Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Module 4 - Solutions of Triangles
Загружено:
Hayati Aini AhmadИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Module 4 - Solutions of Triangles
Загружено:
Hayati Aini AhmadАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Solutions of Triangle
1. Diagram 1 shows a trapezium KLMN, where KL = 7 cm, KN = 8 cm, LM = LN =13 cm, and KN is
parallel to LM.
Calculate
13 cm M
L
(a) ∠NKL and ∠KNL [4 marks]
7 cm 13 cm (b) the perpendicular distance between the
parallel sides KN and LM. [1 marks]
2
K N (c) the area, in cm , of
8 cm
(i) triangle LMN (ii) the trapezium KLMN [5 marks]
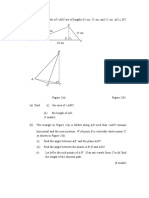
2. Diagram 2 shows a triangle IJK.
J (a) Find the smallest angle in triangle IJK.
3.4 cm [3 marks]
(b) IJKL is a quadrilateral such that KL = 3.5 cm
3.2 cm K
and ∠KIL = 35
5.4 cm Find the two possible values of ∠KLI.
(i)
I Hence sketch the two possible triangles of IKL
(ii) Using the acute angle of ∠IKL, calculate the length of line IL.
(iii) Using the acute angle of ∠KLI, calculate the area of quadrilateral IJKL. [7 marks]
3. Diagram 3 shows a parallelogram PQRST. Given that the area of triangle TQR is 42.28 cm2,
find
(a) the length of SQ [2 marks]
T S 9 cm R
(b) the length of TS [3 marks]
6 cm (c) ∠QSR [2 marks]
(d) the area of triangle PQS
56°
P Q
[3 marks]
4. Diagram 4 shows triangle ABC and triangle ABE. Given that AD = 6 cm, AE = 5 cm, ED = 3 cm,
BC =9 cm, ADC and EDB are straight lines, calculate
(a) ∠ADE [2 marks]
B
(b) the length of BD [2 marks]
(c) the area of triangle ABD [2 marks]
A 50° C (d) the shortest distance from D to AB [4 marks]
D
E
Add Maths Buddy Support SMK BBSL_2011
Вам также может понравиться
- Mathematics D - 5Документ4 страницыMathematics D - 5Aditya GhoseОценок пока нет
- SPM Question Form 4 Solution of TrianglesДокумент6 страницSPM Question Form 4 Solution of TrianglesTee Pei LengОценок пока нет
- Test MathsДокумент5 страницTest MathsBurhan AzharОценок пока нет
- Tkss Prelim 2009 em p2Документ10 страницTkss Prelim 2009 em p2JASON_INGHAMОценок пока нет
- SPM 1993-2021 PAST YEARS Solutions of TrianglesДокумент8 страницSPM 1993-2021 PAST YEARS Solutions of TrianglesTIME DIDA滴答Оценок пока нет
- Further PracticeДокумент6 страницFurther PracticeHo Yen SzeОценок пока нет
- Maa SL: Mathematics: Analysis and ApproachesДокумент14 страницMaa SL: Mathematics: Analysis and ApproachesHaluk BulutОценок пока нет
- Test VectorsДокумент2 страницыTest VectorsBsbsbaОценок пока нет
- Answer All Questions: (48 Marks)Документ5 страницAnswer All Questions: (48 Marks)bidarihassanОценок пока нет
- Maths Question Paper Winter: 0580 - w02 - QP - 4Документ8 страницMaths Question Paper Winter: 0580 - w02 - QP - 4petal100% (1)
- 0580 - w22 - QP - 41 - Parziale 2Документ15 страниц0580 - w22 - QP - 41 - Parziale 2tdjn5zpsb7Оценок пока нет
- 13 Kings Scholarship Maths A Paper 2014 Eton CollegeДокумент6 страниц13 Kings Scholarship Maths A Paper 2014 Eton CollegeakashОценок пока нет
- Newton Solutions of TrianglesДокумент4 страницыNewton Solutions of TrianglesSharvinder SinghОценок пока нет
- Sdoc 04 02 SiДокумент15 страницSdoc 04 02 SichimangokaudzuОценок пока нет
- f4 c10 Solution of TrianglenewДокумент8 страницf4 c10 Solution of Trianglenewnor fazlinaОценок пока нет
- Adv Ex 07 Trigonometry II (Application)Документ12 страницAdv Ex 07 Trigonometry II (Application)Leroy ChengОценок пока нет
- 3143 02 6RP AFP tcm143-700723Документ16 страниц3143 02 6RP AFP tcm143-700723Indulakshmi VG100% (2)
- AMATH Solution of TriangleДокумент12 страницAMATH Solution of TriangleLeneОценок пока нет
- Trigo f3Документ3 страницыTrigo f3ihsanjayatrainingОценок пока нет
- Review Trig GRD 9Документ6 страницReview Trig GRD 9JanvierОценок пока нет
- Mensurations PDFДокумент84 страницыMensurations PDFWaniya AmirОценок пока нет
- Chapter 10: Solution of TrianglesДокумент4 страницыChapter 10: Solution of TrianglesHayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Cambridge International Examinations General Certi Cate of EducationДокумент8 страницCambridge International Examinations General Certi Cate of EducationHubbak KhanОценок пока нет
- Digonostic Test - 10 (2016)Документ1 страницаDigonostic Test - 10 (2016)raamees.durrani242009Оценок пока нет
- Circles L2Документ7 страницCircles L2DanyОценок пока нет
- Latihan Pengukuhan 4 Dec (Ahad)Документ7 страницLatihan Pengukuhan 4 Dec (Ahad)Yun XingОценок пока нет
- PYTHAGORAS THEOREM Test1-3-2021Документ2 страницыPYTHAGORAS THEOREM Test1-3-2021Megh lakhaniОценок пока нет
- Topic - 9 Similarity and CongruencyДокумент9 страницTopic - 9 Similarity and CongruencyJorifОценок пока нет
- Mathematics: PAPER 1 Pure Mathematics 1 (P1)Документ8 страницMathematics: PAPER 1 Pure Mathematics 1 (P1)Private of ScienceОценок пока нет
- SPM 2021 Paper 1Документ8 страницSPM 2021 Paper 1soochin93Оценок пока нет
- Maths 9 Icse Sample Paper 3Документ5 страницMaths 9 Icse Sample Paper 3SHIVKUMAR KRISHNAMURTHYОценок пока нет
- Intso Education: Mathematics Talent Search Olympiad (Mtso) 2016 - 2017Документ4 страницыIntso Education: Mathematics Talent Search Olympiad (Mtso) 2016 - 2017Faiz Khan100% (2)
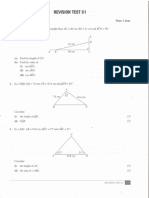
- Revision Test TrigonometryДокумент7 страницRevision Test TrigonometryRNC ArcadeОценок пока нет
- 1a. (4 Marks) Consider The Following Circle With Centre O and Radius RДокумент5 страниц1a. (4 Marks) Consider The Following Circle With Centre O and Radius RAloooОценок пока нет
- Mensuration 2D Figure BasedДокумент8 страницMensuration 2D Figure BasedadiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 - DifferentiationДокумент8 страницChapter 8 - DifferentiationSelvarani NadarajahОценок пока нет
- P. The Radius of The Smaller Circle Is 2 M, The Radius of The Larger Circle Is 6 M and QPRДокумент3 страницыP. The Radius of The Smaller Circle Is 2 M, The Radius of The Larger Circle Is 6 M and QPRTahmid RaihanОценок пока нет
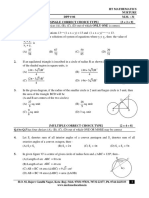
- H.O. 92, Rajeev Gandhi Nagar, Kota (Raj.) Mob. 97831-97831, 70732-22177, Ph. 0744-2423333 WWW - Nucleuseducation.inДокумент2 страницыH.O. 92, Rajeev Gandhi Nagar, Kota (Raj.) Mob. 97831-97831, 70732-22177, Ph. 0744-2423333 WWW - Nucleuseducation.inSatyanshu JhaОценок пока нет
- 2016 Pape1 To 2018 PDFДокумент29 страниц2016 Pape1 To 2018 PDFNancy Sikazwe100% (1)
- 10 SolutionoftrianglesДокумент5 страниц10 SolutionoftrianglesFOO YEE CHOWОценок пока нет
- G9 Mock MathДокумент10 страницG9 Mock Mathlucksonmumba88Оценок пока нет
- C2 A Level Maths Trigonometry Questions AQA OCR Edexcel MEIДокумент4 страницыC2 A Level Maths Trigonometry Questions AQA OCR Edexcel MEIBen Morow JuniorОценок пока нет
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/41Документ20 страницCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/41agnesasus123Оценок пока нет
- Revision Test C1Документ3 страницыRevision Test C1Edu 4 UОценок пока нет
- Right Angled Triangle Trigonometry 2 IB Math SLДокумент4 страницыRight Angled Triangle Trigonometry 2 IB Math SLFransiska KОценок пока нет
- JC 1 Geometry and Trigonometry W4 240129 091736 240201 100035Документ27 страницJC 1 Geometry and Trigonometry W4 240129 091736 240201 100035Adhitya PrasethioОценок пока нет
- C1 June 15 CondensedДокумент5 страницC1 June 15 CondensedStuart GregoryОценок пока нет
- Cosine RuleДокумент28 страницCosine Rule/ “Nu” /Оценок пока нет
- 52 CM 25 CM: D and ADCДокумент1 страница52 CM 25 CM: D and ADCym5c2324Оценок пока нет
- Triangles Imp Questions Paper 1Документ2 страницыTriangles Imp Questions Paper 1Anil KUMARОценок пока нет
- Perimeter L2Документ12 страницPerimeter L2DanyОценок пока нет
- Maths X 1Документ29 страницMaths X 1Govinda PatraОценок пока нет
- Arjuna JEE AIR (2024) : TriangleДокумент3 страницыArjuna JEE AIR (2024) : TriangleMeet ShahОценок пока нет
- 10 Solution of TrianglesДокумент5 страниц10 Solution of TrianglesDa-teen Sabreena BernoulliОценок пока нет
- SPM Mock ExamДокумент10 страницSPM Mock ExamNarendrn KanaesonОценок пока нет
- Modul Jom Tanya Sifu - Integrations & Vectors 2014Документ16 страницModul Jom Tanya Sifu - Integrations & Vectors 2014Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Jom Tanya Sifu@Form 5: Chapter 1: PROGRESSIONSДокумент15 страницJom Tanya Sifu@Form 5: Chapter 1: PROGRESSIONSHayati Aini Ahmad100% (1)
- Linear Law 2014Документ8 страницLinear Law 2014Ainol Bazlin FarhanaОценок пока нет
- Quadratic Equation Set 1@2014Документ1 страницаQuadratic Equation Set 1@2014Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- KMC 2014 School List Registration v1-1Документ15 страницKMC 2014 School List Registration v1-1Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Index Number Set3@2010Документ2 страницыIndex Number Set3@2010Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Index Number - Set1 @2010Документ2 страницыIndex Number - Set1 @2010Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Index Number - Set 2@2010Документ2 страницыIndex Number - Set 2@2010Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Progressions Paper 1@set 5 (Revised Version 2013)Документ2 страницыProgressions Paper 1@set 5 (Revised Version 2013)Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Integration and DifferentiationДокумент7 страницIntegration and DifferentiationHayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Jadual Trial SPM 2013Документ1 страницаJadual Trial SPM 2013Hayati Aini Ahmad100% (1)
- Solutions of Triangle - Set 2Документ2 страницыSolutions of Triangle - Set 2Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Differentiation (Paper 1) - Set 1@2013Документ2 страницыDifferentiation (Paper 1) - Set 1@2013Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Progressions Paper 1@set 8 (Revised)Документ2 страницыProgressions Paper 1@set 8 (Revised)Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Progressions Paper 1@set 7 (Revised)Документ2 страницыProgressions Paper 1@set 7 (Revised)Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Progressions Paper 1@set 6 (Revised)Документ2 страницыProgressions Paper 1@set 6 (Revised)Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Tutorial Vector Q1 - Paper 1Документ1 страницаTutorial Vector Q1 - Paper 1Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Progressions Paper 1@set 3 (Revised Version 2013)Документ2 страницыProgressions Paper 1@set 3 (Revised Version 2013)Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Progressions Paper 1@set 4 (Revised Version 2013)Документ2 страницыProgressions Paper 1@set 4 (Revised Version 2013)Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- 3472 MT - Skema Kertas 2no.14Документ1 страница3472 MT - Skema Kertas 2no.14Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Progressions Paper 1@set 2 (Revised Version 2013)Документ2 страницыProgressions Paper 1@set 2 (Revised Version 2013)Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Progression Paper 1@set1 (Revised Version 2013)Документ2 страницыProgression Paper 1@set1 (Revised Version 2013)Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Knecht Vs UCCДокумент2 страницыKnecht Vs UCCXing Keet LuОценок пока нет
- Gabriela SilangДокумент9 страницGabriela SilangEshaira Morales100% (1)
- Prom 2015: The Great GatsbyДокумент14 страницProm 2015: The Great GatsbyMaple Lake MessengerОценок пока нет
- Presidential Commission On Good Government vs. Gutierrez, 871 SCRA 148, July 09, 2018Документ15 страницPresidential Commission On Good Government vs. Gutierrez, 871 SCRA 148, July 09, 2018calmandpeaceОценок пока нет
- Biotech Bo SeriesДокумент2 страницыBiotech Bo SeriesArlinda Friyanti CallistaОценок пока нет
- Mobile Services: Your Account Summary This Month'S ChargesДокумент4 страницыMobile Services: Your Account Summary This Month'S Chargeskumar JОценок пока нет
- TachometerДокумент7 страницTachometerEngr MahaОценок пока нет
- Chordu Piano Chords Ede Lobas Chordsheet Id - JBQiUlO0NDU PDFДокумент3 страницыChordu Piano Chords Ede Lobas Chordsheet Id - JBQiUlO0NDU PDFKaren RochaОценок пока нет
- The Poetical PolicemanДокумент6 страницThe Poetical PolicemanYiannis KatsanevakisОценок пока нет
- Wedgeworth Sentencing MemorandumДокумент218 страницWedgeworth Sentencing MemorandumActionNewsJaxОценок пока нет
- Chapter Eight Cross-National Cooperation and Agreements: ObjectivesДокумент13 страницChapter Eight Cross-National Cooperation and Agreements: ObjectivesSohni HeerОценок пока нет
- The Hamas CharterДокумент16 страницThe Hamas CharterFrancesca PadoveseОценок пока нет
- Questa Sim Qrun UserДокумент50 страницQuesta Sim Qrun UsertungnguyenОценок пока нет
- Davao October 2014 Criminologist Board Exam Room AssignmentsДокумент113 страницDavao October 2014 Criminologist Board Exam Room AssignmentsPRC Board0% (1)
- CD 116. Villaflor v. Summers, 41 Phil. 62 (1920)Документ1 страницаCD 116. Villaflor v. Summers, 41 Phil. 62 (1920)JMae MagatОценок пока нет
- Parole and ProbationДокумент12 страницParole and ProbationHare Krishna RevolutionОценок пока нет
- Listing of Internet Slang and AcronymsДокумент4 страницыListing of Internet Slang and AcronymsabeegameОценок пока нет
- MURS320: Vishay General SemiconductorДокумент5 страницMURS320: Vishay General SemiconductorAgustin DiocaОценок пока нет
- COM670 Chapter 5Документ19 страницCOM670 Chapter 5aakapsОценок пока нет
- Last Two Verse of Surah AlДокумент5 страницLast Two Verse of Surah AlMhonly MamangcaoОценок пока нет
- 2 - Site Crisis Management Plan TemplateДокумент42 страницы2 - Site Crisis Management Plan Templatesentryx1100% (7)
- Terre vs. Terre DigestДокумент1 страницаTerre vs. Terre DigestPMVОценок пока нет
- VLT - Go MS 90Документ2 страницыVLT - Go MS 90Raghu Ram100% (3)
- Ron Matusalem & Matusa of Florida, Inc., a Florida Corporation, Plaintiff-Counterdefendant v. Ron Matusalem, Inc., a Corporation of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, and United Liquors Corporation, a Florida Corporation, Defendants-Counterplaintiffs, Manuel A. Guarch, Jr. And Luisa Alvarez Soriano, Counterdefendants, 872 F.2d 1547, 11th Cir. (1989)Документ13 страницRon Matusalem & Matusa of Florida, Inc., a Florida Corporation, Plaintiff-Counterdefendant v. Ron Matusalem, Inc., a Corporation of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, and United Liquors Corporation, a Florida Corporation, Defendants-Counterplaintiffs, Manuel A. Guarch, Jr. And Luisa Alvarez Soriano, Counterdefendants, 872 F.2d 1547, 11th Cir. (1989)Scribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- Order RecieptДокумент1 страницаOrder RecieptAnUbHaV TiWaRiОценок пока нет
- Britain and The Resistance in Occupied YugoslaviaДокумент29 страницBritain and The Resistance in Occupied YugoslaviaMarko Cvarak100% (1)
- Swot Analysis MatrixДокумент1 страницаSwot Analysis MatrixAhmed Abdel-FattahОценок пока нет
- The Doctrine of Ultra Vires - Taxguru - in PDFДокумент2 страницыThe Doctrine of Ultra Vires - Taxguru - in PDFSat SriОценок пока нет
- Historical Background of The PNPДокумент1 страницаHistorical Background of The PNPGloria AsuncionОценок пока нет
- Bookkeeping Exercises 2022Документ6 страницBookkeeping Exercises 2022Anne de GuzmanОценок пока нет