Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Rates of Reactions 3 5
Загружено:
api-272358521Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Rates of Reactions 3 5
Загружено:
api-272358521Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Unit 3: Basic Chemistry
Content Outline: Rates of Reactions (3.5)
I.
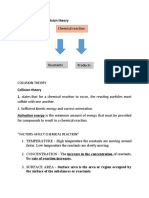
The measure of how quickly new substances form in a chemical reaction is called the
rate of reaction.
A. Four factors that can affect the rate of chemical reactions:
1. Temperature
a. The higher the temperature of a substance or mixture the greater the kinetic
energy of the
reactants. This causes the collision rate and impact force of reactants to
increase, thus increasing the rate of reaction for new substances to be
formed.
2. Concentration of reactants
a. The greater the concentration of reactant material also increases the
likelihood of collisions and the formation of new substances and thus
increases the rate of reaction.
3. Surface area of reactants
a.
In addition, the greater the surface area of solid reactants in a chemical
reaction increases the
possibility of reactant collisions and thus increases the rate of reaction.
4. The presence of an inhibitor or catalyst
a. The substance is called an inhibitor, as this type of substance slows or
inhibits a particular
chemical reaction. An example would be materials added to metals to
inhibit or slow metal oxidation (rust).
b.
Another substance increases the rate of reaction and is called a catalyst.
Catalysts can be
found commonly in living organisms where they are called enzymes.
Enzymes speed up chemical reactions in living things and allow reactions to
take place at lower temperatures (less activation energy) than would be
normal without the enzyme. Enzymes allow organisms to exist at the
relatively low life-sustaining temperatures.
c.
These substances often impact the reaction rate without themselves
being altered in the
reaction. For a chemical reaction to take place there must be at least a
minimum level of combined kinetic energy for particles to collide and react.
i.e. This is called activation energy. Two substances may act to change the
activation energy of a particular reaction.
B. One theory, which is helpful to think of when imagining chemical reactions is called
the Collision Theory.
1. Collision Theory states: Factors which impact the frequency of reactant
collisions will impact the
rate at which a chemical reaction occurs.
Вам также может понравиться
- Factors Affecting Rate of ReactionДокумент6 страницFactors Affecting Rate of Reactionjohnrey_lidres100% (4)
- Collision Theory: Teacher DianneДокумент24 страницыCollision Theory: Teacher DianneDianne CofinoОценок пока нет
- Factors Affecting Chemical Reaction RatesДокумент1 страницаFactors Affecting Chemical Reaction RatesFrank SobelОценок пока нет
- Reaction Rate NOTES HandoutДокумент1 страницаReaction Rate NOTES HandoutHorizon 99Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 3 - Factors Affecting Rate of Reaction and Reactions and Molecular CollisionsДокумент5 страницLesson 3 - Factors Affecting Rate of Reaction and Reactions and Molecular CollisionsJeff ValdezОценок пока нет
- Factors Affecting The Rate of ReactionДокумент2 страницыFactors Affecting The Rate of ReactionMr GaMeR SMОценок пока нет
- Physical Scienc1Документ4 страницыPhysical Scienc1Edel MarianoОценок пока нет
- Lesson 6 Collision Theory and Chemical Reaction RateДокумент33 страницыLesson 6 Collision Theory and Chemical Reaction Ratealliah nibayОценок пока нет
- Physci Simple Collision TheoryДокумент34 страницыPhysci Simple Collision TheoryLovely benzelОценок пока нет
- Second Quarter - Article ReadingДокумент2 страницыSecond Quarter - Article ReadingAlthea Charlene MatiasОценок пока нет
- Rates of Reaction: Factors that Affect Chemical Reaction SpeedsДокумент30 страницRates of Reaction: Factors that Affect Chemical Reaction SpeedsΜαρια ΑνδρεοπουλουОценок пока нет
- Collssion TheoryДокумент3 страницыCollssion TheoryJherby TeodoroОценок пока нет
- Collisiontheory: Teacherdia NneДокумент24 страницыCollisiontheory: Teacherdia NneDianne CofinoОценок пока нет
- Order ID 360731401-Research Paper-Factors Affecting Reaction Rates According To The Collision TheoryДокумент5 страницOrder ID 360731401-Research Paper-Factors Affecting Reaction Rates According To The Collision TheorydonnalarainecatiponОценок пока нет
- Chemical Kinetics & RateДокумент2 страницыChemical Kinetics & RateMontassar DridiОценок пока нет
- Gen_-Chem-2-VELASCO-ENCARNACION-part-2Документ12 страницGen_-Chem-2-VELASCO-ENCARNACION-part-2Edreyan Adong Cortez LimbagaОценок пока нет
- CHEMISTRYДокумент10 страницCHEMISTRYlifep7417Оценок пока нет
- Rate of ReactionДокумент23 страницыRate of ReactionVirly vcОценок пока нет
- Phy Sci StudyДокумент2 страницыPhy Sci StudyHans Kirby Pacatang DumdumОценок пока нет
- Chem 3Документ103 страницыChem 3César ArenasОценок пока нет
- Etulay Online Tutorial: Physical ScienceДокумент39 страницEtulay Online Tutorial: Physical ScienceTara SantosОценок пока нет
- CHEMICAL REACTION AND COLLISION (Autosaved)Документ23 страницыCHEMICAL REACTION AND COLLISION (Autosaved)FRANKLYN TRONCOОценок пока нет
- Reaction Rate NotesДокумент10 страницReaction Rate NotesvinaybharadwajbsОценок пока нет
- Rate of ReactionДокумент12 страницRate of ReactionRobin CabralОценок пока нет
- Kinetics DR JagadishДокумент37 страницKinetics DR JagadishVikas KumarОценок пока нет
- Chemical Kinetics & Equilibrium: Froilan Aron S. Faraon, R.PHДокумент34 страницыChemical Kinetics & Equilibrium: Froilan Aron S. Faraon, R.PHKenneth TrogonОценок пока нет
- Collision Theory of Chemical Reaction: in A Single Phase, Usually A LiquidДокумент1 страницаCollision Theory of Chemical Reaction: in A Single Phase, Usually A LiquidMeg BantoloОценок пока нет
- SciiiДокумент3 страницыSciiiYong JardinianoОценок пока нет
- Chemical Kinetics (Pt. 1) Introduction and Factors Affecting Reaction RatesДокумент13 страницChemical Kinetics (Pt. 1) Introduction and Factors Affecting Reaction RatesRida akhtarОценок пока нет
- AssignmentДокумент5 страницAssignmentAnsel MercadejasОценок пока нет
- Factors Affecting Rates of ReactionsДокумент4 страницыFactors Affecting Rates of Reactionskkanaksingh124Оценок пока нет
- Collision Group2 PhysicalДокумент19 страницCollision Group2 Physicalvjulieanne35Оценок пока нет
- CollisionДокумент30 страницCollisionKutoo BayОценок пока нет
- Rates of Chemical Reactions (1) - Effect of Concentration and Temperature Ws ForДокумент4 страницыRates of Chemical Reactions (1) - Effect of Concentration and Temperature Ws ForAbologyОценок пока нет
- Reaction Rates: Aa + BB PP + QQДокумент6 страницReaction Rates: Aa + BB PP + QQtantormeОценок пока нет
- 1126pm - 47.epra Journals 5023Документ3 страницы1126pm - 47.epra Journals 5023No NameОценок пока нет
- Collision TheoryДокумент46 страницCollision Theoryenero.rosasОценок пока нет
- Kinetics & Equilibrium: Factors Affecting Reaction RatesДокумент2 страницыKinetics & Equilibrium: Factors Affecting Reaction Rateslizaaa333Оценок пока нет
- Unit - The Periodic TableДокумент20 страницUnit - The Periodic TableMaurya AdeshraОценок пока нет
- Week 5.1 Collision Theory and The RateДокумент31 страницаWeek 5.1 Collision Theory and The RatereneicrizaldoОценок пока нет
- Topic 2.3: Kinetics I: 2.3 (A) Factors Affecting The Rate of ReactionДокумент4 страницыTopic 2.3: Kinetics I: 2.3 (A) Factors Affecting The Rate of ReactionLinaОценок пока нет
- Module 4 EdittedДокумент22 страницыModule 4 EdittedMARIE ANN DIAMAОценок пока нет
- Chemical Kinetics ProjectДокумент31 страницаChemical Kinetics ProjectArul VОценок пока нет
- Cohesive DeviceДокумент10 страницCohesive Devicemoralesmarkfrancis9Оценок пока нет
- Rate of Chemical ReactionДокумент3 страницыRate of Chemical Reactionbehatimonzanto0Оценок пока нет
- Rates of ReactionДокумент6 страницRates of ReactionRednaxela OnalaОценок пока нет
- Chemical Reaction Engineering NotesДокумент40 страницChemical Reaction Engineering Noteskrishnaswamy9Оценок пока нет
- Physical ScienceeДокумент16 страницPhysical ScienceejerrylinbermudezОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Chapter 17 NotesДокумент3 страницыChemistry Chapter 17 NotesMario V LopezОценок пока нет
- Simple Collision TheoryДокумент30 страницSimple Collision TheoryJona FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya - 20231114 - 074405 - 0000Документ16 страницJawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya - 20231114 - 074405 - 0000lifep7417Оценок пока нет
- Chemical Kinetics: Factors Affecting Reaction RateДокумент4 страницыChemical Kinetics: Factors Affecting Reaction RateMontassar DridiОценок пока нет
- Factors Affecting Rate of ReactionДокумент3 страницыFactors Affecting Rate of ReactionKyle BantaОценок пока нет
- Copy of Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableДокумент2 страницыCopy of Atomic Structure and The Periodic Tableapi-347844143Оценок пока нет
- Ate of Hemical Eactions: by StudentДокумент17 страницAte of Hemical Eactions: by StudentDyah Ayu pramoda wardaniОценок пока нет
- Chemical Change 1Документ36 страницChemical Change 1CheloGraceTiozonAmparadoОценок пока нет
- Kinetics and Dynamics of Elementary Gas Reactions: Butterworths Monographs in Chemistry and Chemical EngineeringОт EverandKinetics and Dynamics of Elementary Gas Reactions: Butterworths Monographs in Chemistry and Chemical EngineeringОценок пока нет
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersОценок пока нет
- Work, Then Out of The Device by A Wire, and Back To The SourceДокумент1 страницаWork, Then Out of The Device by A Wire, and Back To The Sourceapi-272358521Оценок пока нет
- 10Документ2 страницы10api-272358521Оценок пока нет
- 10Документ1 страница10api-272358521Оценок пока нет
- Fact Hunt - GasesДокумент1 страницаFact Hunt - Gasesapi-272358521Оценок пока нет
- 4 5 Molarity 1Документ1 страница4 5 Molarity 1api-272358521Оценок пока нет
- 5 4 Pressure and GasesДокумент1 страница5 4 Pressure and Gasesapi-272358521Оценок пока нет
- 5 2 Math - The Language of ScienceДокумент2 страницы5 2 Math - The Language of Scienceapi-272358521Оценок пока нет
- Unit 10: Electricity & Magnetism Content Outline: Electromagnetism (10.4) I. ElectromagnetismДокумент1 страницаUnit 10: Electricity & Magnetism Content Outline: Electromagnetism (10.4) I. Electromagnetismapi-272358521Оценок пока нет
- 4 2 Solution ChemistryДокумент1 страница4 2 Solution Chemistryapi-272358521Оценок пока нет
- 5 5 Solving Gas Pressure ProblemsДокумент1 страница5 5 Solving Gas Pressure Problemsapi-272358521Оценок пока нет
- DC Solutions Chemistry PPT 2013-14 ModifiedДокумент22 страницыDC Solutions Chemistry PPT 2013-14 Modifiedapi-272358521Оценок пока нет
- DC PPT Strength of Acids and Bases ModifiedДокумент8 страницDC PPT Strength of Acids and Bases Modifiedapi-272358521Оценок пока нет
- 5 3 Characteristics of GasesДокумент1 страница5 3 Characteristics of Gasesapi-272358521Оценок пока нет
- 4 7 Solubility 1Документ1 страница4 7 Solubility 1api-272358521Оценок пока нет
- 5 1 Math - The Language of ScienceДокумент2 страницы5 1 Math - The Language of Scienceapi-272358521Оценок пока нет
- Chemical Reactions 3 4Документ2 страницыChemical Reactions 3 4api-272358521Оценок пока нет
- Chemical Nomenclature 3 2Документ1 страницаChemical Nomenclature 3 2api-272358521Оценок пока нет
- 4 4 Acids Bases BuffersДокумент2 страницы4 4 Acids Bases Buffersapi-272358521Оценок пока нет
- Chemical Equations 3 3Документ1 страницаChemical Equations 3 3api-272358521Оценок пока нет
- Polyatomic Ions To Know For QuizДокумент1 страницаPolyatomic Ions To Know For Quizapi-272358521Оценок пока нет
- Basic Chemistry 3 1 Part 2 2Документ1 страницаBasic Chemistry 3 1 Part 2 2api-272358521Оценок пока нет
- Basic Chemistry 3 1 - Part 3Документ1 страницаBasic Chemistry 3 1 - Part 3api-272358521Оценок пока нет
- Notes P TableДокумент3 страницыNotes P Tableapi-272358521Оценок пока нет
- Properties of Matter NotesДокумент2 страницыProperties of Matter Notesapi-272358521100% (2)
- Basic Chemistry 3 1 Part 2 1Документ1 страницаBasic Chemistry 3 1 Part 2 1api-272358521Оценок пока нет
- Subatomic Particles 2 4 1Документ2 страницыSubatomic Particles 2 4 1api-272358521Оценок пока нет
- Atomic Theory Project 2 1Документ2 страницыAtomic Theory Project 2 1api-272358521Оценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding 3 1 Part 1 1Документ1 страницаChemical Bonding 3 1 Part 1 1api-272358521Оценок пока нет
- Atomic Theory Project 2Документ2 страницыAtomic Theory Project 2api-272358521Оценок пока нет