Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
PDH Assignmnet Term 2 WK 5
Загружено:
api-319465752Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
PDH Assignmnet Term 2 WK 5
Загружено:
api-319465752Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
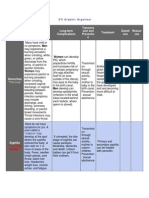
Cause of Infection
Gonorrhoea is transmitted through
sexual contact with the penis,
vagina, mouth, or anus of an
infected partner. Ejaculation does
not have to occur for gonorrhoea to
be
transmitted
or
acquired.
Gonorrhoea can also be spread
perinatally from mother to baby
during childbirth. People who have
had
gonorrhoea
and
received
treatment may be reinfected if they
have sexual contact with a person
infected with gonorrhoea.
Percentage of People
affected in Australia
Gonorrhoea is a very common
infectious disease. In Australia, the
population rate of diagnosis of
gonorrhoea increased from 1998 to
2006 for both males and females,
however from 2006 to 2007 the
population rate of diagnosis of
gonorrhoea declined by 15% among
males and by 6% among females.
How is it treated?
Cured?
Gonorrhoea can be cured with the
right
treatment.
CDC
now
recommends dual therapy (i.e.
using two drugs) for the treatment
of gonorrhoea. It is important to
take all of the medication prescribed
to cure gonorrhoea. Medication for
gonorrhea should not be shared
with anyone. Although medication
will stop the infection, it will not
repair any permanent damage done
by the disease. If a persons
symptoms continue for more than a
few days after receiving treatment,
he or she should return to a health
care provider to be reevaluated.
Sources that are useful for
teenagers wanting to
personally access
information are:
http://www.cdc.gov/std/gonorrhea/st
dfact-gonorrhea.htm
http://www.cdc.gov/std/gonorrhea/st
dfact-gonorrhea-detailed.htm
norrhea#Testing3
STI:
Definition:
Gonorrhoea
is
a
sexually
transmitted disease that is a
venereal disease which involves
the inflammatory discharge from
the
urethra
or
vagina.
Gonorrhoea
is
a
sexually
transmitted illness (STI) that can
infect both men and women. It
can cause infections in the
genitals, rectum, and throat. It is
a
very
common
infection,
especially among young people
ages 15-24 years.
What can happen if it is
not treated?
Untreated gonorrhoea can cause
serious
and
permanent
health
problems in both women and men.
In women, untreated gonorrhoea can
cause pelvic inflammatory disease
(PID). Some of the complications of
PID are:
-formation of scar tissue that blocks
fallopian tubes
-ectopic
pregnancy
(pregnancy
outside the womb);
-infertility (inability to get pregnant);
-long-term pelvic/abdominal pain.
In men, gonorrhoea can cause a
painful condition in the tubes
attached to the testicles. In rare
cases, this may cause a man to be
sterile, or prevent him from being
able to father a child. Rarely,
untreated gonorrhea can also spread
to your blood or joints. This condition
can be life-threatening. Untreated
gonorrhea may also increase your
chances of getting or giving HIV the
virus that causes AIDs.
Signs & Symptoms
Men may not develop noticeable
symptoms for several weeks. Some
men may never develop symptoms.
The first noticeable symptom in men
is often a burning or painful sensation
during urination. Other symptoms
may include:
-greater frequency
urination
or
urgency
of
-a pus-like discharge (or drip) from the
penis (white, yellow, beige, or
greenish)
-swelling or redness at the opening of
the penis
-swelling or pain in the testicles
-a persistent sore throat
Many women dont develop any
outstanding symptoms of gonorrhoea.
When women do develop symptoms,
they tend to be mild or similar to
other infections, making them more
difficult
to
identify.
Gonorrhoea
infections can appear much like
common vaginal yeast or bacterial
infections. Symptoms include:
-discharge from the vagina
-pain or
urinating
burning
sensation
while
-the need to urinate more frequently
-sore throat and fever
Do you have an infection
and not know it?
Any sexually active person can get
gonorrhoea
through
unprotected
vaginal, anal, or oral sex. If you are
sexually active, have an honest and
open talk with your health care
provider and ask whether you should
be tested for gonorrhoea or other STIs.
If you are a sexually active man who is
gay, bisexual, or who has sex with
men, you should be tested for
gonorrhoea every year. If you are a
sexually active women younger than
25 years or an older women with risk
factors such as new or multiple sex
partners, or a sex partner who has a
sexually transmitted infection, you
should be tested for gonorrhoea every
year.
Вам также может понравиться
- A Simple Guide To Sexually Transmitted Infections, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandA Simple Guide To Sexually Transmitted Infections, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Who Is at Risk For Gonorrhea?Документ10 страницWho Is at Risk For Gonorrhea?Anthony ReyesОценок пока нет
- Gonorrhea Fact SheetДокумент2 страницыGonorrhea Fact SheetRebecca Richardson0% (1)
- Am I at Risk For Gonorrhea?: PregnantДокумент5 страницAm I at Risk For Gonorrhea?: PregnantSunny OZОценок пока нет
- GonorrheaДокумент2 страницыGonorrheacmnaychi128Оценок пока нет
- GonorreheaДокумент5 страницGonorreheaSunny OZОценок пока нет
- GonorrheaДокумент13 страницGonorrheaNeo Xiu YangОценок пока нет
- Informe Gonorrea S.S.RДокумент9 страницInforme Gonorrea S.S.RSharon Ramos RocaОценок пока нет
- GonorrheaДокумент4 страницыGonorrheaNader Smadi100% (1)
- Gonorrhea Symptoms and TreatmentДокумент2 страницыGonorrhea Symptoms and TreatmentEnding HIV OklahomaОценок пока нет
- 1 GonorrheaДокумент17 страниц1 Gonorrheabrian mburuОценок пока нет
- GonorrheaДокумент11 страницGonorrheaAbdulla AbasОценок пока нет
- 3 Percent: Ivy Marie R. Maratas BSED Mathematics 1-2 Understanding The Self (GE 1)Документ8 страниц3 Percent: Ivy Marie R. Maratas BSED Mathematics 1-2 Understanding The Self (GE 1)Ivy Marie MaratasОценок пока нет
- PD 2Документ1 страницаPD 2Jane Heart AguilonОценок пока нет
- Sti GonorrheaДокумент6 страницSti GonorrheaSulaiman NajirulОценок пока нет
- The Complications of Unprotected SexДокумент33 страницыThe Complications of Unprotected Seximi ridleyОценок пока нет
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesДокумент76 страницSexually Transmitted Diseasessomaya abdulhakimОценок пока нет
- Understanding The Self Part 2 The Sexual SelfДокумент8 страницUnderstanding The Self Part 2 The Sexual SelfRemart DejosОценок пока нет
- Gonorrhe A: Kayleigh H-Mahedy, Javier Woo, ConnorДокумент8 страницGonorrhe A: Kayleigh H-Mahedy, Javier Woo, ConnorkayleighОценок пока нет
- Gonorrhea: Prepared By: Juan Angelo MangahasДокумент11 страницGonorrhea: Prepared By: Juan Angelo MangahasRobin EdezaОценок пока нет
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases and Methods of ContraceptionДокумент62 страницыSexually Transmitted Diseases and Methods of Contraceptionhohmannjasmin65Оценок пока нет
- Family Planing and Sexually Transmitted DiseasesДокумент34 страницыFamily Planing and Sexually Transmitted DiseasesRina KawamuraОценок пока нет
- Community Wellness Sti Graphic OrganizerДокумент3 страницыCommunity Wellness Sti Graphic Organizerapi-291220650Оценок пока нет
- Gonorrhea: SymptomsДокумент9 страницGonorrhea: Symptomspragna novaОценок пока нет
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) : Team 3 - Group 19 - Class D-2012 University of Medicine and PharmacyДокумент29 страницSexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) : Team 3 - Group 19 - Class D-2012 University of Medicine and PharmacyMikaОценок пока нет
- Non-Gonococcal Urethritis (NGU) : Signs and SymptomsДокумент2 страницыNon-Gonococcal Urethritis (NGU) : Signs and SymptomsIkhfa Yusril BahariОценок пока нет
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesДокумент19 страницSexually Transmitted DiseasesJayvah EstrellaОценок пока нет
- STD OutlineДокумент16 страницSTD OutlineLory TangpusОценок пока нет
- 1 Summarization-Updated (AutoRecovered)Документ6 страниц1 Summarization-Updated (AutoRecovered)Joan SevillaОценок пока нет
- Uts Group3 StdsДокумент24 страницыUts Group3 StdsGracious Angel Bautista IgnacioОценок пока нет
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDS) : Cadenas, Angelo VДокумент68 страницSexually Transmitted Diseases (STDS) : Cadenas, Angelo VAngelo CadenasОценок пока нет
- Sexually Transmitted DiseaseДокумент20 страницSexually Transmitted DiseaseAyesha IqbalОценок пока нет
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases NotesДокумент2 страницыSexually Transmitted Diseases NotesIvan Dennis SalupanОценок пока нет
- Lesson 10: Sexually Transmitted Disease Types of StdsДокумент19 страницLesson 10: Sexually Transmitted Disease Types of StdsJeya Plays YTОценок пока нет
- Gonorrhea: by Siena Kathleen V. Placino BSN-IV Communicable Disease Nursing C.I.: Dr. Dario V. SumandeДокумент38 страницGonorrhea: by Siena Kathleen V. Placino BSN-IV Communicable Disease Nursing C.I.: Dr. Dario V. SumandeSiena100% (1)
- Everything You Need To Know About Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDS)Документ18 страницEverything You Need To Know About Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDS)Myke KierkierОценок пока нет
- Sexually Transmitted InfectionsДокумент8 страницSexually Transmitted InfectionsEmilio Antang JrОценок пока нет
- The Basics: Cervical Cancer PregnancyДокумент9 страницThe Basics: Cervical Cancer PregnancyOm DarnalОценок пока нет
- UTS Activity 3Документ9 страницUTS Activity 3manueljc.pupОценок пока нет
- 7 Most Common Sexually Transmitted DiseasesДокумент3 страницы7 Most Common Sexually Transmitted DiseasesTrixon B. LapidОценок пока нет
- Gonorrhea Term PaperДокумент5 страницGonorrhea Term Paperafdtvuzih100% (1)
- GonorrhoeaДокумент6 страницGonorrhoeapadmja4purohitОценок пока нет
- Sexually Transmitted Disease and HomeopathyДокумент5 страницSexually Transmitted Disease and HomeopathyMihaela Ghica100% (1)
- GonorrheaДокумент9 страницGonorrheaWulan DayuОценок пока нет
- Gonorrhea FSДокумент2 страницыGonorrhea FSbekonondongoanneОценок пока нет
- Chlamydia Vs GonorrhoeaДокумент31 страницаChlamydia Vs Gonorrhoeakyro draxОценок пока нет
- GonoraeДокумент16 страницGonoraeOkta KendaОценок пока нет
- Common STDsДокумент14 страницCommon STDsbryjaytapasОценок пока нет
- Sti InfoДокумент6 страницSti Infoapi-266532629Оценок пока нет
- Bio ProjectДокумент13 страницBio ProjectKarishma TiwariОценок пока нет
- Adapted From: Sexually Transmitted Infections Pamphlet. Public Health Agency of Canada, 2007Документ25 страницAdapted From: Sexually Transmitted Infections Pamphlet. Public Health Agency of Canada, 2007Mohamoud MohamedОценок пока нет
- The Complete Guide to Gonorrhea: Symptoms, Risks, Diagnosis & TreatmentsОт EverandThe Complete Guide to Gonorrhea: Symptoms, Risks, Diagnosis & TreatmentsОценок пока нет
- Ureaplasma Infection, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandUreaplasma Infection, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- The Complete Guide To HIV / AIDs: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risks, Treatments & SupportОт EverandThe Complete Guide To HIV / AIDs: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risks, Treatments & SupportОценок пока нет
- Orchitis, (Inflamed Testis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandOrchitis, (Inflamed Testis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Genital Herpes Diet Guide: A Beginner's 3-Step Guide for Women on Managing Genital Herpes Through Diet, With Sample RecipesОт EverandGenital Herpes Diet Guide: A Beginner's 3-Step Guide for Women on Managing Genital Herpes Through Diet, With Sample RecipesОценок пока нет
- CDC FACT SHEET: Reported STDs in The United States - 2012 National Data For Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and SyphilisДокумент3 страницыCDC FACT SHEET: Reported STDs in The United States - 2012 National Data For Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilistherepubliq.comОценок пока нет
- Restoring Legal Protections For Women and ChildrenДокумент18 страницRestoring Legal Protections For Women and Childrenprotectiveparent100% (1)
- Sexual Orientation, Controversy, and ScienceДокумент57 страницSexual Orientation, Controversy, and Sciencemac as macОценок пока нет
- Hubungan Teman Sebaya Dan Peraturan Remaja................... (Aan Raivi)Документ8 страницHubungan Teman Sebaya Dan Peraturan Remaja................... (Aan Raivi)Aniq Azza NafisahОценок пока нет
- The Sexual Self (Basic Biology of Sexual Behavior)Документ22 страницыThe Sexual Self (Basic Biology of Sexual Behavior)あかさ あかОценок пока нет
- The S ListДокумент63 страницыThe S ListTallebAlQaryoutiОценок пока нет
- Instructional Module in Understanding The Self: School of Teacher EducationДокумент5 страницInstructional Module in Understanding The Self: School of Teacher EducationAlyanna MagkalasОценок пока нет
- The Sexual Satisfaction Index - ENGLISHДокумент3 страницыThe Sexual Satisfaction Index - ENGLISHcpjerrypmathewОценок пока нет
- An Excerpt From "Future Sex"Документ11 страницAn Excerpt From "Future Sex"OnPointRadioОценок пока нет
- Age of Legal ConsentДокумент2 страницыAge of Legal ConsentAnnie BeeОценок пока нет
- Survey QuestionnaireДокумент2 страницыSurvey QuestionnaireChrist LaquioОценок пока нет
- Bondoc Psychology of Sexual CrimesДокумент2 страницыBondoc Psychology of Sexual CrimesCorpuz Mark RemОценок пока нет
- What Is The Difference Between "Oooh!" and "Aaah!"? Ans: About Three InchesДокумент4 страницыWhat Is The Difference Between "Oooh!" and "Aaah!"? Ans: About Three InchesShaliniVyasОценок пока нет
- LGBTQ and Popular CultureДокумент28 страницLGBTQ and Popular CultureMa.Zusette RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Masturbation As Self-CareДокумент2 страницыMasturbation As Self-CareLaris ManizОценок пока нет
- Why People Should Be Against Homosexual Parenting: Daniela Ardila GreiffДокумент2 страницыWhy People Should Be Against Homosexual Parenting: Daniela Ardila GreiffDaniela A. GreiffОценок пока нет
- LGBTДокумент3 страницыLGBTapi-279290977Оценок пока нет
- Sti Booklet Amharic PDFДокумент3 страницыSti Booklet Amharic PDFAbel KibebeОценок пока нет
- Same Sex ParentingДокумент11 страницSame Sex Parentingapi-325216203Оценок пока нет
- Doxy PEPДокумент2 страницыDoxy PEPDoverocks7Оценок пока нет
- ScolДокумент16 страницScolmukhlismandiriОценок пока нет
- RapeДокумент42 страницыRapeVlyn100% (1)
- RA 8353 Inner Page For Sharing PDFДокумент1 страницаRA 8353 Inner Page For Sharing PDFHinabangan MPSОценок пока нет
- Sex Is The "Glue" in A Marriage: Posted On September 18, 2012Документ11 страницSex Is The "Glue" in A Marriage: Posted On September 18, 2012monicajudgeОценок пока нет
- Sex Education Final ExamДокумент4 страницыSex Education Final Examapi-404291045Оценок пока нет
- Issue in The PhilippinesДокумент13 страницIssue in The PhilippinesChristian Punto FedereОценок пока нет
- If You Choose To Have Sex, Know How To Protect Yourself Against Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDS)Документ2 страницыIf You Choose To Have Sex, Know How To Protect Yourself Against Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDS)fuck youОценок пока нет
- Community Centre and Health Care Centre For Transgenders: Shraddha Mirajkar 2BV13AT038 BvbcetДокумент24 страницыCommunity Centre and Health Care Centre For Transgenders: Shraddha Mirajkar 2BV13AT038 BvbcetdafnyОценок пока нет
- Sexual Orientation & GenderДокумент149 страницSexual Orientation & Genderdarkkitten76Оценок пока нет
- LLTP Walkthrough 0.27 PDFДокумент42 страницыLLTP Walkthrough 0.27 PDFPika ChuОценок пока нет