Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Computing GNP
Загружено:
karton11Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Computing GNP
Загружено:
karton11Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING National income accounting refers to a set of rules and techniques that are used to measure
the national income of a country. Singapore follows the concepts and methodology recommended in the United Nations publication A system of National Accounts, 1968 for the compilation of national figures. This is to ensure that Singapore national statistics will be consistent and compared with other countries. National Income National income is a measure of the value of goods and goods produced by the residents of an economy in a given period of time, usually a quarter or a year. National income can be real or nominal. Nominal national income refers to the current year production of goods and services valued at current year prices. Real national income refers to the current year production of goods and service valued at base year prices. In estimating national income, only productive activities are included in the computation of national income. In addition, only the values of goods and services produced in the current year are included in the computation of national income. Hence, gain from resale are excluded but the services provided by the agents are counted. Similarly, transfer payments are excluded as there is income received but no good or service produced in return. However, not all goods and services from productive activities enter into market transactions. Hence, imputations are made for these non-marketed but productive activities eg imputed rental for owner-occupied housing. Thus, national income refers to the market value or imputed value of additional goods and services produced and services performed in the current period. GDP, GNP, NDP and NNP National income in many countries are either in Gross Domestic Product (GDP) or Gross National Product (GNP). Gross Domestic product (GDP) refers to the total value of goods and services produced within the geographical boundary of a country before the deduction of capital consumption. Net Domestic product (NPD) refers to the total value of goods and services produced within the geographical boundary of a country after the deduction of capital consumption. Gross National Product (GNP) refers to the total value of goods and services produced by productive factors owned by residents of the country both inside and outside of the country before the deduction of capital consumption. Net National Product (NNP) ) refers to the total value of goods and services produced by productive factors owned by residents of the country both inside and outside of the country after the deduction of capital consumption.
Relationship between GDP and GNP GNP = GDP + NPIFA (Net Property Income from Abroad) Net Property Income from abroad refers to the difference between income from abroad and income to abroad. Market Price and Factor Cost Market price refers to the actual transacted price and it includes custom duty, excise duty and other indirect taxes but it excludes government grants and subsidies. Factor cost refers to the actual cost of the various factors of production and it includes government grants and subsidies but it excludes indirect taxes. Relationship between market price and factor cost GNP at factor cost = GNP at market price indirect taxes + subsidies GDP at factor cost = GDP at market price indirect taxes + subsidies Transfer Payments Transfer payment refers to government to individuals for which there no economic activity is produced in return by these individuals. Examples of transfer are scholarship, pension. Personal Income and Disposable Income Personal Income refers to the income available to individuals. Disposable income refers to the income that the individuals can actually spend or save. National Income (NNP at factor cost) Less Retained earnings, company taxes Add transfer Payments Personal Income Less CPF, CDAC Disposable Income Measurement of National Income There are 3 approaches to measure national income ie output approach, income approach and expenditure approach.
Theoretically, the national income calculated from the 3 approaches are the same ie Expenditure Approach Expenditure on goods and services $100m Spent = = Output Approach Value of goods and services produced $100m worth of goods and services produced = Income Approach Income Earned by factor owners = Income of $100m
Hence, GDE = GDP + GDI, GNE = GNP = GNI, NDE = NDP = NDI, NNE = NNP +NNI.. But in practice, these measures are usually not equal to one another. Output Approach Output approach measures national income by adding the total value of the final goods and services produced in the year or by adding the value added by each sector of the economy. Value added Value added refers to the difference between the value of gross output of all goods and services produced in a given period and the value of intermediate inputs used in the production process during the same period. In distributive trade, value added is the difference between the gross margin and the cost of intermediate inputs. In the banking sector, value added is the difference between the sum of actual and imputed bank service charges and intermediate inputs. For government services and non-profit institutions, value added is the wages and salaries, and depreciation allowance set aside for consumption of fixed capital. An example on the computation of value added Production Stage Intermediate Goods Wheat Flour Wholesale Bread $0.20 $0.45 $0.95 $0.00 $0.20 $0.45 = $0.20 = $0.25 = $0.50 Value of Sale Costs of Output from previous production stage Value Added
Final Good Retail Bread $1.25 $0.95 = $0.30
Sum of value added at each production stage
= $1.25
Note : Value of final good and sum of value added at each production stage is the same ie $1.25. Double counting or multiple counting of the value of wheat at each production stage is avoided when the value added or final value is used in the computation as the value of wheat is counted only once in the value added method or the final value method. Computation National Output by output approach ie sum of value added by each sector in the economy) Agriculture and Fishing Quarrying Manufacturing Utilities Construction Commerce Transport and Communication Financial and Business Services Other Services eg Government Departments and Statutory Boards Statistical Discrepancies GDP at factor cost Add NPIFA GNP at factor cost Less Capital Consumption NNP at factor cost (National Income) Income Approach Income approach measures national income by adding the income earned by the factor owners that are residents of the country, undistributed company profits and government income from economic participation. It excludes transfer payments and stock appreciation because transfer payments and stock appreciation are not due to goods and services performed. Computation of National Income by Income Approach Income from Employment Income from Self-employment Gross trading profits of companies Gross trading surplus of public corporations Gross trading surplus of general government enterprises Rent, Interest and Dividend
Imputed rent for owner-occupied houses Total Domestic Income Less Stock Appreciation GDP at factor cost Statistical Discrepancies Add NPIFA GNP at factor cost Less Capital Consumption NNP at factor cost (National Income) Expenditure Approach Expenditure Approach measures national income by adding the private consumption expenditure, government consumption expenditure, gross fixed capital formation ie investment expenditure, increase in physical stocks and net exports of goods and servces ie the difference between exports and imports. It only includes expenditure on goods and services to satisfy the needs of final buyers. It excludes expenditure on intermediate of goods and services. Moreover, resale of consumer and capital goods are excluded because the expenditures are on these resale goods, not goods produced in the current period and hence expenditures on resale goods are not counted. Private Consumption Expenditure Private consumption expenditure refers to the final purchases of goods and services by households. It includes expenditure on single use consumption or non-durable goods eg food, durable goods eg TV, washing machines, and services eg hairdressing services and medical services. Household purchases of new houses are treated as investment expenditure and hence residential investments are not included in private consumption expenditure. Instead residential investments are included in investment expenditure. Resale of consumer durables eg second hand TV are excluded as the expenditures are on second hand TV, not TV produced in the current year and hence expenditures on second hand TV are not included in the private consumption expenditure. Government Consumption Expenditure / General Government Expenditure Government consumption expenditure refers to the cost of running the various government departments an public non-profit organizations to provide goods and services for the public. It excludes the expenditure by government on grants, interest subsidies, transfer payments, loans and repayments.
Gross Domestic Fixed Capital Formation / Investment Expenditure Investment expenditure refers to the expenditure on equipments and machinery, residential and non-residential construction, and changes in inventories. An increase in inventories is treated as an investment and a fall in inventories is treated as disinvestment. Resales of capital goods are excluded from investment expenditure. Gross Investment = Net Investment + Replacement Investment Gross investment refers to the new capital goods produced that can be used to the capital stock or to replace the existing worn-out capital goods. Net Investment refers to the new capital goods that are added to the capital stock. Replacement investment refers to the new capital goods that are used to replace the existing worn-out capital goods. Net Exports of Goods and Services Net exports of goods and services refers to the difference between the exports of goods and services and imports of goods and services. Exports of goods and services refers to goods and services that are produced in the country but they are sold to foreigners for their consumption. Imports of goods and services refer to goods and services that are produced by other countries but they are consumed within the country. Computation of National Income by Expenditure Approach Private Consumption Expenditure Government Consumption Expenditure Gross Domestic Fixed Capital Formation / Investment Expenditure Value of Increase in Inventories and Work-in-Progress Total Domestic Expenditure Add Exports of Goods and Services Total Final Expenditure Less Imports of Goods and Services Statistical Discrepancies GDP at market price Less Indirect Taxes Add Subsidies GDP at factor cost Add NPIFA GNP at factor cost Less Capital Consumption NNP at factor cost (National Income)
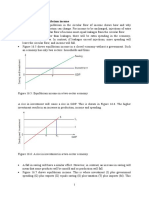
GDP Deflator GDP deflator refers to a price index that shows the average increase in prices of all goods and services produced in the current year as compared to that of a base year. The GDP deflator is used to convert the current year nominal GDP into current year real GDP. Economic growth of a country is calculated by the changes in the real GDP of 2 different years or quarters. Current Year GDP At base year prices = (ie current year real GDP) Current Year GDP at current year prices ie current year nominal GDP --------------------------------------------------------------- X 100 Current Year GDP Deflator
Next Page Back to Main Page
Вам также может понравиться
- Assignment 1 Solution Eco 403Документ2 страницыAssignment 1 Solution Eco 403Mubeen RazaОценок пока нет
- Circular Flow of IncomeДокумент66 страницCircular Flow of IncomeAshish Tewani100% (3)
- Macroeconomics Guide to GDP, GNP & Economic MeasuresДокумент40 страницMacroeconomics Guide to GDP, GNP & Economic MeasuresLakshmi Harshitha YechuriОценок пока нет
- National IncomeДокумент24 страницыNational IncomePranay Sai Garepally100% (1)
- National Income ConceptsДокумент15 страницNational Income Conceptsrinky_trivediОценок пока нет
- EC 124 Chap2 Part - II PDFДокумент8 страницEC 124 Chap2 Part - II PDFAnonymous wFIBMUmt100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Basic Concepts National Income and Input: Gross Domestic ProductДокумент21 страницаChapter 1: Basic Concepts National Income and Input: Gross Domestic ProductZeus TanjiaОценок пока нет
- Chapter Two - Basic Concepts of Macroeconomics: 2.1.1. Gross Domestic Product and Net Domestic ProductДокумент38 страницChapter Two - Basic Concepts of Macroeconomics: 2.1.1. Gross Domestic Product and Net Domestic ProductHani Yab SisОценок пока нет
- National IncomeДокумент21 страницаNational IncomeMurali Krishna Pavan PappuОценок пока нет
- Macro Eco 3Документ113 страницMacro Eco 3br bhandariОценок пока нет
- Module IДокумент61 страницаModule IDHWANI DEDHIAОценок пока нет
- UNIT - IV, National Income Accounting: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) All Output Produced Within A NationДокумент15 страницUNIT - IV, National Income Accounting: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) All Output Produced Within A NationanushreeОценок пока нет
- National IncomeДокумент26 страницNational IncomerajapatnaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 National Income Complete PDF-2Документ67 страницChapter 3 National Income Complete PDF-2shivam kumarОценок пока нет
- Analyzing National Income and GDP ComponentsДокумент28 страницAnalyzing National Income and GDP ComponentsJING LIОценок пока нет
- National Income (Notes) IMBAДокумент27 страницNational Income (Notes) IMBASubham .MОценок пока нет
- National IncomeДокумент30 страницNational IncomeTaruna Dureja BangaОценок пока нет
- National IncomeДокумент5 страницNational IncomeBalaji GajendranОценок пока нет
- Unit 5Документ22 страницыUnit 5Shivam ChandraОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomics, GDP, Well-Being ExplainedДокумент57 страницMacroeconomics, GDP, Well-Being ExplainedSofia KОценок пока нет
- National IncomeДокумент47 страницNational IncomeJannat MalhotraОценок пока нет
- National Income2Документ44 страницыNational Income2Faith100% (1)
- Unit 3Документ43 страницыUnit 3ravi pratapОценок пока нет
- TOPIC 3 - National IncomeДокумент11 страницTOPIC 3 - National IncomeCharlesОценок пока нет
- National Income Part-1Документ10 страницNational Income Part-1Ibrahim MondolОценок пока нет
- Chapter VI Macroeconomics PartДокумент44 страницыChapter VI Macroeconomics PartBereket MuniyeОценок пока нет
- Lecture 11 National IncomeДокумент38 страницLecture 11 National IncomeDevyansh GuptaОценок пока нет
- Difference Between GDP and GNP Explained With ExampleДокумент18 страницDifference Between GDP and GNP Explained With ExampleSouvikОценок пока нет
- Eco Part - 1Документ8 страницEco Part - 1Rajesh Mahesh BohraОценок пока нет
- Managerial Economics National Income PDFДокумент9 страницManagerial Economics National Income PDFSanjeev KumarОценок пока нет
- Measuring Economic Activity: Measuring Economic ActivityДокумент42 страницыMeasuring Economic Activity: Measuring Economic ActivityWAC_BADSECTORОценок пока нет
- GDP, GNI, Income Measures ExplainedДокумент4 страницыGDP, GNI, Income Measures ExplainedRose Ann BalbonaОценок пока нет
- Shwe Htun AssignmentДокумент8 страницShwe Htun AssignmentDrEi Shwesin HtunОценок пока нет
- What is GNP and how does it differ from GDPДокумент3 страницыWhat is GNP and how does it differ from GDPTerry SaguiguitОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomic Data (CH 20) PDFДокумент11 страницMacroeconomic Data (CH 20) PDFAlicia CataláОценок пока нет
- Concepts and Measurement of National IncomeДокумент66 страницConcepts and Measurement of National IncomesubramanianОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomics Goals, Instruments and National IncomeДокумент5 страницMacroeconomics Goals, Instruments and National IncomeIlma Sadan Guji'iiОценок пока нет
- II Module EconomicsДокумент14 страницII Module EconomicsTariq HussainОценок пока нет
- Measurement of Economic PerformanceДокумент14 страницMeasurement of Economic PerformanceGodfrey RushabureОценок пока нет
- Measuring National Income Through GDP, GNP & NNPДокумент5 страницMeasuring National Income Through GDP, GNP & NNPAkshit Kumar100% (1)
- National in Come in IndiaДокумент41 страницаNational in Come in IndiaSunil SunitaОценок пока нет
- Measuring National Output and National Income-Chapter 2Документ48 страницMeasuring National Output and National Income-Chapter 2madanОценок пока нет
- National Income StatisticsДокумент5 страницNational Income StatisticsShingirayi MazingaizoОценок пока нет
- Measuring the National Income AccountДокумент19 страницMeasuring the National Income AccountAmie Lyyn CabrerosОценок пока нет
- c78846b0 1655107671708Документ20 страницc78846b0 1655107671708galaxy dancers 254Оценок пока нет
- National IncomeДокумент20 страницNational IncomeoggyОценок пока нет
- GDP Explained: Measuring a Nation's Economic OutputДокумент52 страницыGDP Explained: Measuring a Nation's Economic OutputShahzod OltiboyevОценок пока нет
- The Total Net Value of All Goods and Services Produced Within A Nation Over A Specified Period of TimeДокумент5 страницThe Total Net Value of All Goods and Services Produced Within A Nation Over A Specified Period of Timekavitachordiya86Оценок пока нет
- MacroeconomicsДокумент35 страницMacroeconomicsrudraarjunОценок пока нет
- MEASURING NATIONAL INCOME CONCEPTS GDP GNP NNPДокумент5 страницMEASURING NATIONAL INCOME CONCEPTS GDP GNP NNPChenkual ThazualaОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomic Data (CH 20)Документ11 страницMacroeconomic Data (CH 20)Alicia CataláОценок пока нет
- National Income MeaurementДокумент9 страницNational Income MeaurementBKMEIN100% (1)
- Chapter Six FundamentalДокумент22 страницыChapter Six FundamentalBikila DessalegnОценок пока нет
- Measuring a Nation's EconomyДокумент62 страницыMeasuring a Nation's EconomyNanaram NhojОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3Документ10 страницLecture 3Hitisha agrawalОценок пока нет
- National income and aggregate demand concepts explainedДокумент22 страницыNational income and aggregate demand concepts explainedHarsh Kumar SainiОценок пока нет
- MODULE 9 MicroДокумент7 страницMODULE 9 MicroGladz De ChavezОценок пока нет
- Gross Domestic ProductДокумент5 страницGross Domestic ProductabdallahmachiliОценок пока нет
- Chater Two Leacture NoteДокумент26 страницChater Two Leacture NoteMelaku WalelgneОценок пока нет
- Economics For FinanceДокумент335 страницEconomics For FinanceKhushal SoniОценок пока нет
- Measuring The Cost of LivingДокумент4 страницыMeasuring The Cost of LivingAmna NawazОценок пока нет
- BOP Sandeep GargДокумент13 страницBOP Sandeep GargRiddhima Dua100% (1)
- BSE Companies DataДокумент31 страницаBSE Companies DatavinithaОценок пока нет
- Eco 415 ElacsticityДокумент5 страницEco 415 ElacsticitySITI0% (1)
- 07a) Income Elasticity of DemandДокумент3 страницы07a) Income Elasticity of DemandBenОценок пока нет
- Stock Exchange IndicesДокумент19 страницStock Exchange IndicesBunu MarianaОценок пока нет
- ImfdataДокумент1 034 страницыImfdataDavid Carlo -sadameОценок пока нет
- Retail Math FormulasДокумент6 страницRetail Math FormulasMurat AnlıОценок пока нет
- Elasitcity DialogueДокумент64 страницыElasitcity DialoguetankianhowОценок пока нет
- Consumer Behavior-2Документ30 страницConsumer Behavior-2ShahenaОценок пока нет
- Quiz Study Unit 5 PDFДокумент3 страницыQuiz Study Unit 5 PDFVinny HungweОценок пока нет
- 1887-Article Text-9343-1-10-20221226Документ14 страниц1887-Article Text-9343-1-10-20221226Avriona RahmadillaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2: Measuring National Output and National Income: Macro Economics Numerical Problem Solving ExercisesДокумент11 страницChapter 2: Measuring National Output and National Income: Macro Economics Numerical Problem Solving Exercisesahmed housniОценок пока нет
- Stoxx Index GuideДокумент370 страницStoxx Index GuideThierry de PortzamparcОценок пока нет
- Mini Case: Stock Valuation at Ragan Engines: Disusun OlehДокумент6 страницMini Case: Stock Valuation at Ragan Engines: Disusun OlehricaОценок пока нет
- Understand Elasticity of Demand and SupplyДокумент20 страницUnderstand Elasticity of Demand and SupplyyelzОценок пока нет
- Calculated Returns ExcelДокумент21 страницаCalculated Returns Exceljpkirch92Оценок пока нет
- Stock Index CalculationsДокумент13 страницStock Index CalculationsilyasОценок пока нет
- Measuring InflationДокумент25 страницMeasuring InflationAnonymous E9ESAecw8x0% (2)
- 58-6-1 EconomicsДокумент11 страниц58-6-1 EconomicsrohitОценок пока нет
- Lec 15. National Income Accounting V3 REVISEDДокумент33 страницыLec 15. National Income Accounting V3 REVISEDAbhijeet SinghОценок пока нет
- Option Calculator MainДокумент10 страницOption Calculator MainVarinder AnandОценок пока нет
- GDP Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент17 страницGDP Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsErsin TukenmezОценок пока нет
- Exercise 2.3 Price ElasticityДокумент2 страницыExercise 2.3 Price ElasticityKarmen ThumОценок пока нет
- Data Extract From World Development IndicatorsДокумент16 страницData Extract From World Development IndicatorsJenny HuỳnhОценок пока нет
- CBoe Options Expiration Calendar 2019Документ1 страницаCBoe Options Expiration Calendar 2019Xay Tonus100% (1)
- ABS Key AggregatesДокумент118 страницABS Key Aggregatesyolejosh479Оценок пока нет