Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lec.18.pptx Tensor̘ Transforma2on̘ Of̘ Stresses̘
Загружено:
Salvadora1Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lec.18.pptx Tensor̘ Transforma2on̘ Of̘ Stresses̘
Загружено:
Salvadora1Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
10/23/11
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
I Main Topics
A Objec2ve
B Approach
C Deriva2on
D Example
10/23/11
GG303
17. Mohr Circle for Trac2ons
From King et al., 1994
(Fig. 11)
Coulomb stress change
caused by the Landers
rupture. The leT-lateral
ML=6.5 Big Bear rupture
occurred along doYed
line 3 hr 26 min aTer the
Landers main shock. The
Coulomb stress increase
at the future Big Bear
epicenter is 2.2-2.9 bars.
10/23/11
hYp://earthquake.usgs.gov/research/modeling/papers/landers.php
GG303
10/23/11
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
II Objec2ve
Transforma2on
Lecture 16
Lecture 18
Stresses to trac2ons
Stresses to stresses
Number of arbitrary planes 1 plane
2 perpendicular planes
Stresses accounted for
Normal and shear stresses
10/23/11
Normal stresses only
GG303
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
III Approach
Vectors
Tensors
vi = ai j v j
i j = ai k a j l kl
Number
of
subscripts
in
quan2ty
being
converted
Number
of
direc2on
cosines
in
equa2on
Equa2on
Key
concept
Total
value
of
each
stress
component
in
one
reference
frame
is
the
sum
of
the
weighted
contribu2ons
from
all
the
components
in
another
frame
10/23/11
GG303
10/23/11
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
V
Deriva2on
A
Descrip2on
of
terms
Term
Meaning
Ax, Ax, Ay Sides of prism
xx/xy
Normal/shear stress on Ax
yy/yx
Normal/shear stress on Ay
xx /xy Normal/shear stress on Ax
xx
Angle from x to x axis
xy
Angle from x to y axis
yx
Angle from y to x axis
yy
Angle from y to y axis
10/23/11
GG303
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
IV Deriva2on
B Contribu2on of xx to xx
w = dimensionless weigh2ng factor
x x = w(1) xx + w( 2 ) xy + w( 3) yx + w( 4 ) yy
A F (1) F (1) A F ( 2 ) Fy( 2 ) Ay Fx(3) Fx( 3) Ay Fx(4 ) Fy( 4 )
= x x(1) x + x x(2 )
+
+
Ax Ax Fx Ax Ax Fy Ax Ax Fx( 3) Ay Ax Fy( 4 ) Ay
2 F
3
10/23/11
x x = ax x ax x xx + ax x ax y xy + ax y ax x yx + ax y ax y yy
GG303
10/23/11
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
B Contribu2on of xx to xx
Start with the deni2on of a stress
vector:
1 xx(1) = Fx(1))/ Ax
First nd Fx(1) associated with xx
2 Fx(1) = xx Axx
Find Fx (1), the component of Fx(1) in
the x-direc2on
3 Fx (1) = Fx(1) cos xx
Now nd Ax in terms of Ax
Ax = Ax cos xx
4 Ax = Ax/cos xx
10/23/11
GG303
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
B Contribu2on of xx to xx (cont.)
3 Fx (1) = Fx(1) cos xx
4 4 Ax = Ax/cos xx
Now subs2tute:
5a xx (1) = Fx (1) / Ax
5b xx (1) = Fx(1) cos xx/ (Ax/cos xx)
5c xx (1) = cos xx cos xx (Fx(1)/ Ax)
5d xx (1) = axx axx xx
Weigh2ng factor w(1)
6 w(1) = axx axx
10/23/11
GG303
10/23/11
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
IV Deriva2on
C Contribu2on of xy to xx
w = dimensionless weigh2ng factor
x x = w(1) xx + w( 2 ) xy + w( 3) yx + w( 4 ) yy
A F (1) F (1) A F ( 2 ) Fy( 2 ) Ay Fx(3) Fx( 3) Ay Fx(4 ) Fy( 4 )
= x x(1) x + x x(2 )
+
+
Ax Ax Fx Ax Ax Fy Ax Ax Fx( 3) Ay Ax Fy( 4 ) Ay
2 F
3
10/23/11
x x = ax x ax x xx + ax x ax y xy + ax y ax x yx + ax y ax y yy
GG303
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
C Contribu2on of xy to xx
Start with the deni2on of a stress
vector:
1 xx(1) = Fx(2))/ Ax
First nd Fy(2) associated with xy
2 Fy(2) = xy Ax
Find Fx (2), the component of Fy(2) in
the x-direc2on
3 Fx (2) = Fy(2) cos xy
Now nd Ax in terms of Ax
Ax = Ax cos xx
4 Ax = Ax/cos xx
10/23/11
GG303
*
*
10
10/23/11
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
C Contribu2on of xy to xx (cont.)
3 Fx (2) = Fy(2) cos xy
4 Ax = Ax/cos xx
Now subs2tute:
5a xx (2) = Fx (2) / Ax
5b xx (2) = Fy(2) cos xy/ (Ax/cos xx)
5c xx (2) = cos xx cos xy (Fy(2)/Ax)
5d xx (2) = axx axy xy
Weigh2ng factor w(2)
6 w(2) = axx axy
10/23/11
GG303
11
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
IV Deriva2on
D Contribu2on of yx to xx
w = dimensionless weigh2ng factor
x x = w(1) xx + w( 2 ) xy + w( 3) yx + w( 4 ) yy
A F (1) F (1) A F ( 2 ) Fy( 2 ) Ay Fx(3) Fx( 3) Ay Fx(4 ) Fy( 4 )
= x x(1) x + x x(2 )
+
+
Ax Ax Fx Ax Ax Fy Ax Ax Fx( 3) Ay Ax Fy( 4 ) Ay
2 F
3
10/23/11
x x = ax x ax x xx + ax x ax y xy + ax y ax x yx + ax y ax y yy
GG303
12
10/23/11
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
D Contribu2on of yx to xx
Start with the deni2on of a stress
vector:
1 xx(3) = Fx(3))/ Ax
First nd Fx(3) associated with yx
2 Fx(3) = yx Ay
Find Fx(3), the component of Fx(3) in
the x-direc2on
3 Fx(3) = Fx(3) cos xx
Find Ay in terms of Ax
Ay = Ax cos xy
4 Ax = Ay/cos xy
10/23/11
*
*
GG303
13
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
D Contribu2on of yx to xx (cont.)
3 Fx (3) = Fx(3) cos xx
4 Ax = Ay/cos xy
Now subs2tute:
5a xx(3 ) = Fx (3) / Ax
5b xx(3 ) = Fx(3) cos xx/ (Ay/cos xy)
5c xx(3) = cos xy cos xx (Fx(3)/Ay)
5d xx(3) = axy axx yx
Weigh2ng factor w(3)
6 w(3) = axy axx
10/23/11
GG303
14
10/23/11
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
IV Deriva2on
E Contribu2on of yy to xx
w = dimensionless weigh2ng factor
x x = w(1) xx + w( 2 ) xy + w( 3) yx + w( 4 ) yy
A F (1) F (1) A F ( 2 ) Fy( 2 ) Ay Fx(3) Fx( 3) Ay Fx(4 ) Fy( 4 )
= x x(1) x + x x(2 )
+
+
Ax Ax Fx Ax Ax Fy Ax Ax Fx( 3) Ay Ax Fy( 4 ) Ay
2 F
3
10/23/11
x x = ax x ax x xx + ax x ax y xy + ax y ax x yx + ax y ax y yy
GG303
15
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
E Contribu2on of yy to xx
Start with the deni2on of a stress
vector:
1 xx(4) = Fx(4) /Ax
First nd Fy(4) associated with yy
2 Fy(4) = yy Ay
Find Fx(4), the component of Fx(4) in
the x-direc2on
3 Fx(4) = Fy(4) cos xy
Find Ay in terms of Ax
Ay = Ax cos xy
4 Ax = Ay/cos xy
10/23/11
GG303
*
*
16
10/23/11
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
E Contribu2on of yy to xx
3 Fx (4) = Fy(4) cos xy
4 Ax = Ay /cos xy
Now subs2tute:
5a xx(4) = Fx(4)/ Ax
5b xx(4) = Fy(4) cos xy/ (Ay/cos xy)
5c xx(4) = cos xy cos xy (Fy(4)/Ay)
5d xx(4) = axy axy yy
Weigh2ng factor w(4)
6 w(4) = axy axy
10/23/11
*
*
GG303
17
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
IV Deriva2on
F Formulas for xx, xy, yx, and yy
1 x x = ax x ax x xx + ax x ax y xy + ax y ax x yx + ax y ax y yy
2 x y = ax x ay x xx + ax x ay y xy + ax y ay x yx + ax y ay y yy
3 y x = ay x ax x xx + ay x ax y xy + ay y ax x yx + ay y ax y yy
4 y y = ay x ay x xx + ay x ay y xy + ay y ay x yx + ay y ay y yy
10/23/11
GG303
18
10/23/11
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
V Example
Find =
i j
given
ij
x x x y
y x y y
xx = 4MPa xy = 4MPa
=
yx = 4MPa yy = 4MPa
x x = 45 , x y = 45 , y x = 135 , y y = 45
10/23/11
GG303
19
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
V Example (cont.)
x x = ax x ax x xx + ax x ax y xy + ax y ax x yx + ax y ax y yy
x x = ( 2MPa ) + ( 2MPa ) + ( 2MPa ) + ( 2MPa ) = 8MPa
x y = ax x ay x xx + ax x ay y xy + ax y ay x yx + ax y ay y yy
x y = ( 2MPa ) + ( 2MPa ) + ( 2MPa ) + ( 2MPa ) = 0MPa
y x = ay x ax x xx + ay x ax y xy + ay y ax x yx + ay y ax y yy
y x = ( 2MPa ) + ( 2MPa ) + ( 2MPa ) + ( 2MPa ) = 0MPa
y y = ay x ay x xx + ay x ay y xy + ay y ay x yx + ay y ay y yy
y x = ( 2MPa ) + ( 2MPa ) + ( 2MPa ) + ( 2MPa ) = 0MPa
10/23/11
GG303
20
10
10/23/11
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
V Example (values in MPa)
xx = - 4
xn = - 4
xx = - 8
xn = - 8
xy = - 4
xs = - 4
xy = 0
xs = 0
yx = - 4
yn = + 4
yx = -0
ys = +0
yy = - 4
ys = -4
yy = 0
yn = 0
n
s
10/23/11
GG303
21
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
V Example
Matrix form
x x
y x
x y ax x
=
y y a y x
T
i j = [ a ] i j [ a ]
ax y xx
ay y yx
xy ax x
yy ay x
ax y
a y y
This expression is valid in 2D and 3D!
10/23/11
GG303
22
11
10/23/11
18. Tensor Transforma2on of Stresses
V Example
Matrix form/Matlab
i j = [ a ] i j [ a ]
>> sij = [-4 -4;-4 -4]
sij =
-4 -4
-4 -4
>> a=[sqrt(2)/2 sqrt(2)/2; -sqrt(2)/2 sqrt(2)/2]
a =
0.7071 0.7071
-0.7071 0.7071
>> sipjp = a*sij*a
sipjp =
-8.0000 0
0 0
10/23/11
GG303
23
12
Вам также может понравиться
- Met 1Документ46 страницMet 1Ahmed AbdelhamedОценок пока нет
- VIBRATION TITLEДокумент49 страницVIBRATION TITLEMark Oliver BernardoОценок пока нет
- Homework4 Revised Solutions 2005 PDFДокумент11 страницHomework4 Revised Solutions 2005 PDFFaridehОценок пока нет
- Aerospace Structures: Chapter 2 (Internal Loads)Документ32 страницыAerospace Structures: Chapter 2 (Internal Loads)John BrennanОценок пока нет
- 3D Stress Components and Principal StressesДокумент71 страница3D Stress Components and Principal Stressesiiscraja100% (1)
- Static Equilibrium: M M M F F FДокумент41 страницаStatic Equilibrium: M M M F F FINMEОценок пока нет
- Example of Two Dimensional ProblemДокумент27 страницExample of Two Dimensional ProblemCapt RezaОценок пока нет
- STRESS-MOHRДокумент5 страницSTRESS-MOHRavinashn1Оценок пока нет
- Yield Criteria in 3D PlasticityДокумент21 страницаYield Criteria in 3D Plasticity한종훈100% (1)
- DX E X A X P: Axial LoadsДокумент5 страницDX E X A X P: Axial LoadsvijshahОценок пока нет
- P4 Stress and Strain Transformation EquationsДокумент32 страницыP4 Stress and Strain Transformation Equationsadnankhan1988Оценок пока нет
- MD 2Документ33 страницыMD 2Wilfredo Nieves OsoriaОценок пока нет
- Plate ElementДокумент11 страницPlate ElementShamaОценок пока нет
- Spring / Mass Systems: KX DT X D MДокумент5 страницSpring / Mass Systems: KX DT X D Mmira0604Оценок пока нет
- Submerged Body, Center of Pressure and BuoyancyДокумент44 страницыSubmerged Body, Center of Pressure and BuoyancyAnish PathakОценок пока нет
- Calculus 2 Final REVISION QUIZ Feb 2021Документ4 страницыCalculus 2 Final REVISION QUIZ Feb 2021Elvis KadagiОценок пока нет
- Module 3: Analysis of Strain: Ohr'S Ircle For TrainДокумент26 страницModule 3: Analysis of Strain: Ohr'S Ircle For TrainVikas Singh SisodiaОценок пока нет
- AOD3Документ8 страницAOD3nalini7723Оценок пока нет
- CE 240 Soil Mechanics & Foundations: Stresses in A Soil Mass I (Das, Ch. 9)Документ27 страницCE 240 Soil Mechanics & Foundations: Stresses in A Soil Mass I (Das, Ch. 9)jorge.jimenezОценок пока нет
- MATH1151 Final Exam ReviewДокумент3 страницыMATH1151 Final Exam ReviewtravissaronОценок пока нет
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: This Examination Paper Consists of 5 PagesДокумент13 страницUniversiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: This Examination Paper Consists of 5 PagesCM Zain CrcoОценок пока нет
- Shaft Sizing Load Fatigue DeflectionДокумент16 страницShaft Sizing Load Fatigue DeflectionMachineryengОценок пока нет
- Aero 2 ExerciseДокумент5 страницAero 2 ExerciseHavner Scherrer CruzОценок пока нет
- Fundamental Mechanics of Materials Equations SummaryДокумент5 страницFundamental Mechanics of Materials Equations SummaryWong Jian MingОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Mechanics of Materials: Normal StressДокумент18 страницChapter 2 Mechanics of Materials: Normal StressPalak AriwalaОценок пока нет
- Plane Stress Vs StrainДокумент53 страницыPlane Stress Vs StrainWondwosen A. LakewОценок пока нет
- Prof. Abousleiman N. Younane Email: Yabousle@ou - Edu Office: SEC, Suite P119Документ57 страницProf. Abousleiman N. Younane Email: Yabousle@ou - Edu Office: SEC, Suite P119Christopher AyresОценок пока нет
- Uncracked Section Example: QuestionsДокумент8 страницUncracked Section Example: QuestionsRaju SkОценок пока нет
- Vibration Analysis of Forced Harmonic OscillationДокумент19 страницVibration Analysis of Forced Harmonic OscillationRakesh BhaskerОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Mechanics of Materials: Normal StressДокумент18 страницChapter 2 Mechanics of Materials: Normal StressManoj ManoharanОценок пока нет
- CE 14 Solid Mechanics (Lecture 10) PDFДокумент35 страницCE 14 Solid Mechanics (Lecture 10) PDFptdcaliguidОценок пока нет
- College of Engineering, Architecture and Technology:: Course Title: Course Number: Course DescriptionДокумент13 страницCollege of Engineering, Architecture and Technology:: Course Title: Course Number: Course DescriptionEdmil Jhon AriquesОценок пока нет
- 11Документ1 страница11sarah medjekdoudОценок пока нет
- 2413, Practice Exam 3, FA14Документ5 страниц2413, Practice Exam 3, FA14Matthew LuОценок пока нет
- ExpansionsДокумент6 страницExpansionsChristopher J CampbellОценок пока нет
- m7 REVIEW PDFДокумент6 страницm7 REVIEW PDFSkyezine Via Kit FoxОценок пока нет
- Mechanic of Solids: Stress and StrainДокумент28 страницMechanic of Solids: Stress and StrainLuis VarelaОценок пока нет
- Kuliah 5 Tegangan BDNGДокумент23 страницыKuliah 5 Tegangan BDNGBrian Halomoan Putra PardosiОценок пока нет
- Variation PlatesДокумент8 страницVariation Platesdebanik13498Оценок пока нет
- Dynamic Force AnalysisДокумент45 страницDynamic Force Analysismayur22785Оценок пока нет
- MEM503 Mechanics of Solids - II Syllabus BreakdownДокумент11 страницMEM503 Mechanics of Solids - II Syllabus BreakdownShubham SharmaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 - Stress TransformationДокумент48 страницChapter 5 - Stress TransformationLai Swee YongОценок пока нет
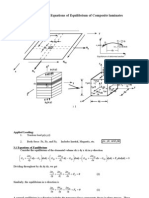
- 5.8.1 Governing Equations of Equilibrium of Composite LaminatesДокумент11 страниц5.8.1 Governing Equations of Equilibrium of Composite LaminatesStefano CanestrelliОценок пока нет
- One Degree of Freedom, Harmonically Excited Vibrations: Forced Harmonic VibrationДокумент15 страницOne Degree of Freedom, Harmonically Excited Vibrations: Forced Harmonic VibrationUmair Mirza100% (1)
- Reading FroudekrylovДокумент6 страницReading FroudekrylovAmphitrite O'ShopОценок пока нет
- Principal StressesДокумент15 страницPrincipal StressesTibebu MerideОценок пока нет
- Theories of Yielding PDFДокумент13 страницTheories of Yielding PDFJowesh Avisheik GoundarОценок пока нет
- Numerical Differentiation: X X X H X H X HДокумент19 страницNumerical Differentiation: X X X H X H X HDini AryantiОценок пока нет
- Logical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeОт EverandLogical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeОценок пока нет
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsОт EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsОценок пока нет
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)От EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Оценок пока нет
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesОт EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesОценок пока нет
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankОт EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- (MVS) Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Occurrence ModellДокумент15 страниц(MVS) Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Occurrence ModellSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- Geo Kids Field BookДокумент7 страницGeo Kids Field BookSalvadora1100% (1)
- Geology Book PDFДокумент54 страницыGeology Book PDFprimesamОценок пока нет
- (MVS) ExhalitesДокумент9 страниц(MVS) ExhalitesSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- (MVS) Petrology of Associated Igneous RocksДокумент36 страниц(MVS) Petrology of Associated Igneous RocksSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- (MVS) Exploration-Resource Assessment GuidesДокумент14 страниц(MVS) Exploration-Resource Assessment GuidesSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- (MVS) Knowledge Gaps and Future Research DirectionsДокумент7 страниц(MVS) Knowledge Gaps and Future Research DirectionsSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- (MVS) Geoenvironmental FeaturesДокумент21 страница(MVS) Geoenvironmental FeaturesSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- (MVS) Geochemical CharacteristicsДокумент23 страницы(MVS) Geochemical CharacteristicsSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- (MVS) Petrology of Metamorphic Rocks Associated With Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide DepositsДокумент14 страниц(MVS) Petrology of Metamorphic Rocks Associated With Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide DepositsSalvadora1100% (1)
- (MVS) Hypogene Ore CharacteristicsДокумент14 страниц(MVS) Hypogene Ore CharacteristicsSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- (MVS) Theory of Deposit FormationДокумент15 страниц(MVS) Theory of Deposit FormationSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- (MVS) Petrology of Sedimentary Rocks Associated With Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide DepositsДокумент11 страниц(MVS) Petrology of Sedimentary Rocks Associated With Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide DepositsSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- (MVS) Weathering ProcessesДокумент11 страниц(MVS) Weathering ProcessesSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- (MVS) Supergene Ore and Gangue CharacteristicsДокумент9 страниц(MVS) Supergene Ore and Gangue CharacteristicsSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- (MVS) Physical Volcanology of Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide DepositsДокумент40 страниц(MVS) Physical Volcanology of Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide DepositsSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- Hydrothermal AlterationДокумент16 страницHydrothermal AlterationSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- (MVS) Historical Evolution of Descriptive and Genetic Knowledge and ConceptsДокумент10 страниц(MVS) Historical Evolution of Descriptive and Genetic Knowledge and ConceptsSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- (MVS) Regional EnvironmentДокумент28 страниц(MVS) Regional EnvironmentSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- (MVS) Geophysical Characteristics of Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide DepositsДокумент19 страниц(MVS) Geophysical Characteristics of Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide DepositsSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- (MVS) IntroductionДокумент8 страниц(MVS) IntroductionSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- (MVS) Deposit Type and Associated CommoditiesДокумент12 страниц(MVS) Deposit Type and Associated CommoditiesSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- Lec.26.2012.pptx OPENING-MODE FRACTURES (JOINTS AND DIKES)Документ20 страницLec.26.2012.pptx OPENING-MODE FRACTURES (JOINTS AND DIKES)Salvadora1Оценок пока нет
- Faults (II) : - Slip Along Faults - Structure Along FaultsДокумент20 страницFaults (II) : - Slip Along Faults - Structure Along FaultsSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- Lec.31.Recap - PPTX Structural Geology RecapДокумент9 страницLec.31.Recap - PPTX Structural Geology RecapSalvadora1Оценок пока нет
- Lec.28b.pptx Folds (II)Документ13 страницLec.28b.pptx Folds (II)Salvadora1Оценок пока нет
- Lec.30a.pptx Folds (III)Документ10 страницLec.30a.pptx Folds (III)Salvadora1Оценок пока нет
- Lec.27.pptx Folds (I)Документ11 страницLec.27.pptx Folds (I)Salvadora1Оценок пока нет
- Research on Revitalizing Urban Voids through Public SpacesДокумент74 страницыResearch on Revitalizing Urban Voids through Public SpacesGeetanjali Bhoite Chavan100% (1)
- Stre Okimi AДокумент73 страницыStre Okimi A2008Muhammad Rifaldi DirgantaraОценок пока нет
- Find Volume of a SphereДокумент6 страницFind Volume of a SpherehelioteixeiraОценок пока нет
- How To Build With CobДокумент33 страницыHow To Build With CobmandritsopoulosОценок пока нет
- Module 5 - BEJAR - ScriptДокумент7 страницModule 5 - BEJAR - Scriptrobejr2013Оценок пока нет
- EGD Objective Type Quiz Questions With HintsДокумент2 страницыEGD Objective Type Quiz Questions With Hintsvipsdgr850% (2)
- Test09 Eoc Geometry ReducedДокумент32 страницыTest09 Eoc Geometry Reducedkristymadimike0% (1)
- Precalculus Enhanced With Graphing Utilities 6Th Edition Sullivan Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFДокумент67 страницPrecalculus Enhanced With Graphing Utilities 6Th Edition Sullivan Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFkevahanhksf100% (8)
- Weaving Architecture: A Study of Women's Role in The VernacularДокумент13 страницWeaving Architecture: A Study of Women's Role in The Vernaculartwentymunoz100% (1)
- Bonding BB3Документ4 страницыBonding BB3DeveshОценок пока нет
- Nonlinear Dynamics-And-Chaos-StrogatzДокумент9 страницNonlinear Dynamics-And-Chaos-Strogatzali.sahebiОценок пока нет
- 6 Freefall 161127184900Документ13 страниц6 Freefall 161127184900CHELCEE C. ENARIOОценок пока нет
- Prac 108A Midterm PDFДокумент2 страницыPrac 108A Midterm PDFSean SullivanОценок пока нет
- Spatial ThinkingДокумент11 страницSpatial ThinkingMicky AjaОценок пока нет
- 7 Maths NCERT Exemplar Chapter 6Документ36 страниц7 Maths NCERT Exemplar Chapter 6Ramesh rajОценок пока нет
- Ch3 Study GuideДокумент7 страницCh3 Study GuideqwertyОценок пока нет
- CXC MATHS Formula SheetДокумент7 страницCXC MATHS Formula SheetEric D Medeci100% (1)
- IKconv 2Документ10 страницIKconv 2Chiranjib ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- Curriculum Map Math 7+ 16-17Документ1 страницаCurriculum Map Math 7+ 16-17st72136Оценок пока нет
- Third Quarter ActivityДокумент39 страницThird Quarter Activityeunica_dolojanОценок пока нет
- Related Rates - SolutionsДокумент12 страницRelated Rates - SolutionsMegan Morse100% (1)
- Curvilinear Motion ComponentsДокумент28 страницCurvilinear Motion ComponentsMohamed DamraОценок пока нет
- Solar Glare Hazard Analysis Tool (SGHAT) Technical Reference ManualДокумент15 страницSolar Glare Hazard Analysis Tool (SGHAT) Technical Reference ManualDanny Sánchez YánezОценок пока нет
- Practice Test 14-Mathematical AptitudeДокумент12 страницPractice Test 14-Mathematical AptituderajatguptОценок пока нет
- Kinema TikДокумент29 страницKinema TikZinger IqraОценок пока нет
- RCT Da CostaДокумент6 страницRCT Da CostaWilldauany SilvaОценок пока нет
- B.voc Interior Design SyllabusДокумент37 страницB.voc Interior Design SyllabusYashmitaОценок пока нет
- Clothes at Rest: Elements For A Sociology of The Wardrobe Saulo B. CwernerДокумент14 страницClothes at Rest: Elements For A Sociology of The Wardrobe Saulo B. Cwernerroroism50% (2)
- B Motion in A Straight LineДокумент24 страницыB Motion in A Straight Linef20230069Оценок пока нет
- Grant - Much Ado About NothingДокумент471 страницаGrant - Much Ado About NothingJuan Salto100% (1)