Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Kucc Flowchart
Загружено:
superxl2009Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Kucc Flowchart
Загружено:
superxl2009Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
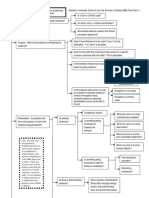
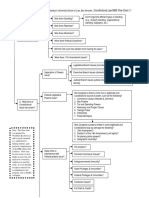
Contracts / UCC Art 2 (Sales)
Governing Law (Common Law vs.
UCC?)
Tips:
(1) If UCC applies, then identify if both parties are also merchants.
(2) If its unclear what type of contract it is, you might need to analyze all contract
issues both under Common Law and UCC rules.
Was there a definite offer?
Mutual Assent
Was it revoked or terminated?
Common law Mirror Image Rule issues
Was there
acceptance?
UCC Battle of the Forms (2-207) issues
Mailbox Rules apply to both C/L and UCC.
Contract
Formation
If there was a failure of consideration,
then does a consideration substitute
(such as promissory estoppel) apply?
Consideration
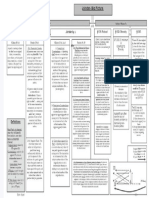
Mistake
Duress
Fraud
Illegality
Defenses to
Formation
Unconscionability
Incapacity
Infancy
A contract was formed, but was there
a 3d party beneficiary or was it
assigned or delegated?
Common law rules vs.
UCC rules differ
A contract was formed, but then was it
modified?
Watch for SOF and Parol
Evid.Rule issues.
A contract was formed, and now what are
the terms under the Parol Evidence Rule?
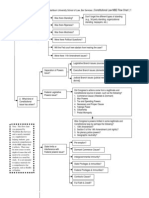
Performance
& Breach
Was there a breach
or anticipatory
repudiation?
C/L Material vs. minor breach
SOF Exceptions?
Note: This flow chart was
prepared by Washburn Bar
Services and is merely
intended as a supplement to
helping students gain
practical comprehension of
the MBE subject that it
reflects. There may be more
issues or more depth of
issues that will need to be
covered by students in a
usual bar study. It is not
intended to replace materials
for a comprehensive bar
program, such as BarBri or
Kaplan.
UCC Risk of Loss rules apply?
UCC Perfect Tender Rule
If there was breach, was there
excuse, discharge, and/or
satisfaction?
SOF
Existence of expressed or implied condition
that hasnt been validly waived?
Excuse
Discharge
Satisfaction
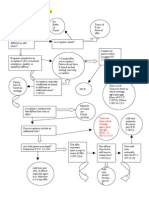
Liquidated Damages
Compensatory
Damages
Expectation / Benefit of the Bargain
Reliance
Impracticability
Remedies
Specific Performance
Rescission
Injunctive relief
Restitution
Cancellation
Impossibility
Frustration of purpose
Reformation
If no contract was formed, can court award reliance or quasi-contract (restitutionary) relief?
Washburn University School of Law, Bar Services
Вам также может понравиться
- Evidence FlowchartДокумент2 страницыEvidence Flowchartsuperxl200989% (9)
- Contracts Attack OutlineДокумент14 страницContracts Attack Outlineseddit60% (5)
- Joinder-Big Picture: R J I R Diver TyДокумент1 страницаJoinder-Big Picture: R J I R Diver Tysafkdjafgh leeeОценок пока нет
- Adrian Fall 1L - Contracts Final OutlineДокумент63 страницыAdrian Fall 1L - Contracts Final OutlineJasmine GaoОценок пока нет
- MBE Study ScheduleДокумент8 страницMBE Study ScheduleEmussel2Оценок пока нет
- Con Law ChecklistДокумент2 страницыCon Law ChecklistAshli Braggs100% (1)
- FlowchartsДокумент6 страницFlowchartsesanchezfloat100% (1)
- Constitutional Law Essay OneДокумент8 страницConstitutional Law Essay OneshizukababyОценок пока нет
- Crim Attack Outline GKДокумент8 страницCrim Attack Outline GKLiliane KimОценок пока нет
- Post Nuptial and Prenuptual Agreement EnforceabilityДокумент1 страницаPost Nuptial and Prenuptual Agreement Enforceabilitysuperxl2009Оценок пока нет
- ConLaw FlowChartДокумент2 страницыConLaw FlowChartAisha Lesley81% (16)
- Federal Courts ChecklistДокумент6 страницFederal Courts ChecklistMatthew CorkeryОценок пока нет
- PR Outline For Midterm and FinalДокумент33 страницыPR Outline For Midterm and FinalDanielleОценок пока нет
- Checklist PRДокумент8 страницChecklist PRDouglas GromackОценок пока нет
- Professional Responsibilities LawyerДокумент3 страницыProfessional Responsibilities LawyerRooter CoxОценок пока нет
- Civ Pro I ChecklistДокумент4 страницыCiv Pro I ChecklistDario Rabak0% (1)
- State ActionsДокумент1 страницаState ActionsKatie Lee WrightОценок пока нет
- Civil Procedure RoadmapsДокумент15 страницCivil Procedure RoadmapsCarolina JordanОценок пока нет
- Contracts II Checklist - Maggs - Spring 2003 - 3Документ15 страницContracts II Checklist - Maggs - Spring 2003 - 3champion_egy325Оценок пока нет
- Essay Format Strict Product Liability (MFG)Документ2 страницыEssay Format Strict Product Liability (MFG)Harley Meyer100% (1)
- Bartlett - Contracts Attack OutlineДокумент4 страницыBartlett - Contracts Attack OutlinefgsdfОценок пока нет
- Torts ChecklistДокумент2 страницыTorts ChecklistnegrilledОценок пока нет
- 1L Fall Civ Pro OutlineДокумент11 страниц1L Fall Civ Pro OutlineEvangelides100% (1)
- Contracts Essay Chart - FaiqДокумент4 страницыContracts Essay Chart - FaiqRahimah Faiq100% (6)
- Personal Jurisdiction Over Defendants in Civil SuitsДокумент27 страницPersonal Jurisdiction Over Defendants in Civil Suitslssucks1234Оценок пока нет
- Ucc and Restatement OutlineДокумент7 страницUcc and Restatement OutlineLauren WoodsonОценок пока нет
- Flowchart - Negligence (Occupier's Liability) : Issue 1: Did The Defendant Owe The Plaintiff A Duty of Care?Документ4 страницыFlowchart - Negligence (Occupier's Liability) : Issue 1: Did The Defendant Owe The Plaintiff A Duty of Care?NDОценок пока нет
- Personal Jurisdiction and Subject Matter Jurisdiction ExplainedДокумент15 страницPersonal Jurisdiction and Subject Matter Jurisdiction ExplainedkoreanmanОценок пока нет
- BA Outline - OKellyДокумент69 страницBA Outline - OKellylshahОценок пока нет
- Battle of The Forms FlowchartДокумент1 страницаBattle of The Forms Flowchartncallan9Оценок пока нет
- Accomplice Common LawДокумент1 страницаAccomplice Common LawLiliane KimОценок пока нет
- The Mother of All Civ Pro Outlines-2Документ100 страницThe Mother of All Civ Pro Outlines-2Hampton TignorОценок пока нет
- ENS CivPro Attack OutlineДокумент4 страницыENS CivPro Attack OutlineseabreezeОценок пока нет
- CONTRACTS II: PAROL EVIDENCE RULEДокумент37 страницCONTRACTS II: PAROL EVIDENCE RULEBrandon YeboahОценок пока нет
- Commerce Clause Flowchart (Mate) PDFДокумент2 страницыCommerce Clause Flowchart (Mate) PDFBrady WilliamsОценок пока нет
- FlowchartДокумент2 страницыFlowchartBre HitchОценок пока нет
- Bar Essays Contracts Short Review Outline PDFДокумент7 страницBar Essays Contracts Short Review Outline PDFno contractОценок пока нет
- Contrascts II Memorize OutlineДокумент3 страницыContrascts II Memorize OutlineAndrew BassОценок пока нет
- Leg Reg Pre WriteДокумент19 страницLeg Reg Pre WriteashleyamandaОценок пока нет
- Real Covenants vs. Equitable ServitudesДокумент1 страницаReal Covenants vs. Equitable ServitudesJeffrey StevensonОценок пока нет
- Contract Law Objective TheoryДокумент122 страницыContract Law Objective Theoryoaijf100% (1)
- Contracts 1 - OutlineДокумент17 страницContracts 1 - OutlineMarlene MartinОценок пока нет
- Scrutiny Categorization ChartДокумент1 страницаScrutiny Categorization Chartsuperxl2009Оценок пока нет
- Torts 1 Rule StatementsДокумент8 страницTorts 1 Rule StatementsNija Anise Bastfield100% (3)
- My Legal Pro Outline Fall 2011Документ54 страницыMy Legal Pro Outline Fall 2011DLRОценок пока нет
- Jason Contracts OutlineДокумент26 страницJason Contracts Outlinethekaybomb100% (1)
- Contracts Final OutlineДокумент19 страницContracts Final OutlineCatherine Merrill100% (1)
- Civil Procedure - Erie EssayДокумент2 страницыCivil Procedure - Erie Essayjustgottabezen100% (1)
- Bar Exam Homicide Classification GuideДокумент1 страницаBar Exam Homicide Classification Guidesuperxl2009100% (1)
- Bar Exam Homicide Classification GuideДокумент1 страницаBar Exam Homicide Classification Guidesuperxl2009100% (1)
- 1L Personal Jurisdiction Final OutlineДокумент2 страницы1L Personal Jurisdiction Final OutlineMichelle ChuОценок пока нет
- When Does the UCC Apply? – Key Factors and TestsДокумент49 страницWhen Does the UCC Apply? – Key Factors and TestsLaura C100% (1)
- Contracts OutlineДокумент33 страницыContracts OutlinejesharerОценок пока нет
- Fall Civil Procedure Outline FinalДокумент22 страницыFall Civil Procedure Outline FinalKiersten Kiki Sellers100% (1)
- FL Con Law OutlineДокумент28 страницFL Con Law OutlineassiramufОценок пока нет
- Criminal Law Pre-WritesДокумент1 страницаCriminal Law Pre-WritesAlex HardenОценок пока нет
- Torts OutlineДокумент57 страницTorts Outlineang3lwings100% (1)
- Contracts and SalesДокумент26 страницContracts and SalesSean Williams100% (1)
- Commerce Clause Cases ExplainedДокумент1 страницаCommerce Clause Cases ExplainedkillerokapiОценок пока нет
- Conditions Step by StepДокумент1 страницаConditions Step by StepLazinessPerSe100% (1)
- PR OutlineДокумент34 страницыPR OutlineroseyboppОценок пока нет
- Fed Court Subject Matter Jurisdiction and Personal Jurisdiction SummarizedДокумент24 страницыFed Court Subject Matter Jurisdiction and Personal Jurisdiction SummarizedNoel CheungОценок пока нет
- Negligence Flow Chart-1Документ1 страницаNegligence Flow Chart-1Shannon LitvinОценок пока нет
- Final Civil Procedure Outline!Документ7 страницFinal Civil Procedure Outline!Kate BroderickОценок пока нет
- 2011 0112 11 13 54 Document1Документ1 страница2011 0112 11 13 54 Document1superxl2009Оценок пока нет
- The Complete Defense: of Risk, Risk RiskДокумент1 страницаThe Complete Defense: of Risk, Risk Risksuperxl2009Оценок пока нет
- MBE Hand Score Request FormДокумент1 страницаMBE Hand Score Request Formsuperxl2009Оценок пока нет
- 2016 05 10 10 52 45 Document2Документ1 страница2016 05 10 10 52 45 Document2superxl2009Оценок пока нет
- Wills Essay Law To Be AppliedДокумент1 страницаWills Essay Law To Be Appliedsuperxl2009Оценок пока нет
- BE Tracker Form With Sig LineДокумент1 страницаBE Tracker Form With Sig Linesuperxl2009Оценок пока нет
- Rules To Be AppliedДокумент1 страницаRules To Be Appliedsuperxl2009Оценок пока нет
- Professional Responsibility Checklist for AttorneysДокумент1 страницаProfessional Responsibility Checklist for Attorneyssuperxl2009Оценок пока нет
- Civil Procedure Checklist - Organize Issues According to Lawsuit TimelineДокумент1 страницаCivil Procedure Checklist - Organize Issues According to Lawsuit Timelinesuperxl2009Оценок пока нет
- TORTS Outline For FinalДокумент24 страницыTORTS Outline For Finalsuperxl2009Оценок пока нет
- Regulatory State Sitaraman 2014Документ59 страницRegulatory State Sitaraman 2014superxl2009Оценок пока нет
- Property Rights Attack OutlineДокумент6 страницProperty Rights Attack Outlinesuperxl2009Оценок пока нет
- Cases and Materials On Employment DiscriminationДокумент1 страницаCases and Materials On Employment Discriminationsuperxl2009Оценок пока нет
- DOS SLTort ChartДокумент1 страницаDOS SLTort Chartsuperxl2009Оценок пока нет
- Pa Contracts BarДокумент1 страницаPa Contracts Barsuperxl2009Оценок пока нет
- Contracts I Roadmap - Selmi - Fall 2003 - 001Документ1 страницаContracts I Roadmap - Selmi - Fall 2003 - 001superxl2009Оценок пока нет
- Busorg ChecklistДокумент2 страницыBusorg Checklistsuperxl2009Оценок пока нет
- ExplanationДокумент1 страницаExplanationsuperxl2009Оценок пока нет
- Con Law1 Unknown5Документ1 страницаCon Law1 Unknown5superxl2009Оценок пока нет
- Contracts I Roadmap - Selmi - Fall 2003 - 001Документ1 страницаContracts I Roadmap - Selmi - Fall 2003 - 001superxl2009Оценок пока нет
- Contracts Where Courts Are Divided: ConsiderationДокумент1 страницаContracts Where Courts Are Divided: Considerationsuperxl2009Оценок пока нет
- Con Law1 Unknown5Документ1 страницаCon Law1 Unknown5superxl2009Оценок пока нет
- Cohabitation and Family Law Issues in Marvin v. MarvinДокумент1 страницаCohabitation and Family Law Issues in Marvin v. Marvinsuperxl2009Оценок пока нет