Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
NCP
Загружено:
Jahmie Rivera0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
2K просмотров4 страницы1. The patient is at low risk for infection, injury from positioning, hypothermia, or contamination during surgery due to aseptic technique and protective measures.
2. Nursing interventions focus on reducing anxiety, preventing positioning injuries, maintaining safety and dignity, and avoiding complications like infection.
3. The patient's position is chosen to properly expose the surgical site while keeping the patient as comfortable as possible without obstructing blood flow or respiration.
Исходное описание:
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документ1. The patient is at low risk for infection, injury from positioning, hypothermia, or contamination during surgery due to aseptic technique and protective measures.
2. Nursing interventions focus on reducing anxiety, preventing positioning injuries, maintaining safety and dignity, and avoiding complications like infection.
3. The patient's position is chosen to properly expose the surgical site while keeping the patient as comfortable as possible without obstructing blood flow or respiration.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
2K просмотров4 страницыNCP
Загружено:
Jahmie Rivera1. The patient is at low risk for infection, injury from positioning, hypothermia, or contamination during surgery due to aseptic technique and protective measures.
2. Nursing interventions focus on reducing anxiety, preventing positioning injuries, maintaining safety and dignity, and avoiding complications like infection.
3. The patient's position is chosen to properly expose the surgical site while keeping the patient as comfortable as possible without obstructing blood flow or respiration.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 4
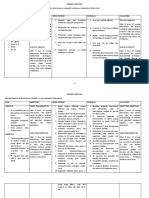
Risk for infection non-irritated, and free The patient is free of Interventions/Activities
of bruising, signs and
Risk for impaired skin Implements aseptic
other than surgical symptoms of physical technique.
integrity related to incision. injury.
Classifies surgical
positioning, Function, sensation, The patient is free from wound.
immobilization, motion, and respiratory signs and
pressure, status will be Assesses susceptibility
maintained or symptoms of injury for infection.
and/or shearing forces related to
improved from baseline Performs skin
Risk of injury related positioning. preparations.
assessment.
to surgical environment, The patient is free from Protects from cross-
extraneous Skin remains smooth,
intact, non-reddened, signs and contamination.
objects and equipment non-irritated and free of symptoms of laser, Monitors for signs and
bruising. electrical, and symptoms of infection.
(laser, electrical and
Sensation, motions, and radiation injury. Minimizes the length of
use of x-rays/radiation) function will be invasive procedure
Risk of hypothermia The patient is at or planning
maintained or improved returning to
from baseline. care.
Interim Outcome
Statement normothermia at the
Core body temperature conclusion Administers prescribed
will remain within prophylactic
Surgery is performed
expected range. of the immediate treatments.
using aseptic technique
and in a manner to postoperative
Outcome Statement Initiates traffic control.
prevent period.
crosscontamination. The patient is free of Administers care to
signs and PNDS Nursing Care invasive device sites.
Skin remains smooth, Plan: Intraoperative
intact, non-reddened, symptoms of infection.
Administers care to Implements protective Monitors body
wound sites. measures to prevent temperature.
injury due
Identifies physical Evaluates response to
alterations that may to electrical sources. thermoregulation
affect procedure-
specific positioning. Implements protective
measures to prevent
Positions the patient. injury due
Implements protective to laser sources.
measures to prevent
skin or tissue injury due Implements protective
to thermal, chemical, or measures to prevent
mechanical injury due
sources. to radiation sources.
Evaluates for signs and Records devices
symptoms of injury to implanted during
skin and invasive procedure.
tissue. Performs required
counts.
Uses supplies and
equipment within safe Evaluates for signs and
parameters. symptoms of laser,
electrical,
Evaluates for signs and
symptoms of injury as a and radiation injury.
result of Implements
positioning. thermoregulation
measures.
aging and answering transient discomfort oreven
ronmental conditions in the
questions provide a sense permanent injury is clear
OR of professionalismand because many positions are
friendliness that can help awk-ward. Hyperextending
•Risk for injury related to
the patient feel secure. joints, compressing arteries,
anesthesia and surgery When dis-cussing what the or pressing onnerves and
patient can expect in bony prominences usually
•Disturbed sensory surgery, the nurse results in discomfort
perception (global) related usescommon, basic simplybecause the position
communication skills, such must be sustained for a
to general as touch and eye con-tact, long period (Meeker&
anesthesia or sedation to reduce anxiety. Attention Rothrock, 1999). Factors to
Goals for care of the to physical comfort consider include the
patient during surgery (warmblankets, position following:
include reducing anx-iety, changes) helps the patient
NURSING DIAGNOSES •The patient should be in
preventing positioning feel more comfort-able.
injuries, maintaining safety, Telling the patient who else as comfortable a position
Based on the assessment
main-taining the patient’s will be present in the OR,
data, some major nursing as possi-
dignity, and avoiding howlong the procedure is
complications. expected to take, and other ble, whether asleep or
diagnoses may
details helps thepatient
include the following: Nursing Interventions prepare for the experience awake.
REDUCING ANXIETY and gain a sense of •The operative field must
•Anxiety related to
The OR environment can control.
expressed concerns due to be adequately exposed.
seem cold, stark, and PREVENTING
surgery or OR frightening to thepatient, •An awkward position,
who may be feeling INTRAOPERATIVE
environment undue pressure on a body
isolated and apprehensive. POSITIONING INJURY
•Risk for perioperative Intro-ducing yourself, The patient’s position on the part, or
addressing the patient by operating table depends on
positioning injury related to use of stirrups or traction
name warmly the sur-gical procedure to
andfrequently, verifying be performed as well as on should not obstruct the
envi-
details, providing his or her physicalcondition vascular
explanations, and encour- (Fig. 19-3). The potential for
paddedshoulder braces
supply. cal deformity (Curet, 2000).
(see Fig. 19-3B).
•Respiration should not be •The patient needs gentle individualized plan of
patient care. The
impeded by pressure of restraint before induction in
intraoperative nurse
arms on case usesthe focused
preoperative nursing
the chest or by a gown that of excitement. assessment documented
The usual position for on thepatient record. This
constricts the neck or
surgery, called the dorsal includes assessment of
chest. recumbentposition, is flat physiologic status(eg,
on the back. One arm is health–illness level, level of
•Nerves must be protected
positioned at the side ofthe consciousness),
from undue pressure. table, with the hand placed psychosocial sta-tus (eg,
palm down; the other is anxiety level, verbal
Improper carefullypositioned on an
positioning of the arms, communication problems,
armboard to facilitate copingmechanisms),
hands, legs, or feet may intravenous infusion
cause seri-ous injury or physical status (eg,
offluids, blood, or surgical site, skin condition
paralysis. Shoulder braces medications. This position
must be well paddedto andeffectiveness of
is used for most ab- preparation; immobile
prevent irreparable nerve dominal surgeries except
injury, especially when joints), and ethical con-
for surgery of the cerns (Chart 19-3).
theTrendelenburg position gallbladder and pelvis(see
is necessary. Fig. 19-3A).
•Precautions for patient The Trendelenburg
position usually is used for
safety must be observed, surgery on thelower
particularly abdomen and pelvis to
obtain good exposure by
with thin, elderly, or obese displacingthe intestines into
patients, or those with a the upper abdomen. In this
position, the headand body
physi- are lowered. The patient is
held in position by
Вам также может понравиться
- Subjective Cues:: Nursing Care ProcessДокумент8 страницSubjective Cues:: Nursing Care ProcessBianca Marithè RejanoОценок пока нет
- Acute Confusion Nursing DiagnosisДокумент4 страницыAcute Confusion Nursing Diagnosisasmika danaОценок пока нет
- As Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Документ4 страницыAs Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Nicole GumolonОценок пока нет
- RRLДокумент3 страницыRRLKevin M. VillacorteОценок пока нет
- GoutДокумент12 страницGoutEarle Jimenez Niervo RN100% (1)
- NCP For Ulnar SurgeryДокумент5 страницNCP For Ulnar SurgeryjiloОценок пока нет
- SLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Документ20 страницSLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Mayzelle RizОценок пока нет
- NCP Readiness RevisionДокумент3 страницыNCP Readiness RevisionimnasОценок пока нет
- Risk For InfectionДокумент5 страницRisk For InfectionRochelle Corneta JoreОценок пока нет
- NCP Sensory PerceptionДокумент2 страницыNCP Sensory PerceptionGina TangneneiОценок пока нет
- ER equipments & drugsДокумент3 страницыER equipments & drugsApple LlanesОценок пока нет
- Discharge Planning BurnsДокумент12 страницDischarge Planning BurnsChaa Maii100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: Tetanus DateДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: Tetanus DateSheryl Ann Barit PedinesОценок пока нет
- Fluid VolumeДокумент2 страницыFluid Volumecoldfire28Оценок пока нет
- Abc BSN 4y1-1 Week 9 Course TaskДокумент1 страницаAbc BSN 4y1-1 Week 9 Course TaskHannah BalunanОценок пока нет
- Health Teaching Plan AMLДокумент2 страницыHealth Teaching Plan AMLInah Floresta BesasОценок пока нет
- Group 9 Sickle Cell Anemia Case Study ActivityДокумент4 страницыGroup 9 Sickle Cell Anemia Case Study ActivityJuliaОценок пока нет
- Post-op Nursing Care Plan for Skin IntegrityДокумент2 страницыPost-op Nursing Care Plan for Skin IntegritySharewin PulidoОценок пока нет
- Degenerative Diseases NCMB316 SEC1 AMENINДокумент4 страницыDegenerative Diseases NCMB316 SEC1 AMENINHermin TorresОценок пока нет
- Risk For InfectionДокумент1 страницаRisk For InfectionEuanne OrellanoОценок пока нет
- CASE-STUDY-DM AmputationДокумент32 страницыCASE-STUDY-DM AmputationJerushamae Castillo0% (1)
- Head NurseДокумент11 страницHead Nursejannet20Оценок пока нет
- FractureДокумент4 страницыFractureRaveen mayiОценок пока нет
- NCP PainДокумент2 страницыNCP PainApril_Ivy_Raga_3835Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy MalaiseДокумент1 страницаNursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy Malaise06eltianОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Objective: Admission DiagnosisДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan: Objective: Admission DiagnosisJe ZalОценок пока нет
- 'Urdaneta City University College of Health Sciences: Bachelor of Science in NursingДокумент4 страницы'Urdaneta City University College of Health Sciences: Bachelor of Science in NursingDan Dan ManaoisОценок пока нет
- Aaa Gastrectomy NCP FinalДокумент13 страницAaa Gastrectomy NCP Finallexzaf100% (1)
- NCPДокумент3 страницыNCPJezza RequilmeОценок пока нет
- NCP Ineffective Cardiopulmonary PerfusionДокумент3 страницыNCP Ineffective Cardiopulmonary PerfusionjamiemapanaoОценок пока нет
- College of Nursing Case Study on Gestational DiabetesДокумент32 страницыCollege of Nursing Case Study on Gestational DiabetesRich-Anne LagarasОценок пока нет
- Republic ActДокумент36 страницRepublic ActjanОценок пока нет
- Focus Charting (F-DAR) : How To Do Focus Charting or F-DAR: Notes Fundamentals of NursingДокумент6 страницFocus Charting (F-DAR) : How To Do Focus Charting or F-DAR: Notes Fundamentals of NursingMichael Angelo SeñaОценок пока нет
- Velez College of Nursing F. Ramos Street, Cebu CityДокумент57 страницVelez College of Nursing F. Ramos Street, Cebu Cityinah krizia lagueОценок пока нет
- Case Study StemiДокумент2 страницыCase Study StemiRajeswari SinnasamyОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент2 страницыNCPNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- PCC Learning DiaryДокумент2 страницыPCC Learning DiaryKenny GustavoОценок пока нет
- Nursing Theorists and their Major ContributionsДокумент22 страницыNursing Theorists and their Major ContributionsG a i l R i c h w e l lОценок пока нет
- Assessing The IntegumentaryДокумент73 страницыAssessing The IntegumentaryHelena Meurial HilkiahОценок пока нет
- Emj Cases : Questions For Case 1Документ8 страницEmj Cases : Questions For Case 1Azmyza Azmy100% (1)
- True CertificateДокумент7 страницTrue CertificateDick Morgan FerrerОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент9 страницNCPLeolene Grace BautistaОценок пока нет
- Nursing care plan for cardiomyopathyДокумент7 страницNursing care plan for cardiomyopathyKym RonquilloОценок пока нет
- Jenny Anne Pimentel - ReflectionДокумент1 страницаJenny Anne Pimentel - ReflectionRona Bersamina AsuncionОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: During 8 Hours Nursing Management: (5) After 8 HoursДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan: Subjective: During 8 Hours Nursing Management: (5) After 8 HoursRawan KhateebОценок пока нет
- Final Major Case StudyДокумент17 страницFinal Major Case Studyapi-546876878Оценок пока нет
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Документ4 страницыNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezОценок пока нет
- NCP TetanusДокумент2 страницыNCP TetanusSugar Capule - Manuel0% (1)
- Ppe4 Reflection AssignmentДокумент11 страницPpe4 Reflection Assignmentapi-318846856100% (1)
- Leg 1 A NCM 107-LMRДокумент4 страницыLeg 1 A NCM 107-LMRAleli DoОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related ToДокумент7 страницIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related TohannahОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент13 страницNursing Care Planyumiko0% (1)
- CORD PROLAPSE GUIDEДокумент2 страницыCORD PROLAPSE GUIDEUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- The Battle Against Covid-19 Filipino American Healthcare Workers on the Frontlines of the Pandemic ResponseОт EverandThe Battle Against Covid-19 Filipino American Healthcare Workers on the Frontlines of the Pandemic ResponseОценок пока нет
- Health Teaching and NCPДокумент6 страницHealth Teaching and NCPKylle AlimosaОценок пока нет
- NCP IntraДокумент1 страницаNCP IntraCharlene Valerie Alviola0% (1)
- The Surgical Team: Intraoperative NursingДокумент4 страницыThe Surgical Team: Intraoperative NursingGiselle Chloe Baluya icoОценок пока нет
- 03 Perioperative NursingДокумент2 страницы03 Perioperative Nursingbunso padillaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Interventions for Infection PreventionДокумент5 страницNursing Interventions for Infection PreventionJezebhel ArestaОценок пока нет
- Perioperative Nursing PhaseДокумент80 страницPerioperative Nursing PhaseMary Ann Sambo OgoyОценок пока нет
- ROCKET STOVE DESIGN GUIDEДокумент9 страницROCKET STOVE DESIGN GUIDEfrola5100% (2)
- Online Statement of Marks For: B.A. (CBCS) PART 1 SEM 1 (Semester - 1) Examination: Oct-2020Документ1 страницаOnline Statement of Marks For: B.A. (CBCS) PART 1 SEM 1 (Semester - 1) Examination: Oct-2020Omkar ShewaleОценок пока нет
- Statement of The Problem: Notre Dame of Marbel University Integrated Basic EducationДокумент6 страницStatement of The Problem: Notre Dame of Marbel University Integrated Basic Educationgab rielleОценок пока нет
- Bianchi Size Chart for Mountain BikesДокумент1 страницаBianchi Size Chart for Mountain BikesSyafiq IshakОценок пока нет
- Business Simulation Training Opportunity - V1.0Документ15 страницBusiness Simulation Training Opportunity - V1.0Waqar Shadani100% (1)
- Overlord Volume 1 - The Undead King Black EditionДокумент291 страницаOverlord Volume 1 - The Undead King Black EditionSaadAmir100% (11)
- 2020 Book WorkshopOnFrontiersInHighEnerg PDFДокумент456 страниц2020 Book WorkshopOnFrontiersInHighEnerg PDFSouravDeyОценок пока нет
- La TraviataДокумент12 страницLa TraviataEljona YzellariОценок пока нет
- The Awesome Life Force 1984Документ8 страницThe Awesome Life Force 1984Roman PetersonОценок пока нет
- Ellen Gonzalvo - COMMENTS ON REVISIONДокумент3 страницыEllen Gonzalvo - COMMENTS ON REVISIONJhing GonzalvoОценок пока нет
- R19 MPMC Lab Manual SVEC-Revanth-III-IIДокумент135 страницR19 MPMC Lab Manual SVEC-Revanth-III-IIDarshan BysaniОценок пока нет
- Sigma Chi Foundation - 2016 Annual ReportДокумент35 страницSigma Chi Foundation - 2016 Annual ReportWes HoltsclawОценок пока нет
- Popular Painters & Other Visionaries. Museo Del BarrioДокумент18 страницPopular Painters & Other Visionaries. Museo Del BarrioRenato MenezesОценок пока нет
- TAX & DUE PROCESSДокумент2 страницыTAX & DUE PROCESSMayra MerczОценок пока нет
- 2013 Gerber CatalogДокумент84 страницы2013 Gerber CatalogMario LopezОценок пока нет
- FSW School of Education Lesson Plan Template: E1aa06cb3dd19a3efbc0/x73134?path JavascriptДокумент7 страницFSW School of Education Lesson Plan Template: E1aa06cb3dd19a3efbc0/x73134?path Javascriptapi-594410643Оценок пока нет
- BI - Cover Letter Template For EC Submission - Sent 09 Sept 2014Документ1 страницаBI - Cover Letter Template For EC Submission - Sent 09 Sept 2014scribdОценок пока нет
- Obtaining Workplace InformationДокумент4 страницыObtaining Workplace InformationJessica CarismaОценок пока нет
- MiQ Programmatic Media Intern RoleДокумент4 страницыMiQ Programmatic Media Intern Role124 SHAIL SINGHОценок пока нет
- Communicative Competence: Noam ChomskyДокумент2 страницыCommunicative Competence: Noam ChomskyKiara Denise SuarezОценок пока нет
- Full Discography List at Wrathem (Dot) ComДокумент38 страницFull Discography List at Wrathem (Dot) ComwrathemОценок пока нет
- DLL - Science 6 - Q3 - W3Документ6 страницDLL - Science 6 - Q3 - W3AnatasukiОценок пока нет
- BCIC General Holiday List 2011Документ4 страницыBCIC General Holiday List 2011Srikanth DLОценок пока нет
- 14 Jet Mykles - Heaven Sent 5 - GenesisДокумент124 страницы14 Jet Mykles - Heaven Sent 5 - Genesiskeikey2050% (2)
- PIA Project Final PDFДокумент45 страницPIA Project Final PDFFahim UddinОценок пока нет
- GASB 34 Governmental Funds vs Government-Wide StatementsДокумент22 страницыGASB 34 Governmental Funds vs Government-Wide StatementsLisa Cooley100% (1)
- AFRICAN SYSTEMS OF KINSHIP AND MARRIAGEДокумент34 страницыAFRICAN SYSTEMS OF KINSHIP AND MARRIAGEjudassantos100% (2)
- RA 4196 University Charter of PLMДокумент4 страницыRA 4196 University Charter of PLMJoan PabloОценок пока нет
- Digi-Notes-Maths - Number-System-14-04-2017 PDFДокумент9 страницDigi-Notes-Maths - Number-System-14-04-2017 PDFMayank kumarОценок пока нет
- Marrickville DCP 2011 - 2.3 Site and Context AnalysisДокумент9 страницMarrickville DCP 2011 - 2.3 Site and Context AnalysiskiranjiОценок пока нет