Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Cells Study Guide
Загружено:
api-233748343Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cells Study Guide
Загружено:
api-233748343Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
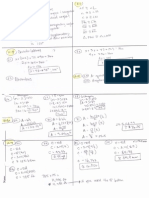
Name ___________________________________
Cells in Science
An Introduction: Chapter 2 (Lesson 1 and 2)
A summary of the chapter
Vocab Word
Chroma- (color)
Multi- (many)
organism
lens
magnification
microscope
Cell
Cell theory
Cell wall
Cell Membrane
Nucleus (control center)
Organelles
Chromatin
Nucleolus
Ribosomes
Cytoplasm
Mitochondria (powerhouses)
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Definition
Prefix that means color: chromatin, n. the genetic material in
the nucleus of a cell, that can be colored with dyes
Prefix that means many: multicellular: having many cells
Is a living thing.
Is a curved piece of glass or other transparent material that is
used to bend light.
This is the condition of things appearing larger than they are.
Is an instrument that makes small objects look larger.
Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living
things.
Is the widely accepted explanation of the relationship between
cells and living things:
All living things are composed of cells.
Cells are the basic units of structure and function in
living things.
All cells are produced from other cells.
The ridgid layer that surrounds the cells of plants and some other
organisms.
Controls which substances pass into and out of a cell.
Everything a cell needs, such as food particles, water, and
oxygen enters here. Wastes leave the same way.
Acts as a cells control center, directing all of the cells
activities.
Cell structures that carry out specific functions within a cell.
Thin strands of material that fill the nucleus and contain
information for directing a cells functions.
Small round structure in the nucleus. The ribosomes are made
here.
Small grain-shaped organelles that produce proteins (important
to cells).
Thick, clear, gel-like fluid. Fills the region between the cell
membrane and the nucleus. It moves constantly within a cell,
carrying along the nucleus and other organelles that have
specific jobs.
Rod-shaped structures powerhouses that float in the cytoplasm
of the cell. They convert energy stored in food to energy in the
cell can use to live and function.
Looks like a maze of passageways. Helps the attached
ribosomes make proteins. The proteins leave the ER and move
to another organelle.
Proteins move here from the ER. The cells warehouse.
Receives proteins and other newly formed materials from the
ER, packages them, and distributes them to other parts of the
cell or to the outside of the cell.
Vacuoles (water-filled sacs)
Water-filled sacs that float in the cytoplasm. They store water,
food, or other materials needed by the cell. Vacuoles can also
store waste products until they are removed. Some animal cells
have them, and some do not.
Chloroplasts (capture energy)
Found in a plant cells cytoplasm. They capture energy from
sunlight and change it to a form of energy cells can use in
making food. Animal cells do not have these, but plant cells and
some other organisms do. They make leaves green because leaf
cells contain many chloroplasts.
Lysomsomes (Recycling center)
Sack-like organelles which contain substances that break down
large food particles into smaller ones. They also break down old
cell parts and release the substances so they can be used again.
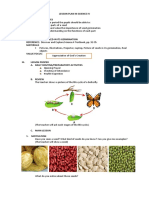
Multicellular (many cells)
Plants and animals are made of many cells.
Unicellular (single cell)
Single-celled organisms
Specialized Cells (division of labor)
Perform specific functions that benefit the entire organism. One
type of cell does one kind of job, while other types of cells do
other jobs.
Cells that work together: A division of labor occurs in multicellular organisms.
tissue
Is a group of similar cells that work together to perform a
specific function.
organ
Contains different kinds of tissues that function together.
Organ system
A group of organs that work together to perform a major
function.
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
Was the first to see living cells through the microscopes.
Golgi Apparatus (warehouse)
Be able to label a Plant cell
Be able to label an Animal cell
Вам также может понравиться
- Sample Interview QuestionsДокумент2 страницыSample Interview Questionsapi-233748343Оценок пока нет
- Needs of Living Things Observation LabДокумент2 страницыNeeds of Living Things Observation Labapi-233748343Оценок пока нет
- Cause of Rev War Long and Short Term Answers 2015Документ1 страницаCause of Rev War Long and Short Term Answers 2015api-233748343Оценок пока нет
- 1 Homework Merged For WeeblyДокумент20 страниц1 Homework Merged For Weeblyapi-233748343Оценок пока нет
- Guided Notes Parrellel Lines With TransversalДокумент2 страницыGuided Notes Parrellel Lines With Transversalapi-233748343Оценок пока нет
- Page 651 654 MergedДокумент2 страницыPage 651 654 Mergedapi-233748343Оценок пока нет
- 1 Chapter Notes Merged 1Документ19 страниц1 Chapter Notes Merged 1api-233748343Оценок пока нет
- Cells Study Guide Part 2Документ1 страницаCells Study Guide Part 2api-233748343Оценок пока нет
- Page 836 Answer KeyДокумент1 страницаPage 836 Answer Keyapi-233748343Оценок пока нет
- P 833 Answer KeyДокумент4 страницыP 833 Answer Keyapi-233748343Оценок пока нет
- Photo Resize Instructions Grade 7Документ1 страницаPhoto Resize Instructions Grade 7api-233748343Оценок пока нет
- Colonies PPT 2014 FinalДокумент39 страницColonies PPT 2014 Finalapi-233748343100% (1)
- American Revolutionary War 12Документ25 страницAmerican Revolutionary War 12api-233748343Оценок пока нет
- Drama One Act Unit CalendarДокумент2 страницыDrama One Act Unit Calendarapi-233748343Оценок пока нет
- Interpret Infinite CampusДокумент1 страницаInterpret Infinite Campusapi-233748343Оценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5783)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Greek CuisineДокумент11 страницGreek CuisineMarvin Joseph TidonОценок пока нет
- Enzymes Improve Fruit Juice Quality and ExtractionДокумент11 страницEnzymes Improve Fruit Juice Quality and ExtractionAhmed ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Dinosaur PDFДокумент74 страницыDinosaur PDFIrineu De Carli Junior100% (4)
- Cell Modification EditedДокумент44 страницыCell Modification EditedGian Miguel FernandezОценок пока нет
- APV Evaporator Handbook Guide to Evaporation Technology and SystemsДокумент68 страницAPV Evaporator Handbook Guide to Evaporation Technology and SystemsvbadsОценок пока нет
- Method Statement Coring&SealingДокумент3 страницыMethod Statement Coring&SealingMOHD SYAFIQОценок пока нет
- English9 Further Practice KeyДокумент5 страницEnglish9 Further Practice KeyNhok'ss Lì'ssОценок пока нет
- Aircraft Materials Construction and Repair: AENG 213Документ24 страницыAircraft Materials Construction and Repair: AENG 213Vince Gabriel AladoОценок пока нет
- Cell Structure and FunctionДокумент13 страницCell Structure and FunctionElisha TanОценок пока нет
- CHAP2Документ8 страницCHAP2Marlhen Euge SanicoОценок пока нет
- Factsheet Botanical Data: de MacaДокумент11 страницFactsheet Botanical Data: de MacaBioComercioPeruОценок пока нет
- Just For Fun Signs & ScentsДокумент13 страницJust For Fun Signs & ScentshiteshОценок пока нет
- Wet To Dry Mode Chage OverДокумент4 страницыWet To Dry Mode Chage OversambhuОценок пока нет
- Seed LPДокумент7 страницSeed LPKim Rose BorresОценок пока нет
- Biology: Practice WorksheetsДокумент20 страницBiology: Practice Worksheetsদেবব্রত মন্ডলОценок пока нет
- Adv With 690 Volts Over 400v PDFДокумент6 страницAdv With 690 Volts Over 400v PDFamarnath jagirdarОценок пока нет
- Bangas Soup Recipe: Beef, Dryfish & Crayfish in Palm Fruit BrothДокумент3 страницыBangas Soup Recipe: Beef, Dryfish & Crayfish in Palm Fruit BrothAARON PATRICK OBUKOHWOОценок пока нет
- Bayaldi Vegetables With Provençal Sauce Recipe - CopieДокумент4 страницыBayaldi Vegetables With Provençal Sauce Recipe - CopieDouBkkОценок пока нет
- Read Aloud Cards G1.U4.W4Документ8 страницRead Aloud Cards G1.U4.W4Lam Thuy LamОценок пока нет
- Transport Mechanism Quiz-1Документ2 страницыTransport Mechanism Quiz-1KLARK ANDREW MASAQUEL MARQUEZОценок пока нет
- Study of Adulteration in Common Medicinal PlantsДокумент61 страницаStudy of Adulteration in Common Medicinal PlantsBillal JohnОценок пока нет
- Micro Satellite Markers Cowpea YmvДокумент12 страницMicro Satellite Markers Cowpea YmvpallavipathОценок пока нет
- Rare and expensive fruitsДокумент10 страницRare and expensive fruitsFlorentina HijОценок пока нет
- Rainier-Packaging Rainier Fruit COMДокумент22 страницыRainier-Packaging Rainier Fruit COMkatysmith1687Оценок пока нет
- Cirrus LeafletДокумент9 страницCirrus Leafletinfo4826Оценок пока нет
- Fitoremediasi KelДокумент8 страницFitoremediasi KelYahya AdjaОценок пока нет
- Grade 5 Science Practice Test: Nebraska Department of Education 2012Документ13 страницGrade 5 Science Practice Test: Nebraska Department of Education 2012Ria SihombingОценок пока нет
- Vsic 2007Документ56 страницVsic 2007nqh2009Оценок пока нет
- PerfumeДокумент33 страницыPerfumejurjizadaОценок пока нет