Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Phenobarbital Sodium
Загружено:
Kevin GonzalesИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Phenobarbital Sodium
Загружено:
Kevin GonzalesАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
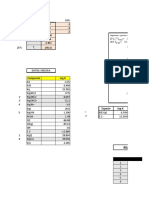
Drug Name Dosage & Route Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindication Nursing Responsibility
Body as a Whole:
PHENOBARBITAL Anticonvulsant Long-acting barbiturate. Long-term management of Sensitivity to barbiturates; Assessment & Drug Effects
Myalgia, neuralgia, CNS
SODIUM Adult: PO 100–300 Sedative and hypnotic effects tonic-clonic (grand mal) manifest hepatic or familial
depression, coma, and death.
mg/d IV/IM 200–600 of barbiturates appear to be seizures and partial seizures; history of porphyria; severe
CNS: Somnolence, • Observe patients receiving large
mg up to 20 mg/kg due primarily to interference status epilepticus, eclampsia, respiratory or kidney disease;
Luminal Sodium nightmares, insomnia, doses closely for at least 30 min to
Child: PO/IV 3–8 with impulse transmission of febrile convulsions in young history of previous addiction
"hangover," headache, ensure that sedation is not excessive.
mg/kg or 125 mg/m2/d cerebral cortex by inhibition children. Also used as a to sedative hypnotics;
anxiety, thinking
Classifications: CENTRAL Neonate: PO/IV 3–4 of reticular activating system. sedative in anxiety or tension
abnormalities, dizziness,
uncontrolled pain; pregnancy • Keep patient under constant
NERVOUS SYSTEM mg/kg/d (max: 5 CNS depression may range states; in pediatrics as (particularly early pregnancy) observation when drug is
nystagmus, irritability,
AGENT; mg/kg/d) from mild sedation to coma, preoperative and (category D), lactation; administered IV, and record vital
paradoxic excitement and
ANTICONVULSANT; depending on dosage, route of postoperative sedation and to sustained release formulation signs at least every hour or more
exacerbation of hyperkinetic
SEDATIVE-HYPNOTIC; Status administration, degree of treat pylorospasm in infants. for children <12 y of age. often if indicated.
behavior (in children);
BARBITURATE Epilepticus nervous system excitability,
Adult/Child: IV 15–18 and drug tolerance. Initially,
confusion or depression or • Lab tests: Obtain liver function
marked excitement (older and hematology tests and
mg/kg in single or barbiturates suppress REM
adult or debilitated patients); determinations of serum folate and
divided doses (max: sleep, but with chronic
ataxia. CV: Bradycardia, vitamin D levels during prolonged
20 mg/kg) therapy REM sleep returns to
syncope, hypotension. GI: therapy.
Neonate: IV 15–20 normal.
Nausea, vomiting, • Monitor serum drug levels.
mg/kg in single or
constipation, diarrhea, Serum concentrations >50 mcg/mL
divided doses
epigastric pain, liver damage. may cause coma. Therapeutic serum
Hematologic: concentrations of 15–40 mcg/mL
Sedative
Megaloblastic anemia, produce anticonvulsant activity in
Adult: PO 30–120
agranulocytosis, most patients. These values are
mg/d IV/IM 100–200
thrombocytopenia. usually attained after 2 or 3 wk of
mg/d
Metabolic: Hypocalcemia, therapy with a dose of 100–200
Child: PO 6 mg/kg/d
osteomalacia, rickets. mg/d.
or 180 mg/m2 in 3
Musculoskeletal: Folic
divided doses IV/IM
acid deficiency, vitamin D • Expect barbiturates to produce
16–100 mg/d (1–3 restlessness when given to patients
deficiency. Respiratory:
mg/kg) in pain because these drugs do not
Respiratory depression. Skin:
Mild maculopapular, have analgesic action.
morbilliform rash; erythema • Be prepared for paradoxical
multiforme, Stevens-Johnson responses and report promptly in
syndrome, exfoliative older adult or debilitated patient and
dermatitis (rare). . children (i.e., irritability, marked
excitement [inappropriate
tearfulness and aggression in
children], depression, and
confusion).
Вам также может понравиться
- MeclizineДокумент2 страницыMeclizineGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- Phenobarbital Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыPhenobarbital Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- PhenerganДокумент2 страницыPhenerganKatie McPeekОценок пока нет
- ClonazepamДокумент2 страницыClonazepamjhezelle05100% (2)
- DiazepamДокумент1 страницаDiazepamkualamonkey100% (1)
- Mycophenolate MofetilДокумент1 страницаMycophenolate MofetilAndyPua100% (1)
- Drug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFДокумент4 страницыDrug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFAlexander Miguel M. AbasОценок пока нет
- Drug study on Biperiden for ParkinsonismДокумент2 страницыDrug study on Biperiden for ParkinsonismMae Ann Bueno CastillonОценок пока нет
- Kalium Durule Brand Name: Potassium ChlorideДокумент3 страницыKalium Durule Brand Name: Potassium ChlorideRon ChristianОценок пока нет
- Drug Study ClozapineДокумент2 страницыDrug Study ClozapineRobert Martin Rivera PuertaОценок пока нет
- GlipizideДокумент3 страницыGlipizideapi-3797941100% (1)
- PhenobarbitalДокумент2 страницыPhenobarbitalhahahahaaaaaaaОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент5 страницDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioОценок пока нет
- Drug Study Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsДокумент2 страницыDrug Study Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsCelline Isabelle ReyesОценок пока нет
- Ritalin LA: Initial, 20 MG PO qAM May Adjust Dose in Weekly 10-mg Incremen TS, Not To Exceed 60 Mg/day (Patients Requiring A Lower InitialДокумент2 страницыRitalin LA: Initial, 20 MG PO qAM May Adjust Dose in Weekly 10-mg Incremen TS, Not To Exceed 60 Mg/day (Patients Requiring A Lower InitialKwin SaludaresОценок пока нет
- BuscopanДокумент3 страницыBuscopanJulie May100% (1)
- Generic Name: Contraindications: Before:: Diamox, Diamox SequelsДокумент3 страницыGeneric Name: Contraindications: Before:: Diamox, Diamox SequelsRomwella May AlgoОценок пока нет
- PhenobarbitalДокумент3 страницыPhenobarbitalChristine Joy Pepito50% (2)
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityДокумент2 страницыCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDan Dan Manaois100% (1)
- Micardis PlusДокумент2 страницыMicardis PlusKristine YoungОценок пока нет
- FebuxostatДокумент14 страницFebuxostatSanjay NavaleОценок пока нет
- Postop Drug2Документ3 страницыPostop Drug2zbestgurlОценок пока нет
- Biperiden Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыBiperiden Drug StudyMelissa Fatima Laurente Dosdos100% (1)
- Drug StudyДокумент6 страницDrug StudyBrix John PortellanoОценок пока нет
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент2 страницыAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbigail BascoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study of ChloramphenicolДокумент3 страницыDrug Study of Chloramphenicolcasimir1128Оценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыDrug StudyXio PauОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент7 страницDrug StudyOlive Keithy Ascaño ReyesОценок пока нет
- Duavent Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыDuavent Drug StudyNicole cuencosОценок пока нет
- Butorphanol Tartrate (Drug Study)Документ2 страницыButorphanol Tartrate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (2)
- AldactoneДокумент2 страницыAldactoneianecunarОценок пока нет
- College of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыCollege of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- CatapresДокумент1 страницаCatapres去約翰Оценок пока нет
- Doxazosin MesylateДокумент2 страницыDoxazosin Mesylateapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- Pharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative AntipsychoticДокумент2 страницыPharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative AntipsychoticBianca Nicole Gacad Fernandez100% (1)
- Fluconazole drug classification, indications, side effects and nursing responsibilitiesДокумент1 страницаFluconazole drug classification, indications, side effects and nursing responsibilitiescen janber cabrillos0% (1)
- TRIAZOLAMДокумент4 страницыTRIAZOLAMEzequiel RosalesОценок пока нет
- Phenobarbital Sodium Antiepileptic Sedative Drug Classification Dosage and Administration Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesДокумент2 страницыPhenobarbital Sodium Antiepileptic Sedative Drug Classification Dosage and Administration Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJeremy_Fabio_5332100% (2)
- Ciprofloxacin and Paracetamol Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыCiprofloxacin and Paracetamol Drug StudyRichard MendejaОценок пока нет
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыOfloxacin Drug StudyMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY LevetiracetamДокумент3 страницыDRUG STUDY LevetiracetamMaria Althea NajorraОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент7 страницDrug StudyHanna Clarisse PataoОценок пока нет
- Escivex 10 2Документ1 страницаEscivex 10 2Havier EsparagueraОценок пока нет
- FINAL Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыFINAL Drug StudycasedraftОценок пока нет
- GENERIC NAME: Clonazepam BRAND NAME: RivotrilДокумент2 страницыGENERIC NAME: Clonazepam BRAND NAME: RivotrildanaОценок пока нет
- Nursing implications of Apidra insulinДокумент1 страницаNursing implications of Apidra insulinChris Denver Bancale100% (1)
- OfloxacinДокумент2 страницыOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Drug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameДокумент2 страницыDrug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NamehahahaОценок пока нет
- Propylthiouracil DSДокумент6 страницPropylthiouracil DSAlexandrea MayОценок пока нет
- Lithium Carbonate Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыLithium Carbonate Drug Studynot your medz duranОценок пока нет
- PrimidoneДокумент6 страницPrimidoneKim SunooОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыDrug StudyKeanu ArcillaОценок пока нет
- Oxymetazoline 2Документ8 страницOxymetazoline 2Febry Dian SinagaОценок пока нет
- Insulin and Ferrous Sulfate Drug StudyДокумент7 страницInsulin and Ferrous Sulfate Drug StudyFuture RNОценок пока нет
- Dulcolax Drug StudyДокумент1 страницаDulcolax Drug Studysweetpixie18100% (1)
- MeperidineДокумент2 страницыMeperidineNinoska Garcia-Ortiz50% (2)
- 4 SeizuresДокумент11 страниц4 SeizuresApple MaeОценок пока нет
- Dosage & RouteДокумент1 страницаDosage & RoutepiasolОценок пока нет
- DRUG STUDY ON PROPOFOL FOR ICU SEDATIONДокумент3 страницыDRUG STUDY ON PROPOFOL FOR ICU SEDATIONAngelica shane Navarro100% (2)
- Injections: 2.5mg/ml in CNS: Drowsiness,: DroperidolДокумент3 страницыInjections: 2.5mg/ml in CNS: Drowsiness,: DroperidolthesarayoОценок пока нет
- Toxic Responses To The LiverДокумент18 страницToxic Responses To The LiversaiibelievesОценок пока нет
- Health Education for MothersДокумент14 страницHealth Education for MothersBhumika RathiОценок пока нет
- Pengaruh Latihan Range of Motion (ROM) Ankle Terhadap Pencegahan Terjadinya Neuropati Dan Angiopati Pada Klien Diabetes MelitusДокумент7 страницPengaruh Latihan Range of Motion (ROM) Ankle Terhadap Pencegahan Terjadinya Neuropati Dan Angiopati Pada Klien Diabetes MelitusRafly PrasetyoОценок пока нет
- Scientific Programme BookletДокумент44 страницыScientific Programme BookletPreetam PatnalaОценок пока нет
- Adolescent Pregnacy, Unwed Mother, Sexual Violence - 3rd BSC 2014Документ236 страницAdolescent Pregnacy, Unwed Mother, Sexual Violence - 3rd BSC 2014sindhujojo0% (1)
- Acute Disease:: Above: Circles of Influence in Self-Management of Chronic DiseaseДокумент10 страницAcute Disease:: Above: Circles of Influence in Self-Management of Chronic DiseaseanburajjОценок пока нет
- PP.c. Teaching Nursing 2023 (Positioning of Patient)Документ14 страницPP.c. Teaching Nursing 2023 (Positioning of Patient)Elsye ResimanukОценок пока нет
- TuberculosisДокумент12 страницTuberculosisanon ymousОценок пока нет
- Students Readiness For The Face-To-Face Classes in Junior and Senior High SchoolДокумент12 страницStudents Readiness For The Face-To-Face Classes in Junior and Senior High SchoolIJAR JOURNALОценок пока нет
- Final Merit List of Candidates for Admission to 1st Year MBBS/BDS CoursesДокумент2 страницыFinal Merit List of Candidates for Admission to 1st Year MBBS/BDS CoursesIftikhar RasheedОценок пока нет
- OPIOID OVERVIEWДокумент3 страницыOPIOID OVERVIEWGerrahОценок пока нет
- Registered General and Psychiatric Nurse Application BrochureДокумент2 страницыRegistered General and Psychiatric Nurse Application BrochureCrystal CharlesОценок пока нет
- Whoqol BrefДокумент18 страницWhoqol BrefPaco Herencia PsicólogoОценок пока нет
- Adverse Morphological Development in Embryonic Zebrafish Exposed To Environmental Concentrations of Contaminants Individually and in MixtureДокумент13 страницAdverse Morphological Development in Embryonic Zebrafish Exposed To Environmental Concentrations of Contaminants Individually and in MixtureTiago TorresОценок пока нет
- The Psychology of Handwriting With Many Facsimiles of Handwriting by William Leslie FrenchДокумент258 страницThe Psychology of Handwriting With Many Facsimiles of Handwriting by William Leslie FrenchandreiОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 036 Urinay DisordersДокумент8 страницChapter - 036 Urinay DisordersClaudina CariasoОценок пока нет
- Hasil MCU 173 Operator Magang Source Jatirogo-3 (Prodia Solo, 12-13 Oktober 2023)Документ35 страницHasil MCU 173 Operator Magang Source Jatirogo-3 (Prodia Solo, 12-13 Oktober 2023)Alvn FauziОценок пока нет
- Arcadis Orbic Arcadis Orbic 3D: Designed For Enhanced Surgical PrecisionДокумент24 страницыArcadis Orbic Arcadis Orbic 3D: Designed For Enhanced Surgical PrecisionHeidi BlueОценок пока нет
- A Review On Cosmetology in AyurvedaДокумент9 страницA Review On Cosmetology in AyurvedaCarla Vieira SoaresОценок пока нет
- Medical Economics Magazine PDFДокумент41 страницаMedical Economics Magazine PDFxtineОценок пока нет
- Julia Miller ResumeДокумент2 страницыJulia Miller ResumejuliaОценок пока нет
- SEO-Optimized title for mercury-sulfur system Pourbaix diagram dataДокумент18 страницSEO-Optimized title for mercury-sulfur system Pourbaix diagram dataFiorelaRosarioJimenezLopezОценок пока нет
- Safety Data Sheet: Dyestone Printgen XA-301Документ4 страницыSafety Data Sheet: Dyestone Printgen XA-301unisourcceeОценок пока нет
- Naskah Soal Asas Bhs. Inggris Kelas 5 Semester Ganjil 2023-2024Документ9 страницNaskah Soal Asas Bhs. Inggris Kelas 5 Semester Ganjil 2023-2024El-Dukasi ChannelОценок пока нет
- Literature Review Outdoor EducationДокумент5 страницLiterature Review Outdoor Educationafdtrajxq100% (1)
- Trauma Case Reports: Jugert Bango, Evan Zhang, Daniel L. Aaron, Amna DiwanДокумент4 страницыTrauma Case Reports: Jugert Bango, Evan Zhang, Daniel L. Aaron, Amna DiwanCristhian Jover CastroОценок пока нет
- Blind Suctioning For BeginnersДокумент7 страницBlind Suctioning For BeginnersMark HammerschmidtОценок пока нет
- Product Training FaceRealityДокумент113 страницProduct Training FaceRealityJazz100% (1)
- Pat Coleby On Vitamin C Treatment For SNAKE BITES Here) Did Much Research On The Use of Vitamin C On Humans. in Turn A Californian VetДокумент2 страницыPat Coleby On Vitamin C Treatment For SNAKE BITES Here) Did Much Research On The Use of Vitamin C On Humans. in Turn A Californian VetharoldpsbОценок пока нет
- Efects of Family Demographics and The Passage of Time On Parents' Difficulty With Their Lesbian, Gay or Bisexua Youth's Sexual OrientationДокумент8 страницEfects of Family Demographics and The Passage of Time On Parents' Difficulty With Their Lesbian, Gay or Bisexua Youth's Sexual OrientationGamer BoyОценок пока нет