Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Embryonic Development of Male Genital System: External Parts
Загружено:
Amal LR0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
10 просмотров2 страницыEmbryonic Development of Male Genital system external parts Wolfian ductepididymis, vas deferens and seminal vesicles Urogenital sinus - urinary bladder, urethra, prostate and the bulbourethral gland Gabernaculumhelps in the migration of the testes.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
New Microsoft Office Word Document.docx
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документEmbryonic Development of Male Genital system external parts Wolfian ductepididymis, vas deferens and seminal vesicles Urogenital sinus - urinary bladder, urethra, prostate and the bulbourethral gland Gabernaculumhelps in the migration of the testes.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
10 просмотров2 страницыEmbryonic Development of Male Genital System: External Parts
Загружено:
Amal LREmbryonic Development of Male Genital system external parts Wolfian ductepididymis, vas deferens and seminal vesicles Urogenital sinus - urinary bladder, urethra, prostate and the bulbourethral gland Gabernaculumhelps in the migration of the testes.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
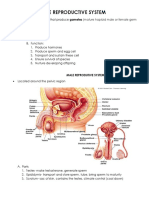
Embryonic Development of Male Genital
system
External parts
Wolfian duct- epididymis, vas deferens
and seminal vesicles
Urogenital sinus urinary bladder,
urethra, prostate and the bulbourethral
gland
Gabernaculum- helps in the migration of
the testes
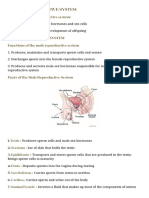
1.Penis Supporting structure
2. Scrotum- Climate control system for the testes
3. Testicles (testes)- Hormonal Input and Sperm
manufacturer
Internal Reports
1. Epididymis- Stores and Matures sperm cells
2. Vas deferens- transports sperms into the
urethra
3. Seminal Vesicles- produces the semen
4. Prostate Gland- Produces fluid that nourishes
the Sperm
5. Bulbourethral gland- for lubrication
The origin
Gonads intermedial mesoderm of mesonephros
in male and paramesonephros in female
Primordial germ cells Future gametes
ectoderm and mesoderm- external genitalia
The indifferent stage
Both sexes has same first stagedeveloped and
differentiated at the 7th week of gestation
-coelomic epithelium
primary germ cords
-primordial germ cells
-mesonephric duct (Wollfian) and tubules
-paramesonephric duct (mullerian tubules) in
females
External Differentiation
Вам также может понравиться
- Reproductive SystemДокумент3 страницыReproductive SystemKeandra TibayanОценок пока нет
- History of EmbryologyДокумент35 страницHistory of EmbryologyAdrienne Chelsea GabayОценок пока нет
- The Reproductive SystemДокумент5 страницThe Reproductive SystemPak LypОценок пока нет
- HumanreproductionpptДокумент59 страницHumanreproductionpptsugi sivamОценок пока нет
- Assessment On The Reproductive System (Rusy Hepitriani)Документ20 страницAssessment On The Reproductive System (Rusy Hepitriani)Sri NadyaputriОценок пока нет
- Science 10 ReviewerДокумент14 страницScience 10 ReviewerMonique FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Science 10Документ3 страницыScience 10Andrea JimenezОценок пока нет
- Human Reproduction CH-03, Bio, Class-XiiДокумент69 страницHuman Reproduction CH-03, Bio, Class-Xiisumitdhakad543Оценок пока нет
- SISTEM REPRODUKSI PADA MANUSIA - Power PДокумент38 страницSISTEM REPRODUKSI PADA MANUSIA - Power PWike RevanalizaОценок пока нет
- Reproductive SystemДокумент75 страницReproductive SystemErnie SyarinaОценок пока нет
- 3rd Monthly Test ReviewerДокумент5 страниц3rd Monthly Test ReviewerLaxen JunioОценок пока нет
- Male Reproductive SystemДокумент28 страницMale Reproductive SystemGenerato, Todd MatthewОценок пока нет
- CH 3Документ8 страницCH 3api-288494741Оценок пока нет
- SCIENCE 10 3rdДокумент4 страницыSCIENCE 10 3rdallyanni cabanatuanОценок пока нет
- Science NotesДокумент26 страницScience Notespiecreamy51Оценок пока нет
- Reproductive - Systems - in - Vertebrates ss2Документ12 страницReproductive - Systems - in - Vertebrates ss2Ezeh PrincessОценок пока нет
- Reproduction & Growth: Form 5Документ203 страницыReproduction & Growth: Form 5Foh Lian HuaiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 28 - The Reproductive SystemДокумент7 страницChapter 28 - The Reproductive Systemtomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2j - Reproductive SystemДокумент42 страницыChapter 2j - Reproductive SystemMARC LOUIE F. BARNACHEAОценок пока нет
- Maternal Nursing: Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент60 страницMaternal Nursing: Anatomy and PhysiologyAmazingMindОценок пока нет
- LTO in ScienceДокумент1 страницаLTO in ScienceNorman M.Оценок пока нет
- 1a. Reproductive OrgansДокумент60 страниц1a. Reproductive OrgansJerrald Meyer L. BayaniОценок пока нет
- Presentation StudentДокумент61 страницаPresentation Studentvsvm2009Оценок пока нет
- Lab Report Bio Experiment 3 - Reproductive, Endocrine & Respiratory System (Group 4)Документ15 страницLab Report Bio Experiment 3 - Reproductive, Endocrine & Respiratory System (Group 4)FARHAH BATRISYIA ABDUL RAHIMОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes Introduction To Reproductive SystemДокумент8 страницLecture Notes Introduction To Reproductive SystemKirstie Goc-ongОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 3 - Reproduction (Science Form 1)Документ13 страницCHAPTER 3 - Reproduction (Science Form 1)w pОценок пока нет
- Reproductive SystemДокумент29 страницReproductive SystemGrace Marfa OreñoОценок пока нет
- Seminar 1Документ8 страницSeminar 1gatorssoccer1313Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 22 Male and Female Reproductive SystemsДокумент56 страницLecture 22 Male and Female Reproductive SystemsChi Chung LeungОценок пока нет
- ReproДокумент6 страницReprorianaОценок пока нет
- Embryology IntermediateДокумент9 страницEmbryology IntermediateMohammed EljackОценок пока нет
- Reproduction in AnimalsДокумент12 страницReproduction in AnimalsYuh moddaОценок пока нет
- 1 - EmbryologyДокумент19 страниц1 - EmbryologynohacksОценок пока нет
- Physiology - Ii Year BemsДокумент10 страницPhysiology - Ii Year BemsKumar M V ScОценок пока нет
- Reproducrive SystemДокумент15 страницReproducrive SystemEfren GuinumtadОценок пока нет
- ReproductionДокумент10 страницReproductionttvignesuwarОценок пока нет
- Male Reproductive SystemДокумент30 страницMale Reproductive SystemRaisashimi M.S.100% (1)
- Reproductive ReviewerДокумент1 страницаReproductive ReviewerMaricel BalagsoОценок пока нет
- Biology NoteДокумент9 страницBiology NotejuliaОценок пока нет
- HP Repro 3Документ3 страницыHP Repro 3Rhzyl Moira CadapОценок пока нет
- Human Reproductive SystemДокумент3 страницыHuman Reproductive SystemHarvey SaludesОценок пока нет
- Urogenital System DevelopmentДокумент2 страницыUrogenital System DevelopmentIshraq AfifiОценок пока нет
- HP ReproДокумент3 страницыHP ReproRhzyl Moira CadapОценок пока нет
- Human Reproduction PDFДокумент4 страницыHuman Reproduction PDFIpshita PathakОценок пока нет
- Urinogenital System of Rabbit: A. Excretory System - Same in Male and FemaleДокумент4 страницыUrinogenital System of Rabbit: A. Excretory System - Same in Male and FemalenelsonОценок пока нет
- REPRODUCTIVEДокумент89 страницREPRODUCTIVEJohn MichaelMackayОценок пока нет
- Human Reproduction - II Puc - Regular NotesДокумент23 страницыHuman Reproduction - II Puc - Regular NotesVasudevОценок пока нет
- REPRODUCTIVESYSTEMДокумент2 страницыREPRODUCTIVESYSTEMMartin, Espencer WinsletОценок пока нет
- Compare and Contrast Plant and Animal Reproduction and DevelopmentДокумент145 страницCompare and Contrast Plant and Animal Reproduction and DevelopmentAuxidyОценок пока нет
- Summary QuestionДокумент4 страницыSummary QuestionwagkangtangaОценок пока нет
- SCIENCE 10 - The Reproductive SystemДокумент9 страницSCIENCE 10 - The Reproductive SystemJyña Khura TanoОценок пока нет
- Bio NotesДокумент180 страницBio NotesjyotibhalaОценок пока нет
- Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.DДокумент21 страницаMa. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.Dchocoholic potchiОценок пока нет
- MCN Module 2.3Документ16 страницMCN Module 2.3Ma. Ydela MeradoresОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive System BSNДокумент23 страницыFemale Reproductive System BSNtintinОценок пока нет
- Reproductive SystemДокумент11 страницReproductive SystemCHESKA LYKA ASILOОценок пока нет
- Gen BioДокумент42 страницыGen BioJoyce Anne Mae AdorioОценок пока нет
- Biology SS2 3RD Term E-NotesДокумент56 страницBiology SS2 3RD Term E-NotesINIOLUWA AKEJU100% (1)
- Male Reproductive System ReviewerДокумент3 страницыMale Reproductive System ReviewerNors SulaboОценок пока нет
- Home Blood Pressure Record SheetДокумент2 страницыHome Blood Pressure Record SheetAmal LRОценок пока нет
- PrenatalДокумент1 страницаPrenatalAmal LRОценок пока нет
- Surface AnatomyДокумент3 страницыSurface AnatomyAmal LRОценок пока нет
- MaternalДокумент14 страницMaternalAmal LRОценок пока нет
- Short StoriesДокумент14 страницShort StoriesAmal LRОценок пока нет
- Feeding Recommendations - IMCI 2014Документ3 страницыFeeding Recommendations - IMCI 2014Amal LRОценок пока нет
- Dua Before StudyingДокумент3 страницыDua Before StudyingAmal LRОценок пока нет
- Growth and DevelopmentДокумент8 страницGrowth and DevelopmentAmal LR100% (2)
- Brain InjuryДокумент19 страницBrain InjuryAmal LRОценок пока нет
- Physical Assessment ToolДокумент21 страницаPhysical Assessment ToolAmal LR100% (1)