Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Unit 7 Map
Загружено:
api-256719324Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Unit 7 Map
Загружено:
api-256719324Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Unit 7: Rational Explorations: Numbers and Their Operations
Sixth Grade Mathematics
Unit Essential Question: How are integers and absolute value used in real world situations?
Common Core Georgia Performance Standards:
MGSE6.NS.5 Understand that positive and negative numbers are used together to describe quantities having opposite
directions or values (e.g., temperature above/below zero, elevation above/below sea level, debits/credits, positive/negative
electric charge); use positive and negative
numbers to represent quantities in real-world contexts, explaining the meaning of 0
in each situation.
MGSE6.NS.6 Understand a rational number as a point on the number line. Extend number line diagrams and coordinate
axes familiar from previous grades to represent points on the line and in the plane with negative number coordinates.
a. Recognize opposite signs of numbers as indicating locations on opposite sides of 0 on the number line; recognize
that the opposite of
the opposite of a number is the number itself, e.g.,
(3 ) =3 , and that 0 is its own
opposite.
b. Understand signs of number in ordered pairs as indicating locations in quadrants of the coordinate plane;
recognize that when two
ordered pairs differ only by signs, the locations of the points are related by
reflections across one or both axes.
c. Find and position integers and other rational numbers on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram; find and
position pairs of
integers and other rational numbers on a coordinate plane.
MGSE6.NS.7 Understand ordering and absolute value of rational numbers.
a. Interpret statements of inequality as statements about the relative position of two numbers on a number line
diagram.
b. Write, interpret, and explain statements of order for rational numbers in real-world contexts.
c. Understand the absolute value of a rational number as its distance from 0 on the number line; interpret absolute
value as magnitude
for a positive or negative quantity in a real-world situation.
d. Distinguish comparisons of absolute value from statements about order.
MGSE6.NS.8 Solve real-world and mathematical problems by graphing points in all four quadrants of the coordinate
plane. Include use of
coordinates and absolute value to find distances between points with the same first coordinate or
the same second coordinate.
MGSE6.G.3. Draw polygons in the coordinate plane given coordinates for the vertices; use coordinates to find the length
of a side joining points
with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate. Apply those techniques in the context of
solving real-world mathematical
problems.
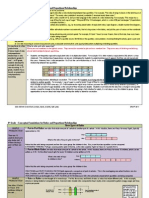
Acquisition Lesson 1
Acquisition Lesson 2
Acquisition Lesson 3
Concept: Introducing Integers
Concept: Compare & Order Rational
Numbers
Concept: Coordinate Plane
Standard(s): GSE6.NS.5, GSE6.NS.6
Standards(s): GSE6.NS.7
Lesson EQs:
When are negative numbers used
Lesson EQs:
Where do I place positive and
and why are they important?
Why is it useful for me to know the
negative rational numbers on the
absolute value of a number?
number line?
How do I use positive and negative How do I use positive and
numbers in everyday life?
negative numbers to represent
What are opposites, and how are
quantities in real-world contexts?
opposites shown on a number line? How do statements of inequality
help me place numbers on a
number line?
Standard(s): GSE6.NS.6b & 6c,
GSE6.NS.8, GSE6.G.3
Lesson EQs:
Why is graphing on the coordinate
plane helpful?
How can I use coordinates to find
the distances between points?
How can I use absolute value to
find the lengths of the sides of
polygons on the coordinate plane?
Вам также может понравиться
- Relations and FunctionsДокумент6 страницRelations and FunctionsTalveda Shreya100% (1)
- New General Mathematics For Secondary Schools 3 TG Full PDFДокумент73 страницыNew General Mathematics For Secondary Schools 3 TG Full PDFmoola66% (41)
- Objective Mathematics Vol 1Документ1 260 страницObjective Mathematics Vol 1Janaka PriyalalОценок пока нет
- Solving Absolute Value Equations and InequalitiesДокумент24 страницыSolving Absolute Value Equations and InequalitiesFerb FletcherОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 NotebookДокумент28 страницUnit 1 Notebookapi-256798980Оценок пока нет
- Poulos 2018 Subgrade PDFДокумент7 страницPoulos 2018 Subgrade PDFWeimar Garcia0% (1)
- Grade 9 Algebra Common Core WorkbooksДокумент3 страницыGrade 9 Algebra Common Core WorkbooksLindaОценок пока нет
- Flipped Classroom Lesson PlanДокумент17 страницFlipped Classroom Lesson PlanAnn PearlОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2: Inequalities and Absolute ValuesДокумент4 страницыChapter 2: Inequalities and Absolute Valueszan2812Оценок пока нет
- Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 6 Parent Tip SheetДокумент2 страницыEureka Math Grade 5 Module 6 Parent Tip Sheetapi-326893495100% (1)
- Ns 6grade 6 Math I Can Statements-Full PageДокумент4 страницыNs 6grade 6 Math I Can Statements-Full Pageapi-337275999Оценок пока нет
- Math Grade 7 Learning Competency K-12Документ4 страницыMath Grade 7 Learning Competency K-12Lino Garcia63% (8)
- Key Standards: Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Framework Student EditionДокумент2 страницыKey Standards: Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Framework Student Editionapi-302577842Оценок пока нет
- Instructional PlanДокумент8 страницInstructional Planapi-402220352Оценок пока нет
- 6th Grade Common Core Standards ChecklistДокумент19 страниц6th Grade Common Core Standards ChecklistKatt DuangmalaiОценок пока нет
- M6u7 Outline Overview 2016Документ20 страницM6u7 Outline Overview 2016api-302577842Оценок пока нет
- 6thgrade Math I Can StatementsДокумент155 страниц6thgrade Math I Can StatementsRhonda GrossОценок пока нет
- Ccss One Per PagДокумент39 страницCcss One Per PagjhooleyОценок пока нет
- Tnready Blueprint g6 MathДокумент9 страницTnready Blueprint g6 Mathapi-282869532Оценок пока нет
- Rational ExplorationsДокумент2 страницыRational Explorationsapi-302577842Оценок пока нет
- FKB 6thgrademath Utahmiddleschoolmathproject ch3 Student WorkbookДокумент130 страницFKB 6thgrademath Utahmiddleschoolmathproject ch3 Student WorkbookSelvi RamasamyОценок пока нет
- 6th Grade Math - Covering and Surrounding Unit PlanДокумент7 страниц6th Grade Math - Covering and Surrounding Unit PlanBecky JohnsonОценок пока нет
- Sixth Math StandardsДокумент3 страницыSixth Math Standardsapi-233655908Оценок пока нет
- Standards-K-12 6th GradeДокумент3 страницыStandards-K-12 6th Gradeapi-296039056Оценок пока нет
- 8 ThgradecurriculumДокумент5 страниц8 Thgradecurriculumapi-254290621Оценок пока нет
- Seventh Math StandardsДокумент3 страницыSeventh Math Standardsapi-233655908Оценок пока нет
- Math Grade 5 08 11Документ6 страницMath Grade 5 08 11api-246939068Оценок пока нет
- 7 Grade Math Instructional GuideДокумент7 страниц7 Grade Math Instructional Guideapi-323730622Оценок пока нет
- Integers and the Coordinate Plane Homework 23.1 AnswersДокумент7 страницIntegers and the Coordinate Plane Homework 23.1 Answersafmtnicya100% (1)
- Grade 6 Sorico Math Unit 3 3 2013-2014Документ4 страницыGrade 6 Sorico Math Unit 3 3 2013-2014api-233707670Оценок пока нет
- 7th Grade Unit C 14-15 MAFS V1 (Updated 5-24-14)Документ10 страниц7th Grade Unit C 14-15 MAFS V1 (Updated 5-24-14)Lizi BakradzeОценок пока нет
- Analysis of California Mathematics Standards To Common Core Standards-Grade 5Документ20 страницAnalysis of California Mathematics Standards To Common Core Standards-Grade 5establoid1169Оценок пока нет
- Iskl Grade 7 MathsДокумент5 страницIskl Grade 7 MathsMathiarasu MuthumanickamОценок пока нет
- Math Grade 4 08 11Документ7 страницMath Grade 4 08 11api-246939068Оценок пока нет
- Second Draft of 6-8 Benchmarks With Standards 8-28Документ9 страницSecond Draft of 6-8 Benchmarks With Standards 8-28justin fellerОценок пока нет
- aprilfl na c1 module 4 family letter checkedДокумент2 страницыaprilfl na c1 module 4 family letter checkedapi-707969415Оценок пока нет
- Numesros y DemostracionesДокумент5 страницNumesros y DemostracionesJESUS ANTONIO RAMOS MORONОценок пока нет
- CCSSI Math Standards 7Документ6 страницCCSSI Math Standards 7establoid1169Оценок пока нет
- Conceptual Foundations - The Number System Part 3Документ5 страницConceptual Foundations - The Number System Part 3api-256719324Оценок пока нет
- Math 7 Syllabus 2014-2015Документ5 страницMath 7 Syllabus 2014-2015api-266524097Оценок пока нет
- "I Can" Common Core!: 6th Grade MathДокумент6 страниц"I Can" Common Core!: 6th Grade Mathapi-303193556Оценок пока нет
- 6th Grade Math Common Core I Can StatementsДокумент6 страниц6th Grade Math Common Core I Can Statementsapi-233930784Оценок пока нет
- Syllabus BBA Entry Test Math PortionДокумент6 страницSyllabus BBA Entry Test Math PortionSyedMaazAliОценок пока нет
- CcssДокумент10 страницCcssapi-2372294750% (1)
- I Can Math 6Документ6 страницI Can Math 6api-365969613Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 2 - Graphing Rational Numbers On A Number LineДокумент9 страницLesson 2 - Graphing Rational Numbers On A Number Linehlmvuong123Оценок пока нет
- Stage 9 Maths Curriculum Framework 2018 (Checkpoint)Документ4 страницыStage 9 Maths Curriculum Framework 2018 (Checkpoint)Mahmoud SalaheldinОценок пока нет
- Fifthgradeunit 2Документ2 страницыFifthgradeunit 2api-264223290Оценок пока нет
- Grade 8 MathxДокумент5 страницGrade 8 Mathxapi-2542992270% (1)
- Mathematics LO Only 0862 - tcm143-592642Документ9 страницMathematics LO Only 0862 - tcm143-592642YiFeiОценок пока нет
- 2nd Quarter Math SkillsДокумент5 страниц2nd Quarter Math Skillsapi-93111231Оценок пока нет
- Working Towards Level 5a: Solving ProblemsДокумент3 страницыWorking Towards Level 5a: Solving ProblemsNicola WardlawОценок пока нет
- Math Grade 3 08 11Документ6 страницMath Grade 3 08 11api-246939068Оценок пока нет
- 6th Grade Math Curriculum MapДокумент6 страниц6th Grade Math Curriculum Mapapi-109360342Оценок пока нет
- Unit A9Документ5 страницUnit A9mstudy123456Оценок пока нет
- CONTENT AREA: Mathematics GRADE LEVEL: Grade 10/high School (HS)Документ17 страницCONTENT AREA: Mathematics GRADE LEVEL: Grade 10/high School (HS)Jaysa Avila SumagaysayОценок пока нет
- Analytic Geometry OverviewДокумент8 страницAnalytic Geometry Overviewsimonjohn spanglerОценок пока нет
- Math StandardsДокумент28 страницMath Standardsapi-312297693Оценок пока нет
- Grade 6 Curriculum MapДокумент6 страницGrade 6 Curriculum Mapapi-260971765Оценок пока нет
- Precalculus Standards StudentДокумент6 страницPrecalculus Standards Studentapi-349359257Оценок пока нет
- M6u7 Parent Letter 2017Документ3 страницыM6u7 Parent Letter 2017api-374154554Оценок пока нет
- Es Table Grade 6 Pba Mya For Parcc FinalДокумент8 страницEs Table Grade 6 Pba Mya For Parcc Finalapi-115680157Оценок пока нет
- K-12 Math Crosswalks Algebra IДокумент17 страницK-12 Math Crosswalks Algebra Iestabloid1169Оценок пока нет
- Melaniemath Term3lessonplan-4Документ7 страницMelaniemath Term3lessonplan-4api-302769288Оценок пока нет
- FunctionsДокумент44 страницыFunctionsSudhakar Chollangi100% (1)
- Unit 5 MapДокумент2 страницыUnit 5 Mapapi-256719324Оценок пока нет
- Gse Math Unit 5Документ108 страницGse Math Unit 5api-256719324Оценок пока нет
- Unit 3 MapДокумент1 страницаUnit 3 Mapapi-256719324Оценок пока нет
- Unit 6 MapДокумент2 страницыUnit 6 Mapapi-256719324Оценок пока нет
- Gse Math Unit 6Документ80 страницGse Math Unit 6api-256719324Оценок пока нет
- Unit 4 MapДокумент2 страницыUnit 4 Mapapi-256719324Оценок пока нет
- Gse Math Unit 4Документ79 страницGse Math Unit 4api-256719324Оценок пока нет
- Gse Math Unit 2Документ79 страницGse Math Unit 2api-256719324Оценок пока нет
- Unit 2 MapДокумент2 страницыUnit 2 Mapapi-256719324Оценок пока нет
- Unit 1 MapДокумент2 страницыUnit 1 Mapapi-256719324Оценок пока нет
- Worth County Middle School 6 Grade GSE Math Course Mapping (July 2015)Документ2 страницыWorth County Middle School 6 Grade GSE Math Course Mapping (July 2015)api-256719324Оценок пока нет
- 6th Math Comprehensive Course OverviewДокумент29 страниц6th Math Comprehensive Course Overviewapi-256719324Оценок пока нет
- Gse Mathematics-Glossary-K-12Документ10 страницGse Mathematics-Glossary-K-12api-256719324Оценок пока нет
- Conceptual Foundations Expressions and InequalitiesДокумент2 страницыConceptual Foundations Expressions and Inequalitiesapi-256719324Оценок пока нет
- Conceptual Foundations - GeometryДокумент5 страницConceptual Foundations - Geometryapi-256719324Оценок пока нет
- Conceptual Foundations Expressions and InequalitiesДокумент2 страницыConceptual Foundations Expressions and Inequalitiesapi-256719324Оценок пока нет
- Conceptual Foundations - The Number System Part 3Документ5 страницConceptual Foundations - The Number System Part 3api-256719324Оценок пока нет
- Ratio Conceptual FoundationsДокумент5 страницRatio Conceptual Foundationsapi-256719324Оценок пока нет
- DEB-TEL-451-2017-206-PPR-M.Sc. (Master of Science) MathematicsДокумент98 страницDEB-TEL-451-2017-206-PPR-M.Sc. (Master of Science) MathematicsFardeenОценок пока нет
- Magnificent Magnitude SeДокумент12 страницMagnificent Magnitude Seapi-261894355Оценок пока нет
- L No 01Документ38 страницL No 01Annas Equity AnalystОценок пока нет
- Mat111 ComplexДокумент33 страницыMat111 ComplexUb UsoroОценок пока нет
- p-Adic Numbers ProjectДокумент51 страницаp-Adic Numbers ProjectAnjali SinghОценок пока нет
- Ch01 - Se Chapter 1 SummaryДокумент13 страницCh01 - Se Chapter 1 SummaryGeorgeОценок пока нет
- Complex Numbers TopicalДокумент11 страницComplex Numbers TopicalBurhan AzharОценок пока нет
- Mathematics EBE 2022 - 2023 - C01Документ18 страницMathematics EBE 2022 - 2023 - C01anna spinelliОценок пока нет
- Complex Numbers ExplainedДокумент47 страницComplex Numbers Explainedpja752Оценок пока нет
- Functions ReviewДокумент13 страницFunctions ReviewAntonio DionisioОценок пока нет
- Absolute Value FunctionsДокумент8 страницAbsolute Value Functionsapi-357579360Оценок пока нет
- Modulus and TransformationsДокумент55 страницModulus and TransformationsDaLilSPОценок пока нет
- MathematicsДокумент167 страницMathematicsDeepak singhОценок пока нет
- Materi:nilai MutlakДокумент82 страницыMateri:nilai MutlaksudahdipakaiОценок пока нет
- BAUET Business Math CourseДокумент310 страницBAUET Business Math Coursesafin kaosarОценок пока нет
- Notes On Complex NumbersДокумент8 страницNotes On Complex NumbersPratip JanaОценок пока нет
- MTE 101 Engineering Mathematics 1 Chapter 1Документ11 страницMTE 101 Engineering Mathematics 1 Chapter 1Kenias NdunaОценок пока нет
- Advanced Algebra Homework AnswersДокумент8 страницAdvanced Algebra Homework Answersafetugndx100% (1)
- Table of Math SymbolsДокумент16 страницTable of Math SymbolsJohn LauОценок пока нет
- Complex Numbers GuideДокумент19 страницComplex Numbers GuideAndenet AshagrieОценок пока нет
- ENGG 2420C Complex Analysis and Differential Equations For EngineersДокумент15 страницENGG 2420C Complex Analysis and Differential Equations For EngineersAnonymous 0CSnf5Оценок пока нет
- Complex Algebra and The Complex PlaneДокумент25 страницComplex Algebra and The Complex Planevic12340590% (1)
- MA 105 Calculus of One and Several Variables: Prof. Inder K. RanaДокумент32 страницыMA 105 Calculus of One and Several Variables: Prof. Inder K. RanaKady PОценок пока нет
- Unit 9 Learning ResourcesДокумент4 страницыUnit 9 Learning Resourcesapi-318119777Оценок пока нет
- Function: Edexcel IAL A Level Pure Mathematics 3 Revision NotesДокумент28 страницFunction: Edexcel IAL A Level Pure Mathematics 3 Revision NotesPrince YugОценок пока нет