Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
SPH3U - Circuit Lab
Загружено:
liamweinertИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
SPH3U - Circuit Lab
Загружено:
liamweinertАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Liam Weinert
SPH3U: Circuit Analysis Lab
May 25, 2013
Purpose:
To practice and verify circuit operations.
Materials:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Power Supply
33 Ohm Resistor - 1
18 Ohm Resistor - 2
Voltmeter
Ammeter
Connecting Wires
Method:
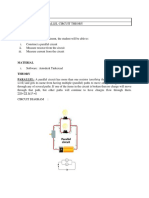
1. Construct Three Circuits: 1 Mixed, 1 Series and 1 Parallel.
2. Measure Voltage Around Each Resistor And Through Each Load.
3. Measure Current Around Each Resistor And Through Each Load.
Observations:
Series Circuit:
VALUES
MEASURE
D
THEORETI
CAL
VS
6V
IS
0.08A
V1
2.85V
I1
0.08A
V2
1.69V
I2
0.08A
V3
1.5V
I3
0.08A
6V
0.087
A
2.87V
0.087
A
1.566
V
0.087
A
1.566
V
0.087
A
VS
6V
IS
0.81A
V1
5.9V
I1
0.2A
V2
5.8V
I2
0.35A
V3
5.6V
I3
0.35A
6V
0.84A
6V
0.18A
6V
0.33A
6V
0.33A
V3
1.32V
I3
0.007
A
0.007
1A
Parallel Circuit:
VALUES
MEASURE
D
THEORETI
CAL
Mixed Circuit:
VALUES
MEASURE
D
THEORET
ICAL
VS
6V
IS
V1
0.14A 4.71V
I1
0.14A
V2
1.32V
6V
0.142
A
0.142
A
1.28V
Calculations:
Series Circuit:
RT = 33+18+18
RT = 69
4.686
V
I2
0.007
A
0.007
1A
1.28V
Liam Weinert
SPH3U: Circuit Analysis Lab
Is = Vs/RT
I1 + I2 + I3 = Is
V3 = IR
May 25, 2013
V1 = IR
V1 = 0.087x33
V2 = IR
Is = 6/69
0.087x18
I1 + I2 + I3 = 0.087A
V2 = 0.087x18
Is = 0.087A
Kirchhoffs Current Law V1 = 2.871V V2 = 1.566V V3 = 1.566V
V3 =
Parallel Circuit:
RT =
1
1 1 1
+ +
33 18 18
RT = 7.07
Is = V/R
V1 + V 2 + V 3 = V s
I3 = V/R
I1 = V/R
Is = 6/7.07
V1 + V2 + V3 = 6V
Is = 0.84A
Kirchhoffs Voltage Law I1 = 0.18A
I1 = 6/33
I2 = V/R
I2 = 6/18
I3 = 6/18
I2 = 0.33A
I3 = 0.33A
Mixed Circuit:
1
RT =
1 1
+
18 18
+ 33
RT = 42
Is = V/R
Is = 6/42
0.142x33
I1 = I s
I2 + I3 = Is/2
I1 = 0.142A
I2 + I3 = 0.0071A
V1 = IR
V1 =
Is = 0.142A Kirchhoffs Current Law Kirchhoffs Current Law V1 = 4.686V
V2 = IR
V3 = IR
V2 = 0.071x18
V3 = 0.071x18
V2 = 1.28V
V3 = 1.28V
Analysis:
1. Theoretical voltage and current were calculated in the calculations section.
2. In all cases but specifically the parallel circuit, it can be seen that the voltage
is always decreases throughout the circuit. This difference between the
measured and theoretical value can be contributed to the fact that the wires
are actually resistors. As a result there is increasing resistance as the circuit
progresses, causing being more resistance as the circuit continues.
Вам также может понравиться
- EE-Lab-2 (0124)Документ6 страницEE-Lab-2 (0124)ali burhan tahirОценок пока нет
- Lab 7Документ10 страницLab 7Rushanda BuchananОценок пока нет
- Lab # 03Документ8 страницLab # 03Muhammad Mushtaq100% (1)
- Linear Circuit Analysis Lab Page 1Документ8 страницLinear Circuit Analysis Lab Page 1Muhammad MushtaqОценок пока нет
- Current Divider RuleДокумент3 страницыCurrent Divider RuleMrinmoy Bin SaadОценок пока нет
- Circuit Theory BasicsДокумент27 страницCircuit Theory Basicsd2electrifiersОценок пока нет
- By: Mr. Augosto M. DirectoДокумент34 страницыBy: Mr. Augosto M. DirectoArt DollosaОценок пока нет
- Kirchhoff's RulesДокумент18 страницKirchhoff's Rulesthonah12100% (2)
- ECE422L Activity No. 03 Series, Parallel and Series-Parallel Circuits MarasiganAA, UmaliGCDДокумент13 страницECE422L Activity No. 03 Series, Parallel and Series-Parallel Circuits MarasiganAA, UmaliGCDAlexis MarasiganОценок пока нет
- Experiment On: Measurement of DC Currents, Voltage, Resistances and Study of Resistance Colour CodeДокумент8 страницExperiment On: Measurement of DC Currents, Voltage, Resistances and Study of Resistance Colour CodeHenok BelaynehОценок пока нет
- Eeen 211 Exp 10Документ20 страницEeen 211 Exp 10Alan ShelengОценок пока нет
- Lab3 Parallel CircuitДокумент6 страницLab3 Parallel CircuitQutaiba Osamah ZakiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2-Electric CircuitsДокумент96 страницChapter 2-Electric Circuitsn nudgeОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Exercise 5 Malabanan, Clarenz Medina 2BSMEДокумент6 страницLaboratory Exercise 5 Malabanan, Clarenz Medina 2BSMEJarish Nacilo-anОценок пока нет
- Compilation of Lab Activity No. 6Документ113 страницCompilation of Lab Activity No. 6Anthony CortezОценок пока нет
- Report Elec Lab 3Документ7 страницReport Elec Lab 3HARITH IZHAMОценок пока нет
- APLR2Документ12 страницAPLR2Adeel YounusОценок пока нет
- Kirchhoff's RulesДокумент5 страницKirchhoff's Rulesamiraaikharah100% (1)
- Current Electricity Part 02Документ91 страницаCurrent Electricity Part 02Vishal MehtaОценок пока нет
- ENGD1004 EEP Lab1 - 2011 - 1Документ8 страницENGD1004 EEP Lab1 - 2011 - 1heskey1234Оценок пока нет
- Series Circuits Ohms LawДокумент13 страницSeries Circuits Ohms Lawidk- accОценок пока нет
- 01 Maxwell Loop Current Theorem VerificationДокумент2 страницы01 Maxwell Loop Current Theorem Verificationjoydeep786Оценок пока нет
- By: Mr. Augosto M. DirectoДокумент34 страницыBy: Mr. Augosto M. DirectoPaul Senen DiduloОценок пока нет
- By: Mr. Augosto M. DirectoДокумент34 страницыBy: Mr. Augosto M. DirectoJames RojasОценок пока нет
- تقرير مختبر الكهرباء 1Документ6 страницتقرير مختبر الكهرباء 1ali dhiaОценок пока нет
- DC CircuitsДокумент34 страницыDC CircuitsPeach BubbleОценок пока нет
- Lab3group11 PDFДокумент13 страницLab3group11 PDFdharwinОценок пока нет
- Kirchoff RuleДокумент19 страницKirchoff RuleluanleОценок пока нет
- NACES, Leidi NADAL, Grazelle QUE, Arl Dominic TUGAHAN, Russdale VanДокумент7 страницNACES, Leidi NADAL, Grazelle QUE, Arl Dominic TUGAHAN, Russdale VanJohn Carlos MislangОценок пока нет
- NACES, Leidi NADAL, Grazelle QUE, Arl Dominic TUGAHAN, Russdale VanДокумент7 страницNACES, Leidi NADAL, Grazelle QUE, Arl Dominic TUGAHAN, Russdale VanJohn Carlos MislangОценок пока нет
- BE Lab ReportДокумент63 страницыBE Lab ReportArenОценок пока нет
- ET Lab2 ReportДокумент7 страницET Lab2 ReportMunisprasad MuniandyОценок пока нет
- Physics Exp 8 GRP 10Документ6 страницPhysics Exp 8 GRP 10Elizabeth Jade ViceraОценок пока нет
- Sulaimani Polytechnic University Engineering Technical College Communication DepartmentДокумент12 страницSulaimani Polytechnic University Engineering Technical College Communication Departmentsarkar salamОценок пока нет
- Resistors in ParallelДокумент4 страницыResistors in ParallelYosif AlanesiОценок пока нет
- Resistance and Logic CctsДокумент9 страницResistance and Logic CctsdeshteyОценок пока нет
- Q.1Find The Total Current Through R3Документ16 страницQ.1Find The Total Current Through R3Waqar100% (1)
- Lab Report Exp Series and Parallel Circuit - Group4 (s25)Документ14 страницLab Report Exp Series and Parallel Circuit - Group4 (s25)FARHAH BATRISYIA ABDUL RAHIMОценок пока нет
- Lab 5 Series and Parallel CircuitsДокумент3 страницыLab 5 Series and Parallel CircuitsJimmyPowellОценок пока нет
- Lab 4Документ4 страницыLab 4Rushanda BuchananОценок пока нет
- EA9 IndividualReport#6 CAÑAДокумент9 страницEA9 IndividualReport#6 CAÑAJaphetRayModestoCanaОценок пока нет
- Circuits I Lab 1 Post ReportДокумент14 страницCircuits I Lab 1 Post ReportGreg KeenerОценок пока нет
- Resistive Circuit PracticeДокумент11 страницResistive Circuit PracticeBrandon BarndtОценок пока нет
- POWER SUPPLY - Extra High Voltage - 6000V.DC.: Instruction SheetДокумент2 страницыPOWER SUPPLY - Extra High Voltage - 6000V.DC.: Instruction SheetlamchunyienОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Project - ConductivityДокумент21 страницаChemistry Project - ConductivityVaibhav AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Exp 03Документ9 страницExp 03Zharlene SasotОценок пока нет
- (Lab Report) : Experiment 03Документ20 страниц(Lab Report) : Experiment 03Little WizardОценок пока нет
- Analysis of DC Circuit Using Mesh and Nodal AnalysisДокумент12 страницAnalysis of DC Circuit Using Mesh and Nodal AnalysisSai AravindОценок пока нет
- Circuits Lab Exp 4 ReportДокумент15 страницCircuits Lab Exp 4 ReportEdamEdamОценок пока нет
- Experiment#2: TheoryДокумент5 страницExperiment#2: TheorySarem AlemuОценок пока нет
- Analysis of DC Circuit Using Mesh and Nodal AnalysisДокумент12 страницAnalysis of DC Circuit Using Mesh and Nodal AnalysisSai AravindОценок пока нет
- Circuit Construction Kit Lab: Part 1: Ohm's LawДокумент13 страницCircuit Construction Kit Lab: Part 1: Ohm's LawRAFIQAОценок пока нет
- Practica 1-Conocer EdLabДокумент10 страницPractica 1-Conocer EdLabhalbanbОценок пока нет
- Ckts 1 Module 3 FinalsДокумент27 страницCkts 1 Module 3 FinalsAdrian Prince LopezОценок пока нет
- Chap2 Beta1313 Part IДокумент85 страницChap2 Beta1313 Part ISimson DianОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Experiment 3Документ15 страницLaboratory Experiment 3JOHN LOUIE SUDEОценок пока нет
- Circuits Lab #6Документ7 страницCircuits Lab #6Bruce WayneОценок пока нет
- Resistors in SeriesДокумент4 страницыResistors in SeriesYosif AlanesiОценок пока нет
- Lab 4 Kirchoff Law Sea19029, Sea19004, Sea19027Документ14 страницLab 4 Kirchoff Law Sea19029, Sea19004, Sea19027Muhammad NaguibОценок пока нет
- StudentДокумент62 страницыStudentliamweinertОценок пока нет
- StudentДокумент62 страницыStudentliamweinertОценок пока нет
- Stats Assignment 1 - HistogramДокумент1 страницаStats Assignment 1 - HistogramliamweinertОценок пока нет
- Hess' Law LabДокумент9 страницHess' Law Labliamweinert90% (20)