Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Class 20 - Fluid Mechanics: Z G V P Z G V P
Загружено:
MertYakarИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Class 20 - Fluid Mechanics: Z G V P Z G V P
Загружено:
MertYakarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
3/31/11
P1 V12
P2 V22
+
+ z1 = +
+ z2
2g
2g
Class 20 Fluid Mechanics
Q
Thursday, March 31st
2
1
2
2
P1 V
P V
+
+ z1 = 2 +
+ z2
2g
2g
If we use the Bernoulli equaAon to model the viscous
system above:
a)Q would be higher than observed
b)Q would be lower than observed
c)Q would be the same
Glycerin at 20C ows upward in a verAcal 75mm diameter
pipe with a centerline velocity of 1.0m/s. Determine the
head loss and pressure drop in a 10m length of the pipe.
P1
V2
P
V2
+ 1 1 + z1 = 2 + 2 2 + z2
2g
2g
P1
V12
P2
V22
+ 1
+ z1 + hP = + 2
+ z2 + hL + hT
2g
2g
3/31/11
Glycerin at 20C ows upward in a verAcal 75mm diameter
pipe with a centerline velocity of 1.0m/s. Determine the
head loss and pressure drop in a 10m length of the pipe.
Fully Developed Turbulent Flow
P1
V2
P
V2
+ 1 1 + z1 + hP = 2 + 2 2 + z2 + hL + hT
2g
2g
Shear Stress in Turbulent Flow
Laminar Flow
Velocity Prole in Turbulent Flow
Turbulent Flow
3/31/11
Water at 80F ows in a 6in diameter pipe with a owrate
of 2.0cfs. What is the approximate velocity at a distance of
2.0in away from the wall? Determine the centerline
velocity.
CalculaAon of Head Loss
Water at 80F ows in a 6in diameter pipe with a owrate
of 2.0cfs. What is the approximate velocity at a distance of
2.0in away from the wall? Determine the centerline
velocity.
Major Head Loss (Viscous Eects in Straight Pipes)
What ow regime is this?
a)Laminar
b)Turbulent
c)Could be either
3/31/11
Moody Chart
Major Head Loss (Viscous Eects in Straight Pipes)
Laminar FricAon Factor:
Turbulent FricAon Factor:
f = (Re,
Turbulent FricAon Factor:
CalculaAng Major Head Loss & Pressure Drop:
1
l V 2
p1 p2 = V22 V12 + ( z2 z1 ) + f
2
D 2
Water ows at a rate of 10gal/min in a new horizontal 0.75in
diameter galvanized iron pipe. Determine the pressure
gradient (p/l) along the pipe.
What does our equaAon simplify to?
l V 2
p
p
=
f
a)
1
2
D 2
l V 2
b)
p1 p2 = ( z2 z1 ) + f
D 2
c)
d)
1
l V 2
p1 p2 = V22 V12 + f
2
D 2
1
l V 2
p1 p2 = ( z2 z1 ) + V22 V12 + f
2
D 2
3/31/11
Water ows at a rate of 10gal/min in a new horizontal 0.75in
diameter galvanized iron pipe. Determine the pressure
gradient (p/l) along the pipe.
l !V 2
p1 ! p2 = f
D 2
Minor Head Loss (Eects Due to Pipe Components)
Examples: Inlets and Exits; Enlargements and ContracAons;
Pipe Bends; Valves and Ficngs
Minor Head Loss - Loss Coecient, KL
hl ,minor
V2
= KL
2g
a)
c)
b)
d)
These pipe entries have a KL of 0.8, 0.5, 0.2 and 0.04.
Which one do you think has the KL of 0.2?
3/31/11
Water ows at a rate of 0.40m3/s in a 0.12m diameter pipe
that contains a sudden contracAon to a 0.06m diameter pipe.
Determine the pressure drop across the contracAon secAon.
How much of this pressure dierence is due to losses and
how much is due to kineAc energy changes?
1
"V 2
p1 ! p2 = ! (V22 !V12 ) + ! (z2 ! z1 ) + K L
2
2
Water ows at a rate of 0.40m3/s in a 0.12m diameter pipe
that contains a sudden contracAon to a 0.06m diameter pipe.
Determine the pressure drop across the contracAon secAon.
What does our equaAon simplify to?
V12
p
p
=
K
1
2
L
a)
2
1
V12
2
2
b)
p1 p2 = (V2 V1 ) + K L
2
2
c)
d)
1
V
p1 p2 = (V22 V12 )+ K L 2
2
2
2
V
p1 p2 = K L 2
2
Water ows at a rate of 0.40m3/s in a 0.12m diameter pipe
that contains a sudden contracAon to a 0.06m diameter pipe.
Determine the pressure drop across the contracAon secAon.
1
"V 2
p1 ! p2 = ! (V22 !V12 ) + ! (z2 ! z1 ) + K L
2
2
3/31/11
Water ows at a rate of 0.40m3/s in a 0.12m diameter pipe
that contains a sudden contracAon to a 0.06m diameter pipe.
Determine the pressure drop across the contracAon secAon.
How much of this pressure dierence is due to losses and
how much is due to kineAc energy changes?
1
V
p1 p2 = (V22 V12 )+ K L 2
2
2
Minor Head Loss - Non-Circular Ducts
Вам также может понравиться
- Pyramids of MontaukДокумент363 страницыPyramids of MontaukRob Gray100% (11)
- RodinДокумент27 страницRodinThe Dead Alewives WatchtowerОценок пока нет
- CCNY LabManualДокумент29 страницCCNY LabManualShady HegazyОценок пока нет
- 02 Pipe - NetworksДокумент24 страницы02 Pipe - NetworksNaveed SheraziОценок пока нет
- Livro WCM - Completo PDFДокумент193 страницыLivro WCM - Completo PDFVicente de CastroОценок пока нет
- Pipe Sizing and Pressure Drop CalculationДокумент7 страницPipe Sizing and Pressure Drop Calculationvino2winОценок пока нет
- aSTM A 751 PDFДокумент5 страницaSTM A 751 PDFTheOne YasirОценок пока нет
- Test 2/ Exam, Fluid Mechanics For W, Vvr120 18 OCTOBER 2011, 14:00-17:00 (Test 2), 14:00-19:00 (Exam)Документ8 страницTest 2/ Exam, Fluid Mechanics For W, Vvr120 18 OCTOBER 2011, 14:00-17:00 (Test 2), 14:00-19:00 (Exam)Prashant KCОценок пока нет
- Hydraulics 6713 Tutorials and SolutionsДокумент42 страницыHydraulics 6713 Tutorials and SolutionsAsun RajaОценок пока нет
- Pipe FrictionДокумент12 страницPipe FrictionWilldenОценок пока нет
- P IpesДокумент15 страницP IpesMelvin EsguerraОценок пока нет
- Viscous Flow in Pipes: CEE 331 Fluid Mechanics March 11, 2014Документ40 страницViscous Flow in Pipes: CEE 331 Fluid Mechanics March 11, 2014Paulo BuenoОценок пока нет
- Lab Experiments Losses in PipeДокумент14 страницLab Experiments Losses in Pipesawmag123Оценок пока нет
- Fluid DynamicsДокумент14 страницFluid DynamicsBabylyn AustriaОценок пока нет
- H16 Manual (Pg1-Pg24) Losses in PipingДокумент24 страницыH16 Manual (Pg1-Pg24) Losses in PipingPung Kang Qin100% (1)
- Ch8 Steady Incompressible Flow in Pressure Conduits (PartB)Документ66 страницCh8 Steady Incompressible Flow in Pressure Conduits (PartB)avinash_friends21Оценок пока нет
- Piping System in Building: Asst. Prof. Channarong AsavatesanupapДокумент59 страницPiping System in Building: Asst. Prof. Channarong AsavatesanupapIatan AlexandruОценок пока нет
- Pipe's Minor LossesДокумент95 страницPipe's Minor LossesJosept RevueltaОценок пока нет
- Elementary Mechanics of Fluids: Flow in PipesДокумент23 страницыElementary Mechanics of Fluids: Flow in PipesAndre Amba MatarruОценок пока нет
- ME 363 - Fluid MechanicsДокумент5 страницME 363 - Fluid MechanicsCristobal MendozaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 5 2Документ15 страницLecture 5 2IbrahimDewaliОценок пока нет
- Fluids - IIIДокумент9 страницFluids - IIIPOONAM RANIОценок пока нет
- Ecw301-321-Topic 1Документ114 страницEcw301-321-Topic 1Chris EliazerОценок пока нет
- Flow Measurements, Hydraulic JumpДокумент34 страницыFlow Measurements, Hydraulic JumpLee CastroОценок пока нет
- Pipe Fitting LossesДокумент5 страницPipe Fitting LossesVrushiket PatilОценок пока нет
- Examen Resuelto Aguas Subterraneas - Fia - Una PunoДокумент27 страницExamen Resuelto Aguas Subterraneas - Fia - Una PunoDickey DesignОценок пока нет
- Flow Through Triangular NotchДокумент7 страницFlow Through Triangular NotchAbdul Razak KaladgiОценок пока нет
- Barnauli ApplicationДокумент24 страницыBarnauli ApplicationMuhammad sheryarОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Steady Flow in Pipelines2Документ12 страницAnalysis of Steady Flow in Pipelines2Shafika AliaОценок пока нет
- Water Hammer ArticleДокумент14 страницWater Hammer ArticleayoungaОценок пока нет
- PipesДокумент25 страницPipesSidesway 26Оценок пока нет
- Tutorial 6 Answer PDFДокумент30 страницTutorial 6 Answer PDFAlaa TelfahОценок пока нет
- FM Minor Losses 1Документ14 страницFM Minor Losses 1mahesh100% (1)
- FLUMECHДокумент4 страницыFLUMECHniel senОценок пока нет
- CH 5Документ3 страницыCH 5علي صباح ريسان جخمОценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Exp1Документ15 страницHydraulic Exp1FikrilAzimAbdulSaniОценок пока нет
- Chapter5 2Документ32 страницыChapter5 2Shida ShidotОценок пока нет
- Set8ans 12Документ9 страницSet8ans 12Teoh Tiong EeОценок пока нет
- Set8ans 12Документ9 страницSet8ans 12Teoh Tiong EeОценок пока нет
- Sheet-1 PipelinesДокумент1 страницаSheet-1 PipelinesKhairy ElsayedОценок пока нет
- Hydraulic TransientsДокумент58 страницHydraulic TransientsjulianvillajosОценок пока нет
- PlumbingДокумент16 страницPlumbingMelvin EsguerraОценок пока нет
- CH 3 2020Документ62 страницыCH 3 2020Emmanuel LazoОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer Lecture Notes 2 (2016)Документ10 страницHeat Transfer Lecture Notes 2 (2016)Michael Belmonte UrdanetaОценок пока нет
- MECH243 - Final - Fall 2017-2018Документ6 страницMECH243 - Final - Fall 2017-2018Majid YassineОценок пока нет
- MATERI - 7 Kehilangan EnergiДокумент11 страницMATERI - 7 Kehilangan EnergiSandro Nainggolan BrabОценок пока нет
- Operation and Safety of Dams ... ..Dr. Ammar H. KamelДокумент9 страницOperation and Safety of Dams ... ..Dr. Ammar H. Kamelfor realОценок пока нет
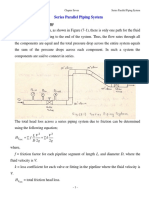
- (Chapter 7) Series Parallel Fluid FlowДокумент10 страниц(Chapter 7) Series Parallel Fluid FlowKarwan GoodОценок пока нет
- Backup of Flowloss - CSДокумент6 страницBackup of Flowloss - CSSri E.Maheswar Reddy Assistant ProfessorОценок пока нет
- Assignment 4Документ10 страницAssignment 4mahmoud EissaОценок пока нет
- Assignment 2012 2nd Year Mechanical EngineeringДокумент17 страницAssignment 2012 2nd Year Mechanical EngineeringFiseha Bogale KibОценок пока нет
- Cive4007 2011 1Документ3 страницыCive4007 2011 1Arvin BhurtunОценок пока нет
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 88Документ1 страницаLecturesNotes (MEE122) 88mhd slmnОценок пока нет
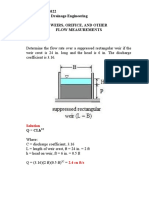
- ABE Review 2022 Irrigation and Drainage Engineering Weirs, Orifice, and Other Flow Measurements Problem 1Документ8 страницABE Review 2022 Irrigation and Drainage Engineering Weirs, Orifice, and Other Flow Measurements Problem 1Niel Crizza Chloe JandaОценок пока нет
- EnergyДокумент9 страницEnergyAhmed Mahmoud AbouzaidОценок пока нет
- Scientific American, Vol. XXXVII.—No. 2. [New Series.], July 14, 1877 A Weekly Journal Of Practical Information, Art, Science, Mechanics, Chemistry, And ManufacturesОт EverandScientific American, Vol. XXXVII.—No. 2. [New Series.], July 14, 1877 A Weekly Journal Of Practical Information, Art, Science, Mechanics, Chemistry, And ManufacturesОценок пока нет
- Physical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsОт EverandPhysical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsA. H. BeckОценок пока нет
- English 311 SyllabusДокумент2 страницыEnglish 311 SyllabusMertYakarОценок пока нет
- 210 NCC 09 Spring 1Документ4 страницы210 NCC 09 Spring 1MertYakarОценок пока нет
- Presentation CriteriaДокумент2 страницыPresentation CriteriaMertYakarОценок пока нет
- 1201 Complex Fourier SeriesДокумент5 страниц1201 Complex Fourier SeriesMertYakarОценок пока нет
- 9 - Projections and Least SquaresДокумент2 страницы9 - Projections and Least SquaresMertYakarОценок пока нет
- ECO280 ProblemSet3Документ1 страницаECO280 ProblemSet3MertYakarОценок пока нет
- ECO280 ProblemSet4Документ2 страницыECO280 ProblemSet4MertYakarОценок пока нет
- MAT210 Midterm 1 Solutions - Spring 2105Документ7 страницMAT210 Midterm 1 Solutions - Spring 2105MertYakarОценок пока нет
- HW 3 DynamicsДокумент2 страницыHW 3 DynamicsMertYakarОценок пока нет
- 10 - Equilibrium and OscillationДокумент2 страницы10 - Equilibrium and OscillationMertYakarОценок пока нет
- Sample Problem 1Документ1 страницаSample Problem 1MertYakarОценок пока нет
- 9 - Projections and Least SquaresДокумент2 страницы9 - Projections and Least SquaresMertYakarОценок пока нет
- 9 - Projections and Least SquaresДокумент2 страницы9 - Projections and Least SquaresMertYakarОценок пока нет
- Dynamics HW 2 Metu Homework 02Документ3 страницыDynamics HW 2 Metu Homework 02MertYakarОценок пока нет
- Q1. The Man Pushes On The 30-kg Crate With A Force F. The Force IsДокумент2 страницыQ1. The Man Pushes On The 30-kg Crate With A Force F. The Force IsMertYakarОценок пока нет
- p1k Pde2577tcuk 052009 PDFДокумент20 страницp1k Pde2577tcuk 052009 PDFwalid8311Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 29 Stability Analysis of Gravity Dams: Forces and General RequirementsДокумент4 страницыLesson 29 Stability Analysis of Gravity Dams: Forces and General RequirementsabshawОценок пока нет
- A Comparative Research On Corrosion Behavior of A Standard, Crack-Free and Duplex Hard Chromium CoatingsДокумент6 страницA Comparative Research On Corrosion Behavior of A Standard, Crack-Free and Duplex Hard Chromium CoatingsKarthi SundarОценок пока нет
- AdventureДокумент2 страницыAdventureAanya NarayanОценок пока нет
- Crop CircleДокумент2 страницыCrop CircledotionmoОценок пока нет
- Microfluidics Fluid Physics at The Nanoliter Scale PDFДокумент50 страницMicrofluidics Fluid Physics at The Nanoliter Scale PDFDavid CoralОценок пока нет
- GS14 Industrial Geophone - GeoSpace TechnologiesДокумент1 страницаGS14 Industrial Geophone - GeoSpace TechnologieshectorОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics Definition, Formulas, Laws and Equations - PhysicsДокумент7 страницThermodynamics Definition, Formulas, Laws and Equations - PhysicsRamaKrishnanGОценок пока нет
- 2 Chapter 2 Motion in A Straight LineДокумент28 страниц2 Chapter 2 Motion in A Straight LineTutor EdОценок пока нет
- Hydrologic CycleДокумент35 страницHydrologic CycleFachri JahriОценок пока нет
- Several Problems of The Polish Physics Olympiad: Waldemar GorzkowskiДокумент4 страницыSeveral Problems of The Polish Physics Olympiad: Waldemar GorzkowskiVikram SaurabhОценок пока нет
- Critical Analysis of Properties of Ready Mix Concrete With Site Mix Concrete of Smart Road ProjectДокумент6 страницCritical Analysis of Properties of Ready Mix Concrete With Site Mix Concrete of Smart Road ProjectGolam Shahriar SakibОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Measurements and ComputationsДокумент16 страницChapter 2 - Measurements and ComputationsKristine May MaturanОценок пока нет
- Soil CompactionДокумент24 страницыSoil Compactionsyah123Оценок пока нет
- Cie - 462 - Test One.09.05.2022Документ2 страницыCie - 462 - Test One.09.05.2022Chris KapendaОценок пока нет
- Xu-2021-Evaluation of The Convective Heat - (Published Version)Документ15 страницXu-2021-Evaluation of The Convective Heat - (Published Version)saja MuhammadОценок пока нет
- National Institute of Technology Durgapur: Department of Chemical EngineeringДокумент2 страницыNational Institute of Technology Durgapur: Department of Chemical Engineeringpiyush dwivediОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Form 4 A NotesДокумент67 страницChemistry Form 4 A NotesJia En TanОценок пока нет
- Martini L4 TemperatureControlДокумент11 страницMartini L4 TemperatureControlJubaer JamiОценок пока нет
- D.C.WДокумент150 страницD.C.Wapi-3808225Оценок пока нет
- Unit I - Force Analysis (9) : Systems and Tribology ConceptДокумент82 страницыUnit I - Force Analysis (9) : Systems and Tribology ConceptSaranОценок пока нет
- Lift Stability AnalysisДокумент23 страницыLift Stability Analysisaiyubi2Оценок пока нет
- PDE ToolboxДокумент7 страницPDE Toolboxbm24Оценок пока нет
- Institute of Seismological Research, Gandhinagar: "SAR Measurements For Earthquake Studies in India"Документ16 страницInstitute of Seismological Research, Gandhinagar: "SAR Measurements For Earthquake Studies in India"Santhosh Kumar BaswaОценок пока нет
- Case Studies in Engineering Failure Analysis: K. Gurumoorthy, Bradley D. Faye, Arindam GhoshДокумент8 страницCase Studies in Engineering Failure Analysis: K. Gurumoorthy, Bradley D. Faye, Arindam GhoshRif SenyoОценок пока нет
- Light NcertДокумент55 страницLight NcertDani MathewОценок пока нет
- Development of A Belt Conveyor For Small Scale Industry: September 2017Документ6 страницDevelopment of A Belt Conveyor For Small Scale Industry: September 2017DatОценок пока нет
























































![Scientific American, Vol. XXXVII.—No. 2. [New Series.], July 14, 1877
A Weekly Journal Of Practical Information, Art, Science,
Mechanics, Chemistry, And Manufactures](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/187114288/149x198/c199ff44cf/1579708199?v=1)