Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
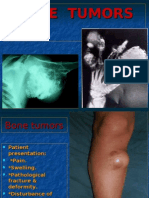
Pathologic Fracture
Загружено:
Andrew Lukman0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
100 просмотров3 страницыKasus Pathologic Fracture
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документKasus Pathologic Fracture
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
100 просмотров3 страницыPathologic Fracture
Загружено:
Andrew LukmanKasus Pathologic Fracture
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
Pathologic Fracture:
1. Latar Belakang
1.1 Definisi:
Fraktur tulang di akibatkan dari penyebab lain yang
menganggu integritas struktur tulang
Fraktur bise terjadi tiba-tiba (spontaneous) atau setelah .
(trivial injury)
1.2 Epidimeologi
1.3 Etiology
1.3.1 Penyakit tulang general
1. Ontogenesis Imperfecta
2. Post Menopausal osteoporosis
3. Metabolic bone disease
4. Myelomatosis
5. Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
6. Pagets diease
1.3.2
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Kondisi local ginak
Chronic Infection
Solitary bone cyst
Fibrous cortical defect
Chondromyxoid fibroma
Aneurysmal bone cyst
Chrondroma
Monostotic Fibrous dysplasia
1.3.3
1.
2.
3.
Tumor Primer Ganas
Chondrosarcoma
Osteosarcoma
Ewings tumor
1.3.4 Metastasis
Carcinoma dari:
Payu darah (50-85%)
Prostat (50-70%)
Hodgkins (50-70%)
Paru-paru (30-50%)
Ginjal (30-50%)
Tyroid (40%)
Melanoma (30-40%)
Bladder (12-25%)
Mechanism of Metastasis:
Route of Metastasis: Contiguous or Hematogenous (more
common)
Release of cells from the primary tumor
Invasion of efferent lymphatic or vascular channels
Dissemination of cells
Endothelial attachment and invasion at distant site
Angiogenesis and tumor growth at distant site
Impending pathologic fractures
61% of all pathologic fractures occur in the femur
80% are peritrochanteric
Parrish and Murray, 1970
increasing pain with advancing cortical destruction of
lesions involving >50% of the shaft diameter
Beals, 1971
lesions >2.5 cm are at increased risk to fracture
Murray, 1974
increased fracture with destruction of > one-third of the
cortex, pain after radiotherapy
Fidler, 1981
% shaft destroyed
Incidence Fx (%)
0-25%
0%
25-50%
3.7%
50-75%
61%
>75%
79%
Patients with tumors destroying >50% of the diameter
of bone require prophylactic internal fixation
Harrington criteria
>50% of diameter of bone
>2.5 cm
pain after radiation
fracture of the lesser trochanter
Limitations:
o only for proximal femur
o doesnt account for tumor biology
Mirels Criteria
Вам также может понравиться
- Referat OsteoporosisДокумент32 страницыReferat OsteoporosisMarzuqi AbdullahОценок пока нет
- UU 5 1997psikotropikaДокумент85 страницUU 5 1997psikotropikaMeilina PutriОценок пока нет
- 2018 CSB520 ANSWERS Skeletal System PathologyДокумент4 страницы2018 CSB520 ANSWERS Skeletal System PathologyNathanОценок пока нет
- Lorentz On 2015Документ23 страницыLorentz On 2015Sanita AurinОценок пока нет
- Final Project PDFДокумент75 страницFinal Project PDFuzzal ahmedОценок пока нет
- MUSKULOSKELETALДокумент79 страницMUSKULOSKELETALkhalishaОценок пока нет
- Bab Ii - AuДокумент43 страницыBab Ii - Auilaaabalqis90Оценок пока нет
- OSTEOSARCOMAДокумент2 страницыOSTEOSARCOMAmarivohОценок пока нет
- Neoplasms of The Musculoskeletal TissuesДокумент21 страницаNeoplasms of The Musculoskeletal Tissuesi dewa wisnu putraОценок пока нет
- Journal OsteochondromaДокумент14 страницJournal OsteochondromaAnggi CalapiОценок пока нет
- Eric OsteomyelitisДокумент22 страницыEric OsteomyelitisJonathan Delos ReyesОценок пока нет
- Bones and Joints Diseases: Bagian Patologi Anatomi Dr. Juliana Lina, SP - PAДокумент26 страницBones and Joints Diseases: Bagian Patologi Anatomi Dr. Juliana Lina, SP - PAsebastian1207Оценок пока нет
- Bone Disease, Any of The Diseases or Injuries That Affect HumanДокумент10 страницBone Disease, Any of The Diseases or Injuries That Affect Humanrichelle joy reyesОценок пока нет
- Death&Birth 00Документ23 страницыDeath&Birth 00kyz79Оценок пока нет
- Theoritical Background CrurisДокумент21 страницаTheoritical Background Crurismutia aОценок пока нет
- BONESДокумент73 страницыBONESsafa_sabaОценок пока нет
- Cagri Karaciklar Fragility Fractures EssayДокумент7 страницCagri Karaciklar Fragility Fractures EssayÇağrıОценок пока нет
- Jurnal OsteochondromaДокумент10 страницJurnal OsteochondromaAnggi CalapiОценок пока нет
- Iii 2 Prelomi KostijuДокумент32 страницыIii 2 Prelomi KostijuDamjan MarinovićОценок пока нет
- Laporan DK 3 Pemicu 2 Musket PDFДокумент37 страницLaporan DK 3 Pemicu 2 Musket PDFMiaОценок пока нет
- Bone and Soft Tissue TumoursДокумент9 страницBone and Soft Tissue TumoursSurgicalgownОценок пока нет
- Here Is A List of Diseases of BonesДокумент2 страницыHere Is A List of Diseases of Bonesmanishsharma.champ01Оценок пока нет
- 1.7.9 Osteochondroma PDFДокумент2 страницы1.7.9 Osteochondroma PDFSofa AmaliaОценок пока нет
- Os 1 251Документ7 страницOs 1 251mukhlis akmalОценок пока нет
- Skeletal DiseasesДокумент3 страницыSkeletal Diseasessweetheart10Оценок пока нет
- Diseases Diseases and Disorders of The Skeletal SystemДокумент3 страницыDiseases Diseases and Disorders of The Skeletal SystemMbagwuMartinEzeugoОценок пока нет
- Pathologic Bone FractureДокумент5 страницPathologic Bone FractureJaysellePuguonTabijeОценок пока нет
- FRACTURESДокумент35 страницFRACTURESMichelle DuОценок пока нет
- What Is Osteoarthritis?: ArthritisДокумент4 страницыWhat Is Osteoarthritis?: ArthritisJohn Mark Alvin TorresОценок пока нет
- ASKEP OsteoporosisДокумент41 страницаASKEP OsteoporosisMaya PinteОценок пока нет
- Osteoporosis: Disease SummaryДокумент10 страницOsteoporosis: Disease SummaryHohai ConcepcionОценок пока нет
- DR - Jimmy-Blok Semester 2-Minilecture Muskuloskeletal OAДокумент55 страницDR - Jimmy-Blok Semester 2-Minilecture Muskuloskeletal OATutde SedanaОценок пока нет
- Osteoporosis 1Документ22 страницыOsteoporosis 1Júlia LedesmaОценок пока нет
- Group 10 NCM 112 - (Osteonecrosis)Документ8 страницGroup 10 NCM 112 - (Osteonecrosis)Jezreel BonaОценок пока нет
- Osteopetrosis - Symptoms, Causes, Treatment - NORDДокумент13 страницOsteopetrosis - Symptoms, Causes, Treatment - NORDRayyan SaleemОценок пока нет
- Instituto SuperiorДокумент7 страницInstituto SuperiorVictor CondoriОценок пока нет
- OsteosarcomaДокумент3 страницыOsteosarcomaGeneral, Juliana Rose A.Оценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Bone MetastasesДокумент5 страницPathophysiology of Bone MetastasesdyahОценок пока нет
- MCQ's in Bone PathologyДокумент6 страницMCQ's in Bone PathologyDood94% (16)
- K32 - Pathology of Bone (Dr. Dody)Документ60 страницK32 - Pathology of Bone (Dr. Dody)faris100% (1)
- 18 Diseases of The Joints 1 - 2021Документ46 страниц18 Diseases of The Joints 1 - 2021Ahmed YTОценок пока нет
- Screening, Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteoporosis: A Brief ReviewДокумент7 страницScreening, Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteoporosis: A Brief ReviewraffellaОценок пока нет
- Bones & Joints Pathology 4thДокумент8 страницBones & Joints Pathology 4thlovelyc95Оценок пока нет
- Module 4 HomeworkДокумент4 страницыModule 4 HomeworkCj LinceОценок пока нет
- Avascular Necrosis: Necrosis Blood Supply JointДокумент9 страницAvascular Necrosis: Necrosis Blood Supply JointAyaba RoselynОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The Upper and Lower Extremities Neoplasms of MusculosДокумент93 страницыAnatomy of The Upper and Lower Extremities Neoplasms of MusculosraihanekapОценок пока нет
- Pathology of OsteoarthritisДокумент2 страницыPathology of OsteoarthritisYogi drОценок пока нет
- Musculoskeletal System Pathology Musculoskeletal System: Structure - Bones and JointsДокумент9 страницMusculoskeletal System Pathology Musculoskeletal System: Structure - Bones and JointsshaifОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology and Etiology of OsteoarthritisДокумент7 страницPathophysiology and Etiology of OsteoarthritisknikmahОценок пока нет
- Post Op of Ulna Radius SinistraДокумент14 страницPost Op of Ulna Radius SinistrawindaОценок пока нет
- Fracture ReportДокумент19 страницFracture Reporteros_mimiОценок пока нет
- Patogenesis Osteoporosis VДокумент15 страницPatogenesis Osteoporosis Vaji pangestuОценок пока нет
- Frakktur Kelompok 15 (English) PDFДокумент45 страницFrakktur Kelompok 15 (English) PDFTri WulandariSemester 1BОценок пока нет
- Patogenesis Osteoporosis V PDFДокумент15 страницPatogenesis Osteoporosis V PDFaji pangestuОценок пока нет
- L 4 Pathology, Bone Tumours (2) Lecture NotesДокумент3 страницыL 4 Pathology, Bone Tumours (2) Lecture Notesamrwheed9Оценок пока нет
- Bones and Soft Tissue - Clinical GateДокумент10 страницBones and Soft Tissue - Clinical GateAkira MasumiОценок пока нет
- BoneДокумент68 страницBonedr_asaleh100% (2)
- Disorders of BonesДокумент3 страницыDisorders of BonesAnonymous 0pSLjJYОценок пока нет
- Pasracoccidioides Host Interaction PaperДокумент20 страницPasracoccidioides Host Interaction PaperAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Schizo 1Документ4 страницыSchizo 1Andrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Pathologic FractureДокумент3 страницыPathologic FractureAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Pathologic FractureДокумент3 страницыPathologic FractureAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Action PotantialДокумент9 страницAction PotantialAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- The Tree by Andrew LukmanДокумент2 страницыThe Tree by Andrew LukmanAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Quiz Week 6 NeuroДокумент3 страницыQuiz Week 6 NeuroAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Vaccine RoutineДокумент1 страницаVaccine RoutineAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Chapel ReflectionДокумент2 страницыChapel ReflectionAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Action PotantialДокумент9 страницAction PotantialAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Hepb VaccineДокумент3 страницыHepb VaccineAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Congenital Female ReproductiveДокумент7 страницCongenital Female ReproductiveAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- PCI ComplicationsДокумент1 страницаPCI ComplicationsAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Anemia During PregnancyДокумент1 страницаAnemia During PregnancyAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Vaccine RoutineДокумент1 страницаVaccine RoutineAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Embryology of The Female Reproductive SystemДокумент5 страницEmbryology of The Female Reproductive SystemAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Coronary Artery Bypass GraftingДокумент1 страницаCoronary Artery Bypass GraftingAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Vaccine RoutineДокумент1 страницаVaccine RoutineAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Vaccine RoutineДокумент1 страницаVaccine RoutineAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Action PotantialДокумент9 страницAction PotantialAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- BacteriaДокумент7 страницBacteriaAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- BacteriaДокумент7 страницBacteriaAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Hepb VaccineДокумент3 страницыHepb VaccineAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- AIHA PathoДокумент3 страницыAIHA PathoAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Chapel ReflectionДокумент2 страницыChapel ReflectionAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Anemia During PregnancyДокумент1 страницаAnemia During PregnancyAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Congenital Female ReproductiveДокумент7 страницCongenital Female ReproductiveAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет
- Church ReflectionДокумент2 страницыChurch ReflectionAndrew LukmanОценок пока нет