Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Guided Discovery Model Original
Загружено:
api-314418210Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Guided Discovery Model Original
Загружено:
api-314418210Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
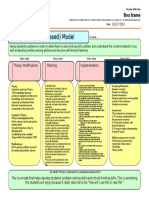
Hierarchic: 4 Main Ideas
Upside down
s
TM
Makes Sense
Sense Strategies
Strategies
Makes
Name: Leah Tabor
2008 Edwin Ellis, All Rights Reserved Published by Makes Sense Strategies, LLC, Northport, AL www.MakesSenseStrategies.com
Date:
Guided Discovery Model
01/28/2016
Is about
A model that provides various examples and allows students to explore the details and relationships of different concepts and
generalizations. The teacher also guides the students to understanding of the topic.
Details
Cognitive Learning Theory:
Learning Depends on
Practice and Feedback
Vygotskys Theory:
Scaffolding/Questioning
students to promote
critical thinking
Details
1) Identify Topics:
-Can come from a variety of sources (standards,
textbooks, teachers, etc.)
-Will work best with concepts or generalizations
2) Specify Learning Objectives:
-Set clear objectives as they can be used as the
framework for thinking and planning
-For concepts the learning objective will be for
students to be able to identify the
characteristics of the concept
-For generalizations the learning objective will be to
describe the relationship between the concepts
3) Prepare Examples and Nonexamples:
-Nonexamples are critical because it helps create a
barrier between similarities and differences.
Helps with understanding
-Important to use high quality examples to help make
up for the lack of background knowledge
-Need however many examples necessary to thoroughly
illustrate the scope of a topic
-Good types of examples include examples with
concrete materials, pictures, models, vignettes,
simulation and role play
Details
1) Introduction:
-Grab students attention and give a conceptual
framework for whats to follow
2) The Open-Ended Phase:
- Intended to promote students involvement and
ensure success from the beginning
-Then have students respond to open ended questions
- Open-ended questions involve students, hold their
attention, increase achievement and participation
3) The Convergent Phase:
-This phase is important in narrowing the students
responses in order to achieve identification of the
characteristics/relationship
-Important to guide the students so their responses
converge
Details
Increasing Motivation:
1) Involvement:
-This model allows teachers to call on
many students quickly and seeing that
success is assured students are more
likely to answer
2) A Sense of the Unknown
-This model allows students to explore
their curiosity in an environment where
the stress of being wrong is eased
4) Closure and Application:
-Closure happens when students are able to verbally
describe the concept of generalizations
-This phase also helps students understand which
information is irrelevant.
-Applications typically involves an assignment of some
kind, but application usually involves additional support
from the teacher
Assessment:
1) Informal Assessment
-Can be done throughout the lesson
2) Make sure the learning objectives are
aligned with the assignment
-Only test on learning objectives and now
recall of information
3) Feedback is essential
Main Idea
Main Idea
Main Idea
Main Idea
Theory
Planning
Implementation
Assessment/Motivation
So what? What is important to understand about this?
This would be beneficial with new concepts that are clearly defined and concrete. A great model that allows the students to get engaged and leads
to understanding through open discussion.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- AMB206 - Assignment 1Документ7 страницAMB206 - Assignment 1Rikky SoОценок пока нет
- 3rd Lesson Plan RecyclingДокумент3 страницы3rd Lesson Plan Recyclingapi-314418210100% (2)
- Problem-Solving: Math, Episode 2: Teacher's GuideДокумент5 страницProblem-Solving: Math, Episode 2: Teacher's Guideapi-314418210Оценок пока нет
- Lets Talk About Stories Shared Discussion With Amazing Grace - ReadwritethinkДокумент5 страницLets Talk About Stories Shared Discussion With Amazing Grace - Readwritethinkapi-314418210Оценок пока нет
- Lesson Plans and Lecture NotesДокумент5 страницLesson Plans and Lecture Notesapi-314418210Оценок пока нет
- An Integrated Lesson Comparing The Butterfly and Frog Life CyclesДокумент5 страницAn Integrated Lesson Comparing The Butterfly and Frog Life Cyclesapi-314418210Оценок пока нет
- Alex Lesson Plan The Water CycleДокумент5 страницAlex Lesson Plan The Water Cycleapi-314418210Оценок пока нет
- Problem-Solving Based Model OriginalДокумент1 страницаProblem-Solving Based Model Originalapi-314418210Оценок пока нет
- My Pedagogic CreedДокумент3 страницыMy Pedagogic Creedapi-314418210Оценок пока нет
- Direct Instruction Model 1-2 UpdatedДокумент1 страницаDirect Instruction Model 1-2 Updatedapi-314418210Оценок пока нет
- Lecture-Discussion Model-2 OriginalДокумент1 страницаLecture-Discussion Model-2 Originalapi-314418210Оценок пока нет
- Jigsaw Model-1 OriginalДокумент1 страницаJigsaw Model-1 Originalapi-314418210Оценок пока нет
- Valle Rand Reid 1988Документ12 страницValle Rand Reid 1988Cirine ZouaidiОценок пока нет
- Identifying Language Registers Used I N The Television CommercialsДокумент8 страницIdentifying Language Registers Used I N The Television CommercialsKristel Jen E. RosalesОценок пока нет
- CTG Action PlanДокумент2 страницыCTG Action Planapi-378658338Оценок пока нет
- Task Based LearningДокумент25 страницTask Based LearningmariaОценок пока нет
- CreativityДокумент15 страницCreativityBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)Оценок пока нет
- Managing Classroom Behavior and DisciplineДокумент226 страницManaging Classroom Behavior and DisciplineMinnie Mattheew80% (5)
- AttitudeДокумент33 страницыAttitudeMansi Mathur100% (1)
- Neo-Behaviorism: Tolman and BanduraДокумент22 страницыNeo-Behaviorism: Tolman and BanduraaileenОценок пока нет
- CompetencyДокумент46 страницCompetencyMery Citra Sondari0% (1)
- Notes For Habit 5Документ2 страницыNotes For Habit 5eieipayadОценок пока нет
- Octopus Culture FinalДокумент10 страницOctopus Culture Finalbhairavi_bhattОценок пока нет
- Characteristics of Charismatic LeadershipДокумент3 страницыCharacteristics of Charismatic LeadershipMuhammad Hashim Memon100% (1)
- Allstate Insurance CompanyДокумент9 страницAllstate Insurance Company1nita123Оценок пока нет
- Goal Setting Powerpoint PresentationДокумент17 страницGoal Setting Powerpoint Presentationsabrahima100% (2)
- Beyond Self ManagementДокумент18 страницBeyond Self ManagementjhosanaОценок пока нет
- OB Presentation - PerceptionДокумент30 страницOB Presentation - PerceptionRohan SinghОценок пока нет
- Logical Levels of Organisations PDFДокумент5 страницLogical Levels of Organisations PDFakmalgondalОценок пока нет
- Direction Function AssignmentДокумент7 страницDirection Function AssignmentUdaypal Singh RawatОценок пока нет
- Tattle Vs TellДокумент15 страницTattle Vs Tellapi-401785060Оценок пока нет
- Complaint ManagementДокумент22 страницыComplaint Managementvijendra chanda33% (3)
- ZM, NZ, MVN, ZV, ZДокумент3 страницыZM, NZ, MVN, ZV, ZMark Anthony RaymundoОценок пока нет
- Is Adolescence A Sensitive Period For Sociocultural Processing?Документ21 страницаIs Adolescence A Sensitive Period For Sociocultural Processing?dgs100% (1)
- Introduction To Johari WindowДокумент3 страницыIntroduction To Johari Windowsudhir letv100% (1)
- Organizational Commitment, Motives & Goal SettingДокумент11 страницOrganizational Commitment, Motives & Goal Settingpriya_ammuОценок пока нет
- Improve Performance With Amo TheoryДокумент4 страницыImprove Performance With Amo TheoryAnand VermaОценок пока нет
- 9 RPMS Coaching NTFДокумент66 страниц9 RPMS Coaching NTFEuropez Alaskha100% (4)
- 1500 Guidance and Counselling EssayДокумент5 страниц1500 Guidance and Counselling EssayAnonymous obRnelM5Оценок пока нет
- Michigan'S Long-Term Care Conference: Coaching Supervision For Consumers and OthersДокумент28 страницMichigan'S Long-Term Care Conference: Coaching Supervision For Consumers and OthersMukeshОценок пока нет
- Budgeted Lesson in Oral ComДокумент4 страницыBudgeted Lesson in Oral ComMike GuerzonОценок пока нет