Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Link-Belt LS-108 Hylab 5 Hydraulic Diagram PDF
Загружено:
KOKОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Link-Belt LS-108 Hylab 5 Hydraulic Diagram PDF
Загружено:
KOKАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
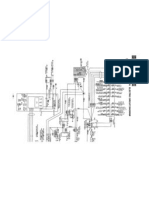
Hydraulic Circuit Outline
ES04-01-0085.0R0S
1 Overall Circuit
9
0.39 to 1.47MPa
(56.6 to 213.2psi)
10
10
PS.12
SOL.20 T
SOL.21 T
B A
R.D. L
B A
F.D. L
B.H.
SOL.29 T
B A
3.D./4.D.
L
57
FRONT
BRAKE
SOL.7
10
B A
10
PS.13
B4
B4
R.D.
6 0.39 to 0.78MPa
PS.4
B B BB BB
1 2 3 4 5 6
T1
(56.6 to 113.1psi)
A1
F.D.
R.D. H
X
P
T
3.D./
4.D.
A3
10
L.H
SWING
PS.6
8
R.H 0.39 to 0.78MPa
(56.6 to 113.1psi)
10
A3
A3
R.D.I
a3
b3
L
1.47 MPa
(213.2psi)
B.H.
23.5MPa
(psi)
0.39 to 0.78MPa
(56.6 to 113.1psi)
A2
10
A9
10
0.39 to 1.47MPa
(56.6 to 213.2psi)
A10
11
3/4.D. H
F
L.T.
b2
B1
R.T.
A1
b1
4th. BRAKE
SOL.13
P
L.T.
A1
a1
a1
PS3
52
29.4 MPa
(4264psi)
P1
P1'
P2'
52
P2
29.4 MPa
(4264psi)
X
0.7MPa
(101.5psi)
B B B B B B
12 1110 9 8 7
X
X
AV
0.7MPa
(101.5psi)
X
Dr 35
BV
AV
BV
9
X
28.4MPa
(4119psi)
36
17
A
SOL.14
PILOT
PRESS CUT
28.4MPa
(4119psi)
36
58
40
B A
X
Dr
19
54
X
a1
X
b
4.5
MPa
(653
psi)
34.3 MPa
(4975psi)
34
T
SOL.34
55
22.5MPa
(3263psi)
Dr
39
38
37
DR
21
B2
A2
0.05MPa
(7.3psi)
4th.
DRUM
AM
FRONT DRUM
(MAIN HOIST)
B1
A1
PB
DR
SOL.12
1.76MPa
(255.3psi)
Dr
Dr
DR
16
X
X 0.7 MPa
(101.5psi)
Av
Bv
12
DR
BM
BV
AV
PS.20
43
4th. CLUTCH
P
5.9 to 6.5MPa
(856 to 943psi)
PS10
PS.21
51
PS4
35
9
10
b1
A11
0.39 to 0.78MPa
(56.6 to 113.1psi)
X
0.10MPa
(14.5psi)
A B AB
2 2 1 1
13
A12
52
DRUM
SELECTION
18
SOL.3
X
T2
PP
P2
SOL.1
B A
15
3.D/4.D.
a2
B A
P1
b2
a2
F.D. H
A8
F
R.T.
P2
17
17
27.4MPa
(3974psi)
1.47 MPa
(213.2psi)
A7
SOL.17
T
10
TRAVEL
(HIGH SPEED)
A6
10
A SOL.11 B A
AUX.
EMERGENCY
BRAKE
B A
b3
L
PS.6
SOL.4
B A
B2
B1
0.39 to 2.94MPa
(56.6 to 426.4psi)
SOL.19
T
R.D.II
14
A2
A5
T
P
53
14
a3
B2
PS2
B A
16
SOL.5
B.H. H
A4
0.39 to 1.47MPa
(56.6 to 213.2psi)
B A
SOL.9
T
b4
H
B3
14
P1
B.H.
PS.5
a4
SOL.2
10
0.39 to 0.78MPa
(56.6 to 113.1psi)
b4
L
H
B3
PS.2
A4
14
56
REAR
CLUTCH
SOL.6
27.4MPa
(3974psi)
F.D.I
27.4MPa
(3974psi)
F.D.II
a4
PS1
A2
PS.1
A4
0.39 to 2.74
MPa
(56.6 to 397.4
psi)
SOL.8 B
MAIN
EMERGENCY
BRAKE
P
B A
B A
PS.3
T
FRONT
CLUTCH
BOOM HOIST SWING
BRAKE
BRAKE
SOL.15
SOL.18
REAR
BRAKE
SOL.10
PB
PA
SWING
R.H
SWING
L.H
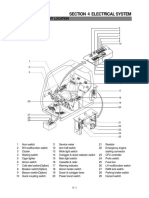
Description
Remote Control Valve
Orifice
Remote Control Valve
Remote Control Valve
Pressure Guage
Pressure Switch
Pressure Switch
Pressure Switch
Pressure Switch
Solenoid Valve
Orifice
Check Block
Control Valve
Flow Control Valve
Control Valve
Solenoid Valve
Throttle Check Valve
Return Filter
Accumlator
Relief Valve
Check Valve
Line Filter
Control Valve
Flow Control Valve
Hyd. Cylinder
Check Valve
Oil Tank
Travel Motor
Gear Pump
Combination Pump
Check Valve
Oil Cooler
Nipple
Hoist Motor (B/H)
Counter Bal. Valve
Hoist Motor (Main & Aux.)
Clutch Ass'y
Rotary Joint
Brake Cylinder
Pressure Switch
No.
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
Description
Check Valve
Control Valve
Swing Motor
Rotary Joint
Retract Cylinder
Take-Up Cylinder
Check Valve
Shuttle Valve
Shut-off Valve
Reducing Valve
Flow Control Valve
Plug
Control Valve
Counter Bal. Valve
Hoist Motor
Remote Control Valve
Pressure Switch
Solenoid Valve
B.H.: Boom Hoist
R.D.: Rear Drum
F.D. : Front Drum
3.D. : Third Drum
4.D. : Fourth Drum
R.T. : Right Travel
L.T. : Left Travel
I
: 1-Speed
II : 2-Speed
H : Hoisting
L : Lowering
F : Forward
B : Backward
R.H.: Right Hand
L.H. : Left Hand
20
3RD. DRUM
LBCE SUPPLY
BOOM
HOIST
37
P
20.6 MPa
(2988psi)
REAR DRUM
(AUX. HOIST)
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
38
37
39
40
7.85MPa
(1139psi)
39
39
40
20.6 MPa
(2988psi)
22
23
PS.9
PS.8
42
38
5.9 to 6.5MPa
(856 to 943psi)
0.4MPa
(psi)
0.10MPa
(14.5psi)
44
24
X
F
C H
G A
25
45
P
RETRACT CYL.
49
26
A
2.94MPa
(426.4psi)
33
0.02MPa (2.9psi)
TAKE-UP CYL.
48
33
47
33
47
20.6 MPa (2988psi)
46
33
20.6 MPa (2988psi)
P3 A2
Psv
31
(FRONT)
a1 X
X a2
(REAR)
48
COUNTERWEIGHT REMOVAL CYLINDER
Pm1
Pm1
P2
P1
P1
P2
32
27
Pi1
R/G
R/G
FORWARD
28
0.2 MPa (29psi)
BACKWARD
BACKWARD
SOL.16
B XA
Pc2
Pc1
FORWARD
T P
ENGINE
P1
30
0504
COUNTERWEIGHT REMOVAL DEVICE
Pi2
28
Pm2
TRAVEL MOTOR(L.H)
25
49
0.02MPa
A1
46
0.3MPa
(43.5psi)
50
Ps
Ps
Pm2
Dr
P2
P3
P4
29
16
PUMP CONTROL
B1
CBJ2165Z-E 1
TRAVEL MOTOR(R.H)
1/14
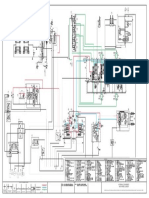
Hydraulic Circuit Outline
ES04-01-0085.0R0S
2 Types And Driven Actuator Of Pumps
Pump Type
Pump No.
Variable Delivery
Pump (Tilting Plate)
P1
R.H. Travel, Boom Hoist, Rear Low 1-Speed, Front High 2-Speed
P2
L.H. Travel, 3rd/4th Drum, Rear High 2-Speed, Front Low 1-Speed
P3
Swing, Retract, Pump Regulator Control
P4
Pilot Line, Clutch Line, Brake Lline, Pump Control,
Counterweight Removal Line, Travel High Speed Line
Fixed Delivery Gear
Pump
Driven Actuator
3 Explanation Of Control Circuit
3.1 Control circuit of pump
In each delivery pump (P1,P2), the amount of delivery can be changed depending upon the loads
applied. The flow-rate is controlled by means of detecting the pressure between the pumps, to restrain a
maximum load in the system. The functions for front drum, rear drum hoist and travel operations can be
performed at the same time. A maximum load is totally controlled in this system by means of detecting
the pressure of pumps (P1,P2) though the pilot line.
Pump P3 is used for swing motion (including retracting motion) only. The horsepower of the pump is
totally controlled, thus the engine can be run without stopping when an overload is applied, as the flowrate at P1 and P2 is cotrolled by swing load pressure.
Pump control
When the pump control switch located on the rear drum control lever is turned on, the discharge amount
of the P1 and P2 pumps are controlled to a minimum.
It can be used to fine-control the hoisting and lowering of the hook. This switch also allows slowing the
front, rear, third, fourth drum, boom hoist, and travel operations.
To Control Device
(Pilot, Clutch, Brake Line)
Gate Lock
Accumulator
Hydraulically Operated
Electrically Operated
From Pilot Line
(R.H. Travel, Boom Hoist,
Rear Low 1-Speed,
Front High 2-Speed)
Front High 2-Speed
Front Low 1-Speed
Rear High 2-Speed
Rear Low 1-Speed
3rd/4th Drum
Boom Hoist
R.H. Travel
L.H. Travel
4-Series Control Valve
From Pilot Line
(L.H. Travel, 3rd/4th Drum,
Rear High 2-Speed,
Front Low 1-Speed)
Counterweight
Cylinder Line
Swing And Retract
Oil Cooler
Sump Tank
Engine
P4
P1
Pump Control
P2 P3
CB04-001
0504
2/14
Hydraulic Circuit Outline
3.2 Pilot circuit
ES04-01-0085.0R0S
L.H. Travel
Control Lever
R.H. Travel
Control Lever
Swing
Control Lever
3rd/4th Drum
Control Lever
Rear Drum
Control Lever
Front Drum
Control Lever
Boom Hoist
Control Lever
To
Tank
To P2 Pump
Regulator
Control Valve
To P2 Pump
Regulator
To P1 Pump
Regulator
To P2 Pump
Regulator
1 Speed
1 Speed
Control Valve
To P1 Pump
Regulator
To P1 Pump
Regulator
2 Speed
Lever
To P2 Pump
Regulator
2 Speed
To P1 Pump
Regulator
"Stop" Side
"Operation"
Side
R.H.
Swing
Accumulator
L.H.
Swing
Motor
Motor
Motor
Motor
Motor
Front Drum
Poilot Pressure
Cut
Rear Drum
4th Drum
Swing Device
Relief Valve
7.84MPa
(1137psi)
Boom Hoist Drum
Hydraulically Operated
Electrically Operated
CB04-002
Counterweight Removal
Device
Engine P1 P2 P3 P4
Line Filter
Hydraulic Power
Source
3rd Drum (LBCE Supply)
The power source in the pilot circuit is pump P4. The pressure of pump P4 is also used for the brakes and clutches of the front, rear, 4th and boom hoist, the brakes in the swing mechanism, counterweight cylinders.
The circuit pressure is controlled at 7.84MPa (1137psi) by the relief valve.
[Hydraulic power source]
The hydraulic power source consists of an accumulator, relief valve and line filter. When the pressure reaches 7.84MPa (1137psi), a relief valve opens to return this hydraulic pressure to a tank.
Even if the engine is stopped, the pressure will not drop suddenly since the reverse of pressurized hydraulic oil is prevented with a check valve. Still, the pressure drop may not be perfectly prevented due to some internal leakage in remote
control (pilot) valves and solenoid valves. In fact, the accumulator is necessary to maintain the circuit pressure constant for a while, by supplying the pressure into the circuit since the circuit pressure will drop to zero instantaneously when
leaking occurs in any part of the circuit as the hydraulic oil is incompressible.
The pressure, however, will gradually drop and finally fall to zero. The accumulator is filled with nitrogen gas (N2) under 4.5MPa (653psi) and the circuit pressure from 7.84MPa (1137psi) to 4.5MPa (653psi) drops gradually but once the
pressure becomes lower than 4.5MPa (653psi), it will drop sharply.
[Pilot pressure cut]
When the lever located at an entrance of the operators cab is pushed forward, pressurized oil is returned to the tank and all the functions are stopped.
It prevents the accident due to forgetting returning the control levers or wrong operations.
0504
3/14
2/14
Hydraulic Circuit Outline
ES04-01-0085.0R0S
3.3 Front and rear drum circuit
Basically the front drum and rear drum circuits are independent of each other. As mentioned before,
pumps P1 and P2 are of the variable delivery type. The P1 and P2 are designed to ensure efficient
functions by restraining a maximum load. In addition, the line speed can be changed from low to high
speed and vice versa with a control valve. In the 2-speed circuit in the high-speed (2-speed) mode, the
front and rear drum are driven with the pressurized hydraulic oil delivered from both P1 and P2 pumps.
The pilot pressure functions the control valve. As this line is explained in 3.2, description will be made
only of the pressure line here. Since the front and rear drums have the same circuits, the front drum is
explained herein.
When the front drum control lever is set to the hoisting position (pulled toward), the pressurized
hydraulic oil of the P2 pump will flow in the direction of the arrow ( ) from the control valve. The oil is
directed to a winch motor through the check valve to rotate the motor and then its pressure will decrease.
The oil will return to the sump tank again through the control valve.
Front Drum Control Lever
Lowering Hoisting
0.39 to 2.74MPa
(56.6 to 397psi)
Rear Drum Control Lever
Lowering Hoisting
0.39 to 2.74MPa
(56.6 to 397psi)
HSOL
LSOL
P4
To Tank
HSOL
LSOL
To P2 Pump
Regulator
To P1 Pump
Regulator
S/C
To P1 Pump
Regulator
To P2 Pump
Regulator
S/C
P2
Control Valve
2-Speed
Control Valve
2-Speed
1-Speed
1-Speed
P1
BSOL
CSOL
BSOL
CSOL
ESOL
Motor
.7MPa
(102psi)
Front Drum
ESOL
Motor
.7MPa
(102psi)
28.4MPa
(4119psi)
28.4MPa
(4119psi)
Rear Drum
Brake Cylinder
Brake Cylinder
Clutch
Clutch
Limit Switch
S/C
Safety
Controller
Overhoist Limit Switch
(Normally Switched ON
When The Weight Is
Applied.)
Front Drum Lock
Toggle Switch
Control Panel
Buzzer
Switch(Front)
Switch(Rear)
Front Drum
Lock Mode
Lock Pawl
Motor
0504
HSOL: Hoisting Stop Solenoid Valve
LSOL: Lowering Stop Solenoid Valve
BSOL: Brake Solenoid Valve
CSOL: Clutch Solenoid Valve
ESOL: Emergency Solenoid Valve
4/14
Auto-Brake Mode
Free Mode
R.H. Control Panel
Hydraulically Operated
Electrically Operated
CB04-003
Hydraulic Circuit Outline
ES04-01-0085.0R0S
When the lever is returned to the neutral position, the hoist side of the control valve is a blocked circuit,
thus the motor will not reverse. Of course, the reverse current of oil can be prevented with a check valve
within the counterbalancing valve. Eventually, a double reverse current preventing system is available
as the control valve with neutral block position also function as a check valve preventing the reverse
current. The control valve alone does not give an effective sealing so, the counterbalancing valve mainly
functions to block the oil flow.
A relief valve set to 28.4MPa (4119psi) is provided in the counterbalancing valve. In normal operation,
this relief valve does not function. If any overloads or problems are produced in the circuit, the main relief
valve 29.4MPa (4264psi) will function prior to this relief valve to protect the circuit. If the pressure is
released instantaneously, the relief valve in the counterbalancing valve may function in some cases. But
the counterbalancing valves will never function to release the pressure unless the main relief valve is out
of order as the latter is set to the lower pressure limit.
When the control lever is set to the lowering position (pushed forward), the pressurized hydraulic oil will
flow in the direction of the arrow (
) from the control valve.
But as the circuit is closed while the pressure is low, the oil does not flow in the circuit. The pilot
pressure exceeds the spring force only when the pressure reaches .7MPa (102psi), and the bypass
circuit is then opened to reverse the motor.
In the case of front drum operation, pump P1 and P2 will run and the motor speed is doubled for the
high speed operation with the control lever shifted at high speed stage. The combined operation of the
front drum high speed and rear drum low speed cannot be got in this circuit, the rear drum operation is
stopped.
[Anti-two block]
When the hook is raised too high (to the head sheave anti-two block switch), the limit switch activates
to send a signal to the solenoid valve HSOL7, so that the pilot line for hoisting is changed over to the tank
port.This will make the control valve return to the neutral position. The motor stops and an audio/visual
alarm Two-block Limit.
[Front and rear drum pawl lock]
The drum pawl lock is provided as a device to prevent the hook or the suspended load from falling.
When the toggle switch is turned to the lock side, the electric motor of the pawl lock is activated and the
pawl is engaged with the drum at the same time a signal is sent to the solenoid valve LSOL 5. The valve
will connect the load lowering pilot line to the tank port. This will return the control valve to the neutral
position. When the toggle switch is on the lock side, pressurized oil from P5 flows to the tank port without
operation even if the control lever is turned to the lowering side. This produces a safety circuit, which
does not damage the machine at all.
[Lever lock]
The function of control lever stops when lever lock switch on the control panel is turned to the lock side.
When lever lock switch is turned to the lock side, a signal is sent to the solenoid valve LSOL5 and
HSOL7. Even if the control lever is set to hoisting/lowering position, the pilot pressure is connected to
tank port, the drum dose not rotate.
0504
5/14
Hydraulic Circuit Outline
ES04-01-0085.0R0S
[Explanation of brake function]
No foot braking is required since the brake is automatically applied when the control lever is placed in
neutral position. But the automatic brake can not be applied when the brake mode is placed at the free
mode (bucket mode) side.
The brake has two systems. One is the automatic brake system and the other is the foot brake (free fall)
system. These two systems can be changed over by the manual select switch on the control panel and
the safety switch on the brake pedal for prevention of accidental changing.
[Automatic brake system]
The automatic brake is activated by a spring force and is released hydraulically. No pilot pressure will
be charged with the front and rear drum control levers placed in neutral position. The BSOL2 and ESOL4
in the automatic brake line activates by the signal sent from the pressure switch 1 which detects the pilot
pressure, to flow out the oil from the release cylinder, to apply brake by a spring force. On the other hand,
on the clutch side, the signal from the pressure switch 1 operates the CSOL6 to continuously guide the
pressurized oil in order to activate the clutch. When the front and rear drum control levers are positioned
to Hoisting (or Lowering), pilot pressure is charged and the BSOL 2 is activated. Pressure oil goes
through BSOL 2 and is blocked briefly by ESOL 4 until 4 is activated, so the brake is not released yet. On
the other hand, when the clutch line reaches 6.5MPa (943psi) the pressure switch 3 is activated and
activates the emergency brake ESOL 4. The brake pressurized oil flows through BSOL 2 and ESOL4,
flowing into the brake release cylinder, releasing the brake.
[Foot brake system]
The free fall (bucket mode) operation is made by selecting the switch of the front and rear drum control
lever at the same time, pushing the brake pedal lightly. With the free fall conditions, the pressurized oil is
directed to the release cylinder of the automatic brake device, and the automatic brake is released. The
braking operation can be made by the foot brake. The brake will be applied through the link mechanism
by pressing the foot pedal.
For safety reasons, if the engine stops for reason or clutch pressure goes below 5.9MPa (856psi), the
ESOL4 is activated by the pressure switch 3 to apply the brake automatically. At the same time, the
lowering stop LSOL5 is also activated to prevent suspended load from falling.
0504
6/14
Hydraulic Circuit Outline
ES04-01-0085.0R0S
3.4 Fourth drum circuit
The fourth drum is driven with the variable capacity pump P2 .
The control lever is common to the third and fourth drum and change the switch on the control panel for the purpose
of use.
The hydraulic circuit for the fourth drum is the same as the front and the rear drum.
However this circuit has not "High speed (2nd speed)".
3rd/4th Drum Control Lever
Lowering Hoisting
.39 to 1.47MPa
(56.6 to 213psi)
P4
HSOL
LSOL
To P2 Pump
Regulator
5
S/C
P2
.7MPa
(102psi)
BSOL
CSOL
ESOL
34.3 MPa
(4975psi)
Clutch
Brake Cylinder
Fourth Drum
Limit Switch
3RD/4TH Drum Lock
Toggle Switch
S/C
Safety
Controller
Overhoist Limit Switch
(Normally Switched ON
When The Weight Is
Applied.)
Control Panel
Buzzer
Fourth Drum
3RD
Switch ( 4TH )
Switch (3RD/4TH SELECT)
Lock Mode
Third Drum : Illustrated By LBCE
HSOL: Hoisting Stop Solenoid Valve
Lock Pawl LSOL: Lowering Stop Solenoid Valve
BSOL: Brake Solenoid Valve
CSOL: Clutch Solenoid Valve
Motor
ESOL: Emergency Solenoid Valve
0504
7/14
Auto-Brake Mode
Free Mode
R.H. Control Panel
Hydraulically Operated
Electrically Operated
CB04-004
Hydraulic Circuit Outline
ES04-01-0085.0R0S
3.5 Boom hoist circuit
This circuit is basically the same as those of front and rear drum winches with the exception that the 2speed control system is not provided.
The pressure for the boom hoist is produced by pump P1. When the control lever is moved to the
hoisting position, (pulled toward the operator), the pressurized hydraulic oil will flow in the arrow ( )
direction as the pilot pressure moves the spool of the control valve.
Boom Hoist Lever
Lowering
Hoisting
.39 to 1.47MPa
(56.6 to 213psi)
P4
Brake/Drum Lock Solenoid Valve
4
Pressure
Switch
3
Drum Lock
22.5MPa (3263psi)
Check Block
Brake
To P1 Pump
Regulator
Control Valve
Drum
1.76MPa (255 psi)
S/C
Safety
Controller
P1
Buzzer
Boom
Overhoist
Limit
Switch
Hydraulically Operated
Electrically Operated
CB04-005
0504
8/14
Hydraulic Circuit Outline
ES04-01-0085.0R0S
The oil passes through a check valve in the counterbalancing valve to rotate the motor, and then returns
to the control valve under low pressure from the motor, and to the sump tank. On the other hand, the
same pilot pressure is detected with a pressure switch and the solenoid valve in the brake line and drum
lock circuit are energized. Thus, the pressure in the pilot line (P4) is directed to the brake cylinder and
drum lock cylinder to release the brake and drum lock before the motor rotates.
When the control lever is returned to the neutral position, the pilot pressure will become low and the
pressure switch will cut off the electric current to the solenoid. Then the spool is changed over and the
pressure in the brake line and drum lock is cut off returning the oil to the tank port. The disk will be applied
again by means of a force produced by a spring of the brake cylinder to lock the drum with secure stop of
the motor. In addition, boom lowering is prevented by the drum lock.
Although a counterbalancing valve is incorporated into this circuit like the front and rear drum circuits,
the disk brake is also used to secure sufficient motor locking. The select switch of free mode is not
provided is the difference from the front and rear drum brake mechanism.
When the control lever is moved to the lowering position (pushed forward), the oil flow direction will be
reversed, flowing in the direction of the arrow (
).The motor can not be reversed since a check valve in
the counterbalancing valve is provided in the return circuit.
The oil is returned to the control valve by opening the bypass circuit with pilot pressure produced from
the self-pressure. With this function, the motor will rotate and the boom can be lowered by rotating the
drum. The pilot pressure can be applied smoothly with a throttle valve provided in the pilot line, thus the
boom can be lowered smoothly. The pilot pressure is 1.76MPa (255 psi). and changes over the functions
of valve as the bypass circuit.
[Boom over hoist limiting device]
When the boom reaches raising limit, the limit switch activates to send signal to the solenoid valve 1, so
that the pilot line for hoisting is changed over to the tank port. This will make the control valve return to the
neutral position. The motor stops, and the buzzer sounds.
0504
9/14
Hydraulic Circuit Outline
ES04-01-0085.0R0S
3.6 Swing circuit
The swings are independent from each other.
The circuit is same as the R.H. swing and L.H. swing.
Retract Cylinder
Swing/Retract Control Valve
Rotating Joint
Brake
Release
Cylinder
Swing Brake
Release Switch
20.6 MPa
(2988 psi)
R.H.
L.H.
Swing
Control Lever
Accumlator
Swing
Motor
L.H. R.H.
.39 to 1.47Mpa
(56.6 to 213psi)
Engine
Relief Valve
P4
Swing Device
Line Filter
P3
P2
P1
Swing Brake Solenoid
Hydraulically Operated
Sump Tank
Electrically Operated
CB04-006
3.6.1 Swing circuit
When the swing lever is pushed forward, (L.H. swing) the oil pressurized by pump P3 will flow in the
direction of the arrow ( ) from the control valve. The pressurized hydraulic oil actuates the swing motor
and returns to the control valve under low pressure and then to the sump tank (
). If the rotation of the
motor is stopped by any external pressure applied, the oil will be bypassed through a relief circuit
(20.6MPa(2988psi)) of the control valve to protect the circuit since the highly pressurized oil is deadlocked in the circuit.
The swing brake release switch on the swing lever is used for parking temporarily after the swing is
stopped, and should not be put into function during swinging. If actuated in swinging, accidents may
occur. There is a method to stop the swing at the required position, in which the swing is stopped by
shifting the control lever slightly in the reverse direction.
Normally, the swing speed is controlled by means of the control lever stroke.
3.6.2 Swing brake circuit
By placing the switch on the swing lever in ON, the pressurized oil is directed in the brake release
cylinder to release a wet-type multi-plate brake.
By placing the switch in OFF, the solenoid valve should be in OFF. The pressurized oil in the brake
release cylinder is drained and the wet-type multi-plate function to brake the swing by spring pressure.
0504
10/14
Hydraulic Circuit Outline
ES04-01-0085.0R0S
3.7 Travel circuit
The travel motor receives the pressurized hydraulic oil from two pumps, which do not flow together.
The pumps P1 and P2 supply the pressurized oil to the R.H. motor and L.H. motor respectively. Discrepancy in discharge of P1 and P2 pumps may cause uneven travelling or unbalanced travelling which
may be increased by circuit resistance. To avoid this trouble, the pressure of both pumps must be
checked and then corrected to be equal in the regulator circuit in this system.
Travel
High Speed
Switch
Forward
P4
R.H. Travel Control Lever
.39 to 1.47Mpa (56.6 to 213psi)
L.H. Travel Control Lever
.39 to 1.47Mpa(56.6 to 213psi)
Backward Forward
Backward
To Tank
To P1 Pump Regulator
To P2 Pump Regulator
Control Valve
P2
Control Valve
P1
Control Panel
Hydraulically Operated
Travel High Speed
Select Solenoid Valve
Shoe Extension
Cylinder
C H
G A
Rotating Joint
.02MPa
(2.9psi)
Electrically Operated
.02MPa
(2.9psi)
20.6MPa
(2988psi)
20.6MPa
(2988psi)
Pm1
Pm1
Backward
Backward
P1
R/C
P2
P1
T
Forward
Pm2
R/C
P2
T
Forward
Ps
Ps Pm2
Travel Motor(L.H)
Right Travel Device
CB04-007
0504
11/14
Hydraulic Circuit Outline
ES04-01-0085.0R0S
3.7.1 Travel circuit
When the travel control lever is pushed forward or backward, the oil pressurized by pump P1 will flow in
the direction of the arrow ( ) as the pilot pressure .39 to 1.47MPa (56.6 to 213psi) changes over the
control valve spool, and reaches the brake valve through a rotating joint. The brake valve opens the
pipeline,directing the pressurized oil to the motor. As the motor has a brake with it, the oil alone can not
rotate it. Therefore, a part of the pressurized oil must be directed to the brake cylinder to release the disk
brake to free the motor. Oil pressure from the motor will become low and the oil will return to the sump
tank under low pressure throuth the control valve along the return circuit.
With the control lever set to the neutral position, the brake valve blocks the oil circuit to stop the motor
and at the same time, the spring releases the oil in the brake release cylinder and the multi-plate brake
applies and the motor drive shaft is secured. This prevents the machine from traveling on a slope.
If any load greater than the rotating torque is applied on to the travel motor, the motor will stop and the
oil pipeline circuit will close resulting in breakage on instruments or piping as the pressure will rise too far.
A safety valve therefore, is necessary to prevent any breakage or damage in the circuit. The pressure is
released to the tank port by opening the bypass circuit with the main relief valve 29.4MPa (4264psi) in
the control valve.
A relief valve (set pressure: 32.4MPa (4699psi)) to release the overpressure is provided in the motor
unit.
3.7.2 High speed circuit
When the travel high speed switch on the control panel is placed in "ON" side, the travel high speed
select solenoid valve is changed over and the control hydraulic oil generated from pump P4 changes
over the speed select valve built in the travel motor through the solenoid valve and the rotating joint.
The regulator in the motor is activated by the pressurized oil and a tilting angle of the tilting plate becomes smaller.
Therefore, the travel operation can be made at high speed with motor speed increased. (The motor
displacement is decreased.)
3.7.3 Shoe extension cylinder circuit
When the travel control lever is placed forward or backward, the oil, as the above mentioned, will flow to
the shoe extension cylinder at the same time the travel motor is started, to give appropriate tension
(adjustment value) shoe extension cylinder automatically. The condition is maintained even if the lever is
placed in neutral.
The pressurized oil is maintained by the check valve, and unless the external pressure is applied, the
shoe does not contract. If the external pressure exceeds 20.6MPa (2988psi), the check valve will be
opened. The check valve releases the pressurized oil to prevent applying excessive force to the shoe
and the drive equiment.
Note: Refer to the operator's manual for tension adjustment value.
3.7.4 Travel brake circuit
When the travel motor is driven, the pressurized oil is directed in the brake release cylinder to release.
With the lever in neutral, the control valve is in neutral and the pressurized oil in the brake release
cylinder is directed to the tank. The brake is actuated by the spring force.
0504
12/14
Hydraulic Circuit Outline
ES04-01-0085.0R0S
3.8 Retract cylinder circuit
The retract cylinder, installed on side frames.
When the retract lever is placed in the Extend side, the pressurized oil with pump P3 will flow in the
direction of the arrow ( ).
When the retract lever is placed in the Retract side, the pressurized oil from pump P3 will flow in the
direction of the dotted arrow (
). If any external pressure is applied, the oil will be bypassed through a
relief circuit (20.6 Mpa (2988 psi)) of the control valve to protect the circuit since the highly pressurized oil
is deadlocked in the circuit.
Swing/Retract Control Valve
Extend
Retract
Rotating Joint
To Swing
P3
Engine
Retract Cylinder
20.6Mpa(2988 psi)
Sump Tank
CB04-008
0504
13/14
Hydraulic Circuit Outline
ES04-01-0085.0R0S
3.9 Counterweight cylinder circuit
The counterweight removal/installation cylinder line is controlled by pump P4. The oil discharged from
the pump P4 usually flows to control devices such as the pilot line, clutch, brake line. The control valve is
used for counterweight removal/installation. When the lever is set to the Extend (lowering) side, the
pressurized oil from P4 pump flows in the direction of arrow ( ), passing through the line filter, control
valve and the cylinder. The oil on the Retract side in the cylinder flows in the direction of dotted line (
),
passing through the flow control valve, control valve and the sump tank. On the other hand, when the
lever is set to the Retract (lifting) side, the oil flows reversely.
When the oil is fed continuously by the P4 pump, its temperature rises causing damages of devices and
piping. A safety circuit for prevention of such damages is provided, where the main relief valve of the
control valve is activated at 20.6Mpa (2988psi) to lead the oil to the sump tank.
Other control devices cannot be used during operation of the counterweight removal/installation cylinder.
To Control Device
Accumulator
P
20.6MPa
(2988psi)
Relief Valve
Line Filter
Engine
Counterweight Removal Clyinder
P3 P4
P1 P2
Sump Tank
0504
CB04-009
14/14
Вам также может понравиться
- 150 Ton Link Belt LS 238HSpecsДокумент6 страниц150 Ton Link Belt LS 238HSpecsYosses Sang Nahkoda0% (1)
- Air Drier PartsДокумент3 страницыAir Drier PartsRajan MullappillyОценок пока нет
- Hydromatik A7VOДокумент20 страницHydromatik A7VOadelmomouraОценок пока нет
- HIDRAULICOДокумент2 страницыHIDRAULICOAlcides Chilo OllachicaОценок пока нет
- Repfllr Pflrts . . I: at BoschДокумент4 страницыRepfllr Pflrts . . I: at BoschEng-Mohammed SalemОценок пока нет
- Zaxis 800 Hydraulic Circuit Diagram: Attach To Vol No.: TT17VE-00Документ1 страницаZaxis 800 Hydraulic Circuit Diagram: Attach To Vol No.: TT17VE-00gustavo caicedoОценок пока нет
- Kobelco-S7yo00807ze01 Electric DiagramДокумент8 страницKobelco-S7yo00807ze01 Electric DiagramDejan Tasic100% (5)
- 345BДокумент2 страницы345BHector Valles100% (1)
- Transmission Control Valve: Shutdown SISДокумент11 страницTransmission Control Valve: Shutdown SIStaller100% (1)
- GR 300EX 1 Operation ManualДокумент290 страницGR 300EX 1 Operation Manualleobond760% (5)
- Pc128us 2 Sebm018419 PDFДокумент1 029 страницPc128us 2 Sebm018419 PDFLuis Carlos Ramos100% (1)
- SH450HD-3B Hydraulics: Sumitomo (S.H.I) Construction Machinery Manufacturing Co.,LtdДокумент24 страницыSH450HD-3B Hydraulics: Sumitomo (S.H.I) Construction Machinery Manufacturing Co.,Ltdsurianto100% (1)
- Cat 318Документ2 страницыCat 318Roman100% (4)
- AS358MДокумент15 страницAS358Mantonio2065100% (1)
- Sany 250Документ9 страницSany 250arifОценок пока нет
- 325C Excavator Electrical Schematic: Machine Harness Connector and Component LocationsДокумент2 страницы325C Excavator Electrical Schematic: Machine Harness Connector and Component Locationsjohn75% (4)
- Opening Guides - E PDFДокумент12 страницOpening Guides - E PDFpedro sanchezОценок пока нет
- 374F Excavator Hydraulic System, 349-1966-07Документ2 страницы374F Excavator Hydraulic System, 349-1966-07Mayumi Lizarme Buezo100% (1)
- Kobelco 6E - Hyd Motors PDFДокумент26 страницKobelco 6E - Hyd Motors PDFHai VanОценок пока нет
- Terex Bendini A 400Документ46 страницTerex Bendini A 400Lenin Valerio40% (5)
- Diagrama Interactivo Cat c18Документ9 страницDiagrama Interactivo Cat c18Miguel PerezОценок пока нет
- 4.9T Kobelco CK90URДокумент3 страницы4.9T Kobelco CK90URandraОценок пока нет
- Caterpillar Excabadora 246d Diagrama HydraДокумент11 страницCaterpillar Excabadora 246d Diagrama Hydrahitler morales gavidia100% (1)
- Grove RT750Документ18 страницGrove RT750Thibeault MesiliОценок пока нет
- SP12C - SP14CJ Service ManualДокумент173 страницыSP12C - SP14CJ Service ManualMMM-MMMОценок пока нет
- 345b Excavator Electrical System Schematic Used in Service Manual Renr1900 - Caterpillar Machinery Repair & TroubleshootingДокумент5 страниц345b Excavator Electrical System Schematic Used in Service Manual Renr1900 - Caterpillar Machinery Repair & TroubleshootingWilliams Burgos67% (3)
- Kobelco RK350 - 2 - 20000103TFДокумент8 страницKobelco RK350 - 2 - 20000103TFEric Hartono100% (1)
- H8 3334Документ746 страницH8 3334Nick MetullyОценок пока нет
- Tadano Gt-550e-2 S GДокумент13 страницTadano Gt-550e-2 S GBui Hoang DucОценок пока нет
- CR4L001 Gru 750-850 - 1 Part 2Документ66 страницCR4L001 Gru 750-850 - 1 Part 2metik22100% (2)
- DAEWOO DOOSAN SOLAR 130LC-V HYDRAULIC EXCAVATOR Service Repair Manual PDFДокумент83 страницыDAEWOO DOOSAN SOLAR 130LC-V HYDRAULIC EXCAVATOR Service Repair Manual PDFdfjjskemmdm38% (8)
- R140-9 Travel MotorДокумент7 страницR140-9 Travel MotorHai VanОценок пока нет
- GR 300EX 1 Operation ManualДокумент286 страницGR 300EX 1 Operation ManualIynsmla100% (1)
- Oilgear Specificl Controls TrainingДокумент26 страницOilgear Specificl Controls TrainingYuriPasenkoОценок пока нет
- Service Training Malaga 365C & 385C Hydraulic Excavators: Francis Apr 12Документ30 страницService Training Malaga 365C & 385C Hydraulic Excavators: Francis Apr 12ait mimouneОценок пока нет
- Sk75sr 3e EuДокумент8 страницSk75sr 3e EuPHÁT NGUYỄN THẾОценок пока нет
- Torque-Hub Planetary Final Drive 7000 Series Service Brakes: Manual WithДокумент66 страницTorque-Hub Planetary Final Drive 7000 Series Service Brakes: Manual WithMarceloGonçalves100% (1)
- T40140 6989561 enGB Om 05-11Документ144 страницыT40140 6989561 enGB Om 05-11ricardoОценок пока нет
- Tadano TM 1800 PDFДокумент151 страницаTadano TM 1800 PDFharounОценок пока нет
- 921E Tier 3 Schematic HydraulicДокумент1 страница921E Tier 3 Schematic HydraulicezeizabarrenaОценок пока нет
- Pumps and Filters: 345D, 349D, and 349D Excavator Hydraulic SystemДокумент2 страницыPumps and Filters: 345D, 349D, and 349D Excavator Hydraulic SystemTeknik Makina100% (1)
- Truck Mounted BSF 3609 H Concrete Pump 14 H 16 HДокумент2 страницыTruck Mounted BSF 3609 H Concrete Pump 14 H 16 HuirОценок пока нет
- NK-300VR: Fully Hydraulic Truck CraneДокумент8 страницNK-300VR: Fully Hydraulic Truck CraneFazri FadillahОценок пока нет
- GR 160N 1 00101Документ14 страницGR 160N 1 00101springcitypartsОценок пока нет
- Wa115-3 Vebm120100Документ174 страницыWa115-3 Vebm120100Augusto Oliveira100% (2)
- R210W 9S NamibiaДокумент10 страницR210W 9S NamibiaTran Trong PhuОценок пока нет
- Hyundai R130W-3 Electrical SystemДокумент49 страницHyundai R130W-3 Electrical SystemHai VanОценок пока нет
- Tana Gseries Ho C110304enДокумент65 страницTana Gseries Ho C110304enNguyen Ngoc100% (1)
- PW130-7K Travel SystemДокумент21 страницаPW130-7K Travel SystemHai VanОценок пока нет
- 966 CatДокумент12 страниц966 CatnajafaliОценок пока нет
- CK1000-II: Hydraulic Crawler CraneДокумент27 страницCK1000-II: Hydraulic Crawler Cranesongyanxin_dlutОценок пока нет
- A11v0 eДокумент32 страницыA11v0 eDhanraj PatilОценок пока нет
- PC78US-8 Electrical Circuit DiagramДокумент13 страницPC78US-8 Electrical Circuit DiagramHai Van100% (2)
- At PDFДокумент200 страницAt PDFchory_1100% (1)
- Diagrama Hidraulico D11R CATERPILLAR 2Документ2 страницыDiagrama Hidraulico D11R CATERPILLAR 2julio cesar100% (1)
- 345 9gs ControllerДокумент2 страницы345 9gs ControllernikosbbwОценок пока нет
- Cat 320cl Schema Hydraulic SystemДокумент2 страницыCat 320cl Schema Hydraulic SystemJuan Pablo Barron Marin97% (37)
- Plano Hidraulico D10T PDFДокумент2 страницыPlano Hidraulico D10T PDFJHOSMAR_22Оценок пока нет
- Group 3 Pilot Circuit: RCV Pedal Remote Control Valve (LH Lever) Remote Control Valve (RH Lever)Документ8 страницGroup 3 Pilot Circuit: RCV Pedal Remote Control Valve (LH Lever) Remote Control Valve (RH Lever)thierrylindoОценок пока нет
- Circuito 312b Cat 6gkДокумент2 страницыCircuito 312b Cat 6gkthierrylindo100% (13)
- Kobelco BME800HD SpecДокумент16 страницKobelco BME800HD SpecKOKОценок пока нет
- Teufelberger TK 16 Evo RopeДокумент2 страницыTeufelberger TK 16 Evo RopeKOKОценок пока нет
- Teufelberger TK 16 Evo RopeДокумент2 страницыTeufelberger TK 16 Evo RopeKOKОценок пока нет
- Zollern WinchДокумент20 страницZollern WinchKOK100% (3)
- American Hoist 9299Документ7 страницAmerican Hoist 9299KOKОценок пока нет
- Bendix Airbrake General CatalogueДокумент132 страницыBendix Airbrake General CatalogueKOKОценок пока нет
- Service Boom Inspection and RepairДокумент60 страницService Boom Inspection and RepairKOK100% (6)
- Braden PD Series Hydraulic WinchДокумент39 страницBraden PD Series Hydraulic WinchKOKОценок пока нет
- Manitowoc 16000 LMI Operation ManualДокумент14 страницManitowoc 16000 LMI Operation ManualKOK100% (3)
- SM 800.40 FlexAirValveДокумент31 страницаSM 800.40 FlexAirValveJosé Emilio D' LeónОценок пока нет
- Hitachi Sumitomo SCX1200-2Документ24 страницыHitachi Sumitomo SCX1200-2Kok Toong Fatt100% (1)
- Sany SR250 - Technical ManualДокумент71 страницаSany SR250 - Technical ManualKOK100% (12)
- Hitachi KH250HD DataДокумент7 страницHitachi KH250HD DataKOKОценок пока нет
- 22 RBДокумент22 страницы22 RBKOKОценок пока нет
- Sany SR250 Heavy Machinery - Product CertificateДокумент2 страницыSany SR250 Heavy Machinery - Product CertificateKOKОценок пока нет
- American Hoist 5299Документ5 страницAmerican Hoist 5299KOKОценок пока нет
- Hitachi Sumitomo SCX1200-2Документ24 страницыHitachi Sumitomo SCX1200-2Kok Toong Fatt100% (1)
- Grove-RT750 NA BrochureДокумент18 страницGrove-RT750 NA BrochureRkr Ashfaq KhanОценок пока нет
- Henry GoodrichДокумент2 страницыHenry GoodrichRyanPhillips50Оценок пока нет
- U000 9600a 11 12 U and G Series Crushers Operation ManualДокумент83 страницыU000 9600a 11 12 U and G Series Crushers Operation ManuallandagoОценок пока нет
- Directional Spool Valves, Direct Operated, With Solenoid Actuation Type WE XH and WE XMДокумент12 страницDirectional Spool Valves, Direct Operated, With Solenoid Actuation Type WE XH and WE XMpedro 1Оценок пока нет
- DEC Pump-Turbine IntroductionДокумент22 страницыDEC Pump-Turbine IntroductionkhanhdanhimОценок пока нет
- EHC - FinalДокумент64 страницыEHC - Finalyahya pamungkasОценок пока нет
- Exercise Solution of Chapter 3Документ8 страницExercise Solution of Chapter 3Engr ShabirОценок пока нет
- Accumulator PDFДокумент25 страницAccumulator PDFJuan Alejandro Cañas ColoradoОценок пока нет
- Manual Sandvik LH621Документ10 страницManual Sandvik LH621Jaime RobОценок пока нет
- Wittke Wizard ManualДокумент160 страницWittke Wizard ManualJeff RyersonОценок пока нет
- Parker Hyd PDFДокумент460 страницParker Hyd PDFAugusto RezendeОценок пока нет
- 416 FДокумент20 страниц416 FVictor Raul Osnayo MamaniОценок пока нет
- John Deere 320dДокумент2 страницыJohn Deere 320dNil Acuña0% (2)
- External Gear Pump High Performance Azpg: RE 10093/2019-09-27 Replaces: 2019-01Документ64 страницыExternal Gear Pump High Performance Azpg: RE 10093/2019-09-27 Replaces: 2019-01layetajОценок пока нет
- Sim HydraulicsДокумент7 страницSim HydraulicsyuvionfireОценок пока нет
- HPG PDFДокумент8 страницHPG PDFabjithОценок пока нет
- Sauer Danfoss H1B Bent Axis Motor Service ManualДокумент64 страницыSauer Danfoss H1B Bent Axis Motor Service ManualJustin100% (2)
- 9500-30 20180101 PartsSpecsДокумент131 страница9500-30 20180101 PartsSpecsLê Phan Đồng HưngОценок пока нет
- Discrete Control ElementsДокумент44 страницыDiscrete Control ElementswaqasahmadzОценок пока нет
- V80814 Parker in-AGB Series Hydraulic Filter InsertsДокумент10 страницV80814 Parker in-AGB Series Hydraulic Filter InsertsPaulPaucarCamposОценок пока нет
- VW Passat B4 - Pressurized Line and Cooling Line - Vehicles With VR6 EngineДокумент6 страницVW Passat B4 - Pressurized Line and Cooling Line - Vehicles With VR6 EngineNPОценок пока нет
- Two Stage, Hi-Low External Gear Hydraulic Pumps: MODELS 1012, 1053 AND 1056Документ4 страницыTwo Stage, Hi-Low External Gear Hydraulic Pumps: MODELS 1012, 1053 AND 1056TonuiОценок пока нет
- Ca25 2015Документ500 страницCa25 2015Bruno RibeiroОценок пока нет
- 5LTR Lab Mixer Machine Details Offer-QuanhuaДокумент2 страницы5LTR Lab Mixer Machine Details Offer-QuanhuaVaittianathan MahavapillaiОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of HydraulicsДокумент101 страницаFundamentals of HydraulicsLuis Nunes100% (1)
- Sistema de FrenoДокумент38 страницSistema de FrenocristianОценок пока нет
- Repuestos Equipos PesadosДокумент71 страницаRepuestos Equipos PesadosIng YÔrland R. BlancoОценок пока нет
- NEXIS V22/36/52: Stainless Steel Vertical High-Efficiency Multi-Stage PumpsДокумент22 страницыNEXIS V22/36/52: Stainless Steel Vertical High-Efficiency Multi-Stage Pumpsjuan0% (1)
- E47 Repair Manual PDFДокумент56 страницE47 Repair Manual PDFcamohunter71100% (1)
- J4011 - PNEUMATIC & HYDRAULIC (Hydraulic Basic)Документ43 страницыJ4011 - PNEUMATIC & HYDRAULIC (Hydraulic Basic)Boy LiverpoolОценок пока нет
- Hybrid Fault-Tolerant Flight Control System DesignДокумент10 страницHybrid Fault-Tolerant Flight Control System DesignAlexander Kim WaingОценок пока нет
- A Pathway to Decarbonise the Shipping Sector by 2050От EverandA Pathway to Decarbonise the Shipping Sector by 2050Оценок пока нет
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionОт EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Power of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesОт EverandPower of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (21)
- RV Living Collection: RV living for beginners, RV travel for the whole family, RV repair and RV mobile solar power: Experience Freedom on the roads alone or with your family with this collection. Learn how to repair your motorhome while using renewable energy!От EverandRV Living Collection: RV living for beginners, RV travel for the whole family, RV repair and RV mobile solar power: Experience Freedom on the roads alone or with your family with this collection. Learn how to repair your motorhome while using renewable energy!Оценок пока нет
- Offshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsОт EverandOffshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsОценок пока нет
- Shorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridОт EverandShorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressОт EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Solar Power Demystified: The Beginners Guide To Solar Power, Energy Independence And Lower BillsОт EverandSolar Power Demystified: The Beginners Guide To Solar Power, Energy Independence And Lower BillsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetОт EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetРейтинг: 2 из 5 звезд2/5 (1)
- Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage Game Changers in Asia: 2020 Compendium of Technologies and EnablersОт EverandCarbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage Game Changers in Asia: 2020 Compendium of Technologies and EnablersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- The Permaculture City: Regenerative Design for Urban, Suburban, and Town ResilienceОт EverandThe Permaculture City: Regenerative Design for Urban, Suburban, and Town ResilienceОценок пока нет
- ISO 50001: A strategic guide to establishing an energy management systemОт EverandISO 50001: A strategic guide to establishing an energy management systemОценок пока нет
- Practical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationОт EverandPractical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- The New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successОт EverandThe New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Live Off Grid: Escape The City, Learn How To Travel Intelligently Using Solar PowerОт EverandLive Off Grid: Escape The City, Learn How To Travel Intelligently Using Solar PowerОценок пока нет
- Practical Methods for Analysis and Design of HV Installation Grounding SystemsОт EverandPractical Methods for Analysis and Design of HV Installation Grounding SystemsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Global Landscape of Renewable Energy FinanceОт EverandGlobal Landscape of Renewable Energy FinanceОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Hydrogen Production and Utilization in Fuel Cell SystemsОт EverandFundamentals of Hydrogen Production and Utilization in Fuel Cell SystemsОценок пока нет
- Electrical Load-Curve Coverage: Proceedings of the Symposium on Load-Curve Coverage in Future Electric Power Generating Systems, Organized by the Committee on Electric Power, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, Rome, Italy, 24 – 28 October 1977От EverandElectrical Load-Curve Coverage: Proceedings of the Symposium on Load-Curve Coverage in Future Electric Power Generating Systems, Organized by the Committee on Electric Power, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, Rome, Italy, 24 – 28 October 1977Оценок пока нет
- Formulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsОт EverandFormulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsОценок пока нет
- Recent Advances in Electrical Engineering: Applications OrientedОт EverandRecent Advances in Electrical Engineering: Applications OrientedОценок пока нет
- Industrial Waste Treatment HandbookОт EverandIndustrial Waste Treatment HandbookРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)