Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Higher Unit 1 Homework
Загружено:
knoxmaths0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
4K просмотров12 страницExercise 1: find the gradient of the line joining the points A(2,8) and B(-4,10) find the equation of the line with gradient 12 passing through the point (5,1) find the value of a. Exercise 2: find the equations of the lines specified as follows: (a) passing through the points a(-I,I) and b(3,-I) and (b) parallel to the line 3x + y + 8 = o. Exercise 3: find the values of a and
Исходное описание:
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PDF или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документExercise 1: find the gradient of the line joining the points A(2,8) and B(-4,10) find the equation of the line with gradient 12 passing through the point (5,1) find the value of a. Exercise 2: find the equations of the lines specified as follows: (a) passing through the points a(-I,I) and b(3,-I) and (b) parallel to the line 3x + y + 8 = o. Exercise 3: find the values of a and
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
4K просмотров12 страницHigher Unit 1 Homework
Загружено:
knoxmathsExercise 1: find the gradient of the line joining the points A(2,8) and B(-4,10) find the equation of the line with gradient 12 passing through the point (5,1) find the value of a. Exercise 2: find the equations of the lines specified as follows: (a) passing through the points a(-I,I) and b(3,-I) and (b) parallel to the line 3x + y + 8 = o. Exercise 3: find the values of a and
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 12
Exercise 1
Find the gradient of the line joining the points A(2,8) and B(-4,10).
. Find the equation of the line with gradient 2 passing through the
point (5,1).
. Find the coordinates of the point where the straight line joining
the points (1,-2) and (-3,4) cuts the x-axis.
. Find the gradient of the lines perpendicular to the lines
(a) 3y = 2x-4 (b) 6x -y +2 = 0
. Find the equation of the line through the point (2,1) and
perpendicular to the line 2x -y + 8 = 0.
|. What angles do these lines make with the positive direction
of the x-axis?
(a) y = %x-ll (b) 5y + 3x-12 = 0
. If x = 1+ 3, find the value of
Give your answer with a rational denominator.
Lb 2a
If x = 49 and y = 27 thenevaluate (xt+ y3)*,
If x—a = 1, thenexpress x m terms of a and b.
x+b
6.
Exercise 2
. The points E and F have coordinates (2,-5) and (-4,a) respectively.
Given that the gradient of the line EF is 2/3 , find the value of a.
Find the equations of the lines specified as follows :
(a) Passing through the points A(-1,1) and BG3,-1).
(b) Passing through (4,-5) and parallel to the line 3x + 2y = 8
Prove that the lines with equations y = -Sx + 2 and
2x — l0y = 15 are perpendicular.
|. Triangle ABC has vertices A(2,6), B(-7,4) and C(4,-8).
Find the equation of BM, the median of triangle ABC.
. Triangle DEF has vertices D(2,3), E(4,9) and F(10,-3).
(a) Find the equation of DH, the altitude of triangle DEF.
() Find the area of triangle DEF.
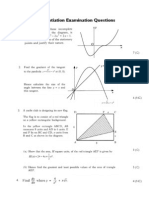
The lines y= 2x +4 and x+y = 13 makeangles
of a° and b° with the positive direction of the x-axis as
shown in the diagram.
wy &
| oy
(a) Find the values of a and b.
(b) Hence find the acute angle between the two given lines.
1
. An air traffic controller sees two planes on
Exercise 3
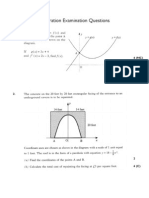
The graph of y = fx) for -I0_ is shown.
Draw separate sketches to show the graphs of
(a) y = ~a%
b)y=#-1
y
1 — The diagram shows y = logwx.
Make a copy of this graph and on it
+—>, sketch the graph of y = logio(x-3).
offi 10%
. ABCD is a parallelogram whose diagonals intersect at E.
A, Band E are the points (-1,0) , (3,-2) and (1,4) respectively.
Find the equation of DC.
Exercise 5
1. Change into degrees: x, 3m, Sn, 2, 50
2 4 6 12 36
2. Change into radians interms of : 270°, 120°, 45°, 210°.
3. Write down the equations of the following trigonometric graphs :
4, Three functions are defined as follows :
f=, gx)=2x, bh) =xtl, xeR
Prove that f(h(x)) = f(x) + h(g(x)).
5. State the largest possible domain for each of these functions :
(@) fx) = _Sx () 9x) = V3¥2x
6. Write down the exact values of :
@) cosn (b) sin3n (©) tan2n
6 4 3
7. Triangle DEF has vertices D(5,8), E(-2,1) and F(6,-1).
(a) Find the equation of EM, the median of triangle DEF.
(b) Find the equation of FP , the altitude of triangle DEF.
(c) Find the coordinates of T , the point of intersection
of EM and FP.
Exercise 6
1. Change to radians : (a) 60° — (b)_ 225° (c) 330°
2. Change to degrees : (a) radians (b) Sm radians (c) 77 radians
5 3 10
3. The diagram shows the graphof y = sinx for O (6) (&K+5P— ©) -X(7-x*)
=
If f(x) = 2Vk and x20, find P(4) .
Exercise 7
. Differentiate the following with respect to x :
(a) (x-3)(x+1) (b) [yx+ 1 (©) 8 =5x+3
vk
x
.. Find the equation of the tangent to the curve y = x°+3x+5
at the point (1,9).
3-
. Calculate the rate of change of f(x) = 6Vx at x =
. Find the gradient of the tangent to the curve ffx) =
at x=4,
VK
. The diagram shows a sketch of the parabola y = f(x). ,
y= fer
(a) Copy the sketch of y = fx).
On your diagram draw the parabola 3
with equation y = —f{x) +3.
(b) State the values of x for which
3-fx) 20. ap
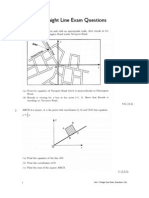
. Paula observes a meteor shower. By her set of axes,
one meteor appears at A(7,8) and disappears at B(1,4).
(a) Calculate
(i) the gradient of the meteor’s flight path
(ii) the acute angle between the flight path
and the horizon (OX), correct to the
nearest degree.
(b) A second meteor, on a parallel path, starts at C(6,2)
and disappears below the horizon at D.
Find the coordinates of D.
Exercise 8
1. Differentiate each of the following functions with respect to the
relevant variable :
(a) f(x) = 3x-2x7 +4 (b) g(u) = wD +2 (©) A) = e+
w
@) bh) = 3x41 (@) gt) =1+1 © he) =ve+2
g x vz
x 3x?
2. Find the equation of the tangent to the curve with equation
y = 1+ x atthe point where x = 1.
x
3. Acurve has equation y = ax? + b , where a and b are constants.
The gradient of the tangent to the curve at the point (3,4) is 6.
Find the values of a and b.
4. Acurve has as its equation y = x(2-x?.
(a) Find the stationary points of the curve and determine their nature.
(b) Write down the coordinates of the points where the curve meets
the coordinate axes.
(c) Sketch the curve.
5. A rectangular garden is laid out as shown. It consists pfa
rectangular lawn of area 30m?. The breadth of the lawn is x metres.
(a) Show that the total area of the garden
isgiven by A = 38+4x+60.
x
(b)Find the value of x (in surd form) for
the garden with minimum area.
Justify your answer.
lL
2.
3.
4,
5.
Exercise 9
A recurrence relation is given by: Ta= Ti+ 3, Ti=7
(a) Find the first 4 terms.
(b) Find an explicit formula for Ts in terms of n.
Repeat qu.1 for the recurrence relation: Va= 0.8Ve1, Vi=5
Given that Une
and Vow
11U, +3 , Us = 10
0.7V. +5 , Vo= 10
(a) Find the first 4 terms of each sequence.
(b) Explain why one of the sequences tends to a limit as n— co
and the other doesn’t.
(©) Find the exact value of the limit of the convergent sequence.
The first three terms of the recurrence relation Unt = mUn+c¢
are 2,11 and 65. Find the values of m and c.
On 1* March, I borrowed £2000 from a good friend who decided
not to charge me any interest.
On the last day of each month I pay back 30% of the outstanding,
balance, but unfortunately have to borrow a further £250 to pay
for food, rent etc.
(a) How much do I owe on 1“ April, 1° May and 1* June ?
(b) Set up a recurrence relation to show the outstanding
balance By, due at the beginning of each month.
(c) Will I ever clear my debts if carry on like this ?
If not, explain what will eventually happen.
. A function f is defined by (0) = 3sin(@+n/3) , 0
Вам также может понравиться
- A5 Summer School 2012 3 FlyerДокумент2 страницыA5 Summer School 2012 3 FlyerknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Recruitment Poster EdinurghДокумент1 страницаRecruitment Poster EdinurghknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Technicians AdvertДокумент1 страницаTechnicians AdvertknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- 16+ EventДокумент1 страница16+ EventknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Zot VacДокумент1 страницаZot VacknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Integration Examination Questions CALДокумент4 страницыUnit 2 Integration Examination Questions CALknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- U2 Trigonometric Formulae and EquationsДокумент4 страницыU2 Trigonometric Formulae and EquationsknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Straight Line Exam Questions CALДокумент3 страницыUnit 1 Straight Line Exam Questions CALknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- U2 Equation of CircleДокумент7 страницU2 Equation of CircleknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Muirfield VacДокумент1 страницаMuirfield VacknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- U2 Factors and Quadratic TheoryДокумент3 страницыU2 Factors and Quadratic TheoryknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Recurrence Relation Examination Questions CALДокумент4 страницыUnit 2 Recurrence Relation Examination Questions CALknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- S3 April Credit Assessment: 1. Calculation 2. Scientific Notation 3. SimilarityДокумент1 страницаS3 April Credit Assessment: 1. Calculation 2. Scientific Notation 3. SimilarityknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Unit1 SummaryДокумент1 страницаUnit1 SummaryknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Differentiation Examination Questions CALДокумент6 страницUnit 1 Differentiation Examination Questions CALknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- U1 Graphs and FunctionsДокумент4 страницыU1 Graphs and FunctionsknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Higher Unit 3 SummaryДокумент1 страницаHigher Unit 3 SummaryknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 SummaryДокумент1 страницаUnit 2 SummaryknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Unit RevisionДокумент7 страницUnit RevisionknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Advanced Higher Maths: Formulae: Essential Trigonometric IdentitiesДокумент5 страницAdvanced Higher Maths: Formulae: Essential Trigonometric IdentitiesknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Differentiation FormulaeДокумент3 страницыDifferentiation FormulaeknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Standard Integrals Formulae 1Документ1 страницаStandard Integrals Formulae 1knoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Credit Past Paper Questions - SolutionsДокумент28 страницCredit Past Paper Questions - SolutionsknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- S3 December Credit AssessmentДокумент1 страницаS3 December Credit AssessmentknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Revision Questions by TopicДокумент82 страницыRevision Questions by TopicknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- S2 Course OutlineДокумент1 страницаS2 Course OutlineknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- S1 Course OutlineДокумент1 страницаS1 Course OutlineknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)