Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings
Загружено:
ParthPatelИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings
Загружено:
ParthPatelАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings
Name: Parth Patel
Topology
Objectives
Part 1: Verify the Default Switch Configuration
Part 2: Configure a Basic Switch Configuration
Part 3: Configure a MOTD Banner
Part 4: Save Configuration Files to NVRAM
Part 5: Configure S2
Background
In this activity, you will perform basic switch configurations. You will secure
access to the command-line interface (CLI) and console ports using encrypted
and plain text passwords. You will also learn how to configure messages for
users logging into the switch. These banners are also used to warn unauthorized
users that access is prohibited.
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 1 of 9
Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings
Part 1:
Verify the Default Switch Configuration
Step 1: Enter privileged mode.
You can access all switch commands from privileged mode. However, because
many of the privileged commands configure operating parameters, privileged
access should be password-protected to prevent unauthorized use.
The privileged EXEC command set includes those commands contained in user
EXEC mode, as well as the configure command through which access to the
remaining command modes are gained.
a. Click S1 and then the CLI tab. Press <Enter>.
b. Enter privileged EXEC mode by entering the enable command:
Switch> enable
Switch#
Notice that the prompt changed in the configuration to reflect privileged EXEC
mode.
Step 2: Examine the current switch configuration.
a. Enter the show running-config command.
Switch# show running-config
b. Answer the following questions:
How many FastEthernet interfaces does the switch have? 24
How many Gigabit Ethernet interfaces does the switch have? 2
What is the range of values shown for the vty lines? 0 -15
Which command will display the current contents of non-volatile randomaccess memory (NVRAM)? show startup-configuration
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 2 of 9
Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings
Why does the switch respond with startup-config is not present? It displays
this message because the configuration file was not saved to NVRAM.
Currently it is only located in RAM.
Part 2:
Create a Basic Switch Configuration
Step 1: Assign a name to a switch.
To configure parameters on a switch, you may be required to move between
various configuration modes. Notice how the prompt changes as you navigate
through the switch.
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# hostname S1
S1(config)# exit
S1#
Step 2: Secure access to the console line.
To secure access to the console line, access config-line mode and set the
console password to letmein.
S1# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
S1(config)# line console 0
S1(config-line)# password letmein
S1(config-line)# login
S1(config-line)# exit
S1(config)# exit
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
S1#
Why is the login command required? In order for the password checking process
to work, it requires both the login and password commands.
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 3 of 9
Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings
Step 3: Verify that console access is secured.
Exit privileged mode to verify that the console port password is in effect.
S1# exit
Switch con0 is now available
Press RETURN to get started.
User Access Verification
Password:
S1>
Note: If the switch did not prompt you for a password, then you did not
configure the login parameter in Step 2.
Step 4: Secure privileged mode access.
Set the enable password to c1$c0. This password protects access to privileged
mode.
Note: The 0 in c1$c0 is a zero, not a capital O. This password will not grade as
correct until after you encrypt it in Step 8.
S1> enable
S1# configure terminal
S1(config)# enable password c1$c0
S1(config)# exit
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
S1#
Step 5: Verify that privileged mode access is secure.
a. Enter the exit command again to log out of the switch.
b. Press <Enter> and you will now be asked for a password:
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 4 of 9
Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings
User Access Verification
Password:
c. The first password is the console password you configured for line con 0.
Enter this password to return to user EXEC mode.
d. Enter the command to access privileged mode.
e. Enter the second password you configured to protect privileged EXEC mode.
f. Verify your configurations by examining the contents of the runningconfiguration file:
S1# show running-configuration
Notice how the console and enable passwords are both in plain text. This
could pose a security risk if someone is looking over your shoulder.
Step 6: Configure an encrypted password to secure access to privileged mode.
The enable password should be replaced with the newer encrypted secret
password using the enable secret command. Set the enable secret password to
itsasecret.
S1# config t
S1(config)# enable secret itsasecret
S1(config)# exit
S1#
Note: The enable secret password overrides the enable password. If both are
configured on the switch, you must enter the enable secret password to enter
privileged EXEC mode.
Step 7: Verify that the enable secret password is added to the configuration file.
a. Enter the show running-configuration command again to verify the new
enable secret password is configured.
Note: You can abbreviate show running-configuration as
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 5 of 9
Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings
S1# show run
b. What is displayed for the enable secret password?
$1$mERr$ILwq/b7kc.7X/ejA4Aosn0
c. Why is the enable secret password displayed differently from what we
configured? The enable secret is shown in encrypted form, whereas the
enable password is in plain text.
Step 8: Encrypt the enable and console passwords.
As you noticed in Step 7, the enable secret password was encrypted, but the
enable and console passwords were still in plain text. We will now encrypt these
plain text passwords using the service password-encryption command.
S1# config t
S1(config)# service password-encryption
S1(config)# exit
If you configure any more passwords on the switch, will they be displayed in the
configuration file as plain text or in encrypted form? Explain why? The service
password-encryption command encrypts all current and future passwords.
Part 3:
Configure a MOTD Banner
Step 1: Configure a message of the day (MOTD) banner.
The Cisco IOS command set includes a feature that allows you to configure
messages that anyone logging onto the switch sees. These messages are called
message of the day, or MOTD banners. Enclose the banner text in quotations or
use a delimiter different from any character appearing in the MOTD string.
S1# config t
S1(config)# banner motd "This is a secure system. Authorized Access Only!"
S1(config)# exit
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 6 of 9
Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings
S1#
When will this banner be displayed? The message will be displayed when
someone enters the switch through the console port.
Why should every switch have a MOTD banner? Every switch should have a
banner to warn unauthorized users that access is prohibited but can also be
used for sending messages to network personnel/technicians (such as
impending system shutdowns or who to contact for access).
Part 4:
Save Configuration Files to NVRAM
Step 1: Verify that the configuration is accurate using the show run command.
Step 2: Save the configuration file.
You have completed the basic configuration of the switch. Now back up the
running configuration file to NVRAM to ensure that the changes made are not
lost if the system is rebooted or loses power.
S1# copy running-config startup-config
Destination filename [startup-config]?[Enter]
Building configuration...
[OK]
What is the shortest, abbreviated version of the copy running-config startupconfig command? cop r s
Step 3: Examine the startup configuration file.
Which command will display the contents of NVRAM? show startup-configuration
Are all the changes that were entered recorded in the file? Yes, it is the same as
the running-configuration
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 7 of 9
Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings
Part 5:
Configure S2
You have completed the configuration on S1. You will now configure S2. If you
cannot remember the commands, refer to Parts 1 to 4 for assistance.
Configure S2 with the following parameters:
a. Name device: S2
b. Protect access to the console using the letmein password.
c. Configure an enable password of c1$c0 and an enable secret password of
itsasecret.
d. Configure a message to those logging into the switch with the following
message:
Authorized access only. Unauthorized access is prohibited and violators
will be prosecuted to the full extent of the law.
e. Encrypt all plain text passwords.
f. Ensure that the configuration is correct.
g. Save the configuration file to avoid loss if the switch is powered down.
Switch>enable
Switch#config t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)#hostname S2
S2(config)#line console 0
S2(config-line)#password letmein
S2(config-line)#login
S2(config-line)#enable password c1$c0
S2(config)#enable secret itsasecret
S2(config)#banner motd $any text here$
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 8 of 9
Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings
S2(config)#service password-encryption
S2(config)#do wr
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 9 of 9
Вам также может понравиться
- 2.2.3.4 Packet TracerДокумент6 страниц2.2.3.4 Packet TracerFrans TariganОценок пока нет
- 2.2.3.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings InstructionsДокумент6 страниц2.2.3.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings InstructionsJosCarr14970% (1)
- 2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsДокумент6 страниц2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsJoyce ChocaОценок пока нет
- 2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsДокумент6 страниц2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settingsjeneil valenzОценок пока нет
- Configure Initial Switch SettingsДокумент5 страницConfigure Initial Switch SettingsHeriyanto TanОценок пока нет
- Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch Settings: ObjectivesДокумент12 страницPacket Tracer - Configure Initial Switch Settings: Objectiveszvezda dieslowОценок пока нет
- 2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsДокумент5 страниц2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsYousef A SalemОценок пока нет
- Configure Switch Settings - Initial Switch Config, Passwords, BannersДокумент6 страницConfigure Switch Settings - Initial Switch Config, Passwords, BannersGiroОценок пока нет
- 2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch Settings - 1207050038 - Faza Mohamad FarsyafatДокумент5 страниц2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch Settings - 1207050038 - Faza Mohamad Farsyafatfaza farsyafatОценок пока нет
- Configure Initial Switch SettingsДокумент6 страницConfigure Initial Switch SettingsБогдан МарчукОценок пока нет
- 2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch Settings AnsweredДокумент5 страниц2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch Settings AnsweredKoro SenpaiОценок пока нет
- 2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings PDFДокумент6 страниц2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings PDFChadОценок пока нет
- Configure Initial Switch SettingsДокумент7 страницConfigure Initial Switch SettingsDaniel PalaciosОценок пока нет
- LAB 03 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsДокумент5 страницLAB 03 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsCorrine LozanoОценок пока нет
- 2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsДокумент5 страниц2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch Settingskds20850Оценок пока нет
- 2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsДокумент5 страниц2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsKaung KaungОценок пока нет
- 2.5.5 Packet Tracer Configure Initial Switch SettingsДокумент5 страниц2.5.5 Packet Tracer Configure Initial Switch SettingsjamesОценок пока нет
- Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsДокумент22 страницыPacket Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsMENDOZA GASPAR PAOLA Ingeniería en Sistemas ComputacionalesОценок пока нет
- 2.2.3.4. Configuring Initial Switch Settings ILMSTUDENTДокумент6 страниц2.2.3.4. Configuring Initial Switch Settings ILMSTUDENTanie lovesuОценок пока нет
- 2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsДокумент5 страниц2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsAnthony Josh LegoОценок пока нет
- Chapter One Lab-3 - Configure Initial Switch SettingsДокумент5 страницChapter One Lab-3 - Configure Initial Switch SettingsFedasa BoteОценок пока нет
- Configure Initial Switch SettingsДокумент9 страницConfigure Initial Switch Settingsabdulrahman khaldiОценок пока нет
- B3 - 322070 - Sai Kamble - Assig - 1Документ17 страницB3 - 322070 - Sai Kamble - Assig - 1sai.22220063Оценок пока нет
- 03 135222 010 114406102443 28092023 053141pmДокумент5 страниц03 135222 010 114406102443 28092023 053141pmasfa rehmanОценок пока нет
- 2.5.5-Configuración de Los Parametros Iniciales Del SwitchДокумент5 страниц2.5.5-Configuración de Los Parametros Iniciales Del Switchpuyo.dc.22Оценок пока нет
- Task 1: Verify The Default Switch Configuration Step 1: Enter Privileged EXEC ModeДокумент20 страницTask 1: Verify The Default Switch Configuration Step 1: Enter Privileged EXEC ModeAdnan YousafОценок пока нет
- PT2234 - Configuring Initial Switch Settings: Part 1: Verify The Default Switch ConfigurationДокумент2 страницыPT2234 - Configuring Initial Switch Settings: Part 1: Verify The Default Switch ConfigurationmanОценок пока нет
- 2.2.3.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings InstructionsДокумент6 страниц2.2.3.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings InstructionsLaura SuarezОценок пока нет
- Configure Switch Settings and PasswordsДокумент2 страницыConfigure Switch Settings and PasswordsmanОценок пока нет
- 2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsДокумент6 страниц2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsRafael DiazОценок пока нет
- 2.2.3.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsДокумент7 страниц2.2.3.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsClareAustinОценок пока нет
- 2.2.4.11 Lab - Configuring Switch Security Features - ScribdДокумент9 страниц2.2.4.11 Lab - Configuring Switch Security Features - ScribdstevehrccОценок пока нет
- Title Build, Configure, and Simulate Switch Setting in Network TopologyДокумент7 страницTitle Build, Configure, and Simulate Switch Setting in Network TopologyHadia RashidОценок пока нет
- 2.3.3.5 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management AddressДокумент8 страниц2.3.3.5 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management AddressNicolas Bonina33% (3)
- 10.1.4-Packet-Tracer - Configure-Initial-Router-SettingsДокумент5 страниц10.1.4-Packet-Tracer - Configure-Initial-Router-SettingsPetru SpînuОценок пока нет
- 2.2.4.11 Lab - Configuring Switch Security Features - ILMДокумент15 страниц2.2.4.11 Lab - Configuring Switch Security Features - ILMJose Maria Rendon Rodriguez100% (1)
- 6.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings InstructionsДокумент4 страницы6.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings Instructionsslider1188Оценок пока нет
- Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings: ObjectivesДокумент8 страницPacket Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings: ObjectivesMENDOZA GASPAR PAOLA Ingeniería en Sistemas ComputacionalesОценок пока нет
- 2.3.3.5 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management Address NewportДокумент4 страницы2.3.3.5 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management Address Newportgerardo1028Оценок пока нет
- 2.5.5 Configure Initial Switch Settings QuisaguanoДокумент7 страниц2.5.5 Configure Initial Switch Settings QuisaguanoFernandoQuisaguanoОценок пока нет
- CCNA1 Chapter 2 Exam - Online AnswerДокумент12 страницCCNA1 Chapter 2 Exam - Online AnswerKaung KaungОценок пока нет
- 2.3.3.4 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management Address - ILMДокумент10 страниц2.3.3.4 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management Address - ILMKevin KimОценок пока нет
- 11.2.4.6 Lab - Securing Network DevicesДокумент8 страниц11.2.4.6 Lab - Securing Network DevicesasdfjklОценок пока нет
- Configure Initial Router SettingsДокумент4 страницыConfigure Initial Router SettingsIzzat NadzriОценок пока нет
- ITNB02 11.2.4.6 Securing Network DevicesДокумент8 страницITNB02 11.2.4.6 Securing Network DevicesShayneNakagawaОценок пока нет
- 11.2.4.6 Lab - Securing Network DevicesДокумент8 страниц11.2.4.6 Lab - Securing Network DevicesRichardWhitleyОценок пока нет
- 11.2.4.8 Lab - Securing Network DevicesДокумент8 страниц11.2.4.8 Lab - Securing Network DevicesParthPatel60% (5)
- Lab - Configuring Switch Security Features: TopologyДокумент9 страницLab - Configuring Switch Security Features: TopologybobОценок пока нет
- 6.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings PDFДокумент4 страницы6.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings PDFSyammirul RashidОценок пока нет
- 2.3.3.4 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management AddressДокумент9 страниц2.3.3.4 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management AddressIchwan Habibie20% (5)
- 2.3.3.4 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management AddressДокумент8 страниц2.3.3.4 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management AddressDaisy Galvan0% (1)
- 6.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router SettingsДокумент4 страницы6.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router SettingsSergio Monte100% (3)
- 6.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings InstructionsДокумент4 страницы6.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings InstructionsJavierOsunaОценок пока нет
- 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring Switch Security FeaturesДокумент10 страниц5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring Switch Security FeaturesShadman SifatОценок пока нет
- Act 1 Building A Simple NetworkДокумент11 страницAct 1 Building A Simple Networkchristine booduanОценок пока нет
- 5 2 2 9 Lab Configuring Switch Security Features ILMДокумент16 страниц5 2 2 9 Lab Configuring Switch Security Features ILMJavier FlorianОценок пока нет
- 11.2.4.6 Lab - Securing Network DevicesДокумент8 страниц11.2.4.6 Lab - Securing Network DevicesHarrison Hayes0% (2)
- 11.2.4.6 Lab - Accessing Network Devices With SSHДокумент6 страниц11.2.4.6 Lab - Accessing Network Devices With SSHParthPatel0% (3)
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3От EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Оценок пока нет
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationОт EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationОценок пока нет
- Lab 7 - Viewing Wireless and Wired NIC InformationДокумент11 страницLab 7 - Viewing Wireless and Wired NIC InformationParthPatelОценок пока нет
- Lab 5 - Configuring A Switch Managment AddressДокумент10 страницLab 5 - Configuring A Switch Managment AddressParthPatelОценок пока нет
- Appendix Packet Tracer - Configuring An Integrated RouterДокумент3 страницыAppendix Packet Tracer - Configuring An Integrated RouterParthPatelОценок пока нет
- 11.2.4.8 Lab - Securing Network DevicesДокумент8 страниц11.2.4.8 Lab - Securing Network DevicesParthPatel60% (5)
- 10.3.1.4 Packet Tracer Multiuser - Implement ServicesДокумент4 страницы10.3.1.4 Packet Tracer Multiuser - Implement ServicesParthPatel0% (1)
- Appendix Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2Документ4 страницыAppendix Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2ParthPatelОценок пока нет
- 11.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting ChallengeДокумент3 страницы11.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting ChallengeParthPatel0% (1)
- 11.2.5.7 Packet Tracer - Backing Up Configuration FilesДокумент2 страницы11.2.5.7 Packet Tracer - Backing Up Configuration FilesParthPatel33% (3)
- 11.3.3.3 Packet Tracer - Using Show CommandsДокумент2 страницы11.3.3.3 Packet Tracer - Using Show CommandsParthPatel0% (1)
- 11.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeДокумент4 страницы11.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeParthPatel0% (1)
- 11.3.2.2 Packet Tracer - Test Connectivity With TracerouteДокумент3 страницы11.3.2.2 Packet Tracer - Test Connectivity With TracerouteParthPatelОценок пока нет
- 11.2.4.7 Lab - Examining Telnet and SSH in WiresharkДокумент9 страниц11.2.4.7 Lab - Examining Telnet and SSH in WiresharkParthPatel100% (2)
- 10.2.2.7 Packet Tracer - DNS and DHCPДокумент4 страницы10.2.2.7 Packet Tracer - DNS and DHCPParthPatelОценок пока нет
- 11.2.4.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring Secure Passwords and SSHДокумент2 страницы11.2.4.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring Secure Passwords and SSHParthPatelОценок пока нет
- 11.2.4.6 Lab - Accessing Network Devices With SSHДокумент6 страниц11.2.4.6 Lab - Accessing Network Devices With SSHParthPatel0% (3)
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1Документ5 страниц8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1ParthPatel33% (6)
- 10.4.1.2 Packet Tracer Multiuser - Tutorial InstructionsДокумент3 страницы10.4.1.2 Packet Tracer Multiuser - Tutorial InstructionsKamijou SekaiОценок пока нет
- 3.3.3.3 Packet Tracer - Explore A Network InstructionsДокумент5 страниц3.3.3.3 Packet Tracer - Explore A Network InstructionsWendhz ÜüОценок пока нет
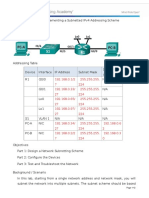
- 9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructДокумент4 страницы9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructGanti nama100% (1)
- Configure and Use FTP ServersДокумент4 страницыConfigure and Use FTP ServersParthPatelОценок пока нет
- 10.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Web and EmailДокумент5 страниц10.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Web and EmailParthPatelОценок пока нет
- 10.2.2.9 Lab - Observing DNS ResolutionДокумент5 страниц10.2.2.9 Lab - Observing DNS ResolutionasdfjklОценок пока нет
- 9.3.1.2 Packet Tracer Simulation - Exploration of TCP and UDP CommunicationДокумент6 страниц9.3.1.2 Packet Tracer Simulation - Exploration of TCP and UDP CommunicationParthPatel0% (1)
- 8.1.4.8 Lab - Designing and Implementing A Subnetted IPv4 Addressing SchemeДокумент12 страниц8.1.4.8 Lab - Designing and Implementing A Subnetted IPv4 Addressing SchemeParthPatel90% (31)
- 8.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeДокумент2 страницы8.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeParthPatel0% (1)
- 7.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeДокумент2 страницы7.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeParthPatel100% (1)
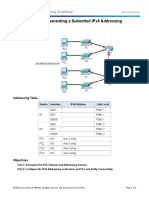
- 8.3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Implementing A Subnetted IPv6 Addressing SchemeДокумент3 страницы8.3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Implementing A Subnetted IPv6 Addressing SchemeParthPatel0% (1)
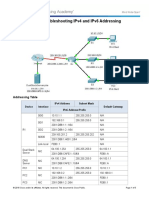
- 7.3.2.9 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting IPv4 and IPv6 AddressingДокумент5 страниц7.3.2.9 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting IPv4 and IPv6 AddressingParthPatel0% (3)
- 8.1.4.6 Lab - Calculating IPv4 SubnetsДокумент7 страниц8.1.4.6 Lab - Calculating IPv4 SubnetscgruОценок пока нет
- 7.3.2.8 Lab - Mapping The InternetДокумент8 страниц7.3.2.8 Lab - Mapping The InternetParthPatel0% (5)
- Minor Consent FormДокумент1 страницаMinor Consent FormGabi WarwickОценок пока нет
- R 23Документ27 страницR 23eeeОценок пока нет
- ICT IGCSE 0417 - ICT ApplicationsДокумент24 страницыICT IGCSE 0417 - ICT ApplicationsMartin Dominguez Colombo American School40% (5)
- CEHv10 Course OutlineДокумент46 страницCEHv10 Course OutlineNaitik Haiking0% (1)
- Yes Bank Sign Updation FormДокумент1 страницаYes Bank Sign Updation FormAbhishek CuléОценок пока нет
- Cloud Security - An Overview: The OWASP FoundationДокумент30 страницCloud Security - An Overview: The OWASP FoundationMostafaElBazОценок пока нет
- Information Technology-P1 - (NOV-08), ICABДокумент1 страницаInformation Technology-P1 - (NOV-08), ICABgundapolaОценок пока нет
- Aadhaar update form detailsДокумент4 страницыAadhaar update form detailsRG ReportingОценок пока нет
- Near Field Communication: A Seminar Report OnДокумент34 страницыNear Field Communication: A Seminar Report OnSonu LovesforuОценок пока нет
- Berna1Документ4 страницыBerna1Kenneth RomanoОценок пока нет
- Pfleeger 9780134093093 Ch01Документ32 страницыPfleeger 9780134093093 Ch01Reemmoq 12Оценок пока нет
- How to configure an authoritative time server in Windows Server to sync with an external sourceДокумент13 страницHow to configure an authoritative time server in Windows Server to sync with an external sourceShahzad MalikОценок пока нет
- Untangle Admin Guide PDFДокумент242 страницыUntangle Admin Guide PDFpeka76Оценок пока нет
- Hack 6Документ9 страницHack 6mobilecrackersОценок пока нет
- SpeedFace-V5L Series Datasheet 202401Документ4 страницыSpeedFace-V5L Series Datasheet 202401nicollededoro22Оценок пока нет
- Lab 1.1Документ1 страницаLab 1.1demisitoОценок пока нет
- Refund of Security-Revised FinalДокумент1 страницаRefund of Security-Revised FinalMinhaj AkbarОценок пока нет
- Safety Valve (IBOP) Service ManualДокумент50 страницSafety Valve (IBOP) Service ManualGiorgiana Rosu100% (4)
- Name Service LdapДокумент322 страницыName Service LdapBiswajit MallickОценок пока нет
- Download Aadhaar cardДокумент1 страницаDownload Aadhaar cardmarika saritha kumariОценок пока нет
- Cheat Sheet for Military Units and ResourcesДокумент1 страницаCheat Sheet for Military Units and Resourcessatwin edyОценок пока нет
- My PHPGeneratorДокумент238 страницMy PHPGeneratorAndres BabativaОценок пока нет
- Gis Continuity AlstomДокумент7 страницGis Continuity AlstomTravis WoodОценок пока нет
- Baxter IPump Operation ManualДокумент194 страницыBaxter IPump Operation ManualIsrael OrdoñezОценок пока нет
- HUAWEI S5700-HI Series Switches DatasheetДокумент10 страницHUAWEI S5700-HI Series Switches DatasheetCurtaItanetОценок пока нет
- Bank A Net UserguideДокумент77 страницBank A Net UserguideKendell JohnsonОценок пока нет
- China Job ScamsДокумент5 страницChina Job ScamsAnonymous gdPp2laОценок пока нет
- Data Privacy Impact Assessment QuestionnaireДокумент10 страницData Privacy Impact Assessment Questionnaireviolet osadiayeОценок пока нет
- WienerДокумент8 страницWienerStish SarnaОценок пока нет
- EToken TMS 2.0 SP3 Installation and Configuration Guide 0Документ273 страницыEToken TMS 2.0 SP3 Installation and Configuration Guide 0popescuiuliaОценок пока нет