Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
21st Physics P4 Mindmap
Загружено:
ClaudiaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
21st Physics P4 Mindmap
Загружено:
ClaudiaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Objects lifted above
the ground have
gravitational potential
energy
A moving object
has kinetic energy
Need to know the
mass and the
velocity
Cars involved
in collisions
come to
sudden stop
Sudden changes in
momentum may
affect passengers
Seat belts,
crumple zones
and air bags
designed to
reduce impact
GPE =
weight x height
Kinetic energy =
x mass x velocity 2
Smaller the time to
stop, the larger the
force and more damage
Work is done by
forces moving
objects
Work done =
Force x distance
GRAVITATIONAL
POTENTIAL
ENERGY
KINETIC
ENERGY
Examples of forces:
Gravity
Air resistance
Friction
Thrust
Upthrust
FORCES
Forces happen when
two things interact
Forces occur in pairs,
Forces
occur
equal
in size
andin pairs,
equal ininsize
and
opposite
direction
opposite in direction
Show forces using arrows
WORK
Forces in same direction add together,
opposite direction then subtract
Overall = resultant force
P4
WAVE MODEL
CALCULATING
SPEED
COLLISIONS
Speed tells you how far
an object travels in a
certain time
GRAPHS
MOMENTUM
Speed Time graphs
This is a measure
of motion
Velocity Time graphs
Momentum =
mass x velocity
Change in momentum =
Force x time
Shows the increase in
speed
Bigger the slope means
the faster the speed
is increasing
The slope of the time
graph measures the
speed of the object
To calculate speed we need
to know
The distance travelled
The time taken
Speed = distance
time
Steeper the slope,
greater the speed
S Bond
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Impulse PPT DemoДокумент18 страницImpulse PPT DemoJonathan M. Abellera100% (1)
- Mechanics For JEE SolutionsДокумент4 страницыMechanics For JEE SolutionsAvik DasОценок пока нет
- WWW - Thinkiit.in: Important DefinitionsДокумент37 страницWWW - Thinkiit.in: Important Definitionsthinkiit100% (2)
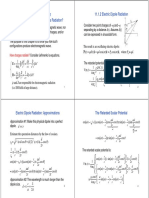
- Chapter 11: Radiation: 11.1 Dipole Radiation 11.1.1 What Is Radiation? 11.1.2 Electric Dipole RadiationДокумент4 страницыChapter 11: Radiation: 11.1 Dipole Radiation 11.1.1 What Is Radiation? 11.1.2 Electric Dipole RadiationMadhumika ThammaliОценок пока нет
- AP Chemistry Chapter 21 - The Nucleus: A Chemist's View: N C He BeДокумент5 страницAP Chemistry Chapter 21 - The Nucleus: A Chemist's View: N C He BeStephenОценок пока нет
- 2021-2.0 Vehicle Dynamics - UploadДокумент74 страницы2021-2.0 Vehicle Dynamics - UploadMudit Maheshwari100% (1)
- Gamma Ray PDFДокумент15 страницGamma Ray PDFfermeskopОценок пока нет
- Summative Test (Force and Motion)Документ3 страницыSummative Test (Force and Motion)Ann ClariceОценок пока нет
- Shootin' Hoops LabДокумент4 страницыShootin' Hoops LabcodythecodemanОценок пока нет
- Experiment 10: Absorption of Beta and Gamma Rays: PurposeДокумент9 страницExperiment 10: Absorption of Beta and Gamma Rays: PurposeRobert Carrillo0% (1)
- MECH 175 - Tutorial Week 1 - SolutionsДокумент4 страницыMECH 175 - Tutorial Week 1 - SolutionsErikson MoralesОценок пока нет
- Physics Unit 2 Question PaperДокумент16 страницPhysics Unit 2 Question PaperqeoobyogОценок пока нет
- 1 3.3 Rectilinear Motion Notes Best To Be Done After 3.7Документ3 страницы1 3.3 Rectilinear Motion Notes Best To Be Done After 3.7Albert ChonОценок пока нет
- Transportation Acceleration CaculationДокумент3 страницыTransportation Acceleration Caculationshadab521Оценок пока нет
- Costant Acceleation - Horizontal Motion Exam Questions 2Документ11 страницCostant Acceleation - Horizontal Motion Exam Questions 2Dominic SavioОценок пока нет
- Module 6 - Laws of MotionДокумент9 страницModule 6 - Laws of MotionTOP ERОценок пока нет
- Engineering ElectromagneticДокумент2 страницыEngineering ElectromagneticPooja PatelОценок пока нет
- FM1 - Work, Energy and Power (M2)Документ64 страницыFM1 - Work, Energy and Power (M2)EliasОценок пока нет
- ECE 476 Power System AnalysisДокумент35 страницECE 476 Power System AnalysisGaylethunder007Оценок пока нет
- CE Module 19 - Buoyancy (Principles)Документ1 страницаCE Module 19 - Buoyancy (Principles)Angelice Alliah De la CruzОценок пока нет
- 1649913681physics Class Ix For Sa-I 2014-15 PDFДокумент73 страницы1649913681physics Class Ix For Sa-I 2014-15 PDFHari KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Examples/Notes: Uniform Rectilinear Motion: V S T S V SBДокумент58 страницExamples/Notes: Uniform Rectilinear Motion: V S T S V SBMary Grace RaymundoОценок пока нет
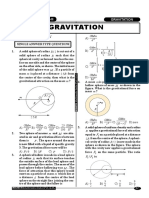
- AVITATION Level 5Документ11 страницAVITATION Level 5Rahul guptaОценок пока нет
- MagnetismДокумент11 страницMagnetismbaymaxОценок пока нет
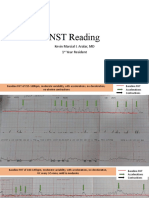
- NST Reading: Kevin Marcial I. Aralar, MD 1 Year ResidentДокумент10 страницNST Reading: Kevin Marcial I. Aralar, MD 1 Year ResidentKevin AralarОценок пока нет
- Work, Energy and Power: Checkpoint 1 (p.194)Документ12 страницWork, Energy and Power: Checkpoint 1 (p.194)U KILLED MY DOGОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan 1Документ3 страницыLesson Plan 1api-491539263Оценок пока нет
- HW3Документ5 страницHW3Brennan FrenchОценок пока нет
- 1.5-1.6 Projectile and Relative Motion TemplateДокумент6 страниц1.5-1.6 Projectile and Relative Motion TemplateAyman HalimeОценок пока нет
- What Is Force?: DefinitionДокумент5 страницWhat Is Force?: Definitionمحمد ایمانОценок пока нет