Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Design of Phenol Plant
Загружено:
api-292667997Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Design of Phenol Plant
Загружено:
api-292667997Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
ABC Corporations Phenol Production Plant:
Design and Economic Evaluation for 300,000 tons/yr
Group 21: Laura Bertrand, Brandon Burns, Amiel Kirtikar, Brandon Lorentz
Economics
Design Objective
ABC Corporation is looking for a cost-effective method of attaining 300,000 tons of phenol
per year as a raw material for their downstream resin production. Currently, phenol is
purchased at $0.64 per pound. Cumene, a raw material in phenol production, can be
obtainable internally for $0.60 per pound. Our technical assignment included designing a
phenol plant, estimating the production cost of phenol per pound, and making an
economically feasible decision for ABC Corporation
Process Overview
Capital Costs
Continuous Process Emissions:
Total Capital Investment (TCI): $271 MM
Total Installed Equipment Cost, MM $
Unit
Coolers, $7.6
Misc, $15.1
Oxidation Reactor
Vent
Reactors, $13.4
Waste
Phase
Waste Flow and Composition
Treatment
(lbmol/hr) (mole %)
Treatment Emission Disposal
Total: 4080
Gas
4%_Oxygen, 96%_Nitrogen
Trace Amounts:
Burning as fuel
Acetone, Cumene,
credit
Carbon Dioxide
Vent to
Atmosphere
Hydrogen
Exchangers, $36.6
Columns, $25.9
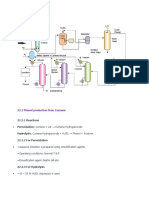
Streams of compressed air and pure cumene are fed into oxidation reactors where the
cumene is oxidized to cumene hydro peroxide (CHP) and a by-product di-methyl benzyl
alcohol (DMBA). Cumene in the vent from the reactors is recovered and recycled back into
the process.
Unreacted cumene, CHP and DMBA are then sent to a distillation column where cumene in
the distillate stream is recycled back to the oxidation reactors. In the bottoms, CHP, DMBA,
and any remaining cumene is then sent to a cleavage reactor. CHP is cleaved to form Phenol
and Acetone and DMBA reacts with the sulfuric acid catalyst in the cleavage reactor to form
alpha-methyl styrene (AMS) and water.
Acetone, water, cumene, AMS, and phenol are then sent through a separation train of
distillation columns to isolate each component. Isolated cumene is recycled back into the
oxidation reactors. AMS is hydrogenated back into cumene, which is also recycled back to
the oxidation reactor. The water stream is sent to a wastewater treatment facility. The byproduct acetone is cooled and stored for sale, and the final phenol product is cooled and
sent to the resins plant.
Column T-100
Partial Condenser
Vent
Hydrogenation
Reactor Vent
Cleavage Reactor
Catalyst and
Organic Waste
Column T-104
Bottoms Waste
Compressor, $16.9
Operating Costs
Total: 23
Gas
Trace Amounts:
Nitrogen
86%_Nitrogen, 12%_Cumene, Phenol, Acetone
Vent to
Atmosphere
2%_Oxygen
Total: 5
Gas
98%_Hydrogen, 2%_Cumene
Trace Amounts:
Burning as fuel
Water, Carbon
Vent to
AMS
credit
Dioxide
Atmosphere
Not Simulated
Solid
Aqueous Sulfuric and Organic
Water-Treatment Salts
Bacterial
process
Digestion
Acid Salts with Sodium Phenolate
Total: 44
Liquid
98%_Water, 2%_Cumene
Trace Amounts:
Water-Treatment Cooling Water
Acetone
process
Total Annual Operating Costs: $483 MM/year
Production Costs, MM$/year
Misc
,$38.6
BTCF,
$91.4
Major Safety Considerations
Utility Costs, MM$/year
Cooling Water,$3.7
Reactions
Misc, $2.3
Cleavage Reactor:
-Rapid CHP decomposition causing a
Runaway Exothermic Reaction
Refrigerant,$0.4
Hydrogenation Reactor:
-Flammability of Hydrogen resulting in explosion
Electricity,$3.5
Oxidation Reactor
Cleavage Reactor
(Main Reaction)
(Main Reaction)
(Side Reaction)
Health & Environment
(Side Reaction)
Utilities,
$46.7
Raw
Materials
(Cumene &
Hydrogen,
$306
Minor Safety Considerations
Steam,$36.9
Oxidation Air Compressor:
-Compressed Air Temperature below 600 F to prevent auto ignition of cumene
Economic Decision
Final Production Cost of Phenol: $0.73 per pound
CHEAPER to BUY Phenol
High Pressure Steam Reboiler:
-600 psi steam used in AMS/Phenol Distillation Column Reboiler
Oxidation Reactor Vent Composition:
-Oxidation reactor vent LOC with cumene is less than 6 mol %
Commercial Uses and Supply Chain of Phenol
Hydrogenation Reactor
Phenol is used in various products:
Simulation:
Epoxy Resins paint coatings
Polycarbonate plastics CDs and domestic electrical appliances
Nylon and Polyamide plastics carpets, nets, and clothing
Antioxidant in rubber manufacture
Intermediate to herbicides and insecticides
Manufacture of surfactants, detergents, and emulsifiers
Precursor to pharmaceuticals aspirin and chloraseptic
Yield of Phenol: 99 %
Benzene
Specifications:
Pressure of oxidation reactor = 80 psia
Temperature of oxidation reactor = 212F
Pressure of cleavage reactor = 14.7 psia
Temperature of oxidation reactor = 176F
Pressure of hydrogenation reactor = 110 psia
Temperature of oxidation reactor = 194F
99.9 % Purity of Acetone
99.99% Purity of Phenol
Various pressures for distillation columns
Phenolic Resins
Naphtha
Cumene
Propylene
Air
Propane
Natural gas
Naphtha
Crude Oil
Phenol
Hydrogen
Air
Water
Crude Oil
Вам также может понравиться
- Phenol ProductionДокумент9 страницPhenol ProductionPlant Design100% (1)
- Phenol Plant CostДокумент3 страницыPhenol Plant CostIntratec SolutionsОценок пока нет
- Production of Aniline From Ammonolysis of Phenol - 2010-CH-09,61,65,87Документ17 страницProduction of Aniline From Ammonolysis of Phenol - 2010-CH-09,61,65,87Shiraz Daud100% (3)
- CEMS Operating & Maintenance ManualДокумент71 страницаCEMS Operating & Maintenance ManualFahmi Ali100% (4)
- Phenol From CumeneДокумент2 страницыPhenol From Cumeneali100% (2)
- KBR PhenolДокумент2 страницыKBR Phenolstavros7100% (2)
- Phenol From Cuemen and TolueneДокумент9 страницPhenol From Cuemen and TolueneAnonymous RJkpep7D0rОценок пока нет
- AnilineДокумент1 страницаAnilineCherry Pearl MiparanumОценок пока нет
- AnilineДокумент2 страницыAnilineKPAC333100% (2)
- PET Production Technical ReportДокумент78 страницPET Production Technical ReportMiguel Eduardo Sanchez Ramos100% (1)
- Production of PhenolДокумент22 страницыProduction of PhenolShubhranshu Kathuria71% (7)
- Production of PhenolДокумент120 страницProduction of PhenolAlyxОценок пока нет
- Engineers Guide - Cumene Peroxidation Process For Phenol ProductionДокумент2 страницыEngineers Guide - Cumene Peroxidation Process For Phenol ProductionEdrian A. Mañalong100% (1)
- Fundamentals of MasstransferandkineticshydrogenationДокумент14 страницFundamentals of MasstransferandkineticshydrogenationRamandhaPrasetyaAdibrataОценок пока нет
- Polyvinylchloride — 2: Main Lectures Presented at the Second International Symposium on Polyvinylchloride, Lyon-Villeurbanne, France, 5 - 9 July 1976От EverandPolyvinylchloride — 2: Main Lectures Presented at the Second International Symposium on Polyvinylchloride, Lyon-Villeurbanne, France, 5 - 9 July 1976A. GuyotОценок пока нет
- Yellowing Behavior of TextilesДокумент8 страницYellowing Behavior of TextilesMohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- General Chemistry 1 2ND QuarterДокумент50 страницGeneral Chemistry 1 2ND QuarterJulienne Bigornia80% (5)
- Phenol PlantДокумент33 страницыPhenol PlantrakeshОценок пока нет
- Cumene To PhenolДокумент73 страницыCumene To Phenolvpsrpuch67% (3)
- Report BTPДокумент47 страницReport BTPvpsrpuchОценок пока нет
- Cumene To Phenol 2Документ73 страницыCumene To Phenol 2vpsrpuch0% (1)
- Side ReactionsДокумент22 страницыSide ReactionsAna Mariel VenturaОценок пока нет
- Production of Aniline by Reduction of Nitrobenzene: Group#2Документ26 страницProduction of Aniline by Reduction of Nitrobenzene: Group#2Arsal MaqboolОценок пока нет
- Presentation CumeneДокумент39 страницPresentation CumeneBis ChemОценок пока нет
- Presentation CumeneДокумент39 страницPresentation Cumeneممدوح الرويليОценок пока нет
- Market SurveyДокумент4 страницыMarket SurveyGenesis LowОценок пока нет
- Project: Design of A Reactor For The Aniline ProductionДокумент19 страницProject: Design of A Reactor For The Aniline ProductionLUIS ESTEBAN VÁSQUEZ CASTANEDAОценок пока нет
- Product Capsule Cumene/Phenol/Acetone: MarketworksДокумент7 страницProduct Capsule Cumene/Phenol/Acetone: MarketworksKevin L. BoyleОценок пока нет
- Methyl Methacrylate Plant CostДокумент3 страницыMethyl Methacrylate Plant CostIntratec Solutions50% (2)
- Project ReportДокумент12 страницProject ReportRabia SabirОценок пока нет
- Phenols in FuelДокумент12 страницPhenols in Fuelvzimak2355Оценок пока нет
- MEK in School SecondДокумент13 страницMEK in School Secondifiok100% (1)
- Cumene A PDFДокумент4 страницыCumene A PDFdanena88Оценок пока нет
- Phosgene-Free Route To Toluene DiisocyanateДокумент399 страницPhosgene-Free Route To Toluene DiisocyanateAhmed AliОценок пока нет
- Manufacture of Phenol From CumeneДокумент8 страницManufacture of Phenol From CumeneFabi OneОценок пока нет
- Direct Route To Phenol From Benzene PDFДокумент316 страницDirect Route To Phenol From Benzene PDFM Arslan AshrafОценок пока нет
- PresentationДокумент47 страницPresentationAsim FarooqОценок пока нет
- Types of Phenol Manufacturing ProcessДокумент4 страницыTypes of Phenol Manufacturing ProcessIsma AzraОценок пока нет
- CUMENEДокумент24 страницыCUMENEhiteshОценок пока нет
- C4 DerivativesДокумент2 страницыC4 DerivativesdaabgchiОценок пока нет
- Cumene ProductionДокумент26 страницCumene ProductionAMOGH JHANWARОценок пока нет
- CumeneДокумент5 страницCumeneNasmiyeth Rodriguez VittaОценок пока нет
- Production of Isopropyl Palmitate-Experimental StudiesДокумент12 страницProduction of Isopropyl Palmitate-Experimental Studiesikaw_3Оценок пока нет
- Economics of Aniline Production ProcessesДокумент4 страницыEconomics of Aniline Production ProcessesfdfОценок пока нет
- Propylene, Propylene Oxide and Isopropanol: Course: Chemical Technology (Organic) Module VIIДокумент12 страницPropylene, Propylene Oxide and Isopropanol: Course: Chemical Technology (Organic) Module VIImaheshОценок пока нет
- Benzene: Chemical Economics HandbookДокумент3 страницыBenzene: Chemical Economics HandbookMaría VásquezОценок пока нет
- Acrylic Acid - MohitДокумент42 страницыAcrylic Acid - MohitvickuОценок пока нет
- Chemical Kinetics On Thermal Decompositions of CumeneДокумент8 страницChemical Kinetics On Thermal Decompositions of CumeneMario Alonso Velasquez FlorezОценок пока нет
- Cumene DatasheetДокумент12 страницCumene DatasheetDiana BanuОценок пока нет
- 0910 4 AbsДокумент9 страниц0910 4 AbsEngr Muhammad AqibОценок пока нет
- Wasteless Economic Method of Production of Phenol and AcetoneДокумент14 страницWasteless Economic Method of Production of Phenol and AcetoneSiswand BIn Mohd AliОценок пока нет
- Maleic AnhydrideДокумент6 страницMaleic AnhydrideTechnologist ChemicalОценок пока нет
- Linear Alkylbenzene Detal ProcessДокумент1 страницаLinear Alkylbenzene Detal Processramirali100% (1)
- 1,3 ButadieneДокумент7 страниц1,3 ButadieneAbdalmoedAlaiashyОценок пока нет
- Production of IsopropanolДокумент9 страницProduction of IsopropanolJohanОценок пока нет
- 64788Документ35 страниц64788ghatak2100% (1)
- Carboxylic Ortho Acid Derivatives: Preparation and Synthetic Applications: Preparation and Synthetic ApplicationsОт EverandCarboxylic Ortho Acid Derivatives: Preparation and Synthetic Applications: Preparation and Synthetic ApplicationsОценок пока нет
- Acetone Reactor Design Complete ProjectДокумент29 страницAcetone Reactor Design Complete ProjectSabeeh Ahmed91% (11)
- Phenol 12Документ2 страницыPhenol 12binaywatchОценок пока нет
- Proceso: Lummus Application: Improved Technology To Produce Highest Quality Phenol andДокумент5 страницProceso: Lummus Application: Improved Technology To Produce Highest Quality Phenol andAdrian Copa JОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ4 страницыChapter 1miza adlinОценок пока нет
- Methanol From Natural Gas by ICI's FIMДокумент9 страницMethanol From Natural Gas by ICI's FIMFer MugrabiОценок пока нет
- Catalyst Catastrophes II: John Brightling and DR Mike RobertsДокумент12 страницCatalyst Catastrophes II: John Brightling and DR Mike Robertsvaratharajan g rОценок пока нет
- Schirmann 2001Документ18 страницSchirmann 2001Mencyn Michelle Kellie EbreoОценок пока нет
- Industrial ChemistryДокумент194 страницыIndustrial ChemistrySiti Mastura Abdul Rahman50% (2)
- The Environment Conservation Rules, 1997Документ49 страницThe Environment Conservation Rules, 1997Kawser Ahmed RaihanОценок пока нет
- Kidde Fire Systems Nitrogen Fire Protection System System DescriptionДокумент6 страницKidde Fire Systems Nitrogen Fire Protection System System DescriptionAbdel KoddousОценок пока нет
- Text Maam MarwiyahДокумент16 страницText Maam Marwiyahkhairunnisa P.O.V.PОценок пока нет
- Claude 3Документ139 страницClaude 3ndayizeyeyavan19Оценок пока нет
- Exemplar - Questions With Answer.Документ12 страницExemplar - Questions With Answer.Liveen .S100% (1)
- Shrink - and Expansion-Fit AnalysesДокумент3 страницыShrink - and Expansion-Fit AnalysesScribdUser11235Оценок пока нет
- How A Century of Ammonia Synthesis Changed The World: FeatureДокумент8 страницHow A Century of Ammonia Synthesis Changed The World: FeatureYuthish KhannaОценок пока нет
- Soil FertilityДокумент75 страницSoil FertilitymarkovitОценок пока нет
- Bronkhorst Manual EL FLOW SelectДокумент51 страницаBronkhorst Manual EL FLOW SelectcccirmusОценок пока нет
- Drying of TransformerДокумент9 страницDrying of TransformerL P KUSHWAHA100% (7)
- Atomic Structure and Amount of Substance QДокумент30 страницAtomic Structure and Amount of Substance Qlucylovesbooks6770Оценок пока нет
- Cross Ref 1Документ7 страницCross Ref 1Devendra KhadeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 05Документ39 страницChapter 05pdaga19691383Оценок пока нет
- Silicon Based Fuels For Space Flight: David Padanyi-Gulyas and Andras D. BodoДокумент6 страницSilicon Based Fuels For Space Flight: David Padanyi-Gulyas and Andras D. BodoBill M. SpragueОценок пока нет
- ChemEngineering 02 00019 v2Документ14 страницChemEngineering 02 00019 v2Amine HamaouiОценок пока нет
- Group2 and 7 RevisedДокумент46 страницGroup2 and 7 Revised123456Оценок пока нет
- Air PollutionДокумент7 страницAir PollutionAsif NawazОценок пока нет
- Doc316 53 01086 PDFДокумент8 страницDoc316 53 01086 PDFMarian AlviОценок пока нет
- Science 7 Module 2Документ32 страницыScience 7 Module 2Lilah BlairОценок пока нет
- AR700-68 - Compressed Gas StorageДокумент103 страницыAR700-68 - Compressed Gas StoragetorolsoОценок пока нет
- A Level Environmental Management NotesДокумент26 страницA Level Environmental Management Notescharumbirakimtontapiwa751Оценок пока нет
- Nitrogen CycleДокумент10 страницNitrogen CyclebellaОценок пока нет
- 6 P Block Elements PDFДокумент91 страница6 P Block Elements PDFShanmugapriya RaguramanОценок пока нет
- Chemical Reaction and EquationДокумент8 страницChemical Reaction and EquationTr Mazhar Punjabi100% (1)