Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Transistor Identification and Testing: Basic Electronics Station Three
Загружено:
sreedhar.tharoor0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
4 просмотров1 страницаA bipolar junction transistor can be thought of in terms of two diodes, as shown below. A good transistor will show a "resistance" of 600-700mV (shown as ohms, but is actually voltage with 99% of digital meters) the purpose of a transistor in electronics is to actively control voltage and current potentials in any circuit design.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
elecc (21).doc
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документA bipolar junction transistor can be thought of in terms of two diodes, as shown below. A good transistor will show a "resistance" of 600-700mV (shown as ohms, but is actually voltage with 99% of digital meters) the purpose of a transistor in electronics is to actively control voltage and current potentials in any circuit design.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
4 просмотров1 страницаTransistor Identification and Testing: Basic Electronics Station Three
Загружено:
sreedhar.tharoorA bipolar junction transistor can be thought of in terms of two diodes, as shown below. A good transistor will show a "resistance" of 600-700mV (shown as ohms, but is actually voltage with 99% of digital meters) the purpose of a transistor in electronics is to actively control voltage and current potentials in any circuit design.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
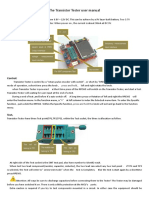
Basic Electronics Station Three:
Transistor Identification and Testing
INSTRUCTIONS: Find the bad ones. Using the digital voltage meter (DVM), measure each transistor in the
container and place the working transistors into their corresponding (labeled) tray (good) (bad)
Transistors can be tested for basic functionality with an analog or digital voltmeter (DVM) or multimeter
DMM). A bipolar junction transistor can be thought of in terms of two diodes, as shown below. As with any
diode, they should conduct in one direction, but not in the other.. This test tells you nothing about gain, voltage
breakdown, or anything else, only that the device is likely to be functional.
Transistor Quick Check
Check in both directions with your multimeter between the base and emitter/collector of each transistor. An
NPN transistor will show a "resistance" of 600-700mV (shown as ohms, but is actually voltage with 99% of
digital meters) with the positive (red) lead of a digital meter connected to the base, and the black lead on emitter
and collector. Reverse red and black and measure again
In case you were wondering (and you are by no means the first to do so), you cannot use two ordinary diodes
wired as shown, as a transistor. Transistor operation relies on the junction between the "diodes" (hence bipolar
junction transistor).
Note: The purpose of a transistor in electronics is to actively control voltage and current potentials in any
circuit design. The transistor is the basis of all semiconductors
Вам также может понравиться
- Measuring Voltage and Resistance with a MultimeterДокумент5 страницMeasuring Voltage and Resistance with a MultimeterNishanth.M nishuОценок пока нет
- Test Electrical Electronic PartsДокумент13 страницTest Electrical Electronic Partshabtemariam mollaОценок пока нет
- How to use a multimeter to measure voltage, current, resistance and test diodes and transistorsДокумент5 страницHow to use a multimeter to measure voltage, current, resistance and test diodes and transistorswaar lockОценок пока нет
- How to Use a Multimeter to Measure Voltage, Current, Resistance & ContinuityДокумент4 страницыHow to Use a Multimeter to Measure Voltage, Current, Resistance & Continuitymario_1303Оценок пока нет
- How To Test A TransistorДокумент5 страницHow To Test A Transistorjuliet coronadoОценок пока нет
- Instruments: Multimeters: A Multimeter Is An Instrument Which Measures Electrical Parameters Such As ACДокумент3 страницыInstruments: Multimeters: A Multimeter Is An Instrument Which Measures Electrical Parameters Such As ACVarunKumarОценок пока нет
- Basic Electronics (Lab Manual)Документ66 страницBasic Electronics (Lab Manual)Abdullah Sohail100% (2)
- Testing Electronics DevicesДокумент4 страницыTesting Electronics DevicesJaideep SinghОценок пока нет
- Basic Electrical Measuring Instruments: by Pramod AДокумент31 страницаBasic Electrical Measuring Instruments: by Pramod Akevinwz1989Оценок пока нет
- MultitesterДокумент3 страницыMultitesterChin-Chin AbejarОценок пока нет
- Using A MultimeterДокумент12 страницUsing A MultimeterJulius PangaribuanОценок пока нет
- Lab Manual Electronics EngineeringДокумент67 страницLab Manual Electronics EngineeringMuhammad Anas ToheedОценок пока нет
- DIY Mega ESR Tester InfoДокумент36 страницDIY Mega ESR Tester InfoBenjamin DoverОценок пока нет
- Digitech MultimeterДокумент7 страницDigitech Multimeterpropaganda65Оценок пока нет
- Testing A CapacitorДокумент4 страницыTesting A Capacitorroman reeseОценок пока нет
- The Transistor Tester User Manual (Newly)Документ7 страницThe Transistor Tester User Manual (Newly)Tanel Laanemägi100% (1)
- 20170621041627transistor Tester User ManualДокумент7 страниц20170621041627transistor Tester User ManualillemariusОценок пока нет
- Lab ManualДокумент65 страницLab ManualHuma MalikОценок пока нет
- Measuring Voltage with a DMMДокумент2 страницыMeasuring Voltage with a DMMguasko9035Оценок пока нет
- ECE For Schoology 5b840106d4169Документ4 страницыECE For Schoology 5b840106d4169Joshua OliverОценок пока нет
- Lab - 1 Handout-ELEC 201Документ9 страницLab - 1 Handout-ELEC 201AmroKashtОценок пока нет
- Nothing Special 4Документ25 страницNothing Special 4Jester SubiaОценок пока нет
- HISTORY OF ELECTRONICSДокумент8 страницHISTORY OF ELECTRONICSTrinidad TalanganОценок пока нет
- Lab Session 01 Introduction To Laboratory Equipments: ObjectiveДокумент10 страницLab Session 01 Introduction To Laboratory Equipments: ObjectiveHuma MalikОценок пока нет
- 1.0 Title:: Experiment No.6Документ9 страниц1.0 Title:: Experiment No.6srisairampoly100% (1)
- Voltage Divider ExperimentДокумент14 страницVoltage Divider ExperimentDave Vic Solis100% (2)
- The Transistor Tester User Manual: PowerДокумент4 страницыThe Transistor Tester User Manual: Powermijam55Оценок пока нет
- Multimeter ExpДокумент3 страницыMultimeter ExpArun JyothiОценок пока нет
- Test A Transistor With A MultimeterДокумент2 страницыTest A Transistor With A MultimeterSyed Muhammad Kaleem UddinОценок пока нет
- Measuring Electricity Using Multi MeterДокумент6 страницMeasuring Electricity Using Multi MeterAddiОценок пока нет
- DIAGNOSE ELECTRONIC FAULTSДокумент7 страницDIAGNOSE ELECTRONIC FAULTSMuhammad ZakiyОценок пока нет
- AY-AT Color Kit Tester Manual PDFДокумент5 страницAY-AT Color Kit Tester Manual PDFJustin NgОценок пока нет
- AY-At Color Kit Tester ManualДокумент5 страницAY-At Color Kit Tester ManualAnais Cullon BermejoОценок пока нет
- Applied Physics: Lab ManualДокумент13 страницApplied Physics: Lab ManualMuhammad Ahsan ShahèénОценок пока нет
- Testing A Transistor With A Digital Multimeter - Inst ToolsДокумент5 страницTesting A Transistor With A Digital Multimeter - Inst ToolsshafieeОценок пока нет
- Test Instruments GuideДокумент3 страницыTest Instruments GuideNipun chamikaОценок пока нет
- Match Transistors for Circuits with <40mΩ MismatchДокумент5 страницMatch Transistors for Circuits with <40mΩ MismatchcrackintheshatОценок пока нет
- Measuring devices and techniquesДокумент3 страницыMeasuring devices and techniquesHafidz YoshiokaОценок пока нет
- Como Usar Multimetro AgilentДокумент4 страницыComo Usar Multimetro AgilentAngélica ValeskaОценок пока нет
- A Multimeter Measures Three Types of Electrical UnitsДокумент2 страницыA Multimeter Measures Three Types of Electrical UnitsIbrahima DioufОценок пока нет
- PCB Experiment 2Документ15 страницPCB Experiment 2gowtham19082005Оценок пока нет
- AssignmentДокумент8 страницAssignmentHxrish DanixlОценок пока нет
- Manual M328 Version ESR Inductance Capacitance Meter Multifunctional Tester DIYДокумент7 страницManual M328 Version ESR Inductance Capacitance Meter Multifunctional Tester DIYJavierhm42Оценок пока нет
- Diode Identification and Testing: Basic Electronics Station TwoДокумент1 страницаDiode Identification and Testing: Basic Electronics Station Twosreedhar.tharoorОценок пока нет
- ME-170A EXPERIMENT 1 INSTRUMENTATIONДокумент8 страницME-170A EXPERIMENT 1 INSTRUMENTATIONandman753Оценок пока нет
- Physics ActivitiesДокумент16 страницPhysics ActivitiesSoumik MahapatroОценок пока нет
- Lab Report NewДокумент13 страницLab Report NewAszman SamianОценок пока нет
- Experiment To Study The Use of MULTI METERДокумент7 страницExperiment To Study The Use of MULTI METERns90Оценок пока нет
- How to use a multimeter to measure voltage, current, resistance and continuityДокумент7 страницHow to use a multimeter to measure voltage, current, resistance and continuityAnonymous OnzJpzОценок пока нет
- How To Use Digital MultimeterДокумент23 страницыHow To Use Digital Multimeternafees100% (2)
- Multimeters: Choosing A MultimeterДокумент7 страницMultimeters: Choosing A MultimeterronniedakingpouОценок пока нет
- EC Components CheckДокумент4 страницыEC Components CheckvrihadОценок пока нет
- Multimeter TutorialДокумент36 страницMultimeter Tutoriallam266Оценок пока нет
- 1 Lab Work ElectronicsДокумент13 страниц1 Lab Work ElectronicsFazil SultankulovОценок пока нет
- Transistor TestingДокумент4 страницыTransistor TestingJerry B CruzОценок пока нет
- How To Use A Multimeter Simplified - A Complete DIY Step by Step Guide On How To Use MultimeterДокумент43 страницыHow To Use A Multimeter Simplified - A Complete DIY Step by Step Guide On How To Use MultimeterWilliam BautistaОценок пока нет
- How To Use A MultimeterДокумент16 страницHow To Use A Multimetershayma ahmedОценок пока нет
- Lab Excersice NO 3Документ6 страницLab Excersice NO 3legasuОценок пока нет
- 1.guidance For The Beginning OHS Professiona12Документ219 страниц1.guidance For The Beginning OHS Professiona12Muhammad Fiqih AgusfianОценок пока нет
- Effective Safety Management SystemsДокумент34 страницыEffective Safety Management SystemsAmir SherafatipourОценок пока нет
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Dos CmdsДокумент2 страницыDos Cmdssreedhar.tharoorОценок пока нет
- Principles Of-Management-Lecture-Notes-For-MbaДокумент29 страницPrinciples Of-Management-Lecture-Notes-For-Mbasreedhar.tharoorОценок пока нет
- The Cause of Global Warming Policy Series 7Документ23 страницыThe Cause of Global Warming Policy Series 7Randeep BimbhОценок пока нет
- Diode Identification and Testing: Basic Electronics Station TwoДокумент1 страницаDiode Identification and Testing: Basic Electronics Station Twosreedhar.tharoorОценок пока нет
- Resistor Value Identification and Testing: Basic Electronics Station OneДокумент1 страницаResistor Value Identification and Testing: Basic Electronics Station Onesreedhar.tharoorОценок пока нет
- Dos CmdsДокумент2 страницыDos Cmdssreedhar.tharoorОценок пока нет
- Basic Electronics: Ion Laser Transistor TroubleshootingДокумент1 страницаBasic Electronics: Ion Laser Transistor Troubleshootingsreedhar.tharoorОценок пока нет