Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Notes of Cyclotron and Moving Coil Galvanometer
Загружено:
kanwal kumar0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
1K просмотров2 страницыcyclotron and moving coil galvanometer
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документcyclotron and moving coil galvanometer
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
1K просмотров2 страницыNotes of Cyclotron and Moving Coil Galvanometer
Загружено:
kanwal kumarcyclotron and moving coil galvanometer
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
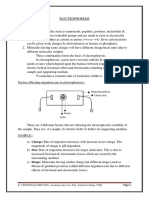
Cyclotron: It is a device developed by Lawrence and
Livingstone and is used to accelerate charged particles like
protons and deuterons. This results in the production of high
energy beam which is then used for artificial disintegration, etc.
A positively charged particle can be accelerated to high energy
with the help of an oscillating electric field, by making it cross
the same electric field time and again with the use of a strong
magnetic field. In the magnetic field the charged particle
experience force. If it enters at right angle to the field then it
describes the circular path. The time period is independent the
radius of the circular path.
It consists of two dees or D-shaped metal chambers D1 and D2.
The dees are separated by a small distance. The two dees are
perpendicular to their plane. P is the position where the ion
source is placed.
The dees are maintained to a potential difference whose polarity alternates with the same frequency as the
circular motion of the particles. The dees are closed in a steel box placed between the poles of a strong
electromagnet. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the dees.
The positive ion P to be accelerated is placed in between the two dees. If at any instant, D1 is at negative
potential and D2 is at positive potential, then the ion gets accelerated towards D1 but since its
perpendicular to B, it describes a circular path of radius r and Lorentz force provides the centripetal force.
Time taken to describe a semicircle is
If this time is equal to the time during which D1 and D2 change their polarity, the ion gets accelerated
when it arrives in between the gaps. The electric field accelerates the ion further. Once the ion is inside the
dee D2, it now describes a greater semicircle due to the magnetic field. This process repels and the ion
goes on describing a circular path of greater radius and finally acquires a high energy. The ion is further
removed from a window W. The maximum energy acquired by the ion source is
The frequency of cyclotron is given by
Limitations of Cyclotron: Only when the speed of the circulating ion is less than 'c' the speed of light, we
find the frequency of revolution to be independent of its speed. At higher speeds, the mass of the ion will
increase and this changes the time period of the ion revolution. This results in the ion lagging behind the
electric field and it eventually loses by collisions against the walls of the dees. The cyclotron is suitable for
accelerating heavy charged particles but not electrons. Cyclotrons cannot accelerate in charged particles. It
is not suited for very high kinetic energy. Electrons can not be accelerated by cyclotrons because the mass
of electron is very small and a small increase in energy of electron makes the electrons move with very
high speed. As a result of it the electron go quickly out of step with oscillating electric field, it is for these
reasons that other accelerating machines such as synchrotron, betatron (for accelerating electrons) have
been developed. Cyclotron can not be used for accelerating uncharged particle like neutrons.
Moving coil Galvanometer
It is a device which is used to measure and detect the small amount of electric charge i.e electric current. It
is most sensitive device and used in many electrical instruments. It is the major basic component of
Aameter and Voltmeter.
Principle: Moving coil galvanometer is based on the fact that when a current carrying rectangular coil is
placed in a magnetic field it experience torque.
Construction: Construction of galvanometer is as
shown in figure. In galvanometer, it consists of
rectangular coil PQRS having N number of insulated
copper coil which is wounded in the nonmagnetic
metallic frame of soft iron as center core. The coil is
suspended by a phosphor-bronze strip through a
torsion head to that it is free to rotate about the vertical
axis. The coil is placed in between two pieces of
magnet. The other end of the coil is connected to the
light spring and finally to the terminal T2 The torsion
head is connected to the terminal T1. A concave mirror
m is placed to the suspension strip to note the
deflection of coil using lamp and scale arrangement.
Theory: When a current I flows through the rectangular
coil, the coil gets deflected, the suspension wire is
twisted and rotating torque is developed on it. If k is
rotating torque per unit angle per unit twist of the strip
then restoring torque through the angle is
If A be the area of the rectangular strip, N be the number of turns, I be the current through the coil and B
be the magnetic field then the torque on the rectangular coil is
Since the rectangular coil is placed in between two concave shaped magnets then the field lines are radial
to the area of the rectangular field. so the area of the rectangular foil is parallel to the magnetic field lines
then,
At equilibrium,
So the deflection of galvanometer is directly proportional to the current on the rectangular coil. Hence we
use linear scale in galvanometer.
Вам также может понравиться
- Pauli Exclusion PrincipleДокумент7 страницPauli Exclusion PrincipleHarlene DraguinОценок пока нет
- ELECTRON CONFIG-WPS Office - RecoverДокумент50 страницELECTRON CONFIG-WPS Office - RecoverLyca RealОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 (Periodic Table)Документ46 страницChapter 4 (Periodic Table)Tunku Hilman Al-nordinОценок пока нет
- Basic Principle and Applications of Paper ElectrophoresisДокумент38 страницBasic Principle and Applications of Paper ElectrophoresisSanty KoshyОценок пока нет
- Buffer SolutionsДокумент3 страницыBuffer Solutionsemad_abdelaal57Оценок пока нет
- Electrophoresis Factor Affecting PDFДокумент4 страницыElectrophoresis Factor Affecting PDFGounder KirthikaОценок пока нет
- Voltaic CellДокумент32 страницыVoltaic CellMahijar Jarullhayati Hassan50% (2)
- D Block ElementsДокумент22 страницыD Block Elementsketan kambleОценок пока нет
- Density and UpthrustДокумент20 страницDensity and UpthrustRanjit SinghОценок пока нет
- LCAO MO Theory Illustrated by Its Application To H2Документ8 страницLCAO MO Theory Illustrated by Its Application To H2maugonzalezsuarezОценок пока нет
- Potentiometry 2021Документ47 страницPotentiometry 2021Adina IqbalОценок пока нет
- S-Block Elements Theory - EДокумент27 страницS-Block Elements Theory - Ethinkiit100% (2)
- Magnetic Properties of Transition Metal Metal ComplexesДокумент9 страницMagnetic Properties of Transition Metal Metal ComplexestharanginiОценок пока нет
- HPLC NotesДокумент50 страницHPLC NotesEmmanuella Offiong100% (1)
- Electroanalytical ChemistryДокумент4 страницыElectroanalytical ChemistrybelleОценок пока нет
- F Block ElementsДокумент4 страницыF Block ElementsAfaf HucynОценок пока нет
- Iub Pha404 Autumn 2022 Ms BasicДокумент52 страницыIub Pha404 Autumn 2022 Ms BasicTanvir FahimОценок пока нет
- Atomic Spectrum HydrogenДокумент7 страницAtomic Spectrum Hydrogenaparajit5054Оценок пока нет
- Nernst EquationДокумент24 страницыNernst Equationcacancella21Оценок пока нет
- Try Polarography and Related MethodsДокумент31 страницаTry Polarography and Related MethodsDana Alaazmi100% (1)
- IR/UV Spectroscopy: U. Mall Lindau, 28.10.2010Документ54 страницыIR/UV Spectroscopy: U. Mall Lindau, 28.10.2010Trishna paulОценок пока нет
- Rutherford and Bohr's Atomic ModelДокумент101 страницаRutherford and Bohr's Atomic Modelthrivikram100% (1)
- 1 IntroductoryДокумент45 страниц1 IntroductoryTuhin Sahu100% (1)
- SCYA7301Документ155 страницSCYA7301Deva MiniОценок пока нет
- Engineering Chemistry-Unit-3-Electrochemistry and Corrosion-1 PDFДокумент17 страницEngineering Chemistry-Unit-3-Electrochemistry and Corrosion-1 PDFManeesh100% (1)
- ATOICV1 8 9 Charge Transfer Spectra NawazДокумент16 страницATOICV1 8 9 Charge Transfer Spectra Nawazsaira mehmoodОценок пока нет
- MicrowaveДокумент41 страницаMicrowaveMaryem MostafaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry The D and F Block Elements PDFДокумент29 страницChemistry The D and F Block Elements PDFMohammed RafiuddinОценок пока нет
- Electochemistry PDFДокумент29 страницElectochemistry PDFAnshu KarmacharyaОценок пока нет
- Braggs LawДокумент4 страницыBraggs LawManoj Manu100% (3)
- ElectrochemistryДокумент43 страницыElectrochemistryShiloh FrederickОценок пока нет
- Chemistry 445 Lecture 18 MO Theory and D-D SpectraДокумент22 страницыChemistry 445 Lecture 18 MO Theory and D-D SpectraAbhinav JainОценок пока нет
- Module 1 SPINELДокумент5 страницModule 1 SPINELDharmendra Kumar SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Magneto ChemistryДокумент7 страницIntroduction To Magneto ChemistryYousuf Raza100% (1)
- Unit V Quantum Mechanics PPT PH101Документ11 страницUnit V Quantum Mechanics PPT PH101Kripanshu Kumar100% (1)
- CH2201 - Main Group ChemistryДокумент21 страницаCH2201 - Main Group ChemistryJohnОценок пока нет
- Molecular Spectroscopy Manmohan Univ PDFДокумент107 страницMolecular Spectroscopy Manmohan Univ PDFakash kumar bhoi100% (2)
- Application of Partition FunctionДокумент2 страницыApplication of Partition FunctionNITISH KUMARОценок пока нет
- 7 - JEE - Chemistry - Electrochemistry - Transport Number or Transference NumberДокумент2 страницы7 - JEE - Chemistry - Electrochemistry - Transport Number or Transference NumberGurmehakdeep BillaОценок пока нет
- Metals and Metallurgical PrinciplesДокумент13 страницMetals and Metallurgical PrinciplesManoj KhanalОценок пока нет
- Ord & CDДокумент30 страницOrd & CDSaravana KumarОценок пока нет
- Lecture 12 - Octahedral Substitution Reactions: 2P32 - Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Dr. M. PilkingtonДокумент13 страницLecture 12 - Octahedral Substitution Reactions: 2P32 - Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Dr. M. PilkingtonAlexa AlexiuОценок пока нет
- Structure of AtomДокумент5 страницStructure of AtomSaurabh DhyaniОценок пока нет
- Electrical Properties of SolidsДокумент4 страницыElectrical Properties of Solidsstephen james100% (1)
- Models of The AtomДокумент13 страницModels of The AtomAbhinav TripathiОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry and ThermodynamicsДокумент7 страницElectrochemistry and ThermodynamicsAhmadPraboeОценок пока нет
- XRAYS Chapter PDFДокумент11 страницXRAYS Chapter PDFAdeel MajeedОценок пока нет
- Magnetism in SolidsДокумент11 страницMagnetism in SolidsNeelam KapoorОценок пока нет
- Characteristics of NanomaterialsДокумент9 страницCharacteristics of Nanomaterialssandhiya padmanabanОценок пока нет
- PhotochemistryДокумент20 страницPhotochemistryAranga100% (1)
- NMR Spectroscopy: Koradiya Ketan N. Inorganic Chemistry, Reg. Roll No-5, Bhavnagar University, Bhavnagar-05Документ41 страницаNMR Spectroscopy: Koradiya Ketan N. Inorganic Chemistry, Reg. Roll No-5, Bhavnagar University, Bhavnagar-05Koradiya Ketan NОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Infrared Spectroscopy-CLASSДокумент18 страницIntroduction To Infrared Spectroscopy-CLASSDr_GSОценок пока нет
- 1.solid State-1-1Документ99 страниц1.solid State-1-1Pranav ThoratОценок пока нет
- Applied Chemistry NotesДокумент6 страницApplied Chemistry NotessajjadmahesarОценок пока нет
- UNIT IV NMR Mass - WatermarkДокумент23 страницыUNIT IV NMR Mass - WatermarkvickyОценок пока нет
- IR SpectrosДокумент41 страницаIR SpectrosKD LoteyОценок пока нет
- A Collection of Problems on Mathematical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsОт EverandA Collection of Problems on Mathematical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsОценок пока нет
- Physics Project On CyclotronДокумент11 страницPhysics Project On CyclotronasishОценок пока нет
- Numericals XiДокумент2 страницыNumericals Xikanwal kumarОценок пока нет
- Physics Paper Xi ClassДокумент2 страницыPhysics Paper Xi Classkanwal kumarОценок пока нет
- Project RhinoДокумент7 страницProject Rhinokanwal kumarОценок пока нет
- Units and DimensionsДокумент1 страницаUnits and Dimensionskanwal kumarОценок пока нет
- Cbse Q Xii BoardДокумент2 страницыCbse Q Xii Boardkanwal kumarОценок пока нет
- Class Test 12 p1 Onwards 30516Документ1 страницаClass Test 12 p1 Onwards 30516kanwal kumarОценок пока нет
- Class Xii Physics QДокумент1 страницаClass Xii Physics Qkanwal kumarОценок пока нет
- Class Xii Physics QДокумент1 страницаClass Xii Physics Qkanwal kumarОценок пока нет
- Class Xi SP 2nd BookДокумент1 страницаClass Xi SP 2nd Bookkanwal kumarОценок пока нет
- QuestionsДокумент2 страницыQuestionsDenise ButlerОценок пока нет
- General Chemistry 1: Quarter 3 - WEEK 2Документ18 страницGeneral Chemistry 1: Quarter 3 - WEEK 2RODEL AZARESОценок пока нет
- Assing 4Документ2 страницыAssing 4KazaValiShaikОценок пока нет
- DELTA VFD-MS300 ManualДокумент512 страницDELTA VFD-MS300 ManualDavidОценок пока нет
- smf28 PDFДокумент4 страницыsmf28 PDFNahed Ep KhaledОценок пока нет
- Transmission & Distribution-QBДокумент3 страницыTransmission & Distribution-QBMuthamizhan ThiyagarajanОценок пока нет
- Unit II: Analysis of Bars of Varying Cross SectionsДокумент15 страницUnit II: Analysis of Bars of Varying Cross Sectionsermias0% (1)
- D. Deg R 1.8 Deg K: Page 1 of 14Документ14 страницD. Deg R 1.8 Deg K: Page 1 of 14Joseph BallenaОценок пока нет
- Fisa Tehnica AHU-01Документ9 страницFisa Tehnica AHU-01Liviu ToaderОценок пока нет
- Ph8151 Py1 Iq RejinpaulДокумент2 страницыPh8151 Py1 Iq RejinpaulriyaОценок пока нет
- 59 - Chemistry QPДокумент9 страниц59 - Chemistry QPrajeevtyagi41Оценок пока нет
- TrichelДокумент12 страницTrichelafgaleanoОценок пока нет
- Ebook Ebook PDF Physical Universe 15th Edition PDFДокумент41 страницаEbook Ebook PDF Physical Universe 15th Edition PDFderek.lewis562100% (39)
- More Accurate Localized Wire Rope Testing Based On Hall Sensor ArrayДокумент2 страницыMore Accurate Localized Wire Rope Testing Based On Hall Sensor ArrayNesanОценок пока нет
- A.1.Input Data: Wind Analysis For Shade Open Structure Based On ASCE 7-05Документ3 страницыA.1.Input Data: Wind Analysis For Shade Open Structure Based On ASCE 7-05Antonysamy SanthanamОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan ECEДокумент3 страницыLesson Plan ECEVenkatesan SwamyОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To The Kinetic Theory of Gases (Cambridge Science Classics) PDFДокумент321 страницаAn Introduction To The Kinetic Theory of Gases (Cambridge Science Classics) PDFShouvik MitraОценок пока нет
- Support Reaction in 3 DimensionДокумент2 страницыSupport Reaction in 3 DimensionEmrE GöktuĞОценок пока нет
- (Benjamin, 1.2, 1.3, 1.5) : Lecture #4: Fundamentals of Water A ND Ionic StrengthДокумент27 страниц(Benjamin, 1.2, 1.3, 1.5) : Lecture #4: Fundamentals of Water A ND Ionic StrengthwastequestОценок пока нет
- Module 5 - BEJAR - ScriptДокумент7 страницModule 5 - BEJAR - Scriptrobejr2013Оценок пока нет
- Self-Focusing and Guiding of Short Laser Pulses in Ionizing Gases and Plasmas PDFДокумент36 страницSelf-Focusing and Guiding of Short Laser Pulses in Ionizing Gases and Plasmas PDFAjit UpadhyayОценок пока нет
- Tray Dryer PDFДокумент3 страницыTray Dryer PDFAlshreef AljeelanyОценок пока нет
- Computer Aided Structural AnalysisДокумент149 страницComputer Aided Structural Analysisenselsoftware.com100% (33)
- Chemistry 1 Class 11Документ254 страницыChemistry 1 Class 11Aniket Sharma100% (7)
- Energized Body - Superpower Wiki - FandomДокумент12 страницEnergized Body - Superpower Wiki - Fandomalex masonОценок пока нет
- Physics Division: Phys 141 Syllabus, PGДокумент7 страницPhysics Division: Phys 141 Syllabus, PGJun YoutubeОценок пока нет
- E6-165-13 - ASME STRESS CLASSIFICATION in Pressure Vessels and PipingДокумент20 страницE6-165-13 - ASME STRESS CLASSIFICATION in Pressure Vessels and PipingLuis Ortiz100% (3)
- 5 1doneДокумент3 страницы5 1doneeperlaОценок пока нет
- Earthing System JKR PDFДокумент19 страницEarthing System JKR PDFameera nabihaОценок пока нет
- Karmaveer Bhaurao Patil College Vashi, Navi Mumbai Autonomous CollegeДокумент21 страницаKarmaveer Bhaurao Patil College Vashi, Navi Mumbai Autonomous Collegemathers maddyОценок пока нет
- PhET Blackbody SpectrumДокумент2 страницыPhET Blackbody SpectrumdsofewnОценок пока нет