Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
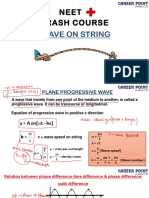
Traveling Wave Is Represented By: Sound:: Path Difference M Constractive Destruactive T T
Загружено:
Emmanuel Bautista-DizonОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Traveling Wave Is Represented By: Sound:: Path Difference M Constractive Destruactive T T
Загружено:
Emmanuel Bautista-DizonАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter
16
Chapter 17
Traveling
wave
is
represented
by:
!sin(kx t + )
#
y(x, t) = ym "or
#cos(kx t + )
$
Where :
k = 2 is; Angular Wave number
, is; The wavelength of the wave
2
, is; Angular frequency,
T
or Angular velocity
(-)
is
for
wave
moving
to
the
right,
(+)
is
moving
to
the
left.
1
f=
frequency
T
, is; Phase cons tan t
v=f =
Wave speed
k
Two
Types
of
mechanical
waves.
Longitudinal,
and
Transverse.
L
is
faster
than
T.
Speed of the wave on a string is :
= 2 f =
v=
is tension, and = mass / length
The speed and the acceleration of the
oscillating particles are:
dy(x, t)
dv(x, t)
v(x, t) =
a(x, t) =
dt
dt
2
vmax = ym
amax = y m
1
Average power : Pave = v 2 y 2m
2
Standing Waves:
y!(x, t) = [2ym sin kx]cos t
Points with zero amplitude: Nodes
Points with maximum displacement: Antinode
Resonant
Frequencies:
v
f =n
n = 1, 2, 3, ......
2L
f,
for
n
=
1,
Is
called
Fundamental
frequency
or
the
first
Harmonics.
Chapter 18
Sound:
Mechanical
Longitudinal
s(x, t) = sm cos(kx t)
p)x, t) = pmax sin(kx t)
pm = v sm
Interference:
If two sources are in phase:
Path difference
" m
Constractive
$
x = #
Destruactive
$%(2m +1)
2
If
out
of
phase
by
180o;
Path difference
" m
Destruactive
$
x = #
Constractive
$%(2m +1)
2
Intensity:
I
=
Power
/
Area
=
P/A=P/4r2
1
I = v 2 s 2m
2
I1 r22
=
I 2 r12
Sound
Level:
I
= 10 log
I 0 = 110 12 W 2
m
I0
Pattern
for
a
sring:
Beats:
fbeat = f1 f2
Doppler
Effect:
v vD
f!=
v vs
v
sin =
Mach cone angle
vs
1
sin
Mach Number
"
%
$
P'
T = (273.16) $ lim '
P3 '
$
# gas0 &
TK
=
TC
+
273.15
Conversion
from
Fahrenheit
to
Celsius:
TF 32 TC
=
180
100
L = Lo T
A = 2 Ao T
V = 3Vo T = Vo T
Where : = 3
Q = mcT
Q = mL
Calorimetry :
(Q
+ QC ) = 0
Вам также может понравиться
- Transverse WavesДокумент27 страницTransverse WavesDivya GovindarajОценок пока нет
- CLASSICAL MECHANICS AND ELECTROMAGNETISMДокумент13 страницCLASSICAL MECHANICS AND ELECTROMAGNETISMmhasan13Оценок пока нет
- Thermal Physics: U NKTДокумент6 страницThermal Physics: U NKTzzyingОценок пока нет
- Physics Unit One Formulas and MotionДокумент32 страницыPhysics Unit One Formulas and MotionAHKEEL LESTER JONESОценок пока нет
- Formula Sheet For PhysicsДокумент6 страницFormula Sheet For PhysicsAsim ButtОценок пока нет
- Binary PSK Receiver Block DiagramДокумент9 страницBinary PSK Receiver Block DiagramefedsfewОценок пока нет
- Physics 130 Formula SheetДокумент3 страницыPhysics 130 Formula SheetNKHICQ1mEbIwОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 15 - Mechanical Waves - R K ParidaДокумент6 страницChapter - 15 - Mechanical Waves - R K Paridasiddharthsrathor04Оценок пока нет
- 1 Synchronization and Frequency Estimation Errors: 1.1 Doppler EffectsДокумент15 страниц1 Synchronization and Frequency Estimation Errors: 1.1 Doppler EffectsRajib MukherjeeОценок пока нет
- ISV SM Ch16Документ61 страницаISV SM Ch16손은결Оценок пока нет
- Digital Communications Formula SheetДокумент13 страницDigital Communications Formula SheetSrikanth Reddy Komatireddy100% (1)
- PHYS1131 Solutions Tut 6 11Документ14 страницPHYS1131 Solutions Tut 6 11Jason Tan100% (2)
- D R S SR R T: Cross-Correlation Function, Is Defined by The IntegralДокумент13 страницD R S SR R T: Cross-Correlation Function, Is Defined by The IntegralSulaiman m SaeedОценок пока нет
- M.E CAD 2015 Advanced Vibration Engineering Spr5106Документ17 страницM.E CAD 2015 Advanced Vibration Engineering Spr5106gurusamyОценок пока нет
- PHYS220 Summer-2020 Sample Exam-1: Part-1: Spring-Mass OscillationДокумент6 страницPHYS220 Summer-2020 Sample Exam-1: Part-1: Spring-Mass OscillationSavio KhouryОценок пока нет
- Cheat Sheet - Exam 3Документ20 страницCheat Sheet - Exam 3textbookwhoreОценок пока нет
- Comm 2Документ122 страницыComm 2Tamrat TamemanОценок пока нет
- ThePhysicsCafe Summary of JC PhysicsДокумент2 страницыThePhysicsCafe Summary of JC PhysicsLim Zer HeanОценок пока нет
- Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsДокумент17 страницWorkbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsashutoshsinghjssОценок пока нет
- Study MaterialДокумент42 страницыStudy MaterialWhite DevilОценок пока нет
- lecture-3Документ37 страницlecture-3Kirubel MulugetaОценок пока нет
- Small Scale Fading in Radio PropagationДокумент15 страницSmall Scale Fading in Radio Propagationelambharathi88Оценок пока нет
- M (T) U (T) : Upper Side Band Lower Side Band Upper Side Band Lower Side BandДокумент5 страницM (T) U (T) : Upper Side Band Lower Side Band Upper Side Band Lower Side BandHaroonRashidОценок пока нет
- P2 FA10 - Derive EOM for periodic forced responseДокумент36 страницP2 FA10 - Derive EOM for periodic forced responseconcord1103Оценок пока нет
- Appendix: Some Defintions: The Energy of A Signal X (T) Is Defined AsДокумент17 страницAppendix: Some Defintions: The Energy of A Signal X (T) Is Defined AsVishal GaurОценок пока нет
- Angel ModulationДокумент8 страницAngel ModulationRi YaОценок пока нет
- Digital Signal Processing NotesДокумент18 страницDigital Signal Processing NotesDanial ZamanОценок пока нет
- Lecture3 Ch2 WavesДокумент24 страницыLecture3 Ch2 WavesLukinОценок пока нет
- Category: Physics FormulasДокумент24 страницыCategory: Physics FormulasKalpana ShankarОценок пока нет
- DSP - Classification of CT SignalsДокумент8 страницDSP - Classification of CT SignalsJunaid KaleemОценок пока нет
- Damped Vibration: Viscous and Coulomb DampingДокумент14 страницDamped Vibration: Viscous and Coulomb DampingEmmanuel KutaniОценок пока нет
- Wave Equation - Lecture NoteДокумент42 страницыWave Equation - Lecture NoteFredo YolendraОценок пока нет
- Midterm Review PDFДокумент16 страницMidterm Review PDFMt RushОценок пока нет
- ECE Formulae BookДокумент39 страницECE Formulae BookThashil Nagaraju Tnr TnrОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 A.C. E.E Prof Dr MoenesДокумент47 страницChapter 4 A.C. E.E Prof Dr Moenesmahmoudaliabdelaziz11Оценок пока нет
- Pulse Amplitude ModulationДокумент86 страницPulse Amplitude ModulationPraful Jagtap100% (1)
- Physics Class 9 FormulasДокумент13 страницPhysics Class 9 FormulasJatin Gupta73% (63)
- Present. Chapter 1 Schrodinger EquationДокумент20 страницPresent. Chapter 1 Schrodinger EquationDwi AnitaОценок пока нет
- DSP Signal Processing FundamentalsДокумент16 страницDSP Signal Processing FundamentalsJc Bernabe DazaОценок пока нет
- Comsysf311 2223 L13Документ13 страницComsysf311 2223 L13Gandhi SaxosОценок пока нет
- Wave Propagation and Power in Lossy DielectricsДокумент17 страницWave Propagation and Power in Lossy DielectricschoiyennОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ26 страницLecture 2Ahmed Diaa AlwakilОценок пока нет
- Adc Ieee Batch 06Документ4 страницыAdc Ieee Batch 06Kavya Sai sriОценок пока нет
- Lecture 17Документ21 страницаLecture 17narvan.m31Оценок пока нет
- Physics 221 Sec. 500 Optical and Thermal Physics Spring 2017Документ21 страницаPhysics 221 Sec. 500 Optical and Thermal Physics Spring 2017Ivanakbar PurwamaskaОценок пока нет
- Formula Sheet PHYS 157Документ1 страницаFormula Sheet PHYS 157Carmen YangОценок пока нет
- Physics Formulas: G G (1-d) RДокумент6 страницPhysics Formulas: G G (1-d) RAitazaz AhsanОценок пока нет
- Waves and the Wave EquationДокумент34 страницыWaves and the Wave EquationFarizalОценок пока нет
- Things To Know For The Physics GRE: Daniel Beller October 28, 2009Документ20 страницThings To Know For The Physics GRE: Daniel Beller October 28, 2009Arif SolmazОценок пока нет
- Boddeker's PHY132 Lecture14Документ4 страницыBoddeker's PHY132 Lecture14bitconcepts9781Оценок пока нет
- Physics of Sound Formula SheetДокумент2 страницыPhysics of Sound Formula SheetCAОценок пока нет
- Signals and Systems 01Документ10 страницSignals and Systems 01nvbondОценок пока нет
- Physics Class 9 FormulasДокумент13 страницPhysics Class 9 FormulasEKLABAY SONIОценок пока нет
- Pulse Compression - 2014Документ46 страницPulse Compression - 2014Luis LombardiОценок пока нет
- MAE107 Homework Solution Frequency Response AnalysisДокумент24 страницыMAE107 Homework Solution Frequency Response AnalysisMelanie Lakosta LiraОценок пока нет
- Engineering VibrationsДокумент43 страницыEngineering VibrationsClayton Roe100% (3)
- EAS 103-Class Work #2: Equally Tempered ScaleДокумент6 страницEAS 103-Class Work #2: Equally Tempered ScaleChristina FishyОценок пока нет
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsОт EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsОценок пока нет
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterОт EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterОценок пока нет
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)От EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Оценок пока нет
- ECE 408 HOMEWORK #3 (CH. 13) Solutions ©dr. James S. Kang: F Rad FДокумент49 страницECE 408 HOMEWORK #3 (CH. 13) Solutions ©dr. James S. Kang: F Rad FEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- History QuestionsДокумент6 страницHistory QuestionsEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- Application For LA CountyДокумент2 страницыApplication For LA CountyEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- Method2 LoadДокумент2 страницыMethod2 LoadEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- History AnswersДокумент3 страницыHistory AnswersEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- Cultural Event ReflectionДокумент3 страницыCultural Event ReflectionEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- DC Motor Control Lab Report Analyzes Methods for Tuning PID ControllerДокумент20 страницDC Motor Control Lab Report Analyzes Methods for Tuning PID ControllerEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- ECE408HW3Документ7 страницECE408HW3Emmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- ECE408HW3Документ7 страницECE408HW3Emmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- FFFB0000 621BFB0C 00000000 B21BFB0C 00000000 1000504C 00000001 D2000000 00000000Документ1 страницаFFFB0000 621BFB0C 00000000 B21BFB0C 00000000 1000504C 00000001 D2000000 00000000Emmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- Digital Filter Design and Analysis StepsДокумент1 страницаDigital Filter Design and Analysis StepsEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- History AnswersДокумент3 страницыHistory AnswersEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- California State Polytechnic Univerity, Pomona: Multi-Stage Amplifier DesignДокумент1 страницаCalifornia State Polytechnic Univerity, Pomona: Multi-Stage Amplifier DesignEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- Lab 7 P 1Документ3 страницыLab 7 P 1Emmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- Lab 7 P 1Документ3 страницыLab 7 P 1Emmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- Lab 7 P 1Документ3 страницыLab 7 P 1Emmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- Digital Piano Guidebook SectionsДокумент51 страницаDigital Piano Guidebook SectionsEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- History AnswersДокумент3 страницыHistory AnswersEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- ECE 220L SyllabusДокумент4 страницыECE 220L SyllabusEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- A Night To RememberДокумент3 страницыA Night To RememberEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- History AnswersДокумент3 страницыHistory AnswersEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- Gilded Age Politics Reading and QuestionsДокумент1 страницаGilded Age Politics Reading and QuestionsEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- Homework 1Документ1 страницаHomework 1Emmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- 132 Q 5 F15Документ1 страница132 Q 5 F15Emmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- Adder-Subtractor using Structural ModelingДокумент5 страницAdder-Subtractor using Structural ModelingEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- Course Topics:: California State Polytechnic University, Pomona ECE205 GradingДокумент1 страницаCourse Topics:: California State Polytechnic University, Pomona ECE205 GradingEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- 4 Bit Magnitude Comparator-2Документ2 страницы4 Bit Magnitude Comparator-2Emmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- 001 VerilogДокумент59 страниц001 VerilogEmmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 4Документ2 страницыLab Report 4Emmanuel Bautista-DizonОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15and16Документ57 страницChapter 15and16yexrewraigne9202Оценок пока нет
- Vibrating String Lab Frequency AnalysisДокумент9 страницVibrating String Lab Frequency AnalysisBrooke McNally100% (3)
- Oscillation MCQДокумент7 страницOscillation MCQUmer KhalidОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes On Biophysics and Bioimaging 2009Документ128 страницLecture Notes On Biophysics and Bioimaging 2009Anonymous 9rJe2lOskx100% (2)
- Waves NotesДокумент13 страницWaves NotescgozzardОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 PhysicsДокумент92 страницыUnit 2 PhysicsRabia Dean100% (2)
- Stationary WavesДокумент16 страницStationary WavesKavya NemaОценок пока нет
- Board Question Paper Physics July 2016Документ4 страницыBoard Question Paper Physics July 2016Rohit GhereОценок пока нет
- 06-11-2021 - SR Iit Co Sc-n120 - Jee Main Model - ptm-1 - QP FinalДокумент14 страниц06-11-2021 - SR Iit Co Sc-n120 - Jee Main Model - ptm-1 - QP FinalDeeip DОценок пока нет
- The Creation of Musical ScalesДокумент38 страницThe Creation of Musical ScalesMatheus ModestiОценок пока нет
- NEET Physics QuestionsДокумент26 страницNEET Physics QuestionsNaman kkОценок пока нет
- JEE Main 2022 PDF DownloadДокумент16 страницJEE Main 2022 PDF DownloadHh HhОценок пока нет
- Ch12 Giancoli7e TestBankДокумент24 страницыCh12 Giancoli7e TestBankHarishChoudharyОценок пока нет
- Fundamental Frequency and HarmonicsДокумент5 страницFundamental Frequency and HarmonicsantoniobhОценок пока нет
- COAS TR P1 18ws1Документ2 страницыCOAS TR P1 18ws1Mahmud RahmanОценок пока нет
- Hemisphere Resonator GyrosДокумент29 страницHemisphere Resonator GyrosShirish PandaОценок пока нет
- Topic 4 & 9 Waves PDFДокумент13 страницTopic 4 & 9 Waves PDFGonzalo PastorОценок пока нет
- The Physics of The Trumpet (Bostjan Berkopec)Документ12 страницThe Physics of The Trumpet (Bostjan Berkopec)carmechanicОценок пока нет
- Bill Adam Clinic Address PDFДокумент5 страницBill Adam Clinic Address PDFSean Borg100% (1)
- Physics: Chapter: MagnetismДокумент17 страницPhysics: Chapter: MagnetismkushalОценок пока нет
- Violin Plates Scientific AmericanДокумент11 страницViolin Plates Scientific AmericanPatrick Dansa100% (1)
- SFA String Methods Course PlanДокумент27 страницSFA String Methods Course PlanFernando MartinezОценок пока нет
- Soal Fisika SMAДокумент3 страницыSoal Fisika SMANevila Nur FaizОценок пока нет
- Physics of Wind Chimes-KimBДокумент20 страницPhysics of Wind Chimes-KimBatiggy05Оценок пока нет
- PHYS 1100 Waves SolutionsДокумент7 страницPHYS 1100 Waves SolutionsLeoncio Santos TressОценок пока нет
- Russian Brothers - Tesla TowerДокумент23 страницыRussian Brothers - Tesla TowerDavide Tanner TainiОценок пока нет
- Mixology Mixing EbookДокумент227 страницMixology Mixing EbookChloe JimzОценок пока нет
- Experiment 108 Transverse Waves - Frequency of Vibration - Online ModifiedДокумент6 страницExperiment 108 Transverse Waves - Frequency of Vibration - Online ModifiedBlank BlankОценок пока нет
- Lesson PLan 6.8Документ5 страницLesson PLan 6.8Josh ArgonzaОценок пока нет
- Physics WorksheetДокумент2 страницыPhysics WorksheetGurvir SinghОценок пока нет