Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
ARF Pathophysiology
Загружено:
kathy100%(9)100% нашли этот документ полезным (9 голосов)
10K просмотров2 страницыThis is a general schematic diagram made by my schoolmates during our ORAL REVALIDA...
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOC или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis is a general schematic diagram made by my schoolmates during our ORAL REVALIDA...
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC или читайте онлайн в Scribd
100%(9)100% нашли этот документ полезным (9 голосов)
10K просмотров2 страницыARF Pathophysiology
Загружено:
kathyThis is a general schematic diagram made by my schoolmates during our ORAL REVALIDA...
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
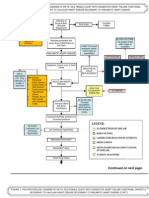
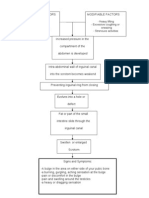
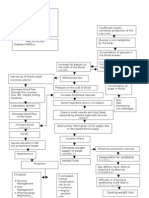
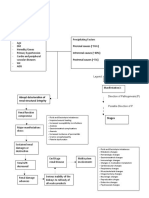
Predisposing Factors Acute Renal Failure Precipitating Factors
- Age - Diabetic nephropathy
- Sex - Glomerulonephritis
- Race - Renal Obstruction
- Cardiovascular
Disorders
Decreased blood flow to the renal arteries
Release of rennin by the juxtaglomerular apparatus
Renin enters the blood stream
Conversion of angiotensinogen in the liver to
angiotensin I
Angiotensinogen I passes through the lung
capillaries
ACE in the Lung capillaries converts Angiotensin I
to Angiotensin II (potent vasoconstrictor)
VASOCONSTRICTION Release of Aldosterone
in the adrenal glands
Sodium retention
Increase Plasma volume
Increase BLOOD PRESSURE
Signs and Symptoms:
Decrease Tissue Perfusion - Decrease Urine output
- Increase BUN
- Increase Serum
Unable to excrete metabolic waste Creatinine
- Edema
- Hypertension
If TREATED: If Not TREATED:
- Dialysis
- Antihypertensive Meds
- Diuretics
- etc.
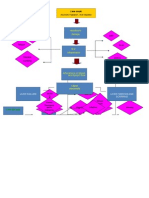
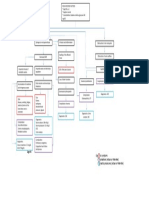
Good Prognosis/ Poor Prognosis Recurrent ARF
(It depends on the patient’s
Coping abilities)
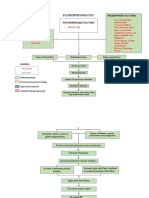
Further damage to the glomeruli
Hypertrophy of the remaining
healthy glomeruli
A number of the hyperthrophied
glomeruli dies
Signs and Symptoms:
- Nocturia
- fatigue
Renal Impairment (40-50%
- lassitude
remaining GFR)
- anorexia
- uremia
Further stimulation of RAAS
(rennin angiotensin aldosterone
system)
Further damage occurs
Signs and Symptoms:
- Muscle cramps
- hypereflexia Renal Insufficiency
- seizure (20-40% remaining GFR)
- nausea and vomiting
- uremic frost
- pruritus
Renal Failure
(10-20% remaining GFR)
ESRD
DEATH
Вам также может понравиться
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Acute Renal Failurekristel_nicole18yaho100% (3)
- Pathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)Документ3 страницыPathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)marshmalou86% (7)
- Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseДокумент3 страницыPrecipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseGrace Jane DionaldoОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Acute Renal Failuresugarmontejo67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)Документ1 страницаPathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)rexale ria100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CKDДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology CKDReymon Mary Janine100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsReina Samson0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of NephrosclerosisДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of NephrosclerosisJessica Damasen Caballero0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryДокумент4 страницыPathophysiology of Acute Kidney Injurymariaclaramutya100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (10)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramДокумент3 страницыChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramJake CaballoОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of HCVDДокумент5 страницPathophysiology of HCVDNicolne Lorraine100% (1)
- Acute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyДокумент2 страницыAcute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyJai - HoОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology ESRDДокумент9 страницPathophysiology ESRDJaye DangoОценок пока нет
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramДокумент3 страницыChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic Diagramnursing concept maps100% (5)
- Diagram of Pathophysiology CancerДокумент5 страницDiagram of Pathophysiology CancerKristaMaeC.Lazo0% (3)
- Hypertension PathophysiologyДокумент2 страницыHypertension PathophysiologyJems60% (5)
- CKD PathoДокумент5 страницCKD PathoJohn MIchael AusaОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Liver CirrhosisДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Liver Cirrhosisgaelty100% (4)
- Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramДокумент3 страницыCongestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramJacinthaVanathayahОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureДокумент4 страницыPathophysiology of Heart FailureTiger Knee100% (2)
- Pathophysio CRF RevisedДокумент2 страницыPathophysio CRF Revisedroseanne18Оценок пока нет
- PatofkuДокумент3 страницыPatofkunisaaa88Оценок пока нет
- Myocardial Infarction: Nonmodifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsДокумент4 страницыMyocardial Infarction: Nonmodifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsHearty ArriolaОценок пока нет
- Acute GlomerulonephritisДокумент1 страницаAcute GlomerulonephritisTaz Bagul MutiОценок пока нет
- Nstemi PathoДокумент2 страницыNstemi PathoSheana TmplОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of AMLДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology of AMLjake251996100% (1)
- Acute Glomerulonephritis PathophysiologyДокумент4 страницыAcute Glomerulonephritis PathophysiologyJanica Marinas100% (3)
- Acute Glomerulonephritis PathophysiologyДокумент4 страницыAcute Glomerulonephritis PathophysiologyChester NicoleОценок пока нет
- CKD PathophysiologyДокумент1 страницаCKD Pathophysiologylloyd_santino67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Embolism (Loria.J)Документ2 страницыPathophysiology of Pulmonary Embolism (Loria.J)Justine Mae Loria0% (1)
- Acute Renal FailureДокумент13 страницAcute Renal FailureGlorianne Palor100% (2)
- C. Pathophysiology (Schematic Diagram) Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsДокумент2 страницыC. Pathophysiology (Schematic Diagram) Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsMarynette MapaОценок пока нет
- HCVD Cad Cva InfarctionДокумент2 страницыHCVD Cad Cva InfarctionMiguel Carlos Tacderan100% (1)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramДокумент3 страницыChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramMeine MheineОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failuretinayko100% (1)
- A Case Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseДокумент103 страницыA Case Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseLouella Mae CoraldeОценок пока нет
- Chronic Renal FailureДокумент3 страницыChronic Renal FailureIvana Yasmin Bulandres100% (2)
- Hernia PathophysiologyДокумент1 страницаHernia PathophysiologyIvan Louise Fajardo Maniquiz83% (6)
- Pathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisДокумент4 страницыPathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisCyrus Ortalla RobinОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaJake Caballo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Peptic Ulcer Disease: Pylori InfectionДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Peptic Ulcer Disease: Pylori InfectionJim Christian Ellaser100% (1)
- ARF PathoДокумент3 страницыARF PathoNikki RodrigoОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology CHFfinalДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology CHFfinaljacj2010Оценок пока нет
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Prepared by D. ChaplinДокумент53 страницыChronic Kidney Disease: Prepared by D. Chaplinmutia aОценок пока нет
- Essential Amino AcidДокумент1 страницаEssential Amino AcidKayki LouiseОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular Disorders Concept MapДокумент4 страницыCardiovascular Disorders Concept MapZairaОценок пока нет
- Cirrhosis Hepatic: DinadewisliДокумент47 страницCirrhosis Hepatic: DinadewisliwilmaОценок пока нет
- Full Name Reaction Catalyzed Tissue Sources Clinical SignificanceДокумент3 страницыFull Name Reaction Catalyzed Tissue Sources Clinical SignificanceCleo SalvadorОценок пока нет
- Drug Study: Assess AnginaДокумент3 страницыDrug Study: Assess Anginadeo_gratias14Оценок пока нет
- Renal Failure DefinisiДокумент4 страницыRenal Failure DefinisiLentinaОценок пока нет
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Документ7 страницPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Tiger Knee100% (3)
- PathoДокумент1 страницаPathoRhabdoОценок пока нет
- 5.06 - HypertensionДокумент3 страницы5.06 - HypertensionJason JungОценок пока нет
- Genitourinary System: Renal FailureДокумент6 страницGenitourinary System: Renal FailureEn ConejosОценок пока нет
- Pharmacologic Management of HypertensionДокумент8 страницPharmacologic Management of HypertensionL2 - MAKILALA, Zion joy B.Оценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology - ESRDДокумент5 страницPathophysiology - ESRDheiyu100% (3)
- Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorДокумент2 страницыPredisposing Factor Precipitating FactorkamotenikimiОценок пока нет
- conceptmap-DIABETES MELLITUSДокумент8 страницconceptmap-DIABETES MELLITUSDonnabell DayudayОценок пока нет
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) : Volume Depletion VascularДокумент7 страницAcute Kidney Injury (AKI) : Volume Depletion VascularJennyu YuОценок пока нет
- Abruptio Placenta PathophysiologyДокумент4 страницыAbruptio Placenta Pathophysiologyjamie carpioОценок пока нет
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- HR Report FinalДокумент16 страницHR Report FinalkathyОценок пока нет
- The Three Musketeers by Alexandre DumasДокумент729 страницThe Three Musketeers by Alexandre DumasBooks100% (5)
- Placenta Previa PathophysiologyДокумент1 страницаPlacenta Previa Pathophysiologykathy85% (20)
- DIC PathophysiologyДокумент1 страницаDIC Pathophysiologykathy100% (1)
- Liver CirrhosisДокумент76 страницLiver Cirrhosiskathy100% (2)
- Substance DependenceДокумент157 страницSubstance DependencekathyОценок пока нет
- CP On OsteomyelitisДокумент147 страницCP On Osteomyelitiskathy50% (2)
- ER PowerpointДокумент144 страницыER Powerpointkathy100% (1)
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus PathophysiologyДокумент8 страницSystemic Lupus Erythematosus Pathophysiologykathy92% (24)
- CP On Pre-EclampsiaДокумент152 страницыCP On Pre-Eclampsiakathy100% (2)
- Guillain Barre Syndrome PathophysiologyДокумент4 страницыGuillain Barre Syndrome Pathophysiologykathy100% (13)
- CP-Guillain Barre SyndromeДокумент35 страницCP-Guillain Barre Syndromekathy60% (5)
- CHNДокумент59 страницCHNkathy100% (1)
- THESIS in NURSINGДокумент47 страницTHESIS in NURSINGkathy85% (40)
- CP Placenta PreviaДокумент95 страницCP Placenta Previakathy60% (5)
- CP On Breast CancerДокумент100 страницCP On Breast Cancerkathy50% (2)
- CP On Calculous CholelithiasisДокумент102 страницыCP On Calculous Cholelithiasiskathy100% (3)
- CVAДокумент116 страницCVAkathy100% (1)
- CP On AmoebiasisДокумент77 страницCP On Amoebiasiskathy100% (1)
- Unidirctional Anti Covid-19 Gate Using Motion SensorДокумент45 страницUnidirctional Anti Covid-19 Gate Using Motion SensorMuhammad SalmanОценок пока нет
- Diabetes in PregnancyДокумент5 страницDiabetes in PregnancyDoxo RubicinОценок пока нет
- JPMM 18 (2) OBrienДокумент15 страницJPMM 18 (2) OBriensjfindcОценок пока нет
- First Draft Code of Ethics For Midwives in EthiopiaДокумент32 страницыFirst Draft Code of Ethics For Midwives in Ethiopiamiadjafar463Оценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент14 страницDrug StudyCj LowryОценок пока нет
- The Role of Advertising in High-Tech Medical Procedures: Evidence From Robotic SurgeriesДокумент79 страницThe Role of Advertising in High-Tech Medical Procedures: Evidence From Robotic SurgeriesEve AthanasekouОценок пока нет
- Transgenic AnimaliaДокумент4 страницыTransgenic AnimaliaGalino Julia Cristine A.Оценок пока нет
- Script For OrientationДокумент2 страницыScript For OrientationAngela CudiaОценок пока нет
- Pet Food 2Документ73 страницыPet Food 2AB100% (1)
- Behavior and Social SciencesДокумент10 страницBehavior and Social SciencesRoxana Alexandra BogosОценок пока нет
- A Study On Knowledge and Practice of Mothers of Under-Five ChildrenДокумент6 страницA Study On Knowledge and Practice of Mothers of Under-Five ChildrenRirin PurbaОценок пока нет
- MainДокумент10 страницMainAnna SamsudinОценок пока нет
- Formula For Essiac Tea (Cancer)Документ12 страницFormula For Essiac Tea (Cancer)paulxe100% (5)
- Pharmacology, Pathology, Genetics: QP Code: BNN203Документ1 страницаPharmacology, Pathology, Genetics: QP Code: BNN203Mamta KumariОценок пока нет
- Jpog August 2013 IdДокумент51 страницаJpog August 2013 IdHasyim PurwadiОценок пока нет
- PNDT Act RulesДокумент32 страницыPNDT Act RulesVeerendra BaliОценок пока нет
- Formulating An Effective Response - A Structured ApproachДокумент22 страницыFormulating An Effective Response - A Structured ApproachMelo MedecieloОценок пока нет
- Stroke:: What Should Nurses Need To Know About Stroke?Документ68 страницStroke:: What Should Nurses Need To Know About Stroke?Suci Aning TОценок пока нет
- Cl2 Material Safety Data SheetДокумент11 страницCl2 Material Safety Data SheetChristian CoboОценок пока нет
- Personal StatementДокумент1 страницаPersonal StatementTaiwo Oyeniyi100% (2)
- Bài Kiểm Tra Thường Xuyên Lần 2Документ3 страницыBài Kiểm Tra Thường Xuyên Lần 2Hoctienganh HhОценок пока нет
- Intensive Care Management of The Head Injured Patient: Review ArticleДокумент14 страницIntensive Care Management of The Head Injured Patient: Review ArticlerickyGKОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 4: Modifiable Risk Factors of Lifestyle Diseases: SmokingДокумент4 страницыCHAPTER 4: Modifiable Risk Factors of Lifestyle Diseases: SmokingShimah100% (2)
- Summary Notes - Topic 9 Transport in Animals - CIE Biology IGCSEДокумент5 страницSummary Notes - Topic 9 Transport in Animals - CIE Biology IGCSEMadhan Reddy SuddalaОценок пока нет
- Speech by Deputy Minister Mhaule at Media Briefing 15 January 2021.finalДокумент5 страницSpeech by Deputy Minister Mhaule at Media Briefing 15 January 2021.finaleNCA.comОценок пока нет
- Cell DivisionДокумент28 страницCell DivisionPalagiri MadhuОценок пока нет
- Barneys Farm SeedsДокумент46 страницBarneys Farm SeedsPedro MarquesОценок пока нет
- PrepositionsДокумент10 страницPrepositionsZahoor Ul HaqОценок пока нет
- Drugs-1.ppt 0Документ22 страницыDrugs-1.ppt 0Esraa BahaaОценок пока нет
- Fitness Calculator Python ProjectДокумент12 страницFitness Calculator Python ProjectNishitha NeelamОценок пока нет