Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals
Загружено:
Lawrence 'Lorenzo' AzureАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals
Загружено:
Lawrence 'Lorenzo' AzureАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
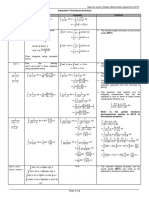
Calculus Cheat Sheet
Standard Integration Techniques
Note that at many schools all but the Substitution Rule tend to be taught in a Calculus II class.
( )
a f ( g ( x ) ) g ( x ) dx = g (a ) f ( u ) du
b
u Substitution : The substitution u = g ( x ) will convert
g b
using
du = g ( x ) dx . For indefinite integrals drop the limits of integration.
Ex.
1 5x
cos ( x3 ) dx
1 5x
cos ( x3 ) dx =
u = x 3 du = 3x 2 dx x 2 dx = 13 du
5
cos
1 3
8
= 53 sin ( u ) 1 =
x = 1 u = 1 = 1 :: x = 2 u = 2 = 8
3
Integration by Parts : u dv = uv - v du and
a u dv = uv
b
a
5
3
( u ) du
( sin (8) - sin (1) )
- v du . Choose u and dv from
a
integral and compute du by differentiating u and compute v using v = dv .
Ex.
xe
u=x
xe
-x
-x
dx
Ex.
dv = e- x
du = dx v = -e - x
dx = - xe + e dx = - xe - e
-x
-x
-x
-x
+c
3 ln x dx
u = ln x
5
dv = dx du = 1x dx v = x
ln x dx = x ln x 3 - dx = ( x ln ( x ) - x )
5
= 5ln ( 5) - 3ln ( 3) - 2
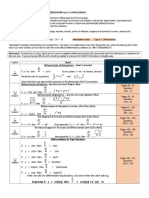
Products and (some) Quotients of Trig Functions
For sin n x cos m x dx we have the following :
For tan n x sec m x dx we have the following :
1. n odd. Strip 1 sine out and convert rest to
1.
2
2
cosines using sin x = 1 - cos x , then use
the substitution u = cos x .
2. m odd. Strip 1 cosine out and convert rest
2.
to sines using cos 2 x = 1 - sin 2 x , then use
the substitution u = sin x .
3. n and m both odd. Use either 1. or 2.
4. n and m both even. Use double angle
3.
and/or half angle formulas to reduce the
4.
integral into a form that can be integrated.
Trig Formulas : sin ( 2 x ) = 2sin ( x ) cos ( x ) , cos 2 ( x ) =
Ex. tan 3 x sec5 x dx
tan
sin5 x
cos x dx
(sin x ) sin x
sin x
sin x sin x
cos x dx = cos x dx = cos x dx
(1- cos x ) sin x
=
dx
( u = cos x )
cos x
= - (1-u ) du = - 1-2u +u du
u
u
Ex.
x sec5 xdx = tan 2 x sec 4 x tan x sec xdx
= ( sec2 x - 1) sec 4 x tan x sec xdx
= ( u 2 - 1) u 4 du
n odd. Strip 1 tangent and 1 secant out and
convert the rest to secants using
tan 2 x = sec 2 x - 1 , then use the substitution
u = sec x .
m even. Strip 2 secants out and convert rest
to tangents using sec2 x = 1 + tan 2 x , then
use the substitution u = tan x .
n odd and m even. Use either 1. or 2.
n even and m odd. Each integral will be
dealt with differently.
2
1
1
2 (1 + cos ( 2 x ) ) , sin ( x ) = 2 (1 - cos ( 2 x ) )
( u = sec x )
= 17 sec7 x - 15 sec5 x + c
Visit http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu for a complete set of Calculus notes.
2 2
= 12 sec2 x + 2 ln cos x - 12 cos 2 x + c
2005 Paul Dawkins
Вам также может понравиться
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)От EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Оценок пока нет
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsОт EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsОценок пока нет
- Integration Techniques Summary v3Документ2 страницыIntegration Techniques Summary v3bushlalaОценок пока нет
- 1 Matrices and Determinants SJKДокумент40 страниц1 Matrices and Determinants SJKannas04100% (1)
- Indices LogДокумент25 страницIndices Logadeskitoku100% (1)
- Solving Differential Equations in JavaДокумент36 страницSolving Differential Equations in Javamalekan2005100% (1)
- RD Sharma Class 11 Maths Chapter 11 Trigonometric EquationsДокумент17 страницRD Sharma Class 11 Maths Chapter 11 Trigonometric EquationsBhushan kumarОценок пока нет
- Theory of Equations Part 1Документ56 страницTheory of Equations Part 1Naveen kumar100% (1)
- Matlab by Rajesh Bandari YadavДокумент55 страницMatlab by Rajesh Bandari Yadavhyma kadakatla100% (2)
- Equations and GraphsДокумент15 страницEquations and Graphsyusi rizaОценок пока нет
- Integral EquationsДокумент46 страницIntegral EquationsNirantar YakthumbaОценок пока нет
- 10 Step Lesson PlanДокумент5 страниц10 Step Lesson Planapi-325889338Оценок пока нет
- Counting Principles, Permutations & CombinationsДокумент19 страницCounting Principles, Permutations & CombinationsPrashantTrehanОценок пока нет
- Ch02 - Limits and ContinuityДокумент61 страницаCh02 - Limits and ContinuityArmandinho CaveroОценок пока нет
- Polynomial FunctionsДокумент81 страницаPolynomial FunctionsJessica CagbabanuaОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Unit PlannerДокумент9 страницMathematics Unit Plannerapi-284842151Оценок пока нет
- Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, DivisionДокумент8 страницAddition, Subtraction, Multiplication, DivisionIntan BaiduriОценок пока нет
- BINOMIAL SeriesДокумент25 страницBINOMIAL SeriesBench AminОценок пока нет
- Factoring WorksheetДокумент6 страницFactoring WorksheetmeroelmeОценок пока нет
- Dynamic ProgrammingДокумент14 страницDynamic ProgrammingRuchi GujarathiОценок пока нет
- Volumes of RevolutionДокумент7 страницVolumes of RevolutionDegresFernandezPalomaОценок пока нет
- Visible Surface DeterminationДокумент62 страницыVisible Surface DeterminationqwdfghОценок пока нет
- CPSC Algorithms Cheat SheetДокумент6 страницCPSC Algorithms Cheat SheetRya KarkowskiОценок пока нет
- Fraction Tips S 1Документ6 страницFraction Tips S 1Dinesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Fourier Series LessonДокумент41 страницаFourier Series Lessonjackson246Оценок пока нет
- Volumes With Know Cross Sections Calculus ProjectДокумент2 страницыVolumes With Know Cross Sections Calculus ProjectJennifer Bramlett Cook50% (2)
- Surds and IndicesДокумент5 страницSurds and Indicesburgesss87Оценок пока нет
- Calculus Indefinite IntegralДокумент9 страницCalculus Indefinite Integralnicusor.iacob5680Оценок пока нет
- Codeforces TutorialДокумент72 страницыCodeforces TutorialNeeraj SharmaОценок пока нет
- Types of Discontinuities: Quick OverviewДокумент6 страницTypes of Discontinuities: Quick OverviewQurban HanifОценок пока нет
- Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыCheat SheetVarun NagpalОценок пока нет
- Integrals of Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsДокумент11 страницIntegrals of Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsEvelynn LynnОценок пока нет
- CSIR Mathematical Sciences Solved June 2011Документ25 страницCSIR Mathematical Sciences Solved June 2011Pradyuman SharmaОценок пока нет
- ProbabilityДокумент12 страницProbabilitykinkoiОценок пока нет
- PN CekoДокумент20 страницPN CekoVishnu Prakash SinghОценок пока нет
- Trig Formula SheetДокумент3 страницыTrig Formula Sheetpcam11Оценок пока нет
- Mathematics FormulasДокумент2 страницыMathematics FormulasgopalmyneniОценок пока нет
- Vector Algebra Facts SheetДокумент3 страницыVector Algebra Facts SheetСветлана Дашкевич ЛисовскаяОценок пока нет
- Fourth Semester Probability and Queuing Theory Two Marks With Answers Regulation 2013Документ63 страницыFourth Semester Probability and Queuing Theory Two Marks With Answers Regulation 2013PRIYA RAJI100% (2)
- de Moivres TheoremДокумент18 страницde Moivres TheoremAbdullah SaeedОценок пока нет
- 1 DR Samah IntegrationДокумент19 страниц1 DR Samah IntegrationKhaled Ahmed100% (1)
- Logic Proof NotesДокумент59 страницLogic Proof NotesHai L. NguyenОценок пока нет
- EXPONENTSДокумент11 страницEXPONENTSIffa Nadifa RizaОценок пока нет
- l3 DifferentiationДокумент4 страницыl3 Differentiationapi-287224366100% (2)
- Basic Trigonometry NotesДокумент14 страницBasic Trigonometry NotesKeri-ann Millar50% (2)
- Topic 4: Indices and Logarithms: Jacques Text Book (Edition 4) : Section 2.3 & 2.4Документ22 страницыTopic 4: Indices and Logarithms: Jacques Text Book (Edition 4) : Section 2.3 & 2.4Ateef HatifaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Algorithms: Dynamic ProgrammingДокумент25 страницIntroduction To Algorithms: Dynamic ProgrammingjaydipОценок пока нет
- Linear Algebra in DetailsДокумент88 страницLinear Algebra in Detailsyousef shabanОценок пока нет
- Differential Equations Chapter 8 ReviewДокумент18 страницDifferential Equations Chapter 8 Reviewtalonx11Оценок пока нет
- Difference Between Rational and Irrational NumberДокумент3 страницыDifference Between Rational and Irrational NumbernishagoyalОценок пока нет
- Matrices WДокумент21 страницаMatrices WNur SyahadahОценок пока нет
- Networking Essentials Exam NotesДокумент6 страницNetworking Essentials Exam NotesHelen Shi100% (1)
- Binomial TheoremДокумент24 страницыBinomial TheoremDipankar KumarОценок пока нет
- Linear Algebra NotesДокумент93 страницыLinear Algebra NotesalijazizaibОценок пока нет
- Wk5 - Solution of Algebraic and Transcendental EquationsДокумент14 страницWk5 - Solution of Algebraic and Transcendental EquationsFazelah YakubОценок пока нет
- Functions of Several VariablesДокумент10 страницFunctions of Several VariablesAlex S. ConstantinescuОценок пока нет
- Math 12Документ339 страницMath 12abdullah naseerОценок пока нет
- 8.indefinite IntegrationExerciseДокумент46 страниц8.indefinite IntegrationExerciseDina KoutonОценок пока нет
- Introduction To LimitsДокумент24 страницыIntroduction To LimitsJessa Mae100% (1)
- Calculus Cheat Sheet IntegralsДокумент5 страницCalculus Cheat Sheet Integralsapi-322359712Оценок пока нет
- ExamДокумент2 страницыExamLawrence 'Lorenzo' AzureОценок пока нет
- CollisionsДокумент15 страницCollisionsLawrence 'Lorenzo' AzureОценок пока нет
- Fake Resume Writing Workshop TemplateДокумент1 страницаFake Resume Writing Workshop TemplateLawrence 'Lorenzo' AzureОценок пока нет
- Al-Kitaab Study Guide and Activities - Lesson-1Документ2 страницыAl-Kitaab Study Guide and Activities - Lesson-1Lawrence 'Lorenzo' AzureОценок пока нет
- N220PS0301Документ1 страницаN220PS0301Lawrence 'Lorenzo' AzureОценок пока нет
- Math 8 F15 Notes Week 4 Applications of IntegrationДокумент6 страницMath 8 F15 Notes Week 4 Applications of IntegrationLawrence 'Lorenzo' AzureОценок пока нет
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/31Документ20 страницCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/31Nisha zehraОценок пока нет
- 02n6a PDFДокумент4 страницы02n6a PDFĐiện Tử Điện LạnhОценок пока нет
- Work - Pulley Lab WorksheetДокумент5 страницWork - Pulley Lab WorksheetNiyah fairОценок пока нет
- Cpo Math HelperДокумент49 страницCpo Math Helperapi-202178433Оценок пока нет
- Cls Jeead-18-19 Xii Phy Target-5 Set-2 Chapter-1Документ34 страницыCls Jeead-18-19 Xii Phy Target-5 Set-2 Chapter-1Abhash AnandОценок пока нет
- CA6 ContactorsДокумент36 страницCA6 ContactorsAbhishek mishraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13 - Electrical PropertiesДокумент18 страницChapter 13 - Electrical PropertiesThành Phương Tấn100% (1)
- MicrocontrollersДокумент1 страницаMicrocontrollersprettyswagОценок пока нет
- VHF Gysel 3 DB Power Divider/Combiner: Veljko Crnadak, Member, IEEE, and Siniša TasićДокумент4 страницыVHF Gysel 3 DB Power Divider/Combiner: Veljko Crnadak, Member, IEEE, and Siniša TasićAndy NGОценок пока нет
- Project Report On NTPC RGCCPДокумент39 страницProject Report On NTPC RGCCPVidya VijayanОценок пока нет
- Technical Data Sheet Ultem (Pei) : (Polyetherimide)Документ3 страницыTechnical Data Sheet Ultem (Pei) : (Polyetherimide)Dynamic SaravananОценок пока нет
- Exp 1 Pelton Wheel TurbineДокумент8 страницExp 1 Pelton Wheel TurbineNabilahJasmiОценок пока нет
- Using Newton's Law of Motion To Explain How Rocket WorkДокумент5 страницUsing Newton's Law of Motion To Explain How Rocket WorkHkmat ElshawwaОценок пока нет
- 《固体物理导论》 习题解答.charles Kittel.2004年第8版.introduction to Solid State Physics Solution ManualДокумент61 страница《固体物理导论》 习题解答.charles Kittel.2004年第8版.introduction to Solid State Physics Solution ManualSane LeeОценок пока нет
- AP Physics1 Student Workbook SE Unit5Документ39 страницAP Physics1 Student Workbook SE Unit5akbalonur85Оценок пока нет
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentДокумент14 страницMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentREHANОценок пока нет
- MomentsДокумент17 страницMomentsAbhay KumarОценок пока нет
- AssignmentДокумент9 страницAssignmentrslunaОценок пока нет
- 3EK8 Medium-Voltage Surge Arresters: Catalog Hp-Ar 28.1 2018Документ12 страниц3EK8 Medium-Voltage Surge Arresters: Catalog Hp-Ar 28.1 2018J. Harold Calvo M.Оценок пока нет
- Miracle Condensing UnitsДокумент51 страницаMiracle Condensing Units11HAYDAR ALWI TRI WIDODO -Оценок пока нет
- NTC71 5Документ15 страницNTC71 5Joao LucasОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 - ConsumerizationДокумент51 страницаChapter 5 - ConsumerizationFaiz MohdОценок пока нет
- Katalog Pedrollo 4SR Pumpi PDFДокумент16 страницKatalog Pedrollo 4SR Pumpi PDFzare25100% (1)
- Three Dimensional Time in A Nutshell by Peter J CarrollДокумент9 страницThree Dimensional Time in A Nutshell by Peter J CarrollhodmedodvortezОценок пока нет
- 1N34AДокумент1 страница1N34AfreddyОценок пока нет
- CH 5Документ46 страницCH 5Chala1989Оценок пока нет
- Charging of RefrigerantДокумент14 страницCharging of RefrigerantMARIO BULANADIОценок пока нет
- Manual Eb30Документ80 страницManual Eb30Ignacio Quispe MaytaОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry WorksheetДокумент6 страницElectrochemistry WorksheetVincent van GoghОценок пока нет
- PumpsДокумент122 страницыPumpsFour AyesОценок пока нет