence of CD18 molecule. This leads to the inability to synthesize integrins, Integrins are necessary for
leukocytes to exit the blood stream. It manifest as recurrent skin infection WITHOUT PUS, delayed detachment of the umbilical cord and poor wound
healing.
* 10 to 30% of pt with SLE have lupus anticoagulant the most frequent cause of prolong PTT and false + ve VDRL. Lupus anticoagulant can cause
Antiphospholipid Ab $ defined by antiphospholipid Ab with hypercoagulobility (venous and arterial thromboembolism) and repeated 2nd and 3rd trimester
miscarriages.
* NK cells recognize and kill cells with dec MHC I Ag on their surfaces, such as virus infected cell and tumor cell. They are large lymphocyte and contain
perforin and granzymes in their granules. NK cells kill target cell by inducing apoptosis.
* IgA protease is produced by N. meningitidis and N. gonorrhoeae which cleaves secretory IgA at its hinge region and rendering it ineffective. IgA inhibit
action of pili and fimbriae and other surface Ag of microbes that mediate mucosal adherence and penetration.
* Local defense against candida is performed by T cells VS. systemic infection by Candida prevented by neutrophils. For this reason localized candidiasis
is common in HIV pt where as neutropenic individuals are more likely to have systemic infection.
* IL4 and IL5 are the main cytokines that stimulates the growth and differentiation of B Cells after exposure to Ag. Specially IL4 is responsible for B cell
growth and Iso type switching. IL4 stimulates the secretion of IgE and predisposed to Type I hypersensitivity reactions. IL4 also stimulate differentiation of
TH0 (naive) T helper cell into TH2 helper cells (increasing the TH2 helper population). On other hand IL5 B cell differentiation, IgA production and eosinophil
activity and is imp against parasitic infection.
* IL2 is the first IL produced by TH1 cell after contact with Ag.
* IL12 stimulates development of CD4+ T cells CD8+ T cells and B cells. IL2 also stimulate differentiation of naive T helper cells into TH1 cells. IL12 def may
results into severe mycobacterial infection due to inability to mount strong cell - mediated granulomatous immune response. TX is IFN .
* IFN secreted by T cells contribute in granuloma formation.
* Distruption of macrophages killing may occur after ingestion silica particles as in silicosis, for that reason pt with silicosis has increased susceptibility to TB.
* Digeorge $ cause by maldevelopment of 3rd and 4th Brachial (pharyngeal) pouches due to deletion of ch 22. It may also associated with absence of
parathyroid, cleft palate, mandibular deformity, low set ears and aortic arch abnormality.
* HIV virus via envelop protein gp120 attaches to CD4 protein as a primary receptor and chemokine receptor CCR5 serve as a co receptor. If cell does not
express CCR5 co receptor than HIV will bind to CD4 protein but will not enter the cell.
* Gonococcal infection does not result into lasting immunity because N. gonorrhoeae modify their mem protein by antigenic variation. Ab generation during
one infection will only be specific for the single antigenic epitope. Remember recurrent gonococcal infection occur due to terminal complement def (C56789)
* Acute hemolytic transfusion reaction is an eg of Ab mediated type II hypersensitivity R. Anti ABO Ab in the recipient bind to the donors corresponding Ag.
These AgAb complex will activates complement sp C3a and C5a (anaphylatoxin) and as well C5,6,7,8,9 (mem attack complex). Anaphylatoxin cause
vasodilatation and symptoms of shock while mem attack complex RBC lysis.
* Organ rejection divide into 3 form Hyper acute, Acute and chronic.
Acute rejection occur with in weeks of transplantation and primarily mediated by Host T lymphocytes (that acts against donor MHC (HLA) Ags) and
mononuclear infiltrate. It can be prevented with Calcineurin inhibitor and Corticosteroids.
Chronic rejection shows interstitial fibrosis mediated by host T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes as well as Ab. (occur in months to years later)
* Helper T cells (TH0 or naive) are those who have not contacted Ag. These cells possess the T cell receptor (TCR), CD3 and CD4 protein on their surfaces.
When Ag - MHC II complex is presented to naive TH0 cells, both CD4 and TCR interact with Ag - MCH II Complex while CD3 transmit the signal to the cells
interior. The activated T cell now differentiate into TH1 or TH2 T cells. If the Ag is presented by the macrophages (Ag - MHC I complex) than macrophage
will produce IL12 that stimulate the differentiation into TH1 subset. IL4 is released by the other type of Ag presenting cell which facilitate differentiation into
TH2 subset.
* T lymphocytes or thymocytes are initially produced in bone marrow, but they migrate to thymus for maturation during 1st trimester. In thymus the process of
TCR gene rearrangement, positive selection and negative selection, expression of extracellular mem marker and co - stimulatory molecule occur. Pro T cell
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
20
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
arrive at the thymus as double negative (lacks both CD4 and CD8 Ag), Next in process with TCR gene rearrangement expression of both CD4 and CD8 will
occur. Next, the process of + ve and - ve selection occur with cells that fail either of these tests being eliminated by apoptosis. - ve selection occur in the
medulla in which T cells that possess TCRs and bind with high affinity to self Ag or self MHC class I or II (autoreactive) are eliminated.
* Pt with post Streptococcal glomerulonephritis will present with edema and hematuria with the Hx of strep infection such as impetigo, cellulitis, pharyngitis.
The infection must be caused by Group A hemolytic streptococcus. This is an eg of Type III (Immune complex mediated) hypersensitivity.
* Tetnospasmin travel by retrograde axonal transport into the CNS. Tetnospasmin heavy chain binds ganglioside receptor and light chain inhibit release of
glycine and GABA form inhibitory neuron. Absence of these NT results into causes sustained muscle contraction of tetanus, such as masseter muscle spasm
(lockjaw), Ophisthotones, dysphagia, and facial muscle spasm (risus sardonicus). Prevent by Tetanus toxoid vaccination. Tetanus Immunoglobin use in acute
tx or for tetanus prophylaxis after contaminated wound injury.
* Serum sickness is type III hypersensitivity reaction occurs 5 to 10 days after exposure to Ag. It produces fever, urticaria, glomerulonephritis and
lymphadenopathy also arthralgia, pruritic rash, vasculitis with vessel wall fibrinoid necrosis and neutrophil infiltration due to systemic deposition of circulating
immune complex in arteries and arterioles. Sulfonamide drugs can provoke this reaction. Type III hypersensitivity typically activate complement at local site
where immune complex contain IgG or IgM complement fixing Ab have been deposited; this often cause hypocomplementemia (dec C3).
* ELISA assay is serologic test that detect presence or absence of Ab in human serum. ELISA is the first test done in assessment of pt with suspected HIV
infection, the positive ELISA is than confirmed by WESTERN BLOT. In ELISA (indirect form) known Ag such as HIV Ag is fixed to the bottom of the well
than pts serum is added to these wells, HIV Ag fixed to the well react to Ab present in pts serum the preparation will washed to remove unbound pts Ab and
remaining AgAb complex in well is exposed to 2nd Abs, this Ab are Anti human IgG Ab which will bind pts fixed Ag. The 2nd Ab are coupled to substrate
modifying enz, wash the preparation so excess unbound enzyme linked Ab are removed. Later apply substrate such as CHROMOGEN which will converted
by enzyme to chromogenic or fluorescent signal.
* Poison Ivy is one form of contact dermatitis and is type IV hypersensitivity reaction mediated by T lymphocytes. Cutaneous lesion in Poison Ivy dermatitis
are typically linea erythmatous papules, vesicle or bullae that are pruritic.
* pt with Ankylosing spondylitis , Reactive arthritis ( Reiters dis) are associated with inflammatory bowel dis, and psoriatic arthritis are seronegative
spondyloarthropathies so called due to absence of serum Rheumatoid factor have higher incidence of HLA B27 expression
* Hilar lymphadenopathy, pulmonary infiltration and non caseating lung granuloma in African women is DX of Sarcoidosis.
* Polymyositis present with symmetric proximal muscle weakness of arms and leg, serum creatinine kinase elevated along with Anti - jo - Antibodies. Muscle
biopsy reveal inflammation, necrosis and regeneration of muscle fibers. Preceding damage to myocyte due to over expression of MHC Class I protein on
sarcolemma with subsequent infiltration of CD8 T lymphocytes and myocyte damage occur. Polymyositis is associated with high risk of malignancy.
* Polymyalgia Rheumatica is manifest by bilateral stiffness of shoulder and pelvic girdle muscles, fever and wt loss. PR is associated with temporal arteritis.
* Eaton Lambert $ characterized by Ab against the presynaptic Ca++ channels that prevent release of Ach (cause symptoms of myasthenia gravis). EL$ is
paraneoplastic $ associated with small cell carcinoma of lung that cause muscle weakness that improve with activity
* Palpable skin lesion + abdominal pain + arthralgia & renal involvement is suggestive of Henoch Schonlein Purpura, predominantly in children b/w age 3 10. HSP typically occur due to Ag exposure (after bacterial or viral inf) lead to IgA production and immune complex formation, this immune complex deposit
on blood vessels and in renal messengium, activate complement with resultant inflammation in susceptible person. HSP manifest as a form of
leukocytoclastic vasculitis with Inc circulating IgA containing Immune complex.
* Mutation of the FAS protein is thought to prevent apoptosis of auto - reactive lymphocytes which results into autoimmune dis eg SLE.
* Erythroblastosis fetalis and Hemolytic dis of newborn results from anti fetal erythrocyte Ag IgG antibodies. This is type to hypersensitivity in Mother.
* Nongonococcal urethritis + Conjunctivitis (possible ant uveitis) + arthritis are classic Triad of Reiters $. Arthritis occur typically after GU (nongonococcal) or
GI infection. RS belongs to group of seronegative spondyloarthropathy and cause sarcoiliitis in 20% pts.
* Hyper IgM $ results from an inability of B cells to undergo isotype switching to other Ig isotypes (IgA, G, E, D). The syndrome results from genetic absence
of CD40 ligand on B cells or Enz def imp for DNA modification during isotype switching. It show lymphoid Hyperplasia and recurrent sinopulmonary inf.
* TH2 lymphocytes secrete IL4 and IL13 which togather promote B lymphocyte class switching for IgE synthesis.
* TH2 also secrete IL5 which activate eosinophila and promote IgA synthesis.
* IFN from Helper T cells activate macrophages. TNF is growth factor involve in tissue regeneration and repair.
* E Coli O157:H7 cause hemolytic - uremic $, a rare condition affecting childrens under age 10. Commonly contracted after eating under cooked ground beef.
* The presence of HBeAg (marker of viral replication and infectivity) Inc the risk of vertical transmission of virus. Because of this newborn of all mothers with
active hepatitis B are passively immunized (HBIG) at birth followed by active immunization with recombinant HBV vaccine.
* Lipooligosaccharide of N, meningitidis is analog of the G -ve Rods. LOS acts as Endotoxin & is associated with many of the toxic effect of meningococcal
dis.
* E coli are the frequent cause of neonatal meningitis, second to group B streptococci. Capsular K1 Ag of E coli is a virulence factor that allow the bacteria
to survive hematogenous spread and to establish meningeal inf.
* Lipid A is toxic component of LPS of E Coli that cause sepsis, it cause activation macrophages with wide spread release of IL1 and TNF which
results into sign and symptoms of shock, fever, hypotension, diarrhea, oliguria, vascular compromise and DIC.
* E coli is dominant flora in intestinal tract of humans. E coli cause 80% of UTI, P- fimbriae are most imp virulence factor of uropathogenic E coli, with
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
21
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
out
P- fimbriae E Coli would not be able to bind uroepithelial cell and simply be washed away.
* Dimorphic fungi form molds (with hyphae) at ambient temp (25 -30), and yeast at (single body) at body temp (37). Imp Dimorphic fungi are
* Facial pain and headache in pt with diabetic ketoacidosis are highly suggestive of Mucormycosis (mucor, Rhizopus, Absidia). Rhizopus has affinity for
ketoacidosis and hyperglycemia because of its enz hetoreductase. Mucomycosis proliferate in blood vessels and cause necrosis of the downstream tissue,
black necrotic scar seen in nasal cavity is characteristic. Mucormycosis can rapidly spread to CNS cause confusion neurologic deficit and death.
* Viridian Streptococcus notably S. mutans, and S. sanguis are normally present in mouth. This organism also cause bacterial endocarditis, deep wound inf,
abdominal abscesses and septicemia. Viridans streptococci are able to adhere to the surface of tooth enamel (cause tooth decay) and heart valve and
multiply in those location due to their ability to produce dextran using sucrose as substrate thus cause infection. Dental procedure may lead to Strep viridans
bacteremia where it adhere to fibrin and when fibrin and platelet adhere to endothelial site of new or old injury (like damage valve, vessels plaque etc) strept
viridians get flourished and cause dis. Remember without preexisting injury to cell Strept Viridans can not adhere and cant cause endocardtis where as
Staph Aureus can adhere to intact endothelium without preexisting lesion.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
22
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Enterococcus, normal colonic flora capable of growing in hypertonic 6.5% NaCl and bile. Genitourinary manipulation like catheter, instruments can lead to
enterococccal entry into the blood and Endocarditis.
* HBsAg of HBV must coat the HDAg of HDV before it can infect hepatocytes and multiply.
* Protein A of Staph Aureus binds to Fc portion of IgG at Complement binding site thus preventing the activation of complement, this results into dec
production of C3b and impaired opsonization.
* Travelers diarrhea pathogen produce heat labile (LT. choleragen like) and heat stabile (ST) enterotoxin. LT activates adenylate cyclase leading to Inc IC
cyclic AMP and ST activates guanylate cyclase lead to Inc IC cyclic GMP. Both cause water and electrolyte loss and bloody diarrhea.
* Staph Aureus strain that produce Toxic shock toxin (TSST - 1) are responsible of most cases of TSS. TSST - 1 act like superantigen and activate large
numbers of helper T cells and variable no of region of T lymphocyte receptors with resultant release of IL2 form activated T cells and IL1 & TNF form
macrophages. these IL cause Capillary leakage, circulatory collapse, hypotension, shock, fever, skin findings and multi organ failure.
* Tetanus can be prevented by proper immunization with childhood series and with booster immunization every 10 yrs there after in adulthood. Immunized
mother can pass IgG through placenta provide passive immunity against neonatal tetanus until the child receives its first tetanus vaccine at the age of 2
months of age. Neonatal tetanus can be caused by C tetani colonization from umbilical stump.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
23
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Cryptococcus neoformans (has round oval encapsulated cell with narrow based bud) present in pigeon dropping cause meningitis in HIV and
immunosuppressed pt, mode of transmission is respiratory route. Cryptcoccus virulence factor is its thick polysaccharide capsule. Cryptococcal inf can be Dx
by India ink stain of CSF, Latex agglutination of CSF, methamine stain of tissue or Subouraud's agar culture. TX is Amphotericin B or Flucytosine for
meningitis and fluconazole for life long prophylaxis. (see below)
* Nonseptate hyphae that branch at wide angle are characteristic of Mucor & Rhizopus species. These fungi cause paranasal sinus in immunosuppressed pt.
* Candida albicans form germ tubes (sprouts of true hyphae from yeast cells)if incubated in 37 degree C in serum for 3 hrs. this test help to differentiate C.
albicans from other candida species.
* Spherules (round structure containing endospores) are found in the tissue of coccidioides immitis. C. immitis cause lung dis and disseminated mycosis but
usually do not cause meningitis (or very rare to cause meningitis).
* * MacConkey agar is used to grow many of the enteric bacteria. MacConkey is a bile salt containing agar which restrict the growth of most G + organism.
* Thyermartin agar used to grow Neisseria species. This heated blood agar, or chocolate agar is supplemented with vancomycin, polymixin, & nystatin.
* Blood agar contain bile and hypertonic saline can be used to culture enterococci, while Strept bovis and Group D strept will grow in bile but will not grow in
hypertonic saline.
* Bordet - Gengou medium is used to culture brodetella pertusis the causative agent of whooping cough.
* C diptheriae is cultured on cysteine - tellurite agar, the resultant colonies are Black in color. The bacterium produce IC polyphosphate granule called
metachromatin granules that can be detected microscopically by methylene blue staining
* A resolved HBV inf is suggested by moderate to high level of Anti - HBsAg and Anti - HBcAg with no detectable viral Ags.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
24
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Bug Media used for isolation
H. influenza -- Chocolate agar with factors V (NAD) and X (hematin)
N. gonorrhoeae -- Thayer-Martin media
B. pertussis -- Bordet-Gengou (potato) agar
C. diphtheriae -- Tellurite plate, Lfflers media
M. tuberculosis -- Lwenstein-Jensen agar
Lactose-fermenting enterics -- Pink colonies on MacConkeys agar
Legionella -- Charcoal yeast extract agar buffered with iron and cysteine
Fungi -- Sabourauds agar
Stains
Congo red Amyloid; apple-green birefringence in polarized light (because of -pleated sheets).
Giemsas --- Borrelia, Plasmodium, trypanosomes, Chlamydia.
PAS (periodic Stains glycogen, mucopolysaccharidesacid-Schiff); used to diagnose Whipples disease.
Ziehl-Neelsen -- Acid-fast bacteria.
India ink -- Cryptococcus neoformans.
Silver stain -- Fungi, Legionella.
* If HBeAg persist for several months and host Ab remains at low level, suspect Chronic Hepatitis B inf with high infectivity.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
25
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Strep Peumoniae (lancet shaped in pairs) is most common cause of meningitis in adults. Strept pneumoniae often follow a pulmonary infection specially
Alcoholics, sickle cell anemia, asplenic pts are at Inc risk.
* Impetigo cause by Strept pyogenes (catalase positive). it is unique among hemolytic because it is sensitive t bacitracin.
* Strep pneumoniae express capsular polysaccharides that inhibit phagocytosis, strain lacking capsular are not pathogenic.
* S pnemoniae is capable of undergo transformation by taking up free DNA form neighboring bacteria and are said to be COMPETENT (through this bacteria
that lacks capsule can acquire capsule). Strep Pnemoniae, H influenza, and N meinigitidis are the bacteria who has this ability.
* Conjugation is Pilus mediated transfer of DNA, it occur in many bacteria but first describe in E coli.
* In Transduction DNA from one bacteria can transform in other bacteria by bacteriophage (virus).
* Mucosal invasion is essential pathogenic mech of Shigella through M cells in Payers patches, it than escape the phagosome and spread laterally to other
epithelial cell and release exotoxin called Shiga toxin. An A subunit of Shiga Toxin inhibit 60S ribosomal subunit to stop protein syn & subsequent cell death.
* Bacterial invasion is not necessary for some exotoxin causing illnesses, such as S aureus, botulism, B cereus food poisoning.
* proliferate in lymphnode (mesenteric lymphnode) is the characteristic of Salmonella Typhi and Yersinia enterocolitica. When Yersenia enterocolitica causes
lymphnode inf which results into enlarge inflamed lymphnode clinical picture often confuse with appendicitis hence term Psuedoappendicitis.
* Cryptococcus neoformans meningitis Dx by India ink in CSF vs. Cryptococcal pnemoniae is Dx by Mucicarmine stain of lung tissue.
* C. diptheria initially effect oropharynx and spread dis via AB exotoxins (A is Active subunit cause ribosylation which inactivate Elongation factor 2 thus
cause cell death, and B subunit Binds for penetration). Neural and Cardiotoxicity are serious potenial sequelae thats why immunization is imp.
* Most common cause of E coli bacteremia and shock is urinary tract infection. Predisposing factors are BPH, fecal incontinence, neurogenic bladder
secondary to DM, catheter. (E coli are also the most common cause of UTI, cystitis, acute pyelonephritis).
* 2nd most common cause of UTI is Staphylococcus saprophyticus commonly in women.
* Mycoplasm pneumoniae inf can results into cold agglutinin formation. EBV and malignancy can also cause cold agglutination. Cold Agglutinins are Ab
specific for RBC and cause clumping (agglutination) at low temp.
* Vibrio cholera and E coli enterotoxin cause pure watery diarrhea, these toxin donot cause cell death so no blood, pus or leukocyte can be seen in stool.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
26
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* M. pneumoniae can cause hemolysis due to antigenic similarity b/w M pnemoniae mem Ag and RBC mem Ag, so when immune system mount response
against M. pneumoniae it also destroy RBC and cause anemia. These Ab are called Cold agglutinin. After resolving the inf the anemia resolves
spontaneously. M. pneumoniae can also cause rare Steven - Johnson $ and joint pain.
* Aspergillosis commonly effect lung of immunosuppressant pt (HIV, malignancy etc) and present with hemoptysis, granuloma and fungal ball. Aspergilosis
has predilection for blood vessels, spread hematogenously and cause infarct in the skin, paranasal sinus, kidney, endocardium, brain. Amphoteracin is the tx
for invasive aspergillosis. Asthmatic pt can suffer allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, repeated bouts can lead to bronchiactasis, Tx is steroids.
* HBsAg is noninfective envelop glycoprotein. Infected hepatocyte may produce large quantity of HBsAg and exceeding the amount of HBcAg.
* Hydrocelphalus + Intracranial calcification + Chorioretinitis (yellow /white cotton like scar on retina) is classic Triad of toxoplasmosis. Effected neonate also
has hepatosplenomegaly, rash, seizures and altered muscle tone and ocular movement. Congenital Toxoplasmosis is transmitted transplacentally during first
6 month of pregnancy. commonly acquired form Cat feces.
* HCV is genetically unstable because lack proofreading 3' 5' exonuclease activity in its RNA polymerase, and its envelop glycoprotein contain
hypervariable region prone to frequent genetic mutation.
* virulent Mycobacteria grow as serpentine cord enrichmedia secondary to presence of cord factor. Cord factor establish virulence by inhibiting neutrophil,
mitochondrial destruction and induced release TNF.
* meningiococcal sepsis may cause DIC, hemorrhagic destruction of bilateral adrenal glands, this finding is known as Waterhouse - Friderichson $. N
meningitides does not necessarily include meningitis.
* S. Bovis endocarditis and Bacteremia are associated with GI lesion (colon cancer) in more than 25% of pts. pt must be worked up for malignancy.
* M protein is the major virulence factor for Strep pyogenes, it mediate bacterial adherence, inhibit phagocytosis and complement activation, where as
streptolysin O Ag of S. Pyogenes lyses RBC and polymorphonuclear leukocytes, it is streptolysin O which is responsible for Ab production. (test by ASO titer
which is Anti streptolysin O titer).
* Erythma gangrenosum is strongly associated with pseudomonas bacteremia and septicemia due to exotoxins which trap in skin vessels in neutropenic,
hospitalized, burn pt or in pt with indwelling catheter. (P. aeroginosa can be identified by its non lactose fermenting state)
* Pts with indwelling catheter are at Inc risk of UTI with E Coli, Strep Saprophyticus, K. pneumoniae, Protius mirabilis and P, aeroginosa.
* Acid fast stain identifies mycolic acid in the organism (mycobacteria and Nocardia) by applying ANILLINE dye (Carbofuchsin).
* Mucormycosis (broad nonseptate hyphae with right angle) is opportunistic infection cause paranasal sinus infection in Diabetes or immunosuppressed pt.
remember aspergillosis also effect paranasal sinus but can be differentiate by V shape branch (45 angle).
* H. Influenza is blood loving so require X (hematin) and V (NAD+) factor for growth. This can be accomplished by growing H Influenza with S aureus
because S. Aureus produce factor X and factor V called Satellite Phenomenon.
* S Aureus most common cause of tricuspid endocarditis in IV drug abusers whereas P. aerogeninosa is 2nd most common in this population.
* Gonococci use their pili to mediate adherence to mucosal epithelium. Each gonococcus possesses ability to modify pilus by process called antigenic
variation, thus avoid host defense and decline possibility to make vaccine.
* Staph Epidermidis and Staph Saprophyticus are both coagulase negative and are empirically treated with Vancomycin due to multiple drug resistance.
* Staph epidermidis is most common cause of endocarditis & arthritis in pt with prosthetic valve and prosthetic joint respectively. it is susceptible to
novobiocin.
* Rheumatic fever is autoimmune reaction that follows by Strept pyogenes pharyngitis. Tx is Vancomycin.
* Universal prenatal screening for group B colonization by vaginal - rectal culture at 35 - 37 weeks gestation is recommended to identify colonized women
who require INTRAPARTUM antibiotics (Penicillin or Ampicillin) to prevent neonatal Group B Streptococcal sepsis, pneumonia and meningitis.
* Staph saprophyticus is responsible for almost half of all UTI in sexually active young women. Staph saprophyticus is uniquely resistant to novobiocin.
* Nontypeable strain of H Infulenza do not form antiphagocytic capsule and are part of normal flora of upper respiratory tract but can cause infection.
Immunity against nontypable strain or types other than type B is not conferred by vaccination with Hib vaccine.
* Transmission of HAV is via fecal oral route, contaminated water or food with steamed shellfish are common culprit in USA.
* In USA typhoid commonly occur in those who travel where disease is endemic. Typhoid fever cause initial diarrhea or constipation than
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
27
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
hepatosplenomagaly, Rose spot on abdomen and possible hemorrhagic enteritis with bowel perforation.
* Methcillin resistant S aureus (MRSA) are resistant to beta lactam antibiotics including betalactamase resistant antibiotics, because MRSA alter penicillin
binding protein.
* H Influenza type B can cause acute epiglotitis typically shows rapidly progressing fever, severe sore throat, drooling and progressive airway obstruction in
unimmunized, improper immunized and as well as fully immunized pts.
* HBV genome consist of partially double - stranded circular DNA, replication accomplished through reverse transcriptase DNA polymerase that creates an
intermediate + single stranded RNA templet and double stranded DNA progeny. Double stranded DNA templet + RNA Progeny double stranded DNA.
* C diptheriae is non motile, uncapsulated G + Rod, its cytoplasm contain metachromatic granules that stain with ALANINE dye like methylene blue. Its
clumps resembles chinese letters or join in V or Y shape chains.
* Hematogenous Osteomyelitis of long bones most commonly occur in children and frequently caused by Staph aureus after some bacteremic event.
* Pulmonary anthrax also called woolsorters disease cause by inhalation of spores while working with goat hairs and hides. Hemorrhagic Mediastinitis as
widened mediastinum on chest X rays is an imp clue.
* Anthrax appear as long chains in serpentine or medusa head form microscopically, it produce anti phagocytic capsule which contain D - glutamate.
* Staph aureus food poisoning cause rapid nausea, vomiting and abdominal cramping (usually due to mayonnaise containing product). VS. similar picture
can be seen in food poisoning caused by bacillus cereus ( due to reheated fried rice).
* Hypo - Hyper pigmented skin patches that become more visible after tanning are characteristic of Pityriasis versicolor caused by Malasazia furfur. KOH
preparation of skin scraping reveals spaghetti and meatballs appearance on light microscopy.
* N. meningitidis gain access to CNS by first colonizing the nasopharynx and subsequently invading the mucosal epithelium and gaining access to blood
stream and reach choroid plexus to gain access to CNS through BBB and initiate inflamation.
* H Influenza vaccine composed of polyribosyl-ribitol- phosphate (PRP), a component of Hib capsule conjugated with diptheria and tetanus toxoids. It induce
Ab production and memory B lymphocytes.
* Blastomycosis dermatitidis may cause flu like symptoms, cough with sputum, hemoptysis, dyspnea and pleuritic chest pain. Pulmonary Blastomycosis is
characterized by granuloma formation.
* HAV can be inactivated by water chlorination, bleach, formalin, UV irradiation or boiling to 85 C for a minute.
* Spleen serve both as site of Ab synthesis, and reservoir of phagocytic cells to remove pathogens from circulation. Asplenic pt are prone to infection by
Encapsulated Organism such as Strept Pneumoniae, H. influenza, N. meningitidis. (polysaccharide vaccination against those bacteria is imp in asplenic
pts)
* Histoplasma capsulatum is present in bird and bat dropping and is endemic in Mississippi and Ohio river vally.
* Coccidioides immitis cause pulmonary dis in immunocompetent individuals, endemic in south western US associated with cave exploration. It is also an
etiologic agent of San joaquin vally fever.
* Legionnaires disease has propensity to cause dis in smokers characterized by high fever, Cough chest pain, accompanied with diarrhea, headache, and
confusion. Lab shows hyponatremia. Tx of choice is Erythromycin.
* Legionella require special media for growth which contain L- cysteine and culture on charcoal - yeast agar. is caused by inhalation of aerosolized water
from natural water resources, air conditioner, water based cooling sys, humidifying sys, even tap water in hospitals
* Mycoplasm pneumonia commonly affect youngs (walking pneumonia) cause mild fever, mild anemia, cough and atypical pneumonia. Chest X rays give
impression of severe pneumonia. organism is wall less and will not appear on gram stain.
* It is Peptidoglycan cell wall that these bacterias can survive osmotic stress. Penicillin and cephalosporin disrupt peptidoglycan cell wall of bacterias.
* Anterior nares is most common site of methcellin sensitive and methcillin resistant Staph aureus in 25 -30% of general population.
* Colonization of aspergillosis occur in old lung cavities for eg from TB, emphysema, sarcoidosis. aspergillus do not invade the lung but live inside the cavity
and make Fungus Ball or aspergilloma, it cause cough and hemoptysis. On X ray aspergilloma appear radiopaque that shifts position.
** Failure of HCV vaccine production is attribute to remarkable variety of antigenic structure of HCV.
* H. capsulatum can survive Intracellularly with in macrophages cause fever, wt loss, painful oral ulcer lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly.
* Candida albican is normal inhabitant of GI tract including oral cavity in 40% of population.
* HEV is SS RNA enveloped virus spread through fecal oral route. associated with high mortality rate in infected pregnant women.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
28
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Mucicarmine stain detect polysaccharide capsule of Cryptococcus neoformans (red stained capsule), which is the virulence factor. note the narrow based
bud. Remember C neoforman is neurotropic fungus cause dis via respiratory route in immuno suppressant pt eg. HIV, Kidney transplant etc cause subacute
or chronic meningioencephalitis.
* Digoxin will Inc cardiac contractility by blocking the Na+ - K+ ATPase in cardiac myocyte which lead to Inc IC Ca++ with resultant Inc Force of
contraction.
Digoxin also dec AV node conduction by Increasing parasympathetic tone (slowing down conduction through AV node) thats why can also be used as 2nd
line tx in atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response.
* Ca++ channel blocker such as diltiazam and cardioselective beta blocker are first line for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response.
* Digitalis toxicity shows fatigue, blurry vision, change in color perception, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headache, dizziness, confusion,
and delirium. Bradycardia from Inc AV node block results into junctional escape beats, sustained junctional escape rhythem and eventually ventricular
tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation highly mortal. Also Inc plasma K+ is an additional clue in digitalis toxicity (remember the higher the tissue conc of
digitalis toxicity higher the serum K+ will be).
* Mefepristone (RU - 486) is an progesterone antagonist have 5 times higher affinity for progesterone receptor) used for therapeutic abortion up to 49 days
after conception. vs. Misoprostol - PGE1 analogue has limited success in pregnancy termination if use alone thats why it comes with combination with
mifepristone for better efficacy. In addition misoprotol used for the prevention of NSAID induced GI ulcer.
* Biphosphonate are structural analogue of pyrophosphate, an important component of hydroxyapatite. These drugs are used in the tx of osteoporosis,
paget disease of bone, malignancy induced hypercalcemia. administer drug with plenty of water and pt may stay upright for 30 minutes to prevent reflux
esophagitis.
Biphosphonate inhibit Ostoclaet activity and bone Resorption.
* Nitroglycerine is primarily a vasodilator and cause dec in preload thus dec myocardial O2 demand. It may lead to reflex tachycardia due to relative
hypotension that the body responds by catecholamine release. that can be treated with beta blockers.
* Drug induced lupus has been linked to drug that are metabolized by N- acetylation in liver for eg. Hydralazine, and Procainamide. Those who are slow
acetylators are at great risk for developing lupus like $. discontinuation of drug resolves the disorder.
* Milrinone is Phosphodiesterase inhibitor it activity can Inc cardiac contractility because phosphodiestrase normally metabolize cAMP, its inhibition results
into Inc cAMP with resultant Inc in conductance of Ca++ channel in sarcoplasmic reticulum which further Inc the force of contraction. on other hand Inc cAMP
in vascular smooth muscle cause vasodilatation and hypotension. that why cant use in hypotensive pt.
* Trimethprim, methotrexate and primethamine inhibit dihydrofolate reductase.
* Enterococci produce aminoglycoside - modifying enz that transfer different chemical groups (acetyl, adenyl, ph) to aminoglycoside molecule thus impair its
binding to ribosomal subunit.
* Eternacept is TNF inhibitor, used in moderate to severe RA particularly in those who ail to respond methotrextae. Its serious adverse affects are
including reactivation TB, fungal inf, atypical pneumonia. Do not use in pt with underlying inf. Other TNF are infliximab, adalimumab.
* First line Tx for acute gouty arthritis is NSAIDs however Colchicine is some time used to tx acute condition with 80% success rate. Colchicine inhibit
microtubule polymerization by binding to subunit of microtubule and prevent their aggregation, this in turn inhibit mem dependant function by effecting
cytoskeletal of cell which results into chemotaxis & phagocytosis & reducing leukotriene B4. Common adverse effect are nausea, abdominal pain & diarrhea.
* Lidocaine (Class IB) binds rapidly depolarizing and depolarized cells specially in Ischemic myocardial tissue, thats why this agent is choice for the
prevention and treatment of post MI arrhythmias. Currently Amiodarone has replaced the lidocaine in the management of ventricular tachycardia.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
29
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Class III antiarrythmic such as Amiodarone, sotalol, ibutelide, dofetilide will slow K+ efflux from ventricle myocyte with resultant prolong repolarization and
prolong refractory period.
* The absolute contraindication to the use of OCPs are
1. Prior Hx of thrombotic event or stroke.
2. Hx of estrogen dependant tumor.
3. Women over age 35 who smokes
4. Hypertriglyceridemia
5. Decompensated or active liver dis (due to impaired steroid metabolism)
6. pregnancy
* Clavulanic acid, sulbactum and Tazobactam are beta lactamase inhibitor.
* Direct arteriolar vasodilator like Hydralazine, Minoxidil are effective antihypertensives. It may cause reflex sympathetic activation with resultant tachycardia
and edema, to counter act these effect these agents are given in combination with sympatholytic and diuretics.
* Anthracycline is chemotherapeutic agent (also doxorubicin, daunorubicin) form free radical in myocardium and resultant dose related Dialated
cardiomyopathy (both chambers). This side effect can be prevented by DEXRAZOXANE which is Iron chelating agent thus dec free radical formation.
* Adenosine is quick acting drug of choice in PSVT with half life of 10 sec. It commonly cause chest burning (bronchospasm), flushing and high grade block.
Adenosine is also used for chemical stress test.
* Paralytic action of nondepolarizing neuromuscular junction blocker can be reversed with neostigmine (anticholinestrase). vs. Depolarizing neuromuscular
blocking effect like with succinyl choline cant be reversible instead it largely depends on its catabolism by plasma cholinestrase.
* Nitrate mimic the action of endothelial drive relaxing factor (Nitric Oxide). Nitric oxide increases cGMP with resultant dec IC Ca++ and dec activity of myosin
light chain kinase which further dec myosin dephosphorylation and smooth muscle relaxation.
* Infertility in PCOS is clomiphene and wt loss. Clomiphene is estrogen analogue and block the estrogen receptor in hypothalamus there by the blocking
negative feed back, as a result hypothalamus continuous secreting GnRH which further release FSH and LH and ultimately stimulate ovulation.
* Post operative urinary retention is common complication due dec micturition reflex activity, dec detrusor contractility and Inc vasical sphincter tone. This can
be tx with muscarinic agonist BETHANECHOL (alpha blocker).
* Interaction b/w phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor ( like sildenafil, vardenafil) and nitrates is important because cGMP is metabolized by phosphodiestrase,
pt on phosphodiestrase inhibitor will lead to additional cGMP accumulation inside the cell. Additional cGMP due to both Inc synthesis (from nitrate) and dec
degradation (from PDE inhibitor) will cause profound hypotension because of extreme vasodilatation.
* Osteoporosis (dec bone density) with HTN / CHF can be treated ideally with hydrocholorothiazides because it Inc the absorption of Ca++ in distal covulated
tubule. Hydrochlorothiazide also cause hypocalciuria thus dec the formation of Ca++ stones therefore is ideal for pt who has renal calculi or are stone
producer. (studies shown that pt on thiazides have relatively higher bone mineral densities.
* Amiodarone is class III antiarrythmic that also exhibits properties of class I, II, and IV agents. Amiodarone is known to prolong QT interval via effect on K+
mediated repolarization (phase 3) of myocardial cells. Prolong QT interval may increased the risk of torsades de pointes but interestingly Amiodarone is
associated with low risk of torsades de pointes unlike Class IA and Class III agent.
* Ca++ channel blockers selectivity -- Verapamil has most effect on heart where as Nifidipine is most is most selective for peripheral vasculatures on other
hand Diltiazam has selectivity some where in the middle. Common side effects are constipation, gingival hyperplasia. bradycardia / AV node block (with
verapamil)
* Methotrexate is 1st line tx in pt with moderate to severe Rheumatoid arthritis (60 - 70% improvement in dis). Lefleunomide and TNF inhibitor can be used
in combination with methotraxate if pt is not responding to methotrextae alone. Methotrextate cause stomatitis and liver function abnormalities.
* Local adverse effect of chronic topical corticosteroid use include, atrophic thinning of derm associated with loss of dermal collagen, drying, cracking thinning
of skin, telangiectasia and ecchymoses.
* Heparin is the drug of choice in acute venous thrombosis and thromboembolism. Heparin inhibit antithrombin III where as Warfarin is used for the
prevention of recurrent venous thrombosis. Warfarin inhibit Vit K dependant carboxylation of glutamic residues of clotting factor II, VII, IX & X (vit K
dependant).
* In pregnant women use Heparin for deep venous thrombosis because warfarin is teratogenic.
* Heparin is the drug of choice for prevention of venous thrombosis in non ambulatory pt or in pts undergoing elective surgery.
* Warfarin is entirely metabolized by cytochrome P450 sys, drugs that inhibit P450 will Inc anticoagulant activity of warfarin whereas drug that Inc P450 will
dec the anticoagulant activity of warfarin.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
30
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Dec vit K synthesis (cause by antibiotics) or dec intake (malelimentation or malabsorption dis) will potentiate warfarin activity.
* Inhibition of anticoagulant activity of protein C can predispose pt to warfarin induced skin necrosis, this complication typically occur during the first week of
warfarin therapy. When warfarin is started Protein activity reduces by 50% in one day but other procoagulant vitamin K dependant actor (II, IX, X) declines at
slower rate, this results in transient hypercoagulable state. Risk of warfarin induced skin necrosis Inc in pt with protein C def, as well pt started with large
dose of warfarin.
* Clopedogrel & Ticlopidine (block interaction of ligands with receptors in pletelet and inhibit ADP) are useful in tx and prevention of Ischemic strokes,
coronary $, and peripheral vascular dis. it can be taken with aspirin for additional effect or also it is drug of choice in pt allergic to aspirin. Clopedogrel is
preferred because serious side effect with ticlopidine like neutropenia, fever, mouth ulcer. CBC must be monitored biweekly for first 3 months in pt with
ticlopidine.
* Another anticoagulant Dipyridamol and cilostazol Inc cAMP by decreasing phosphodiestrase activity
* Abciximab is Gp IIb / IIIa blocker thus prevent pletelet and fibrinogen contact. (remember GP IIb / IIIa def cause Glanzmann thrombesthenia a inborn
coagulation disorder)
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
31
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Causes of vit B12 def -- pt with Achlorhydria (in elderly), vegetarian diet, terminal ileal dis, bacterial over growth,
* Heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) more commonly lead to paradoxical thrombosis rather than bleeding. HIT is serious disorder caused by Antibodies
to heparin and pletelet factor VI. HIT can be tx with ARGATROBAN which is direct thronbin inhibitor.
* Sickle cell anemia therapy include Hydroxyurea (antineoplastic drug) which Inc Fetal hemoglobin synthesis (unknown mechanism). Inc Fetal hemoglobin
confer protection against the polymerization of sickle cells (resolves pain crises). Other drug use in sickle cell anemia is Gardos channel blocker hinder the
efflux of K+ and water from cell, preventing dehydration of erythrocytes and reducing the polymerization of HbS.
* Hemolytic anemia is the possible side effect of dapsone in G6PD deficient pt. G6PD def anemia is characterized by hemolytic anemia precipitated by
oxidative stress (drugs infection). peripheral blood typically shows bite cells and hienz bodies.
* Chloramphenicol can lead to both Dose - dependant (reversible) and Dose - independent (Often Irreversible) pancytopenia (aplastic anemia)
* Refampin resistance occur due genetic mutation in the bacterial DNA -dependant RNA polymerase. Refampin is used as a monotherapy in prophylaxis
of H Influenza and N. meningitidis. and as a multi drug therapy for mycobacterial infection, leprosy etc.
* Inhaled and systemic glucocorticoids are most effective anti inflammatory agent for Chronic asthma prevention and treatment. High IV dose glucocorticoids
(not inhaled) are generally reserved for the initial management of acute asthma exacerbation
* Amphoteracin B binds ergosterol of fungal cell, however it also binds cholesterol of human tissue to some extent causing toxicity. Common adverse effect
are nephrotoxiticity, hypokalemia, and hypomagnesaemia.
* Acetaminophen toxicity can be tx with sulfahydryl group supplementation provided by N- acetyl cysteine. Nacetyl cysteine also act as glutathione
substitute and bind to toxic metabolite.
* Isoniazid is chemically similar to vit B6 (pyridoxine) it inhibit mycolic acid synthesis in mycobacteria with resultant cell wall and virulence factor disruption.
Isoniazid causes B6 def, neuropathy, hepatotoxicity & also P450 induction.
* Refampin Inc the activity of P450 with resultant dec the serum level of protease inhibitor, thats why Rifabutin should be given for mycobacterial inf in HIV
pt instead of refampin.
* Protease inhibitor (anti HIV) inhibits cleavage of polypeptide precursor into mature viral protein. Side effects are hyperglycemia (due to Inc insulin
resistance), lipodystrophy, drug interaction due t inhibition of cytochrome P450.
* Lipodystrophy leads to fat deposition on back (buffalo hump) and abdomen (central obesity) and dec adipose tissue of the extremities (peripheral wasting).
* Theophyline intoxication tx include gastric lavage followed by activated charcoal administristation (reduces absorption) and cathartics (Inc elimination GI
tract) beta blocker is the drug of choice for Theophylline induced arrhythmia and benzodiazepine for the tx of theophylline induced siezures. The major
reason of morbidity and mortality is seizures , tachy arrhythmia are the other major concern.
* Refampin -- bacterial DNA dependant RNA polymerase inhibitor thus inhibit transcription with subsequent absence mRNA and its derived protein. Refampin
resistance is acquired by modification in refampin binding site on DNA dependant RNA polymerase.
* Ethambutal cause Optic neuritis with resultant color blindness, central scotomata and dec visualacuity. All reversible upon discontinuation of drug.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
32
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Isoniazid inhibit mycolic acid synthesis, drug must be processed by mycobacterial catalase peroxidase for activation for this reason resistance can be occur
either by nonexpression of catalase peroxidase enzymes or through gene modifiication of izoniazid binding site on that enz (remember Catalaze peroxidase
is essential for mycolic acid in mycobacteria.
* Those who use inhaled corticosteroid must be instructed about oral rinsing to prevent Oropharyngeal Candidiasis.
* Azoles Antifugnal inhibit Demethylation of Lanosterol into Ergosterol, thus suppressing the synthesis of fungal cell mem, Azoles does that by inhibiting
fungal cytochrome P450, therefore P450 inducers Increases azoles metabolism with resultant dec serum conc of Azoles. these drugs are Fungistatic.
* Gresiofulvin interact with fungal Microtubules inhibiting mitosis , its iaccumulation into keratin tissue make it good anti dermatophyte inf.
* Main classes of Antifungal -- 1. Polyenes (Amphoteracin B, Nystatin) -- binds ergosterol molecules in fungal cell mem creating pores and cause lyses.
2. Azoles (ketoconalzole etc) -- inhibit ergosterol synthesis.
3. Echinocandins (Caspofungin & Micafungin) -- Inhibit Glucan synthesis (component of fungal cell wall)
4. Pyrimidines (Flucytosine) -- convert to 5 florouracil in fungus and interfere with fungal RNA and protein synthesis.
* Pulmonary HTN can be tx with Bosentan, an endothelial receptor antagonist which dec pulmonary arterial pressure and lessen the progression of vascular
and right ventricular hypertrophy. (Endothelin is potent vasoconstrictor and stimulant of endothelial proliferation). Ultimate tx of Pulmonary HTN is lung
transplant.
* Eternacept is humanized monoclonal Ab that binds to TNF thus dec its conc. Its an anti-inflammatory agent used in the tx of RA, psoriasis & psoriatic
arthritis.
* Cromolyn and Nedocromil act indirectly by inhibiting mast cell degranulation, thats why theses agents are good for prophylaxis of asthma or in pts with
seasonal symptoms, aspirin induced asthma, exercise induced asthma. Drug is not effective in acute attack & general less effective than glucocorticoids.
* Simvastatin dec and Chlosetyramine Inc hepatic cholesterol synthesis. Agents that inc hepatic cholesterol synthesis (such as fibrate and bileacid binding
agent) are associated with inc risk of gall stones.
* Nicotinic acid (Niacin B3) use for the tx of dyslipidemia, it dec the synthesis of hepatic triglycerides and VLDL and in part suppresses free fatty acid
release from peripheral tissue. It also dec the conversion of VLDL into LDL thus dec LDL too. It also Inc HDL by 25 - 30% (more than any available drug in
market). Serious side effect Inc Uric acid level (gout), hepatotoxicity (with high doses) and hyperglycemia. Facial flushing & warmth tx with aspirin.
* ACE break down bradykinin. bradykinin is a potent vasodialator that is why it ACE inhibitor cause angiedema by increasing bradykinin conc.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
33
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Fibrates are 1st line tx for hypertriglyceridemia (20-50% ), if further dec needed add Niacin, finally fish oil (Omega 3) is also use full ( TG by 20-30%).
* Ezetimibe selectively inhibit intestinal absorption of cholesterol it dec serum TG modestly and Inc HDL modestly. It is used in conjunction with Statin
therapy.
* Bile acid binding resins (cholestyramine, colestipol, colsevelam) binds bile acid in GIT thus interrupting enterohepatic bile circulation and hepatic
LDL. Main side effect GI upset, gall stones, impaired absorption of nutrient and drugs and hypertriglyceridemia and Inc VLDL by liver, that is why bile acid
binding resins should not be used in pt with hypertriglyceridemia.
* Dipyridamole and Colistazol inhibit pletelet phosphodiestrase (enz responsible for break down of cyclic AMP). Cilostazol in addition inhibit pletelet
aggregation also directly vasodilates. Cilostazol is used in the tx of intermittent claudication.
* First dose hypotension is common with ACE inhibitor specially in those who are hyponatremic, hypovolemic (due to diuretics), high renin aldosterone level,
renal impairment and heart failure. To minimize the risk use low dose first time.
* Amlodipine is also Ca++ channel blocker with same side effects.
* Gemfibrozil also Inc cholesterol excretion by liver along with reduction of serum LDL thus Inc the risk of gallstone formation.
* ACE inhibitor dec serum AT II, aldosterone, Inc Na++ excretion, Inc serum K+ (care full with pt who are on K+ sparing diuretics), dry cough, angioedema
(due to Inc bradykinin) and first dose hypotension.
* Energy of myocardial function comes from glycolysis, glucose oxidation and fatty acid oxidation, although fatty acid oxidation results in greater ATP
production, it requires more O2 in comparison to glucose utilization & glycolysis. Despite its more O2 requirement fatty acid is the main source of energy
production (60%) where as glucose provide 30% and glycolysis 5%. Thus Fatty acid oxidation inhibitor shift energy production to glucose oxidation therefore
decreasing myocardiocyte O2 and toxic built up of Fatty acid metabolite production.
* Aldosterone excess cause HTN, hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis and depress Renin. Tx for Conn $ is spironolactone and Eplerenone. Most frequent
side effect is gynecomastia approx 1% with eplerenone, and 9% with spironolactone.
* Hypoaldosterone is the cause of Type IV renal tubular acidosis.
* Statins are metabolized by P450 except Pravastatin. Drugs that inhibit P450 (such as erythromycin) increases the statin effect also side effect like statin
induced myopathy and rhabdomyolysis with potential for acute renal failure due to Inc myoglobinuria. (pravastatin is tx of choice in pt with P450 inhibitor)
* Azithromycin does not have a significant effect on P450. Inhibitor of P450 are ketoconazole, HIV protease inhibitor, grapefruit juice.
* Niacin can potentiate the effect of some antihypertensive agents due to its vasodilatory effect, dose adjustment is required.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
34
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Fenoldopam is parenteral selective dopamine - 1 receptor agonist, it cause arteriolar dilation (dec systemic vascular resistance) and natriuresis with
resultant decreased BP. Since fenoldopam is dopamine agoinst it also improve renal perfusion. good drug
* Statins inhibit HMG CoA reductase (rate limiting enz in hepatic cholesterol synthesis) thus Inc hepatocytes expression of surface LDL receptors & increases
uptake of circulating LDL.
* ACE inhibitor reduces the efferent arteriole resistance and subsequent dilation which results into dec hydrostatic P in glomerular capillaries and ultimately
dec GFR and renal perfusion P. Inc in serum creatinine upto 30% with in 2 - 5 days can be expected in most pt, this Inc subsides with in 2 - 3 weeks if not
discontinuous the drug. (be careful in pt with Acute renal failure and renal artery stenosis pt because of ACE inhibitor induced efferent dilation
which those pts need to maintain renal function).
* Regulation of AT aldosterone system involves 3 major pathways, 1. Macula densa 2. Intrarenal baroreceptors 3. Beta adrenergic receptors. Sympathetic
stimulation via nor EN of 1 receptors located on juxtaglomerular cells stimulates renin release. That is why Beta blocker can reduce AT I, AT II and
aldosterone levels but decreasing Renin (this effect weakly correlate with plasma renin level and its efficacy are more likely due to reduce cardiac output
secondary to negative chronotropic and inotropic activity) Beta blocker has no effect on ACE thus do not effect bradykinin level.
* Nitroprusside has quick onset and short duration of action used in hypertensive emergencies. Nitroprusside initially metabolized to cyanide and than to
thiocyanate by liver rhodanase, this disadvantage can lead to cyanide toxicity. Sodium thiosulfate is used to treat cyanide toxicity by donating sulfur to
liver rhodanase to enhance conversion of cyanide to thiocyanate.
* Serum HDL < 40 mg/dL in male and < 50 mg/dL in female is associated with Inc risk of coronary artery dis. use Niacin to dec the risk (HDL 25 - 35%)
* nor EN infusion can cause local tissue necrosis at IV site due to 1 mediated constriction. Such necrosis can be prevented infiltration through out the
effected area with 10-15cc of sodium chloride solution containing 5-10 mg of Phentolamine mesylate ( blocker that cause vasodilation). This antidote must
be given with in 12 hr of extravasation to be effective (use hypodermic needle).
* The cutaneous flushing of niacin is mediated by prostaglandins and can be prevented with pretreatment with aspirin.
* Capsacin reduce pain by dec the level of subs P in peripheral nervous sys.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------* Basement mem splitting on microscopy seen in Alport $ and Memranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN) type I. In Alport $ symptoms accompanied
with deafness and occular manifestation vs.
* MPGN shows granular deposit on immunoflorescense & proliferative messengial cells and Inc messengial matrix with lobular appearance on light
microscopy
* Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis shows IgM and C3 deposit in sclerotic area of the glomeruli on immunoflorescense.
* Anti GBM Ab react with 3 chain of collagen type IV, found in glomerular basement mem is characteristic of Good pasture $, a condition characterized by
pulmonary hemorrhage (hemoptysis) and Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis, On light microscopy there is a glomerular crescent formation and on
immunoflorescense shows linear deposit of IgG and C3 along the glomerular basement.
* ANCA (anti neutrophill cytoplasmic Ab) associated RPGN, there is no Ig and complement deposit, pt present with renal failure pulmonary symptoms
(cough, dyspnea, hemoptysis) and upper respiratory tract symptoms like epistaxis, mucosal ulceration, chronic sinusitis), Crescent are found on light
microscopy.
Remember RPGN type I is associated with Wageners granulomatosis, high serum c- ANCA is Dx (no Ig / complement deposit) vs. RPGN type II
is associated with immune complex mediated dis.
Remember crescent formation on light microscopy is Dx of RPGN (crescent consist of glomerular parietal cell, monocytes, macrophages and fibrin),
crescent eventually eventually become sclerotic , disrupting glomerular function and causing irreversible renal injury.
* Wegeners granulomatosis is also a cause of RPGN type III (pauci immune) -- shows nephritis, upper and lower RTI, crescent formation, absence of
deposits on immunoflorescense and elevated c- ANCA.
* Histological picture of Post streptococcal GN ----------- Enlarge hypercellular glomeruli,
Lumpy bumpy granular deposit of IgG and C3 on immunoflorescense
Electron dense deposit on the epithelial side of basement mem.
* Dermatitis herpetiformis is rare condition -- erythematous, pruritic papules, vesicles and bullae that appear bilaterally on extensor surface. Dermatitis
herpetiformis is strongly associated with Celiac dis.
* Nephrotic $ regardless of cause lead to Inc glomerular capillary permeability (leak of plasma protein), dec colloid osmotic P with fluid shift into interstitium
which further causes Inc in aldosterone and resultant Na+ and water retention with subsequent hyperlipidemia and lipiduria.
* ATN (due to hemorrhage, MI, sepsis) provoked initial ischemic change usually pass unnoticed by physicians, Proximal and thick ascending loop of henle
are located in outer medulla this area has normal blood supply even in normal condition so any ischemic problem will effect this area first. So If significant
tubular damage occur oliguric phase (maintenance stage) follows in 24 to 36 hrs, during this stage urine out put dec and metabolic changes of Acute renal
failure manifest. these changes are
1. Inc in EC fluid vol can cause et gain, edema, and pulmonary vascular congestion.
2. hyperkalemia (if hyperkalemia occur > 6.0mEq/L peak T wave appear on ECG can cause fatal ventricular arrhythmia)
3. Retention of H+ and anions (sulfate, phosphate , urate) with resultant Inc anion gap and metabolic acidosis. Inc BUN and creatinine.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
35
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
4. dec conc of Na+ and Ca++ and Inc Phosphate and Mg++.
5. Urine analysis reveal pathognomonic muddy brown cast, low urinary osmolarity (<350), high urine Na+ (>30).
In spite profound damage nephron in ATN have excellent regenerative capacity, recover follow with in 1 - 2 week if pt survive Oliguric phase. Dialysis help in
survival & recovery. (Recovery phase associated with dec urinary electrolytes where as hypokalemia is the most serious complication in recovery phase)
* Medullary sponge kidney is relatively common and benign congenital disorder caused by cystic dilatation of medullary collecting duct and do not
involve renal cortex. kidney stones are most common complication of medullary sponge kidney and eventually lead to CRF.
* Bullous pemphigoids is characterized by autoantibodies against hemidesmosomes along the basement of the dermal - epidermal junction.
* Painless hematuria of 2 - 3 days with Upper respiratory tract inf suggest IgA nephropathy (Berger dis). Dx made by Ig A deposit on mesengium of glomeruli
on immunoflorescense. Remember when IgA nephropathy is accompanied by extra renal symptoms such as abdominal pain, vomiting, intestinal bleeding,
intussusceptions and prupuric rash on extensor surface of arm leg buttocks the diagnosis is Henoch - schonlein purpura.
(Like IgA nephropathy Post streptococcal GN is also associated with respiratory tract inf but these 2 condition can be separated by timing of renal symptoms,
which is 2 - 3 days for IgA nephropathy and few weeks in PSGN where as C3 level is low in PSGN and normal in IgA nephropathy)
* Central retinal artery occlusion present with sudden, painless and permanent monocular blindness. Fundoscopic shows pale retina & cherry red macula.
* Diabetic retinopathy manifest by blurry vision, poor night vision, floaters, and dec peripheral vision. Fundoscopy reveal aneurysm, cotton wool exudate, dot
and blot hemorrhage and new retinal vessels.
* Ethylene glycol (found in antifreeze, coolants, hydraulic brake flluids) rapidly absorbs in GI & metabolized to glycolic acid which is toxic to renal tubules,
Oxalic acid which precipitate as Calcium oxalate in renal tubules. It Manifest as oliguria , anorexia & flank pain also cause high anion - gap metabolic
acidosis.
* Psoriasis is characterized by hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, rete ridge elongation, mitotic activity above the epidermal basal layer cell. and reduced or absent
stratum granulosum. neutrophil may form spongiotic clusters in superficial dermis and the parakeratotic stratum corneum (Munro microabcesses)
* Acanthosis is describes as Inc in thickness of stratum spinosum. (commonly associated with psoriasis)
* Dyskeratosis is abnormal premature keratinization of abnormal keratinocytes (can be associated with squamous cell carcinoma)
* Hyperkeratosis (retention of nuclei in stratum corneum due to incomplete keratinization) also associated with Actinic keratosis.
* Hypergranulosis (excessive granulation in stratum granulosum) is associated with Lichen planus.
* Spongiosus is the primary histologic finding in eczematous dermatitis such as contact dermatitis.
* Seborrheic keratosis is benign epidermal tumor appear as Tan to Brown round flat greasy coin like lesion (stuck on appearance).
* Mastocytosis is the benign, pruritic skin infiltration by the mast cell, scratching cause degranulation mast cell and urticaria, some time flushing and syncope.
* Lichen planus is characterized by 5 Ps Polygonal, planar, pruritic, purplish plaque & finely reticulated scale (Wickham's striae) on the plaque may be
present.
* Comedocarcinoma (Ductal carcinoma in situ) is characterized by pleomorphic, high grade cell with central necrosis.
* Sclerosing adenosis ( central acinar compression and distortion) is a common finding in Fibrocystic dis.
* Mammary duct actesia is characterized by ductal dilation, inspissated breast secretion and chronic granulomatous inflammation in periductal & interstitial
area.
* Phyllode tumor appear similar to fibroadenoma but Inc cytologic atypia and over growth architecture described as LEAF LIKE.
* Nephrotic $ is a hypercoagulable state, sudden onset of abdominal or flank pain hematuria and left side varicocele together suggest renal vein thrombosis,
a well known complication of nephrotic $ due to loss of anticoagulant factor specially Antithrombin III. (Left testicular vein empties into renal vein .big left
testis)
* Chronic NSAIDs use cause Chronic Interstitial nephritis, shows patchy inflammation, fibrosis, scarring of papillae, tubular atrophy. Manifest as Inc serum
creatinine, polyurea, nocturia, or Fanconi $ ( aminoaciduria, glycosuria, hypophosphatemia, hypouricemia) and mild proteinuria <1 gm/day.
* Minimal change Dis (nephrotic $) occur in children b/w age 2 - 8 yrs old. characterized by diffuse effacement of foot processes of podocytes, renal function
is normal rapid respond to corticosteroids.
* Membranous glomerulopathy is 2nd most common cause of Nephrotic $ in adults. it can occur secondary to underlying tumor, inf, or certain medication. It
is characterized by diffuse thickness of GBM with Spike and Dome appearance on methenamine silver stain on light microscopy and granular deposit on
immunoflorescense.
* PSGN shows Inc serum anti - streptolysin (ASO) titer, Inc anti - DNAse B titer, Dec serum C3 and total complement cryoglobin is present, C4 is normal..
* Age is an imp prognostic factor in PSGN. 95% of affected children and 60% of affected adults recover only.
* The most common cause of Achondroplasia is an activating mutation of Fibroblast growth factor receptor -3 at the epiphyseal growth plate which results in
short, thick tubular long (appendicular) bones and normal Axial (spine ) length.
* Short stature in growth hormone / IGF - 1 def is proportional that is both axial and long bones are proportionally short.
* Rickets (vit D def) -- defective mineralization of matrix lead to bow legs, bony prominence on costochondral junction (rachitic rosary), Indentation in the
lower ribs (Hutchinson grove), softening of the skull (cranio tabes), hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, hypotonia.
* With age stroma of lens undergo sclerosis leading to dec lens elasticity which with ciliary muscle weakness cause Presbyopia (inability of lens to focus on
near object). This is not pathologic process instead is age related change. In myopic (near sighted) individuals age related presbyopia may lead to
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
36
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
improvement in distant vision. imp
* Dystonia (idiopathic) is sustained involuntary muscle contraction which force certain part of the body into abnormal and painful posture. this movement
affect single (focal dystonia / spasmodic torticollis) or multiple muscle or even entire body
* White postmenopausal female has lower bone mass than black postmenopausal women may be due to reason of Inc fat stores in black women. Inc black
women may have higher estrogen than white women. Remember Estrogen loss accelerate the loss of bone mass mainly through dec osteoblastic activity
and Inc osteoclastic activity with resultant osteoporosis.
* Osteoporosis (porous bones) characterized by loss of total bone mass and resultant tabecular thinning and persistence of primary, unmineralized spongiosa
in the medullary canals.
* Subperiosteal resorption is characteristic of hyperparathyroidism.
* Vit D def results into excessive unmineralized osteoid and subsequent low mineral density.
* Two major types of bone in adult skeletal are Trabecular and Cortical. Trabecular (spongy or cancellous bone) is 15% of total bone and is metabolically
more active. vs. Cortical bone (long bones) contribute a mechanical support and is a site of muscle attachment. Osteoporosis is primarily involve trabecular
or spongy bone, vertebra are predominantly trabecular and Neck of femur is 50% trabeculi that is why osteoporosis involve typically these two area most.
* Crest $ (limited scleroderma) manifest with calcinosis, raynaud phenomenon, esophgeal dysmobility, sclerodactyly and talangiectasias, Anti- centromere Ab
are present in 40% pts. where as Anti topoisomerase I Ab are highly specific Systemic sclerosis.
* Hypercalcemia in sarcoidosis is caused by Inc formation of 1,25- dihydroxy Vit D by activated macrophages with resultant sec PTH.
* Atopic dermatitis (eczema) common inflammatory disorder of childhood. Presents with Pruritus and erythmatous weeping papule and plaque that occur due
to certain environmental factors. Atopic dermatitis is associated with atopic diseases such as Allergic rhinitis and Asthma.
* Gluten enteropathy is associated with dermatitis herpetiforformis that occur on extensor surface of the extremities. Frequently Tx gluten free diet.
* Myopathy of dermatomyositis manifest with the proximal muscle weakness, pt complains difficulty rising from sited position, climbing stairs, combing hairs
etc. The CK level is elevated and Anti Jo1 Ab are specific. Cutaneous manifestation of dermatomyositis included, Gottron papules (voilaceous with light
scales over bony prominences of hand), heliotrope rash (voilaceous & erythmatous of upper eye lid and periorbital skin), Both are specific for dis.
* Avascular necrosis of femoral head is associated with sickle cell dis, SLE, steroid therapy and alcoholism. Manifest as acute onset of hip pain without
swelling erythma and temperature change. Test of choice MRI.
* Fibromyalgia chronic disorder of women b/w age 20-50 yrs. It is characterized by wide spread musculoskeletal pain with stiffness (more in morning ad
exacerbate with excersize), paresthesia, poor sleep and emotional change. Tenderness in different points 11 - 18 predetermined points is required for Dx of
fibromyalgia (such as symmetrical tender painful muscle, joints, tendons, spin of scapula, fat bad of knee, lateral epicondyle etc)
* Shaken baby $ is combination of Subdural hematoma with bilateral retinal hemorrhage in infant. suspicion of child abuse should be reported.
* Low back pain and morning stiffness that improves with activity in young man suggest spondylitis, a chronic inflammatory reaction. The sarcoiliac and
epiphyseal joints are commonly effected. Ankylosing spondylitis is associated with HLA B27.
* Enthesitis (enthesopathies) is inflammation of the site of insertion of tendon into bone cause pain and swelling. Achilles tendon insertion, tibial tuberosity,
patella, trochanter and distal ulna are most commonly effected site.
* Pulmonary involvement occur if Enthesitis involve postvertebral or costosternal junction may lead to limited expansion of chest wall due to pain and
resultant hypoventilation or rarely fibrosis (1%).
* Anterior uveitis occur in 20-30% of pts with Ankylosing sppondylitis, presents pain, blurred vision, photophobia and conjunctival erythma. Most common
cardiovascular complication of Ankylosing spondylitis is Ascending aortitis with resultant dilatation of aortic ring and insufficiency.
* Hematogenous osteomyelitis (predominant in male children) metaphysis of long, without proper tx progress to suppurative osteomyelitis with necrotic bone
(sequestrum) serve as reservoir for infection and becomes covered by poorly constructed shell of the new bone (Involucrum). Tx Antibiotic and debridement
of the necrotic bone. Proximal tibia, distal femur, and proximal humerus are the common site involved. Most common agent is Staph Aureus and 2nd most
common is Strep pyogenes. In diabetic with chronic wound suspect pseudomonas.
* Hemochrmoatosis gene HLA-H is present on short arm of ch 6 and appear to effect iron absorption.
* Gene mutation of hemochromatosis prevent expression the HFE protein on the basolateral surface of intestinal cell where it normally bind with transferrin
receptor to facilitate transferrin- Iron complex endocytosis into the cell, any unregulated expression results into excessive amount of iron absorption. Most
imp complication of hemochromatosis are Liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Late complication is Bronze diabetes (triad of skin hyperpigmentation,
DM, pigment cirrhosis with hepatomegaly.
* Alcohol- Induced Hepatic Steatosis occur due to dec free fatty acid oxidation secondary to excess NADH production by two major alcohol metabolism
enzymes, Alcohol dehydrogenase and Aldehyde dehydrogenase.
* Extrahepatic biliary atresia occur due to obstruction of Extrahepatic bile duct, Pt develop persistent jaundice begins around 3rd and 4th week of life,
accompanied by dark urine, acholic stool and hyperbilirubinemia. Liver biopsy shows marked intrahepatic bile ductular proliferation, portal tract edema,
fibrosis and marked parenchymal cholestasis.
* Liver in Wilson dis may present as asymptomatic liver functional abnormalities to in fully developed case Macronadular chronic hepatitis / portal HTN.
Neuro symptoms are typical basal ganglia atrophy, movement disorder, ataxia, slurred speech, drooling, depression, paranoia, catatonia, etc. The Gold
standard for dx is liver biopsy shows >250 mcg/gram dry wt. Common DX test is serum ceruloplsamin <20mg/dL in conjunction with Kayser Fleischer rings
(slit light exam).
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
37
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Hepatitis B inf cause hepatic cytoplasm accumulation of HBsAg, shows granular eosinophilic (ground glass) appearance.
* Dubin Johnson $ (rare / benign) characterized by bilirubin glucronides excretion across canalicular mem with resultant conjugated hyperbilirubinemia that is
not associated with hemolysis. Grossly the liver is black, histologically epinephrine metabolites with in the lysosomes can be seen, Urinary corproporphyrin is
high.
* Estrogen induced cholesterol hypersecretion and Progestrone induced gallbladder hypomotilty are responsible for the Inc incidence of Cholelithiasis in
women who is pregnant or using oral contraceptives. (Hypomotility not responding to cholecystokinine is common in western world lead to cholelitiasis, Risk
factors are pregnancy, rapid wt loss, prolong use of total parentral nutrition or octereolide and high spinal injury)
* Non obstructing gallstones r black typically due to Intravascular hemolysis vs. Brown are typically sec to biliary inf In which injured hepatocyte and
bacteria release Glucuronidase, these enz hydrolyse bilirubin glucoronides & Inc the amount of unconjugated bilirubin with resultant soft, greasy,
cholesterol & mucin glycoprotein containing brown pigment stones formation which r radiolucent. Both types r associated with acute calculus cholecystitis.
* Acute Acalculus Cholecystitis is an acute inflammation of gallbladder in the absence of gall stones. commonly seen in very ill hospitalized person.
* Porcelain gallbladder is diagnosed on abdominal radiograph as a rim of Ca++ deposit that out line the gall bladder, (it is defined as bluish brittle calcium laden gall bladder). it is associated with gallbladder carcinoma (in 11-33% pt ). Cholecystetomy is recommended before it cause cancer.
* Primary Bile cirrhosis, a chronic liver dis characterized by autoimmune destruction of intrahepatic bile duct and cholestasis commonly in middle age women.
It manifest as pruritus, fatigue, hepatosplenomegaly, Xanthomatous lesion in eyelids or skin and tendon. As dis progresses jaundice, steatorrhea, portal HTN
and osteopenia develop. Lab shows, AP and cholesterol and IgM, diagnosis is confirmed by Anti mitochondrial Ab. Other autoimmune dis may also
present.
Histologic finding in primary bile cirrhosis include granulomatous inflammation of interlobular bile duct with macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells and
eosinophill infiltration.
* Viral hepatitis cause diffuse swelling or ballooning degeneration with resultant lobular architect disruption and necrosis (bridging necrosis) of hepatocytes. In
response to hepatocellular injury and death mononuclear inflammation develop in sinusoid and oral tracts.
* Halothane toxicity present with fever, nausea, myalgia, arthraglia and rash, tender hepatomegaly and jaundice may observed. Lab shows Inc serum
aminotransferases and prolong PT. leukocytosis and eosinphilia is common.
* HBV encodes for HBx protein, a subs that disrupts growth control of infected cells by activating multiple growth- promoting genes. HBx protein also binds
with P53 apparently impeding its growth suppressing activities.
* 1 AT def eventually cause panacinar emphysema (75-85% pts). Smokers with this condition will develop emphysema with median age of 40 yrs where as
non smokers with this condition will develop emphysema with median age of 53 yrs.
* Stable Chronic hepatitis C will slowly progress to cirrhosis.
* The most common out come of person infected from acute HBV with mild and subclinical symptoms is complete recovery (>95%) ?
* Regular monitoring of feto protein is recommended & is useful in evaluation of cirrhotic pts who are at Inc risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
* Hypertrophic Cardiomypathy (HCM) is characterized by asymmetric ventricular septal hypertrophy and variable dynamic left ventricular out flow which
produce systolic ejection murmur. Dec LV end diastolic vol Inc the obstruction which enhance of murmur of HCM, such as on standing suddenly or valsalva
maneuver will dec the venous return this accentuate the murmur of HCM.
* Squatting, sitting, or lying supine increases the venous return thus Inc right and left ventricular preload.
* Sustained hand griping Inc the systemic vascular resistance and thus reduce the gradient across the LV outflow tract.
* CEA is associated with Colorectal cancer, Since CEA is also elevated in pts with benign dis thats why this marker is used as a aid in staging, planning
surgical tx and determining prognosis. CEA is not recommended as a screening test for colorectal cancer.
* Reye $ (due to salisylates use in febrile Children) -- cause hepatic failure and encephalopathy. Histologic findings are Microvesicular steatosis of
hepatocytes (without inflammation) and cerebral edema.
* Cholescintigraphy (HIDA scan) uses IV radiolabled agent take by hepatocytes and excreted into bile, if the cystic duct is patent radiolabled agent will enter
the gallbladder and organ will visualized. or if the duct is not patent organ will not be visualized.
* High level of Afalatoxin is associated with G:G T:A transversion in codon 249 of the P53 gene, this mutation thought to greatly Inc the risk of developing
hepatocelular carcinoma.
* Estrogen influence facilitates the biosynthesis cholesterol by increasing HMG- CoA reductase activity. Small amount of cholesterol in the bile become
solublized by detergent like bile salts and phosphatidylcholine. This solubilization of cholesterol is inhibited by Clofibrates (7 - hydroxylase) thus results in
excess cholesterol secretion in bile. Cholesterol and mixed stone together comprise 80% of all gallstones in western population.
* Staph Aureus cause hepatic abscess through hematogenous seeding of the liver. where as Enteric bacteria cause hepatic abscess by ascending the biliary
tract or by direct invasion. (in developing countries the incidence of hepatic abscess is secondary to parasitic infection, commonly ameba or echinococcus)
* Prolong course of total parenteral nutrition is complicated by gallstone formation, incidence is as high as 44% in these pts. Exogenous cholecystokinin
administration will typically prevent gallstone formation in pts on total parenteral nutrition.
* Follicular lymphoma is B cell origin & present with painless "waxing & waning" lymphadenopathy. Characteristic t14:18 & over expressed bcl-2
oncogene.
* Ab against islet cell, HLA class II gene makeup HLA DQ, HLA DR), leukocytes infiltration (insulitis) r seen in type I DM. vs. Amyloid deposition is
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
38
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
characteristic of type II DM.
* P53 is tumor suppressor gene that control cell division and apoptosis.
* hCG has structural similarity to TSH. Inver high conc which may observe in some testicular tumor it can stimulate TSH and with resultant hyperthyroidism.
* hCG also has structural similarities with TSH, FSH, and LH.
* Hereditary breast cancer is associated with mutation of BRCA- 1 and BRCA- 2, these are tumor suppressor genes that function in gene repair and
regulation of cell cycle. Mutation of gene is associated with Inc risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
* Metalloproteases are Zn - containing enz that degrade extracellular matrix, they participate in normal tissue modeling and in tumor invasion through the
basement mem and connective tissue.
* MEN 1 ---------- Parathyroid tumor (hypercalcemia) + Pancreatic tumor (Gastrin) + Pituitary adenoma (PL. ACTH)
MEN 2a -------- Parathyroid tumor (hypercalcemia) + Medullary Carcinoma of Thyroid (calcitonin) + Pheochromocytoma
MEN 2b --- Marfanoid Habitus / Mucosal neuroma + Medullary Carcinoma of Thyroid (calcitonin) + Pheochromocytoma
* Most common cause of hypothyroidism in Iodine sufficient area is Hashimoto thyroiditis. Manifest as symptoms of hypothyroidism with diffuse enlarged
gland and Anti thyroid peroxidase Ab in serum. Mononuclear, lymphocyte and plasma cell infiltration with the formation of germinal center is very
characteristic.
* Reidal thyroiditis is characterized by extensive fibrosis of thyroid gland.
* Mixed cellular infiltration (neutrophil, lymphocytes, histiocytes) with occasional multinucleated giant cells is seen in Subacute de Quervain thyroiditis (may
be due too virus). Subacute de Quervain thyroiditis present mixed features first with thyrotoxicosis, Inc ESR, and markedly reduced radioactive iodine uptake
than later hypothyroid phase for few months. most pt respond to NSAIDs for pain and inflammation and recover fully. Remember subacute de Quervain
thyroiditis release stored thyroid hormones (do not Inc synthesis of TH or do not express autoantibodies) secondary to thyroid inflammation that is why Iodine
uptake is dec.
* Branching papillary structure and concentric calcification (psammoma bodies) are typical of papillary thyroid cancer. Another characteristic feature are
ground glass nucleus with intra nuclear grooving.
* Amenorrhea in pts with anorexia nervosa is due to loss of pulsatile secretion of GnRH hypothalamus (no in pituitary or ovary). low GnRH level results in sec
dec in FSH, LH, and estrogen progesterone. Low estrogen over the long term can result in osteoporosis. Advise pt to gain wt (fat Inc her GnRH) so her
menses come back. Other approach is administration of pulsatile GnRH which will normalized the estrogen.
* Diabetic mellitus + necrolytic erythmia (elevated erythmatous rash in groin area) + anemia comprise the typical picture of GLUCAGONOMA.
* Endothelium is identified with special stain for CD34 and von Willibrand factor.
* Most common CNS tumor of childhood is Pilocystic astrocytoma (1st common) and Medulloblastoma (2nd common). Pilocystic astrocytoma has both
cystic and solid component where as Medulloblastoma is always solid.
* Over night dexamethasome test used in work up with Cushing $. In normal person this test cause ACTH and cortisol suppression where as in endogenous
Cushing $ pt will not show the suppression of ACTH and cortisol. Early morning cortisol is moderately depressed if test shows elevated baseline ACTH
along with moderately low cortisol suggest pituitary adenoma on other hand elevated baseline ACTH along with elevated cortisol than ectopic production of
hormone is suspected; more over if there is low baseline ACTH with little / no cortisol suppression over night than Cushing $ is of adrenal origin.
* Type I DM is due to autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cell, involve both genetic and environmental factor such as viral infection, environmental
toxins.
* Hyperaldosteronism (Conn $) characterized by HTN, hyporeninemia, hypernatremia, hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis. Hypernatremia is rare because of
the phenomenon called "aldosterone escape" in which Inc NaCl absorption lead to ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide) which cause diuresis and Na+ loss, for this
reason pt with aldosteronism do not manifest edema.
* Painless gross hematuria suggest urinary bladder carcinoma (transitional cell carcinoma), tumor penetration into bladder wall is major determinant of
prognostic factor.
* Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) characterized by t 9 22 (Philadelphia ch22), bcr - abl proto oncogene product called bcr - abl fusion protein has
tyrosine kinase activity that can be inhibited by IMATINIB. leukocyte Alkaline phosphatase score. Blast crisis can occur and carry worse prognosis.`
* IMATINIB is tyrosine kinase inhibitor sp for bcr - abl fusion protein. it competitively binds ATB binding sites on the abl portion thus dec its activity.
* Back pain not relieved by rest or position change is typical of neoplastic bone dis. Bone metastasis in prostate cancer is blastic (sclerotic) and detect by
radionuclide bone scanning.
* Small cell carcinoma show evidence of neuroendocrine differentiation (can be stain for neuroendocrine markers such as neuron specific enolase,
chromagranin, synaptophysin). Some small cell carcinoma express neurofilaments, Neurosecretory granules, and hormones.
* Vimentin is found in the cells of mesenchymal origin used in the diagnosis of sarcomas.
* Hydrochlorothiazide cause hypercalcemia by Inc the reabsorption of filtered Ca++, Inc serum Ca++ may suppress PTH. (good in renal stone formers)
* Oral contraceptives reduced the risk of non hereditary ovarian and endometrial cancer. multiparity and breast feeding also dec the risk of ovarian cancer.
* Exophthalmos and Pretibial Myxedema (non pitting edema with thickening of skin) are specific of Grave dis.
* MI is the most common cause of death in pt with DM.
* Administration of ADH distinguishes central DI from nephrogenic Diabetic insipidus.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
39
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Damage to posterior pituitary gland cause transient polyurea. vs. damage to hypothalamic nuclei or pituitary stalk can cause Diabetes Insipidus.
* Bromodeoxyuridine is thymidine analog, since nucleotide uptake occur in S phase , large no of tumor cell will uptake those nucleotide (bromodeoxyuridine)
in high quantity. this high uptake suggest high proliferation and poor prognosis.
* Li - Fraumeni $ (AD) associated with variety of tumor carcinomas and sarcomas due to mutation in P53 gene.
* Schilling test help to differentiate b/w dietary def of vit B12 or malabsorption $. Low absorption of cobalamine not corrected by Intrinsic factor is indicative
of mal absorption $ such as ileal dis, pancreatic insufficiency and bacterial over growth.
* The most helping RBC index in making the DX of hereditary spherocytosis is MCHC (mean corpuscular hemoglobin conc). The elevated MCHC indicates
mem loss and red cell dehydration. Dx is best confirmed by osmotic fragility test. Pt with hereditary spherocytosis are at Inc risk of aplastic anemia (due to
parvovirus B19) and pigmented gall stone due to Inc hemolysis.
* Bleeding is common in uremia due to qualitative pletelet disorder. The pletelet count, PT and PTT are normal, signify that the defect is in pletelet function
which improves after dialysis. (no of dializable pletelet inhibitory factors have been shown to inhibit pletelet function)
* Von willibrand factor def cause impairment of pletelet function --- prolong bleeding time, prolong PTT and dec pletelet aggregation in response to
Ristocetin.
* Ristocetin aggregation test is used to measure vWF - dependant pletelet aggregation. Ristocetin activates GP Ib-IX receptors and make them available for
vWF binding so when vWF is dec poor pletelet aggregation results.
* Warfarin - induced skin necrosis (due to coagulation) occur in pt with protein C and S def. Protein C and S is natural anticoagulant thats why rapid drop in
factor VII and protein C results in transient procoagulation / anticoagulation imbalance which cause relative hypercogulable state with thrombotic occlusion of
small of microvasculature and skin necrosis. tx is discontinuous warfarin and administer fresh frozen plasma to replenish protein C.
* Hemorrhagic abnormalities are also common in SLE because of anti RBC, pletelet and leukocytes Ab. It is characterized by spherocytosis, +ve direct
coomb test and extra vascular hemolysis. Hemolysis in SLE is type II hypersensitivity.
* Factor VIII is synthesized by liver and stored in endothelial cell. Desmopressin acetate (synthetic vasopressin) releases factor VIII from endothelium and
used in the tx f mild to moderate hemophilia A is X linked recessive disorder. (remember Hemophilia B is factor IX def)
* Dec level of factor VIII and IX lead to failure to convert prothrombin into thrombin. (addition of thrombin in the blood of pt with hemophilia will result in clot).
* Asplenia (of any cause) pt r at risk of inf particularly encapsulated organism, eg. hemophillus influenza, sterp penumoniae. Recommend vaccine to avoid
inf.
* Salmonella is the most common cause of osteomyelitis in children with sickle cell dis, Staph aureus is 2nd most common in this group.
* Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria is neither paroxysmal nor nocturnal it is characterized by classic triad of hemolytic anemia + hypercoagulable state +
pancytopenia. It is stem cell disorder, the def of CD55 and CD59 protein (this protein cause inactivation of complement) is the DX of paroxysmal nocturnal
hemoglobinuria. (Dark color urine in morning).
* G6PD has X- linked recessive inheritance where a hereditary spherocytosis follow autosomal dominant pattern.
* Burr cells are RBC with short evenly spaced projections, seen in Uremia, pyruvate kinase def, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia.
* Schictocytes (helmet cell) are fragmented RBCs associated with micro antipoetic hemolytic anemia (DIC, HUS, TTP) and due to prosthetic cardiac valves.
This hemolytic anemia is characterized by dec serum hepatoglobin and Inc LDH and Bilirubin.
* Bite cells r typical of oxidant induced damage as in G6PD def. Bite cell occur when splenic monocytes macrophage system removes Heinz bodies from
RBC.
* Target cells have bulls eye morphology with central conc of hemoglobin associated with obstructive liver dis, thalasemia, Iron def anemia, asplenia.
* Acanthocytes are the cells with irregularly spaced surface projections with vary in length and width associated with abetalipoproteinemia. Spur cells are
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
40
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
extreme form of acanthocytosis.
* Tear drop cells typically seen in myelofibrosis or in metastatic cancer because RBCs must squeeze through these fibrous strand and appear as tear drop.
* Inherited causes of hypercoagubility should be consider in young or older than 50 yrs pt with thrombosis and no obvious explanation. Remember factor V
Leiden mutation cause factor Va resistance to inactivation by activated protein C, it may account for approx 20% of cases of atypical venous thrombosis.
* Protein C has anti coagulant effect, remember cancer induced thrombotic event is not resistant to protein C
* Retained dead fetus in uterus is associated with DIC and progressive hypofibrinogenemia. monitoring fibrinogen and pletelet count is helpful in early
identification of DIC. DIC is characterized by Microangiopathisc hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, Prolong PTT, prolong PT, low fibrin, elevated fibrin
split product (D - dimers) and low factor V and VIII.
* Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) and Hemolytic uremic $ (HUS) are characterized by fever, neurologic signs, acute renal failure,
thrombocytopenia and microangiopathic hemolytic anemia. TTP is usually seen in adults with predominant neurologic signs where as HUS is seen in
childrens with predominant renal failure and mild CNS signs after infection. Since TTP and HUS involve isolated activation of pletelet (unlike DIC) PT. PTT,
fibrinogen, factor V and VII are normal and pt do not bleed.
* Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) only shows thrombocytopenia (due to Ab complex) and fever is absent. Lab shows normal PT, PTT. In ITP
pletelet are so sticky that bleeding is uncommon unless pletelet count is < 10,000/cmm.
* Pt with sickle cell trait are resistant to malaria because
* Sickle cell trait pt has normal peripheral smear, indices, reticulocytes count & MCHC values. However the blood will sickle when sodium metabisulfite is
added
* Pt who r heterozygous for the sickle cell trait (Hb AS) have some Hemoglobin composed of HbS (35 -40%), they r generally protected from sickle cell crisis,
aplastic crisis, and sequestration crisis due to > 50% normal hemoglobin. they are usually asymptomatic but they may develop hematuria and has limited
ability concentrate urine. vs.
Homogygous for sickle cell dis Hb SS (>80%) may have severe dis with all above mentioned crisis and autosplenectomy.
* Glycogen appear pink purple with periodic acid Schiff reaction.
* Lipofuscin , insoluble yellow pigment composed of cholesterol and phospholipids complexed with protein, associated with aging or "wear and tear".
remember excessive hemosidrin accumulation appear as golden yellow pigment.
* Most cases of HUS occur after Enterohemorrhagic E coli (O157:H7 type) producing shiga like toxin with resultant bloody diarrhea. Under ground beef is the
most common cause of HUS.
* Fever, rash , oliguria 1 - 3 week after antibiotic tx highly suggestive of Drug induced Acute interstitial nephritis. Common offenders are lactam antibiotics
sulfonamide, NSAIDs, Rifampin, & Diuretic. Peripheral eosinophilia and eosinophiluria is important clue, symptoms resolves completely after cessation of
drug.
* Uric acid stones are the only type of renal stones that are radiolucent and can be detected on ultrasound or CT scan, associated with gout,
myeloproliferative disorder, high protein diet, low fluid intake, and with certain inborn error. All other stones are radiopaque and can be seen on plain X ray
film.
* Partial Mole have triploid Karyotype, pt present with vaginal bleeding and lower abdominal pain. Unlike complete mole partial mole are associated with low
risk of invasive trophoblastic dis.
* Papillary necrosis occur in Sickle cell dis, DM, analgesic nephropathy, obstructive pyelonephritis. Colicky flank pain, bloody urine , and tissue fragment is
characteristic. Pt with papillary necrosis due to ureter obstruction may shows the same signs where as pt with chronic papillary necrosis may remain
asymptomatic until gross hematuria or tissue fragment in urine occur.
* Ischemic tubular necrosis present with oliguria and muddy brown granular cast, common in very ill hospitalized pt.
* Presence of ectopic endometrium out side the uterus is called Endometriosis. Ovaries are common site of implantation, the ectopic tissue respond to
hormonal variation and bleed during menses, with time blood undergo hemolysis and induce inflammatory response with resultant distortion of organ and
adhesion these collection of whole process called endometriomas (chocolate cyst). Nodularity of the uretrolateral ligament and fixed retroversion of the uterus
are commonly found on vaginal examination. pt usually complains of dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia (due to retroversion implant on the ureterosacral ligament),
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
41
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
painful defecation due to pelvic adhesion (dyschezia). Ectopic tissue produce prostaglandin which interfere with ovulation and tubal function. Inc risk of
infertility.
* Endometrial hyperplasia occur due to influence of the Inc estrogen on endometrium cause major vaginal bleeding. Inc risk of uterine adenocarcinoma.
* Polycystic ovarian $ characterized by multiple small follicular cyst in the ovaries with cortical fibrosis, hirsutism, oligomennorrhea and infertility.
* Tertiary syphilis characterized by, tabe dorsalis (neurologic sequlae), subacute meningioencephlitis, aortic aneurysm, gummas (white gray granulomatous
rubbery lesion that may ulcerate occur on subcutaneous tissue, bone liver and other organ).
* Positive VDRL of CSF is DX of neurosyphilis.
* Condylomata lata is wart like genital lesion in secondary syphilis.
* Granuloma inguinale is STD caused by Calymmatobacterium granulomatis, it is characterized by inguinal swelling, ulcer, abscess and fistulas. The Gram
stain of the lesion reveal Rod shaped intracytoplasmic inclusion called Donovan bodies.
* Condylomata acuminata are anogenital wart caused by HPV 6 and 11 which has low oncogenic potential.
* Cyanotic toe and renal failure in elderly who received invasive vascular procedure (angiography, agnioplasty, aortic surgery) is characteristic of
atheroembolic dis of the renal artery. (due to procedure cholesterol debris dislodge and trap into any site of the body in small vessels and cause infarct). The
kidney failure will develop few day to week after procedure many never recover their full renal function.
* Hyperplastic arteriolar changes found in hypertensive nephropathy
* Tubular obstruction after chemotherapy suggest urate crystals from tumor lysis $. It mat lead to Acute renal failure.
* Progesterone is required for endometrial stromal cell to grow and differentiate into decidual cells that accommodate pregnancy, the withdrawal of
progesterone (or antiprogestin RU-486 antiabortificant administration) will cause apoptosis in the endometrial cell.
* Gestational Choriocarcinoma is aggressive malignant tumor that arise from TROPHOBLAST, (histologically composed of abnormal proliferation of
cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast) characterized by yellow soft bulky intrauterine mass with area of necrosis and hemorrhage. Most commonly
preceded by an evacuated hydatidiform mole. However it can also occur after abortion, normal or ectopic pregnancy. Lung is the most common site of
metastasis. (remember no villi are present).
* Renal cell carcinoma composed of large cells with clear cytoplasm and eccentric nuclei. Classic Triad is hematuria, flank pain, and palpable mass.
paraneoplastic $ are common Lung is the most common site of metastasis.
* Most common site of ectopic pregnancy is the AMPULLA OF FALLOPIAN TUBE. Main risk factor of ectopic pregnancy is Pelvic inflammatory dis. Major
complication of Ectopic pregnancy is tubal rupture with hemorrhage, vaginal bleeding, and abdominal pain which may further complicate by low BP,
tachycardia, oliguria. The Hx of amenorrhea is important in making the Dx. Vaginal examination shows slightly enlarge soft uterus.
* Multiple Sex partner is imp significant risk for the development of squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix due to Inc risk of transmission of carcinogenic
strains of HPV 16,18,31,33. Other risks are cigarette smoking, lower socioeconomic group, early coitarche.
* Family history of cancer is imp Risk factor for the development of breast and ovarian malignancy.
* Nulliparity, early menarche, obesity increases the risk of Endometrial cancer. these factor are associated with Inc estrogen stimulation of endometrium.
* Kartagener $ (ARD) cause by mutation in Microtubule - Associated Protein DYNEIN in 50% of pts (variable penetrance). It is characterized by male
infertility, situs - inversus and bronchiactasis.
* Normal vesicoureteral junction does not allow retrograde flow of urine. any anatomical abnormality in this area or Inc bladder pressure results into
vesicoureteral reflux which further lead to passage of pathogens to the kidney and cause pyelonephritis. remember without vesicoureteral reflux ascent of
pathogens to kidney is impossible.
* Calcium oxalate and Calcium phosphate are the most common type of kidney stones (75 - 8%). 50% of calcium nephrolithiasis is associated with
idiopathic hypercalciurea with normal plasma Ca++ level.
* Benign prostate hyperplasia can cause reflux nephropathy and eventually hydronephrosis, renal interstitial atrophy and scarring. Prolong obstruction can
lead to permanent damage and chronic renal failure early detection and prompt tx is imp.
* Polycystic ovarian $ is characterized by obesity hirsutism and oligomenorrhea. PCO$ occur due to abnormality of the hypothalamic - pituitary - ovarian
system. Androgen (testosterone & androstenedione) and LH level are elevated where as FSH is normal. An Inc LH/FSH ratio (>3) is characteristic. Tendency
toward insulin resistance and lipid profile abnormalities. Pt with PCOS are at Inc risk of developing endometrial Adenocarcinoma.
PCO$ is associated with following signs and symptoms.
1. Menstrual irregularity (most often oligomenorrhea) and infertility (due to anovulation)
2. Hormonal dysregulation (elevated testosterone, androstenedione and LH , dec progesterone, acyclic estrogen production)
3. Inc insulin resistance lead to obesity (high risk of developing type II DM)
4. Hirsutism and acne (due to Inc androgen --- testosterone and andostenedione)
5. Lipid profile abnormality (Inc risk of atherosclerosis and coronary artery dis)
6. Bilateral ovarian enlargement with multiple cystic follicles.
* Cystinuria results from defect in renal proximal tubule which results in dec resorption of AA cystine. Clinical manifestations are cystine Stone formation from
young age, urine analysis shows pathognomonic HEXAGONAL cystine CRYSTALS. Tx of cystinuria involves hydration and alkalinization of urine. Sodium
Cyanide - Nitroprusside test which detect cystine sulfahydryl group is diagnostic. (when cyanide added to the urine cystine converts into cysteine,
nitroprusside than bind cysteine and cause purple discoloration).
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
42
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Fibroadenoma is the most common tumor of the breast typically arise in young adult women, it is characterized by well demarcated spherical nodules of
different size uni or bilaterally, often consist of myxoid stroma and some time compresses epithelium - lined glandular and cystic spaces.. Fibroadnoma Inc in
size during luteal phase of menstrual cycle or during lactation.
* Serial measurements of - hCG should be performed following evacuation of hydatidiform mole. persistent elevated or rising level indicates development
of invasive mole or Choriocarcinoma.
* Fracture in post menopausal women follow minimal trauma is highly suggestive of Osteoporosis. In primary Osteoporosis serum Ca++ and PTH level are
typically in normal range. There are two type of bones in body, the cortical or compact bone makes up the shaft of the bone and outer envelop of all bones;
Postmenopausal osteoporosis typically involves CANCELLOUS BONE which is predominant present in vertebral column, distal radius, hip and neck of the
femur. Osteoporosis can be Dx by Dual X Ray Obsorptiometry. (2.5 standard deviation below the mean)
* Hepatic processing of bilirubin occur in 3 key steps. 1. Carrier mediated uptake of bilirubin at sinusoidal mem. 2. Conjugation of bilirubin with glucoronic
acid by uridine diphosphate glucronyltransferase (UGT) in endoplasmic reticulum. 3. biliary excretion of the water soluble, nontoxic bilirubin glucronides.
Disruption of this process can be fatal as seen in Crigler Najjar $.
* Bacteria reduces bilirubin into urobilinogen in colon, small fraction of these urobilinogen return to the liver through the enterohepatic circulation which later
either re enter the GI tract or be excreted through urine. The urobilinogen that remains in the colon are excreted in the feces and contributes its dark
coloration.
* Crigler Najjar $ type I (ARD) is disorder of bilirubin metabolism caused by genetic lack of UGT enz needed to catalyze bile glucuronidation. when bilirubin
when not correctly enzymatically processed by liver cause unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia , indirect bilirubin level is typically 20 - 25 mg/dL in these infants.
* Conjugated bilirubin is water soluble and loosely bound with albumin and excreted in urine in contrast unconjugated bilirubin tightly bound with albumin and
is highly insoluble in water and cant be filtered by glomeruli and there fore not be able to excreted in urine which further results into deposition of
unconjugated bilirubin in various tissue including brain.
* Dubin Johnson $ (ARD) characterized by absence of biliary transport protein MRP2 (multi drug resistance protein 2) which is used in hepatocellular
excretion of bilirubin glucuronides into bile canaliculi. This makes liver look dark in appearance. DJS pt are asymptomatic and suffer no serious adverse
effect.
* Rotor $ is a rare (ARD) disorder characterized by asymptomatic conjugated hyperbilirubinemia that results from numerous defect in uptake and excretion of
bilirubin pigments although pt is jaundiced but enjoys normal life expectancies.
* A moderately elevated alkaline phosphatase of unclear etiology should be followed up with - glutamyl transpeptidase.
* Sun light convert 7 - dehydrocholesterol cholecalciferol (Vit D3), than 25 - hydroxylation occur in liver and the kidney by enzyme 1 - hydroxylase
which is the final step in active 1,25 - dihydroxy vit D synthesis.
* 25 - hydroxy Vit D is metabolically inactive and is converted to the active form by 1 - hydroxylase . Circulating PTH also augment the conversion of 25 hydroxy Vit D to 1,25 - dihydroxy vit D. In case of 1,25 - dihydroxy vit D excess the kidney have an enz 24 - hydroxylase which convert 25 - hydroxy vit D into
biologically inactive 24,25 - dihydro vit D.
* In cirrhotic pt gynecomastia arise from hyperestrinism secondary to livers inability to metabolize circulating estrogen. Other manifestation of hyperestrinism
in cirrhotic pt is palmar erythma, spider angioma, testicular atrophy in male and dec body hairs.
* First step in intimal hyperplasia is vascular Endothelial cell injury, Injured endothelium may secret factors (PDGF, FGF, endothelin 1) that promote SMC
migration and proliferation (how ever smooth muscle cell are directly responsible for intimal thickening after intimal injury), than migration of the smooth
muscle cells (SMC) across the internal elastic lamina and into the intima followed by SMC proliferation and collagen, elastin and proteoglycan synthesis to
produce a neointima which results in intimal hyperplasia.
* Ammonia initially enters circulation through GIT after having been created during enterocyte catabolism of glutamine and bacterial catabolism of dietary
protein in colon. Ammonia than enter the liver through vein for detoxification of urea. In liver damage detoxification ability of liver is compromised and
ammonia accumulates in blood with resultant hepatic encephalopathy . factors that precipitate ammonia balance are hypovolemia, GI bleed, hypokalemia,
metabolic alkalosis, hypoxia, sedative usage, hypoglycemia and inf.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
43
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Cholestasis can be arise secondary to hepatocellular dysfunction or biliary obstruction (whether intrahepatic or Extrahepatic). Both obstructive or
nonobstructive cholestasis are characterized by the deposition of bile pigment with in hepatic parenchyma and presence of green - brown plug in dilated bile
canaliculi. This results in intestinal malabsorption, nutritional def of fat soluble vit etc.
* Risk factor of Osteoporosis are smoking, menopause, corticosteroid therapy, physical inactivity, Caucasian race, low total body wt and alcohol use.
* Statistically Black female have higher bone density than Caucasian female.
* Plaque instability depends significantly on mechanical strength of the fibrous cap. Inflammatory macrophages may reduce plaque stability by secreting
metalloproteinases which degrade collagen.
* Atherosclerosis initiated by repetitive endothelial injury which lead to chronic inflammatory state in the under lying intima large elastic arteries as well as
Intima of large and medium size muscular arteries.
* Renal artery atherosclerosis and stenosis cause renovascular HTN due to excessive renin - angiotensin - aldosterone system activity, Any hypervolemia
and Inc TPR would tend to elevate both SBP and DBP.
* After age 50 the pattern of isolated systolic HTN become quite common due to age related dec in compliance of the aorta and its proximal major branches
(probably due to vessel wall structure and function including atherosclerotic changes related stiffening). SBP >160 mmHg and DBP < 90 mmHg is found in
20 - 30% of all people 80 yrs & older.
* Hypercalcemia is associated with Squamous cell cancer and several other tumor due to over production of Parathyroid hormone - related peptide and is
term the Humoral Hypercalcemia of Malignancy.
* The primary abnormality in Paget dis of bone is excessive osteoclast bone resorption (might be due to childhood inf of osteoclast by Paramyxovirus).
Osteoclast in the paget dis are typically very large and contain upto 100 nuclei (normal is 2-4 nuclei), the bone turn over is markedly high and lead to chaotic
bone formation. they originate form mononuclear phagocytic cell lineage. The 2 most important factors for osteoclastic differentiation are produced by
osteoblast these are M - CSF (monocyte colony stimulating factor) and RANK - L (receptor activated nuclear factor kappa beta ligand). Osteoclast precursor
& mature osteoclast posses receptor for M- CSF, and RANK - L. (Osteoclast are positive for Tartrate - resistant acid phosphatase)
* Paget disease of bone is characterized by multiple bone lesion specially long bone & skull in old age group. (the Paget dis of breast is unrelated to bone
dis)
* The chest pain of pericardiitis is sharp & pleuritic may exacerbate by swallowing and relieved by leaning forward. Early onset of pericarditis typically occur 2
- 4 days after transmural MI. It represents the inflammatory reaction to cardiac muscle necrosis that occur in visceral & parietal pericardium. VS. Dressler $
is late onset of pericarditis typically occur from 1 week to few months after MI. (thought to be from autoimmune polyserositis). Tx for both is aspirin or
glucocorticoids.
* Pain of MI is constant, substernal and crushing in nature.
* Jerval and Lange - Nielson $ (ARD) and Romano - ward $ are the most common congenital long - QT syndrome.
* Jarvel & Lange - Nielson $ accompanied with by congenital neurosensory deafness. Pt present with unprovoked syncopal episodes (high risk of sudden
cardiac death due to torsades de pointes).
* Jervell & Lange - Nielson $ and Romano - Ward $ are thought to result form mutation in K+ channel protein that contribute the delayed rectifier current (IK)
of the cardiac action potential.
* Verrucous Endocarditis (Libman - Sack Endocarditis) occur in 25 % of SLE pts. Its is characterized by the small cardiac valvular vegetation on either side of
valve resulting in fibrotic valve thickening and deformity. SLE can cause acute coronary $ at young age.
* In SLE thrombosis occur due to hypercoagulable anti phospholipid Ab.
* Chrug - Strauss $ is polyarteritis nodosa - associated condition along with lung vasculitis, severe asthma, and eosinophilia. The vascular lesion are
necrotizing granulomas which can cause coronary arteritis with out valvular lesion (valves are avascular that why r not effected)
* Foramen Ovale is remain patent in 20 - 30 % normal adults but it is functionally closed because left atrial P is greater than right atrial P. However any
condition that raise the right atrial P above the left atrial P can produce right to left shunt, hypoxia paradoxical embolization may results. Patent Foramen
Ovale should be suspected in any person who develop venous thrombosis and later with stroke.
* Tuberculous caseous pericarditis (b/w visceral & parietal pericardium) is comm casuse of Chronic Constrictive pericarditis (fibrous tissue encase the heart).
Pt with Chronic Constrictive Pericarditis presents with Kussmaul' s sign and elevated jugular venous P on inspiration due to Inc venous return and restriction
of right hart filling. (On inspiration jugular vein collapse in normal person)
* A holosystolic murmur at apex is of mitral regurgitation vs. Holosystolic murmur at left sternal border is of Ventricular septal defect.
* A loud P2 is hard in pulmonary HTN.
* S3 heart sound is due to rapid diastolic ventricular filling with large vol of blood (ventricle vol overload), or due to reduced ventricular compliance (reduced
diastolic function). In contrast Chronic Constrictive pericarditis reduced ventricular compliance via external force and tend to cause pericardial knock heard
early in diastole (shortly after S2). S3 ventricular gallop - - - - - - - ?
* Mid systolic click is classically heard in pt with mitral valve prolapse.
* Systolic ejection murmur occur in aortic stenosis which radiates to the carotids.
* Congenital disorder and Cardiac associations.
1. Down $ ---- Endocardial cushion defect (Ostium primum ASD, regurgitant AV valves)
2. DiGeorge $ ---- Tetralogy of fallot and aortic arch anomaly.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
44
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
3. Friedreich's ataxia ---- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
4. Marfan's $ ---- Cysticmedial necrosis of aorta.
5. Tuberous sclerosis ---- valvular obstruction due to cardiac Rhabdomyomas.
6. Turner $ ---- Coarctation of aorta.
* Janeway lesion are small, erythmatous possibly hemorrhagic lesion that may appear on the sole of the feet and palm of hands in pt with bacterial
endocarditis. These lesions are caused by septic micro emboli from intracardial vegetation to cutaneous blood vessels)
* Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is most common case of ventricular fib in individual younger than 30 yrs and is the most common cause of sudden cardiac
death in younger athlete. (past medical Hx is imp)
* Mid systolic click followed by systolic murmur is generally produced by floppy mitral valve (mitral valve prolapse) with regurgitation. Tricuspid valve click
occur due to defective valve leaflet at tricuspid area.
* Squatting Inc venous return (preload) and also raises peripheral vascular resistance thus augment afterload.
* Mitral valve prolapse is thought to caused by defect in mitral valve connective tissue protein which predisposes to myxomatous degeneration and stretching
of the valve leaflet by chronic hemodynamic stress.
* Acute transmural MI cause chest pain not relieved by rest or nitroglycerine with diaphoresis, dyspnea, nausea, light headedness and palpitation. Peaked T
wave are the first EKG sign (reflect localized hyperkalemia) and ST- segment elevation follows with in minutes to hrs; and Q wave appear with in hrs to days.
* A stable atheromatous lesion without over lying thrombus but obstructing >75% of the coronary artery lumen would like to cause stable angina. and if the
same plaque contain superimposed thrombus on, it would more like to cause unstable angina.
* Interstitial myocardial granuloma (aschoff bodies) are typically found in Acute Rheumatic Carditis. In Aschoff bodies the plump macrophages with abundant
cytoplasm and central nuclei containing slender ribbon of chromatin are called Anitschkow cells.
* Congenital bicuspid aortic valve are strongly associated with accelerated Calcific aortic stenosis which become clinically significant in 6th decade. vs. On
other hand Senile Calcific stenosis of aortic valve generally become symptomatic in 8th decade.
* Pulmonary HTN generally presents with exertional dyspnea (possible excertional syncope) due to inability of right heart to Inc cardiac out put against Inc
pulmonary vascular resistance for this reason BP may fall during excersize. Chronic condition may lead to corpulmonale and corpulmonale may lead to
sudden cardiac death due to lethal cardiac arrhythmia.
* Ingestion of Fenfluramine, Dexfenfluramine and Phenteramine for > 3 month is associated with secondary pulmonary HTN.
* Changes after MI
0 - 4 hr -------------------------------------------- minimal change (myocyte hypereosinophilia occur)
4 - 12 hr ------------------------------------------- Early coagulation necrosis, edema, hemorrhage, wavy fiber
12 - 24 hr ----------------------------------------- Coagulation & marginal contraction band necrosis.
1 - 5 days ----------------------------------------- Coagulation necrosis and neutrophilic infiltration
5 - 10 days --------------------------------------- Macrophage phagocytosis of dead cells.
10 - 14 days -------------------------------------- granulation tissue and neovascularization.
2 week - 2 month ------------------------------- Collagen deposition and scar formation.
* Neonate with PDA can be tx with PGE1 inhibitor such as Indomethacin and Ibuprofen. Delayed closure of PDA is associate with prematurity, perinatal
stress, congenital rubella and fetal alcohol $. pt typically presents with continuous machinery murmur best heard at left upper sternal border. Ductus
arteriosus is remnant of 6th aortic arch that connects aorta with pulmonary artery.
* Progressive fatigue can be the sign of low cardiac out put. Lower extremity edema suggest RH failure and elevated central venous P this could be due to
left heart failure.
* dystrophic calcification is hall mark of cell injury and death, most common site of calcific injury include age is aortic calcification and atheromatous plaque.
* Non bacterial thrombotic endocarditis (NBTE) often involves hypercoagulable state may be associated with cancer. When hypercoagulability is the result of
procoagulant effect of circulating product of cancers the resulting cardiac valve vegetation are called Marantic Endocarditis. Pathophysiology of NBTE is
similar to that of Trousseaus syndrome which also induced by disseminated cancer.
* List of precursor protein or peptides responsible for localized amyloidosis.
1. Cardiac atria ----- atrial natriuretic peptide
2. Thyroid gland ------- Calcitonin
3. Pancreatic islet --------- islet amyloid protein (amylin)
4. Cerebrum ? cerebral blood vessels ------- - amyloid protein
5. Pituitary gland ------ prolactin.
* Immunoglobin light chain cause multi organ amyloid deposit in primary amyloidosis.
* Normal changes in aging heart include , dec in left ventricular chamber apex to base dimension., development of sigmoid shape ventricular septum,
myocyte atrophy and interstitial fibrosis and accumulation of cytoplasmic lipofuscin pigment. vs. hypertensive heart develop concentric hypertrophy of LV.
* Ruptured ventricle is complication of transmural myocardial infarction occur 3 - 7 days after the onset of total ischemia when coagulative necrosis,
neutrophil infiltration, enzymatic lysis of connective tissue have substantially weakened the infarcted myocardium (Mean 4 - 5 days. Range 1 -10 days).
* Free wall rupture cause cardiac temponade which limits the ventricular filling during diastole, as P Inc the venous return to heart dec, these events lead to
profound hypotension and pulseless electrical activity and death. Physical examination shows shortness of breath, muffled heart sound & Inc jugular venous
P.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
45
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Dynamic ventricular outflow obstruction occur when hypertrophic septum bulges into left ventricle outflow tract it is seen in 25% of pts with hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy. The septal hypertrophy is asymmetric and produce systolic ejection murmur and syncopal episodes.
* Major determinant of whether or not coronary artery plaque will cause ischemic myocardial injury is the Rate at which it occludes the involved artery. A
slowly developing occlusion allows formation of collaterals and could prevent myocardial necrosis. On other hand thin fibrous cap, rich lipid core, and active
inflammation in the atheroma would all dec plaque stability and potentially promote coronary artery occlusion via superimposed thrombosis.
* dilated cardiomyopathy of LV is characterized by LV Systolic dysfunction (often time signs of CHF) vs. Diastolic dysfunction occur in hypertensive heart
dis with concentric ventricular hypertrophy and also in Restrictive cardiomyopathy.
* Asymmetrical concentric hypertrophy is characteristic of cardiomyopathy due to HTN.
* Fibrous thickening with endocardial plaque limited to the right heart are characteristic of Carcinoid $. Carcinoid classically produce episodes of flushing,
abdominal cramping, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea due to production of serotonin, kallikrein, bradykinin, histamine, prostaglandin & tachykinin by carcinoid
tumor.
Lab shows Inc urinary excretion of serotonin metabolites (5 - hydroxyindoleacetic acid). Serotonin is actively degraded by pulmonary vascular endothelial
monoamine oxidase thats why it does not effect left heart. Pulmonary stenosis and restrictive cardiomyopathy may results from this condition.
* Diamond shaped (cresendo - decrescendo) systolic ejection murmur is characteristic of aortic stenosis, it starts after 1st heart sound and typically ends
before A2 component of 2nd heart sound. most commonly cause by degenerative (senile) calcinosis of aortic leaflets. (heard loud in early diastole)
* Recurrent cyanotic spells that pt counter it by squatting suggest Tetralogy of fallot is the most common cyanotic heart dis seen in children after infancy. It is
characterized by pulmonary stenosis, VSD, right ventricular hypertrophy, and over riding aorta.
* Aortic valve infective endocarditis tend to produce aortic stenosis and aortic regurgitation (commonly due to Rheumatic heart dis) may produce ejection
murmur that radiates to carotids.
* Concentric ventricle hypertrophy uniformly thicken the ventricular wall while the outer dimension of the ventricle remain virtually unchanged thus narrowing
the ventricular cavity. It is often seen in pt with longstanding HTN (due to pressure overload).
* Syndhams chorea is the most common acquired chorea of childhood and is sole neurologic manifestation of Acute Rheumatic fever. Syndham chorea is
thought to be CNS autoimmune reaction precipitated by group A Hemolytic streptococcal sore throat inf after 2 - 3 months. Anti neuronal Ab bind to
caudate and subthalamic nuclei and cause the symptoms.
* Differential cyanosis is restricted to the lower body in the child suggest PDA with Late - Onset Reversal of Shunt flow (from left - to - right to Right - to - left)
, where as whole body cyanosis occur in pt with septal defect or tetralogy of fallot. Adult form of COA can limit lower extremity exercise tolerance but does
not cause cyanosis.
* Splinter or flame shaped hemorrhage occur in nail bed as a consequence of microemboli, Infective endocarditis. where as janeway lesion occur in sole of
the feet and palm for the same reason and it is nontender.
* Bacterial endocarditis is the most common cause of fatigue and new cardiac murmur in young adult. pt also show two - fold elevated creatinine indicating
50% reduction of GFR, accompanying with hematuria and proteinuria due to nephritic $. In some pt Bacterial endocarditis may be complicated Acute diffuse
proliferative glomerulonephritis secondary to circulating immune complex deposition on mesengium and subendotheium of glomeruli.
* Hypertrophic cardiomayopathy often cause sudden cardiac death in young athlete, it is due to autosomal dominant mutation in cardiac sarcomere protein.
Most common protein involved is - myosin heavy chain.
* Approx 1/3 of dilated cardiomyopathy are genetic, due to Autosomal dominant mutation of cardiac myocyte cytoskeletal protein (Dystrophin) or
mitochondrial enz.
* Homogenous deposition of eosinophilic hyaline material in the intima and media of small arteries and arterioles is characterizes Hyaline Arteriolosclerosis
which is typically produced by long standing nonmalignant HTN and / or diabetes.
* Malignant HTN produce hyperplastic arteriosclerosis, consist of homogenous onion like concentric thickening of the wall of arterioles. This morphologic
pattern is results from laminated smooth muscle cell and reduplicated basement mem.
* Osler Weber Rendu $ (Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia) is autosomal dominant dis marked by telangiectesia in skin and mucous mem. rupture of
these telangiectasia may cause epistaxis, GI bleeding and hematuria.
* Pulmonary embolism is common in hospitalized pt and cause wedge shaped infarct. This condition is precipitated by hypercoagubility of any cause.
* Persistent lymphedema predisposed to the development of lymphangiosarcoma. This may arise 10 yrs after radical mastectomy. with axillary lymphnode
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
46
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
dissection for breast cancer.
* Cystic medial degeneration is myxomatous changes in the media of large arteries. Medial degeneration is characterized by fragmentation of elastic tissue
and by separation of the elastic and fibromuscular component of tunica media by cleft like spaces. Such medial degeneration is frequently found in aortic
dissection (dissecting hematomas) in humans. It is associated Marfan $
* Giant cell arteritis is characterized by granulomatous inflammation of the media of the branches of carotid artery, commonly after 50 yrs of age. Jaw
claudication is the most common symptom it can cause irreversible blindness if ophthalmic artery is involved. Prevent complication by Prednisone
* Sever retrosternal pain radiate to back is classic presentation of aortic dissection, it extend through the media along the aorta in both proximally and distally
and can compress major arteries.
* Benign glomus tumor (glomangioma) are small red blue under the nail bed and is very tender, originate from modified smooth muscle cell that regulate
thermoregulatory function of dermal glomus bodies.
* PAN is segmental, transmural, necrotizing, inflammation of medium to small sized arteries. Renal artery involvement is often prominent, vessels of Heart,
GIT and liver are also commonly involved, 1/3 pt presents cutaneous manifestation of palpable purpura. (lung is rarely involved)
* Pt with very high diastolic BP (> 120mmHg) often has hyperplastic arteriolosclerosis, present as onion skin concentric thickening of the wall of arterioles as
a result of laminated smooth muscle cell and reduplicated basement mem, it dec GFR and renal perfusion. this lead to further Inc in BP and vicious cycle
occur and results in malignant naphrosclerosis (Renin - angiotensin - aldosterone system play major role)
* Cavernous hemangioma present at birth or develop later in life, it presents as soft blue compressible mass. Microscopy reveal dilated vascular spaces.
* Strawberry hemangioma (capillary hemangioma) are benign vascular tumor of childhood, appear in the first week of life initially grow rapidly and typically
regresses by 5 - 8 yrs of age. These tumor are composed of capillaries separated by connective tissue.
* Cystic hygroma (lymphangioma) are benign tumor that consist of dilated lymphatic spaces lined by endothelium. Most commonly occur on neck. these
tumor are lobulated , compressible and usually transilluminate.
* Cherry hemangioma is most common benign vascular proliferation in adults. usually appear first in childhood and regress by age 5 - 8 yrs. Once occur in
adult life do not regress spontaneously.
* Thromboembolism is not a frequent complication of varicose vein but due to serious threat it demand attention.
* Aortic aneurysm of tertiary syphilis begins with vasa vasorum endarteritis and obliteration results in inflammation, ischemia and weakening of aortic
adventia.
FTA - ABS is the test specific for syphilis.
* Major cause of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) is atherosclerosis, which with time weaken the underlying media of aortic wall.
* Self limiting small vessel Leukoclastic Angiitis associated with IgA and C3 deposition is typical of HSP, most commonly occur after recent inf in children of
3 - 11 yrs of age. Most children presents with skin lesion with or without abdominal pain & arthralgia. Important complication are renal failure or
glomerulonephritis.
* Fatty streak is the earliest lesion of atherosclerosis present in all individuals after age 10. Composed of lipid filled foam cells derived from macrophages and
smooth muscle cells that have engulfed lipoprotein commonly LDL.
* Monckeburg Medial calcific sclerosis characterized by calcified deposit in muscular arteries in person aged > 50 yrs. Visible radiologically and often time
palpable physically. they typically donot narrow the lumen.
* Intermittent muscle pain reproduced by excersize and relieved by rest suggest claudication, it is almost always the complication of atherosclerotic large
arteries.
* Chrug - Strauss $ is idiopathic systemic vasculitis associated with adult onset asthma, Eosinophilia, and P - ANCA. Pt often has Hx of allergy, mono or
poly neuropathy and paranasal sinus abnormalities.
* Temporal (giant cell) arteritis is characterized by granulomatous inflammation of the media and is most common form of systemic vasculitis in adult. It
commonly involve branches of carotid artery, specially temporal artery. Manifest by headache, facial pain, jaw claudication and visual deterioration, it
respond well to glcocorticoids.
* Wagners granulomatosis is characterized by necrotizing upper and lower respiratory tract (nasal ulceration / hemoptysis), and rapidly progressive
glomerulonephritis, C- ANCA (which may target neutrophil proteinase 3) is associated with WG.
* Pt with adult type Coarctation of aorta may die of HTN associated complication, such as left ventricular failure, ruptured dissecting aneurysm, and
intracranial hemorrhage due to intracranial aneurysm (like berry aneurysm in circle of willis)
* Abdominal pain due to acute pancreatitis is the most likely presentation for Hyperchylomicronemia (hypertriglyceridemia). Pt with this disease are not
usually at Inc risk for premature coronary artery dis. skin xanthomas may be present in Hypertriglyceridemia but tubular / tendon xanthomas and
xanthelasmas are present in hypercholesterolemia (high LDL).
* In normal individual heparin releases endothelium - bound lipases, encouraging the clearance of triglycerides from circulation. If pt is lipoprotein lipase
deficient than heparin induced lipase activity will significantly reduced.
* Buerger's dis is commonly seen in cigarette smoker with onset before age 35. Manifest as intermittent claudication of calf, foot and hand severe distal pain
even at rest, cold sensitivity, distal ulceration and gangrene, superficial nodular phlebitis and raynaud phenomenon. Tx include smoking cessation.
* Segmental Transmural inflammation of the arterial wall of medium to small size with fibrinoid necrosis is characteristic of PAN. (lung are spared). Moat
common initial symptoms are fever, abdominal pain, peripheral neuropathy, weakness and wt loss, diffuse muscular pain may also be seen. PAN is
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
47
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
associated with Hepatitis B infection in 10 - 30% of cases.
* Morphine tolerance is common problem in treating pain. Activation of NDMA receptors by glutamate is believed to enhance morphine tolerance by Inc
phosphorylation of opioid receptors, Inc adenylate cyclase activity or Inc nitric Oxide levels. NMDA receptor blocker like Ketamine block the action of
glutamate and effectively dec morphine tolerance.
* In tetralogy of fallot squatting provide relief because squatting Inc the total systemic peripheral resistance thus Inc the Pulmonary vascular resistance which
permit the greater fraction of cardiac output to pass through the lung and improve arterial oxygenation. (thus dec right to left shunt & Inc pulmonary blood
flow)
* Mastocytosis is mast cell proliferation that occur in bone marrow and other organ which further cause histamine release that results into Inc gastric acid
secretion which inactivate pancreatic and intestinal enz and casing diarrhea. GI ulceration, cramp, nausea and vomiting may occur. Inc histamine also cause
flushing, hypotension, syncope, tachycardia, and bronchospasm. skin manifestation is pruritus, urticaria, dermatographism are typical.
* Tumor cell $ occur when tumor with high cell turnover are treated with chemotherapy, the lysis of tumor cause K+, phosphorus and uric acid to released into
serum and can provoke variety of problems such as uric acid precipitation in distal tubule and collecting duct (uric acid precipitate in acidic environment).
Prevention can be achieved by alkalinization of urine and hydration as high pH and urine flow prevent crystallization of uric acid.
* Aromatase androstenidione to estrone and testosterone to estradiol in ovary, Imp in estrogen synthesis in ovary, testis, placenta, brain, liver, muscle and
adipose tissue.
* Aromatase def in embryonal life results in high androgen level and low estrogen level this high androgen enter the maternal circulation and cause virilization
in mother. on other hand at birth affected female infant will have ambiguous or male type genitalia (Female Pseudohermaphrodism) which in adult life
manifest as Primary amenorrhea, tall stature (because estrogen is necessary for fusion of epiphyses). Male infant will manifest as tall stature , osteoporosis
with no genital abnormality.
* Inc armoatase level lead to estrogen excess causing gynecomastia in boys and precocious puberty in females. Pt of both sexes will be short stature due
early closure of epiphyses.
* Duodenal ulcer are not associated with Inc risk of carcinoma.
* In mitral regurgitation with left sided heart failure pts heart will pump some blood forward (Forward stroke vol or FSV) and some blood goes backward
(Regurgitant stroke vol or RSV). If the systolic retrograde flow resistance b/w the LV and LA, the preload and the contractility remain the same, the amount of
blood flows forward and backward is determined by the left ventricular after load (systolic intraventricular P). The lower the average left ventricular after load,
the lower will be the average systolic P gradient driving regurgitant flow into the LA and the lower will be the RSV. Moreover FSV will be Inc. This will Inc the
forward - to - regurgitant vol ratio. Thus arterial vasodilator therapy which act to dec LV after load tend to dec RSV and Inc FSV in pt with mitral regurgitation.
* Renal calculi can be prevented by Inc citrate and high fluid intake.
* Mitral stenosis due to abnormal valve may produce opening snap in early diastole shortly after the A2. Opening snap shortly after mitral valve opens.
* In Achalasia esophageal body peristalsis is dec and LES relaxation is poor. It presents with dysphagia, chest pain, food regurgitation, and aspiration.
Barium swallow shows dilated esophagus and a "Bird Beak" deformity of LES.
* Virulence factor of H. pylori are 1. urease ( enz that form ammonia from urea causing Inc in pH, Enz is essential for survival) 2. Adhesins (subs that enable
the bacteria to adhere) 3. Proteases and phospholipases (enz that break gastric mucosa.
* H. pylori can not live in intestinal epithelium (due to Inc pH) that is why presence of H pylori in duodenum indicated the gastric type metaplasia in intestine.
It is thought that H. pylori colonization of stomach Inc the gastric acid production which lead to acid injury to duodenal mucosa and inducing gastric
metaplasia.
* The abnormal activation of trypsin with in the pancreas is a central event in the pathogenesis of the Acute necrotizing pancreatitis. All proteolytic pancreatic
enz are activated by trypsin including it self (self activation) which lead to pancreatic autodigestion. Activation due to gene mutation results in hereditary
pancreatitis.
* Nocturnal palpitation and Involuntary head pounding with exertion (high amplitude pulsation of Intracranial arteries due to large ventricular vol ejection) can
be a sign of widened pulse P (Remember the pulse P = peak systolic arterial P - end diastolic arterial P). The most likely cause of repetitive widened pulse P
together with large left ventricular stroke vol and heart murmur is Aortic regurgitation.
* Ischemic precondition with sublethal ischemic insult can protect the affected myocardium against the subsequent greater ischemic insult (due to
developing resistance to infarction).
* Myocardial stunning is a less severe form of ischemia - induced reversible loss of contractile function. Brief ischemic episode (< 30 min) followed by
reperfusion can produce myocardial stunning, and full recovery is usually over hrs to days. On other hand repetitive stunning can results in hibernation that
can be reversible by reperfusion too.
* Ventricular remodeling involve change in mass, vol, shape and myocyte composition to compensate the Inc hemodynamic load.
* Wide fixed splitting of S2 which does not vary with respiration is characteristic of Atrial septal defect. ASD create L to R shunt due to high P in L atrium
which results in Inc blood flow of pulmonary artery which further can cause laminated medial hypertrophy of pulmonary arteries (due to high P and Inc
resistance) at this point L to R shunt reverses and flow become R to L. This switching manifest as late onset cyanosis with clubbing and polycythemia.
Eisenmenger $ is the name for reversal shunt which eventually lead to right heart failure and death.
* Pt with severe Acute mitral regurgitation will develop pulmonary HTN and pulmonary edema. vs. Chronic mitral regurgitation will acquire Inc in left atrial
compliance therefore less prone to pulmonary HTN / edema but are more prone to atrial enlargement, fibrillation and mural thromboembolism.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
48
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Deglutition ( swallowing) is a complex process that include 3 phases.
Oral phase --- is voluntary in which food bolus is collected at the back of the mouth and lifted upward to the post wall of the pharynx. This initiates the
Pharyngeal phase --- which consist of involuntary pharyngeal muscle contraction that propel the bolus to the esophagus. During Esophgeal phase --- food
enters the esophagus and stretches the wall; peristalsis begin just above the site of distention and propel the food downward, relaxation of the lower
esophageal sphincter (LES) follows and food enter the stomach.
* Cricopharyngeal muscle dysfunction occur due to diminish relaxation of pharyngeal muscle during swallowing, more force is required to move the bolus
downward. More intense contraction of the pharyngeal muscle Inc the oropharyngeal intraluminal P, with time pharyngeal mucosa will herniate through the
muscle fiber in the zone of weakness (post hypopharynx) forming a zenker's diverticulum. A traction diverticulum alternatively consist of all layer of the wall.
Pt with cricopharyngeal dysfunction manifest as high dysphagia, difficulty swallowing felt at throat, coughing choking and nasal regurgitation. When Zenkers
diverticulum form the retention of food with regurgitation occurs days later, food aspiration may cause pneumonia, lateral diverticulum can be palpable as a
lateral neck mass.
* Atrial regurgitation cause vol overload in LV (not P overload). The adaptation to vol overload is eccentric hypertrophy, that is chamber dilation due to Inc
end diastolic vol with predominantly "in series synthesis" of new myocardial sarcomeres. vs. Concentric hypertrophy is the response to P overload
involves "in parallel deposition" of new sarcomers, which produced net ventricular thickening and reduction in ventricular chamber size (dec EDV). P overload
may occur in aortic stenosis and systemic HTN.
* Major causes of HIV - associated Esophagitis are Candida, Cytomegalovirus, and Herpes virus. They all cause dysphagia and Odynophagia for right
treatment exact Dx is important. following is the endoscopic and microscopic criteria for causative agents.
* Systolic ejection murmur accentuate on standing ---------- hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy.
* Early diastolic decrescendo murmur dec by amyl nitrite ---------- Aortic regurgitation
* Late Diastolic murmur eliminated by atrial fibrillation ----------- mitral and tricuspid stenosis.
* Brain natriuretic peptide is elevated in pt with heart failure and is often used as a lab test in pt suffering from CHF exacerbation. Brain Natriuretic peptide is
released by ventricles when they are stretched as in CHF (systolic dysfunction). It acts along with Atrial natriuretic peptide to case vasodilation and diuresis.
Both ANP and BNP activate guanylate cyclase which induces an Inc of Intracellular cyclic GMP.
* 5 reductase convert testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) which mediate development of the external genitalia in male fetus. Male neonate with 5
reductase def are born with feminized external genitalia that typically musculinized at puberty. small phallus and hypospadius are commonly found.
* Significant Inc in blood saturation b/w two right sided vessels or chamber indicate left to right shunt, VSD is most common cause which produce
Holosystolic murmur loud over the left mid sternal border.
* Most common heart dis that produce early cyanosis is tetralogy of fallot.
* Inc pulmonary P in pulmonary circulation results in transudation of fluid into lung interstitium & air spaces. This decreases the lung compliance & O2
diffusion.
* Lactase def individual have Inc stool osmotic Gap, Inc breath hydrogen content and Dec stool pH upon lactose challenge.
* Lactose tolerance test --- 50gm of lactose administered orally, with blood levels measured at 0, 60 and 120 minutes. If blood glucose Inc <20 mg and the
Individual experience symptoms such as abdominal pain, flatulance, diarrhea and vomiting, the DX of Lactose intolerance is confirmed.
* Diastolic heart failure is characterized by normal ventricular contractile performance (EF) but a dec in ventricular compliance. As a result ventricular EDP
must be Inc to achieve a normal Ventricular EDV and stroke vol. vs. Systolic heart failure is a dec in ventricular contractile performance which requires Inc of
ventricular EDV and therefore also EDP to achieve a normal stroke vol. (remember Diastolic failure Inc only EDP vs. systolic failure Inc both EDP & EDV)
* In severe Mitral regurgitation the most reliable auscultatory finding is left sided S3 gallop which indicates left ventricular overload due to high regurgitant vol.
Donot correlate Intensity of holosystolic murmur with regurgitant vol. Left side S4 suggest end stage decompensation of severe MR to the left ventricle
failure. however may pts with MR do not have left ventricle failure.
* Atrial fibrillation is most likely precipitating factor in sudden onset of heart failure in pt with aortic stenosis, because sudden loss of the contribution of
normal atrial contraction (loss of atrial systolic kick) dec left ventricle preload which can further reduce the cardiac out put and produce severe hypotension.
Many pt with AS have concentric LV hypertrophy and therefore reduced LV compliance which produce even profound affect with atrial fib. Loss of atrial kick
may also Inc pulmonary venous P which has an additional on heart. That is why cardioversion is indicated in Acute atrial fib in these pt.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
49
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* An accessory AV conduction pathway pre - excites the ventricle (pre excitation $) and manifest clinically as Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT)
in an other wise normal individual. The base line EKG (not in the setting of PSVT) of a pt shows triad of abnormalities which correspond the ventricular pre excitation physiology (Wolff Parkinson White $) ----- 1. Short PR interval (<0.12 sec). 2. Delta wave at the start of QRS complex, 3. Widened QRS interval.
* Best auscultatory indicator of mitral stenosis is the length of interval b/w A2 and the opening snap (OS). the shorter the interval more severe the stenosis.
OS occur due to the tensing of the mitral Valve leaflet after the valve cusps have completed their opening excursion. The more thickened and fibrotic the
mitral valve the earlier this tensing occurs. (In modern practice the MS severity is measured by Mean transvalvular P gradient via 2 - D doppler Echography)
* An Inc in LV prepoad (left EDV) in association with eccentric LV hypertrophy is major lasting hemodynamic compensation to the vol overload of aortic
regurgitation.
* Diffuse esophageal spasm (DES) occur due to uncoordinated contraction of esophagus. These contraction are both inefficient in propelling food and cause
symptom of dysphagia and chest pain. This chest pain mimic unstable angina thus complete cardiac work up should be done in pts suspected of having
DES.
* LV dysfunction can lead to Inc pulmonary arterial P. reactive change in the pulmonary vasculature (endothelial dysfunction resulting in vasoconstriction)
may also contribute to pulmonary HTN. Hypoxia induced vasoconstriction play a major role in pulmonary HTN in COPD pt.
* In coronary artery dis, coronary vessel occlusion can bypassed by the natural existence and compensatory recruitment of coronary collateral vessels to help
myocardium distal to occluded vessel.
* Adenosine and dipyridamol r selective vasodilator of coronary vessel and are also used in myocardial perfusion imaging studies. In certain conditions these
agents may cause redistribution of blood flow through coronary micro vessels and possibly reversing collateral blood flow. vessels in ischemic area are often
maximally dilated these agent cause selective vasodilation in non ischemic region thus divert blood flow from ischemic area to non ischemic area. This
phenomenon is known as Coronary steel, dec blood flow to ischemic area may lead to hypoperfusion and potentially worsen existing ischemia.
* Cardiac temponade clinically presents : >10 mmHg drop in systolic BP on inspiration (pulsus paradoxus), tachycardia, hypotension, Inc jugular P, and
muffled heart sound.
(Beck's triad is hypotension, distended neck vein and tachycardia all suggest Cardiac temponade)
* S4 gallop ( also called atrial sound or atrial gallop) is presystolic sound immediately precede S, Left sided S4 heard best at the apex where as Right side S4
heard best along the left sternal border (tricuspid area) with the pt in supine position. S4 occur due to sudden rise in end diastolic ventricular P caused by
atrial contraction against the ventricle that has reached the limit of its compliance. Thus S4 may suggest any condition that causes stiff ventricle, vol
overloaded L heart of any cause (LV hypertrophy, long standing HTN etc). Normal atrial contraction is required to generate S4.
* First step in screening malabsorption is Sudan III stain which identify presence of fat in stool. Quantitative analysis, >7gm fat confirm the DX.
* Most definitive tx of serotonin $ is surgical excision. when there is dissemination Octeriolide (somatostatin analog) is used to control the symptoms by
inhibiting secretion of many hormones. Octeriolide also used in VIPoma (pancreatic tumor).
* Pancreatic psuedocyst is the common complication of acute pancreatitis. It is the collection of fluid rich in enz and inflammatory debris, the wall consist of
granulation tissue and fibrosis. Unlike true cyst psuedo cyst are not lined with epithelium.
* PAS stain is particularly effective at highlighting polysaccharides of the fungal cell wall, mucosubstances secreted by epithelia and basement mem.
* Diastase can be use in conjunction with PAS to demonstrate glycogen. (diastase digest glycogen and form maltose and glucose ( giving a - ve reaction).
* Iron stains blue with Persian blue stain.
* Neuro lipid can be identified by Nile red stain and Sudan black stain.
* Dermatitis herpetiforme is auto immune disorder associated with celiac dis (hypersensitivity to gluten). Skin biopsy shows neutrophil, fibrin and IgA at the tip
of dermal papilla forming microabscesses. Other manifestation are diarrhea, steatorrhea, malabsorption (villous atrophy & inflammation of lamina propria). All
these changes are reversible upon gluten withdrawal.
* In healthy bowel dietary calcium binds to oxalate, enabling oxalate excretion. In crohn dis calcium binds instead with lipids making it unavailable to bind
with oxalate as a result oxalate absorbs and form urinary stones.
* Colonic diverticulas usually develop due to Inc Intraluminal Pressure and are composed of mucosa and submucosa in over 60 yrs of age. The most
common site is sigmoid colon (are pulsion by mechanism so are false). It may be asymptomatic or manifest as painless bleeding or acute diverticulitis.
Chronic constipation is the risk factor. where as out pouching that occur in during fetal life contain all layers of the wall such as mekels diverticulum (true
diverticulum).
* Atherosclerosis most commonly involve the abdominal aorta, followed by coronary artery, popliteal artery, internal carotid artery and circle of willis.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
50
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
* Barret esophagus is intestinal metaplasia of esophgeal epithelium due to GERD, pts are at high risk of developing adenocarcinoma. Early Dx and regular
monitoring is important.
* Squamous cell carcinoma comprise 50% of esophgeal cancers in USA commonly occur in male over 50 yrs of age. It presents with progressive dysphagia
first for liquid than for both liquid and solid with wt loss. The most imp risk factor is alcohol and tobacco use. Plummer - vinson $, Achalasia and corrosive
stricture are other risk factors.
* Pain associated with duodenal ulcer typically occur 2 - 4 hr after meal or with an empty stomach where as pain due to gastric ulcer occur immediately after
meal and respond poor to antacid. Most duodenal ulcer are located to first portion of duodenum (duodenal bulb) with in 3 cm of pylorus. Gastric ulcer tend to
occur commonly at the lesser curvature at the functional border b/w body and antrum.
* Gastric Erosion defined as mucosal defect and does not penetrate the muscularis mucosa, it usually occur with acute errosive gastritis which results from
short term severe mucosal injury with inflammation and mucosal destruction. Common causative agent are NSAIDs, surgery, head trauma (Cushing ulcers),
Burns (curling ulcers), smoking and alcohol.
* Adenocarcinoma in ulcerative colitis tend to arise from area of dysplasia in macroscopically normal intestine, they are more aggressive and tend to occur at
multiple sites simultaneously. In ulcerative colitis 1. rectum is always involve, 2. inflammation involve only mucosa and submucosa. 3. mucosal damage is
continuous.
* Chronic mesentric ischemia is most commonly caused by atherosclerotic narrowing of the celiac trunk, superior mesentric artery and Inferior mesentric
artery. Triad of symptoms are
1. Epigastric or periumbilical pain occur 30 - 60 min after food intake. Atherosclerotic arteries r unable to dilate in response to Inc blood requirement after
meal. 2. wt loss (many pt avoid food to prevent pain associated with eating.
3. Pt report severe pain but physicians examination will usually appear benign
* Size of adenomatous polyp determine their malignant potential. Adenoma < 1 cm are unlikely to undergo malignant transformation where as adenoma > 4
cm are very likely to progress to adenocarcinoma. K - ras proto-oncogene mutation facilitate the growth by uncontrolled cell proliferation.
* There are two morphologic variant of gastric adenocarcinoma. Intestinal type form solid mass that project into the stomach lumen and is composed of
glandular - forming cuboidal and columnar cell. vs. Diffuse carcinoma infiltrates the stomach wall and displays a Signet - ring pattern.
* Toxic megacolon is well recognized complication of ulcerative colitis. Plain X ray should be used for DX. Barium contrast studies are contraindicated die to
risk of perforation.
* When mucosa of terminal ileum is inflamed (as in crohns dis), bile acid are not reabsorbed and lost in feces, as a result lesser bile stores dec and ratio of
cholesterol / bile acid Inc which can results into cholesterol gall stones.
* Unlike sporadic Colon cancer, HNPCC does not involve mutation of proto-oncogene or Anti - oncogene. Instead HNPCC cause by inherited mutation in one
of the 4 gene responsible for DNA mismatch repair. The product of these genes "proof read" DNA during replication. Pt with HNPCC inherit a mutation in
one allel of the gene and mutation of the second allel occur in adult life. When two dysfunctional copies are present malignancy develop.
* Hereditary non polyposis colon cancer (HNPCC) is also called Lunch $. It leads to Colonic adenocarcinoma at young age (< 50 yrs of age), along with
predisposition for extra intestinal malignancies.
* APC mutation is required for the emergence of small adenomatous polyps from normal clonic mucosa. This mutation constitutes First step in adenoma - to
-carcinoma sequence. APC gene mutation is found in most cases of sporadic colon cancer and in all Familial polyposis $.
* K - ras proto oncogene is responsible for Inc in the size of adenomatous polyps.
* The Adenoma - to - carcinoma sequence is a series of gene mutation that lead to the development of colon adenocarcinoma. This sequence include 3
stages, each stage is associated with particular gene mutation, P53 anti - oncogene mutation is the part of final step in the sequence and lead to malignant
transformation of preexisting large adenomatous polyps.
* Def of lipoprotein lipase (LPL) leads to impaired degradation of chylomicrons. LPL def is the defect underlying Familial hyperchylomicronemia which results
in Inc serum Triglycerides. Young pt with familial hyperchylomicronemia often present with acute pancreatitis due to high triglycerides. Eruptive xanthomas,
lipidemia retinalis (pale pink milky appearance of retinal blood vessel) may also present. LPL only found in extrahepatic tissue, adipocytes, cardiomyocytes
and skeletal muscle cells.
* Gastroesophgeal junction incompetence is the primary mechanism responsible for GERD. This incompetence is most commonly caused by transient lower
esophgeal sphincter relaxation and hypotensive lower esophgeal sphincter.
* Pill - induced esophagitis is commonly seen with tetracycline and potassium chloride.
* 80% of acute pancreatitis is caused by gall stones and chronic alcoholism. Other 20% less common causes are acquired hyper triglyceridemia (>1000
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
51
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
USMLE WORLD NOTES
mg/dL)
* High level of triglycerides lead to Inc production of free fatty acid. Normally fatty acid exist in serum bound to albumin, if serum triglyceride level is higher
than 1000 mg/dL , the conc of free fatty acid exceeds the binding capacity of albumin and lead to direct injury to acinar cells and pancreatic capillaries. Thus
hypertriglyceridemia cause acute pancreatitis via direct tissue toxicity.
* Submucosal (Meissner) and myenteric (Auerbach) autonomic plexi are absent in Herchsprung dis.
*Anal fissure is the tear in the lining of anal canal distal to the dentate line that occur most often on the posterior midline. Pt complain of severe tearing pain
associated with the passage of bowel movements. Skin tags may be present. It is associated with low fiber diet and constipation.
* Crohns dis cause transmural inflammation of area of GI tract. The involvement of all layers of the intestinal wall explains the common complication of the
crohn dis, the stricture and the Fistula formation.
* NOD2 protein appear to act as an Intracellular microbial receptor that trigger the NF - kB pathway. NF - kB is a transcription factor responsible for cytokines
production in the immune response to pathogen. It has been proposed that NOD2 mutation linked with Crohn dis reduces the activity of NF - kB protein
thereby allowing the inflammation - induced intracellular microbes to persist.
* CEA level Inc in colon cancer as well as in other malignancies and certain benign diseases. CEA can not be used to DX colon cancer but is helpful for
detecting dis recurrence.
* Shigella invades the GI mucosa by first gaining access to M cells in payers patches through endocytosis. Shigella subsequently lyses the endosome,
multiply and spread laterally into other epithelial cell, causing cell death, ulceration with hemorrhage and diarrhea.
* Colon adenocarcinoma is most common GI malignancy and is most frequently located in ascending colon. Pt with cancer in this location tend to present
with malaise and microcytic anemia. vs. rectosigmoid colon is the most common place for Colorectal carcinoma.
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
52
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Prepared by Irfan Mir
STRICTLY FOR EDUCATION PURPOSE ONLY.
USMLE WORLD NOTES
53
NOT FOR COMMERCIAL USE OR SALE
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Food SafetyДокумент71 страницаFood SafetyManisanthosh KumarОценок пока нет
- How Ict Is Changing Education: How To Name ItДокумент9 страницHow Ict Is Changing Education: How To Name ItManisanthosh KumarОценок пока нет
- MRCP2 Rapid Revision NotesДокумент125 страницMRCP2 Rapid Revision NotesManisanthosh Kumar100% (1)
- Des MurgyДокумент24 страницыDes MurgyManisanthosh KumarОценок пока нет
- Oral Case Presentation Benchmarks - : Identifying Information & Chief ConcernДокумент9 страницOral Case Presentation Benchmarks - : Identifying Information & Chief ConcernManisanthosh KumarОценок пока нет
- Morgagni Hernia: Brian Belyea Radiology Elective Block 8 February 27, 2004Документ18 страницMorgagni Hernia: Brian Belyea Radiology Elective Block 8 February 27, 2004Manisanthosh KumarОценок пока нет
- Usmle Study Tip 4Документ10 страницUsmle Study Tip 4ninja-2001Оценок пока нет
- Keplan Q BankДокумент385 страницKeplan Q BankManisanthosh KumarОценок пока нет
- Pegasus Bilet Hatti +90 850 250 0 737: YazdırДокумент2 страницыPegasus Bilet Hatti +90 850 250 0 737: YazdırManisanthosh KumarОценок пока нет
- DNB Paediatrics Question BankДокумент58 страницDNB Paediatrics Question BankManisanthosh KumarОценок пока нет
- Ori Hofmekler - Warrior NewsletterДокумент49 страницOri Hofmekler - Warrior NewsletterBigNat7774100% (2)
- PPP QuestionsДокумент3 страницыPPP QuestionsHarun MohamedОценок пока нет
- Pentose Phosphate Pathway: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, Ph.D.Research ScholarДокумент22 страницыPentose Phosphate Pathway: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, Ph.D.Research ScholarDr. M. Prasad NaiduОценок пока нет
- Metabolisme EritrositДокумент50 страницMetabolisme EritrositRamdhana ZaqifahОценок пока нет
- g6pd Group 5 A2Документ39 страницg6pd Group 5 A2Kristian CadaОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrate Complete Notes (B.pharm 2nd Sem)Документ25 страницCarbohydrate Complete Notes (B.pharm 2nd Sem)DIPENDRA KUMAR KUSHAWAHAОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry of The EyeДокумент38 страницBiochemistry of The EyeYusuf Almalik SaputraОценок пока нет
- Hexose Monophosphate ShuntДокумент38 страницHexose Monophosphate ShuntJohn Raniel IsidroОценок пока нет
- Chapter 18 HandoutДокумент8 страницChapter 18 HandoutreynandОценок пока нет
- Hexose Mono Phosphate (HMP) ShuntДокумент28 страницHexose Mono Phosphate (HMP) ShuntVishesh JainОценок пока нет
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayДокумент7 страницPentose Phosphate PathwayElla BangalanОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrate Metabolism-1Документ27 страницCarbohydrate Metabolism-1RESHMA I MBAОценок пока нет
- Glucose 6 Phosphate Dehydrogenase DeficiencyДокумент29 страницGlucose 6 Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiencypurplelavender12Оценок пока нет
- Carbohydrate MetabolismДокумент83 страницыCarbohydrate Metabolismapi-3826907100% (5)
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayДокумент14 страницPentose Phosphate PathwaymarkОценок пока нет
- Hema TFST MergedДокумент94 страницыHema TFST MergedMICHAEL RYAN T. BAAОценок пока нет
- Biochem 2nd Sem Lec#1Документ7 страницBiochem 2nd Sem Lec#1Jopau ArtaizОценок пока нет
- Hexoses Monophosphate ShuntДокумент38 страницHexoses Monophosphate ShuntMohammad Mirza AziziОценок пока нет
- HMP Pathway and Its Significance - PPTX Version 1Документ40 страницHMP Pathway and Its Significance - PPTX Version 1Alana GeorgeОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry: Pharmaglimps-A Glimpse of PharmacyДокумент38 страницBiochemistry: Pharmaglimps-A Glimpse of PharmacySHRIKANTОценок пока нет
- Hopkin c.10Документ22 страницыHopkin c.10Argus SavageОценок пока нет
- 7 HMP Shunt Pathway RO PDF v1Документ9 страниц7 HMP Shunt Pathway RO PDF v1Radwa MohamedОценок пока нет
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayДокумент19 страницPentose Phosphate PathwayPankaj Kumar KunduОценок пока нет
- 2 - Carbohydrate MetabolismДокумент30 страниц2 - Carbohydrate MetabolismcayyoanisОценок пока нет
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayДокумент10 страницPentose Phosphate PathwaySania SaeedОценок пока нет
- Which One of Following Statements About The Fed and Fasting Metabolic States Is CorrectДокумент2 страницыWhich One of Following Statements About The Fed and Fasting Metabolic States Is Correctalvina damayantiОценок пока нет
- Uronic Acid Pathway and HMP PathwayДокумент3 страницыUronic Acid Pathway and HMP PathwaykanhaОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrate Metabolism SamplexДокумент13 страницCarbohydrate Metabolism SamplexCherie ThompsonОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Mcqs for 2nd Year Mbbs Www Edu Apnafort Com TRẮC NGHIỆM HAYДокумент69 страницCarbohydrate Metabolism Mcqs for 2nd Year Mbbs Www Edu Apnafort Com TRẮC NGHIỆM HAYTrần Tiến Đạt0% (1)
- AKTUBiochemistry BP203 TNotesДокумент64 страницыAKTUBiochemistry BP203 TNotesMonica Nguyen100% (1)