Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ultrasound: Receiving The Echoes
Загружено:
Zahid IbkОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ultrasound: Receiving The Echoes
Загружено:
Zahid IbkАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
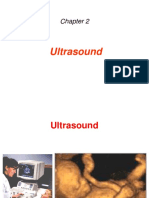
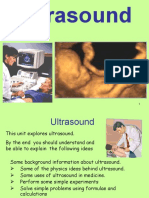
Ultrasound
A sound wave is typically produced by creating short, strong pulses of sound. The electrical wiring and
transducers are encased in a probe. The frequencies present in this sound wave can be anywhere between 2
and 13 MHz; well above the capabilities of the human ear. Any frequency above the capabilities of the
human ear is referred to as 'ultrasound'
The choice of frequency is a trade-off between the image spatial resolution and the penetration depth into the
patient. Higher frequencies give higher resolution images but dont penetrate as deeply into tissue.
To make sure the sound is transmitted efficiently into the body the transducer face has a rubber coating. In
addition, a water-based gel is placed between the probe and the patient's skin.
The sound wave is partially reflected from the interface between different tissues and returns to the
transducer. This return is an echo. Sound that is scattered by very small structures also produces echoes.
Receiving the echoes
The return of the sound wave to the transducer results in the same process that it took to send the sound
wave, just in reverse. The return sound wave vibrates the transducer's elements and turns that vibration into
electrical pulses that are sent from the probe to ultrasound scanner where they are processed and transformed
into a digital image.
Advantages
It is non-invasive, accurate and considered risk-free.
Does not result in damage to cells in the body.
Is updated continuously, real-time picture.
Image is available immediately
For pregnancies they are accurate at dating and give parents the opportunity to pick up any major physical
abnormalities
Disadvantages
Precise images are produced from near the surface of the body, but images from deeper into the body result
in progressively poorer resolution.
Relies on the expertise of the sonographer
For pregnancy ultrasound images, only after 18 weeks are scans likely to show anything but major problems
with the baby.
KEY POINTS THAT YOU ARE REQUIRED TO KNOW FOR YOUR EXAM:
HOW AN ULTRASOUND WORKS AND PRODUCES IMAGES
WHY AN ULTRASOUND IS POTENTIALLY BETTER THAN AN X-RAY
WHAT THE DISADVANTAGES OF AN ULTRASOUND ARE
Вам также может понравиться
- Lecture 14 Ultrasound (Additional Slides)Документ53 страницыLecture 14 Ultrasound (Additional Slides)fatima ghaniОценок пока нет
- Ultrasound PhysicsДокумент9 страницUltrasound PhysicsawansurfОценок пока нет
- Basic Principles of Ultrasound.: Dr/Abd Allah Nazeer. MDДокумент50 страницBasic Principles of Ultrasound.: Dr/Abd Allah Nazeer. MDAmeer MattaОценок пока нет
- Ultrasound WRDДокумент13 страницUltrasound WRDNaty SeyoumОценок пока нет
- Ultrasonography Machine: SR - No Topic Name Page NoДокумент30 страницUltrasonography Machine: SR - No Topic Name Page NoLakhan YogiОценок пока нет
- Lect 13 Ultrasound Machine ContinuesДокумент57 страницLect 13 Ultrasound Machine Continuesfatima ghaniОценок пока нет
- 2006 Physics NotesДокумент7 страниц2006 Physics NotesnealОценок пока нет
- B-Scan Part 1Документ41 страницаB-Scan Part 1Aisha TahirОценок пока нет
- UltrasoundДокумент78 страницUltrasoundAmeer MattaОценок пока нет
- Interaction of Ultrasounds Wave With MatterДокумент4 страницыInteraction of Ultrasounds Wave With MatterbjhbjhОценок пока нет
- Ultrasound in Medicine - p1Документ10 страницUltrasound in Medicine - p1husseinОценок пока нет
- UZVДокумент56 страницUZVGoran MaliОценок пока нет
- UltrasoundДокумент19 страницUltrasoundAli AliОценок пока нет
- A Hearing Aid Is An Electroacoustic Body Worn Apparatus Which Typically Fits in or Behind The WearerДокумент7 страницA Hearing Aid Is An Electroacoustic Body Worn Apparatus Which Typically Fits in or Behind The WearerBryan WilsonОценок пока нет
- Ostate TesticlesДокумент7 страницOstate Testiclesgreathari1998Оценок пока нет
- Basics of Ultrasound OKДокумент38 страницBasics of Ultrasound OKGloria TaneoОценок пока нет
- ULTRASOUNDДокумент14 страницULTRASOUNDpriyadharshini100% (1)
- SP 4f - Ultrasound (Notes)Документ2 страницыSP 4f - Ultrasound (Notes)nisalielisha rodrigoОценок пока нет
- Ultrasonic Imaging System: Hardik Tiwari (20SCE1010441) Aman Mittal (20SCSE1010518)Документ10 страницUltrasonic Imaging System: Hardik Tiwari (20SCE1010441) Aman Mittal (20SCSE1010518)Aman AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Us Mri Ct-ExamДокумент68 страницUs Mri Ct-ExamgetachewОценок пока нет
- Ultrasound BasicsДокумент12 страницUltrasound BasicsJ100% (1)
- Medical Physics Syllabus Notes - Daniel WilsonДокумент14 страницMedical Physics Syllabus Notes - Daniel WilsonPosclutoОценок пока нет
- Basic Physics UltrasoundДокумент106 страницBasic Physics Ultrasoundtasawwur zahoorОценок пока нет
- Biology ProjectДокумент13 страницBiology ProjectHome MarufОценок пока нет
- UltrasoundДокумент20 страницUltrasoundyechale tafereОценок пока нет
- Obstetric Ultrasound: What Is Obstetrical Ultrasound Imaging?Документ6 страницObstetric Ultrasound: What Is Obstetrical Ultrasound Imaging?Activity ManagerОценок пока нет
- Radiology Techniques - 1Документ10 страницRadiology Techniques - 1IraqiОценок пока нет
- Ultrasound BasicsДокумент2 страницыUltrasound Basicspiano543Оценок пока нет
- Venkanna - CH, M.Tech (E.I.), 104018Документ22 страницыVenkanna - CH, M.Tech (E.I.), 104018venkannacОценок пока нет
- Principle and Application of UltrasonographyДокумент6 страницPrinciple and Application of Ultrasonographyabhinav24624Оценок пока нет
- Martin (2015) - Physics of UltrasoundДокумент4 страницыMartin (2015) - Physics of Ultrasoundgatorfan786Оценок пока нет
- Basicsofultrasound 170807183128Документ145 страницBasicsofultrasound 170807183128Bunga FaridaОценок пока нет
- A Scan Biometery-PrintДокумент16 страницA Scan Biometery-PrintSadegh ShebaniОценок пока нет
- Ultrasound ImagingДокумент20 страницUltrasound ImagingSitanshu SatpathyОценок пока нет
- A Scan BiometryДокумент19 страницA Scan BiometryJeanna Salima100% (1)
- CM Principles of Ultrasound PPДокумент16 страницCM Principles of Ultrasound PPVũ Hoàng AnОценок пока нет
- .Prepare Patient For Abdominal Ultrasonography? . Preparing A Patient For Abdominal Ultrasonography Involves Several Steps ToДокумент21 страница.Prepare Patient For Abdominal Ultrasonography? . Preparing A Patient For Abdominal Ultrasonography Involves Several Steps Toss solutionsОценок пока нет
- Biomedical InstrumentationДокумент35 страницBiomedical Instrumentationfaizfrasat123Оценок пока нет
- Nama: Putu Deva Prihananta NIM: 18081001 Prodi: Teknik ElektromedikДокумент3 страницыNama: Putu Deva Prihananta NIM: 18081001 Prodi: Teknik ElektromedikDeva PrihanantaОценок пока нет
- Ultrasound 9.0Документ9 страницUltrasound 9.0Nikita GosineОценок пока нет
- Mark H. Apostadero, MDДокумент81 страницаMark H. Apostadero, MDYuan LiОценок пока нет
- Physics of UltarasoundДокумент195 страницPhysics of Ultarasoundhossam62683% (6)
- Samady Ultrasound Principles Tech Big Sky NotesДокумент76 страницSamady Ultrasound Principles Tech Big Sky NotesrayОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Ultrasound ImagingДокумент11 страницFundamentals of Ultrasound ImagingAryan Shukla100% (1)
- Basics of Ultrasound ImagingДокумент8 страницBasics of Ultrasound ImagingBMT100% (3)
- Practical Physics of UltrasoundДокумент31 страницаPractical Physics of UltrasoundJazib ShahidОценок пока нет
- Questions From Last Lecture ?: Is It RightДокумент39 страницQuestions From Last Lecture ?: Is It RightPirin Pin PinОценок пока нет
- Physics of UltrasoundДокумент4 страницыPhysics of Ultrasound{Phantom}100% (1)
- Physics Lab.Документ25 страницPhysics Lab.Hunter X HunterОценок пока нет
- D 50 483 491 PDFДокумент9 страницD 50 483 491 PDFlambanaveenОценок пока нет
- Doppler Basics: DR - Priyatamjee BussaryДокумент79 страницDoppler Basics: DR - Priyatamjee BussarydrsanndeepОценок пока нет
- Medical Physics - U6 Physics PresentationДокумент52 страницыMedical Physics - U6 Physics Presentationanmolz.ghОценок пока нет
- Introduction To The Physical Principles of Ultrasound Imaging and Doppler Peter N Burns PHDДокумент26 страницIntroduction To The Physical Principles of Ultrasound Imaging and Doppler Peter N Burns PHDCatarina Dos ReisОценок пока нет
- How Does Ultrasound Work?Документ7 страницHow Does Ultrasound Work?shishichanОценок пока нет
- Medical Physics Notes - Physics HSCДокумент29 страницMedical Physics Notes - Physics HSCBelinda ZhangОценок пока нет
- UltrasoundДокумент104 страницыUltrasoundlrp sОценок пока нет
- What Is General Ultrasound ImagingДокумент12 страницWhat Is General Ultrasound Imagingfatah.ozilОценок пока нет
- Ultra Sound IN Medical Imaging: Mohammad Amir Final Year MbbsДокумент46 страницUltra Sound IN Medical Imaging: Mohammad Amir Final Year MbbsArif Rahman WardhaniОценок пока нет
- Interferences and Types of ProbesДокумент48 страницInterferences and Types of ProbesyahyaОценок пока нет
- Physics - Chapter 12.1 - 12.3Документ6 страницPhysics - Chapter 12.1 - 12.3Zahid IbkОценок пока нет
- Centre of MassДокумент1 страницаCentre of MassZahid IbkОценок пока нет
- Notes On Activities For Teachers/ Technicians For Chapter 1: Activity 1.1Документ3 страницыNotes On Activities For Teachers/ Technicians For Chapter 1: Activity 1.1Zahid IbkОценок пока нет
- Monthly Test: Physics On Waves & ElectricityДокумент1 страницаMonthly Test: Physics On Waves & ElectricityZahid IbkОценок пока нет
- CT Scanning InfoДокумент1 страницаCT Scanning InfoZahid IbkОценок пока нет
- Physics Notes Zahid I. B. Khan: EchanicsДокумент6 страницPhysics Notes Zahid I. B. Khan: EchanicsZahid IbkОценок пока нет
- Label The EyeДокумент1 страницаLabel The EyeZahid IbkОценок пока нет
- Abraj Al-Bait Towers Makkah Saudi ArabiaДокумент19 страницAbraj Al-Bait Towers Makkah Saudi ArabiaZahid IbkОценок пока нет
- Question MechanicsДокумент5 страницQuestion MechanicsZahid IbkОценок пока нет
- Course Outline Linear AlgebraДокумент2 страницыCourse Outline Linear AlgebraZahid IbkОценок пока нет
- Md. Jahedur Rahman, SL# 19: District July August September October November DecemberДокумент1 страницаMd. Jahedur Rahman, SL# 19: District July August September October November DecemberZahid IbkОценок пока нет
- Mark Scheme Unit 2 (WPH02) June 2014Документ16 страницMark Scheme Unit 2 (WPH02) June 2014Zahid IbkОценок пока нет
- Mechanics BeamsДокумент27 страницMechanics BeamsZahid IbkОценок пока нет
- Solid MechanicsДокумент16 страницSolid MechanicsZahid IbkОценок пока нет