Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Heat of Displacement
Загружено:
brian_cheng_15Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Heat of Displacement
Загружено:
brian_cheng_15Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
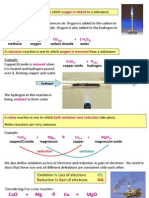
Heat of Displacement The heat of displacement is the heat that is released when 1 mol of metal is displaced from its
salt solution by a more electropositive metal. Example 1 1 mol of copper, Cu, is displaced from a copper(II)sulphate, CuSO4, solution by zinc, Zn to release 210 kJ of heat. Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) Zn(s) Cu2+(aq) ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) H = -210 kJ mol-1 H = -210 kJ mol-1
The heat of displacement of copper by zinc can be defined as follows: The heat of displacement of copper by zinc is the heat that is released when 1 mol of copper metal is displaced by zinc. The displacement reaction of copper by zinc is an exothermic reaction because the temperature of reaction increases. Energy Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq)
H = -210 kJ
Cu(s) + ZnSO4(aq) Example 2 Calculate the changes of temperature when excess zinc, Zn is added to 50 cm 3 of 0.1 mol dm-3 iron(II)sulphate, FeSO4 solution. The thermochemical equation for the displacement if iron, Fe by magnesium, Mg is: Mg(s) + Fe2+(aq) Mg2+(aq) + Fe(s) H = -200 kJ mol-1
[Specific heat capacity, c: 4.2 J g-1 C-1; Density of solution, 1.0 g cm-3] Solution: Number of moles of FeSO4 solution
Chapter 4 Thermochemistry
Вам также может понравиться
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersОценок пока нет
- Oxidation and ReductionДокумент39 страницOxidation and ReductionlisalisoОценок пока нет
- 3.0 ThermochemistryДокумент35 страниц3.0 ThermochemistryRoddick BongОценок пока нет
- Electrolysis HLДокумент34 страницыElectrolysis HLRyan BoukaaОценок пока нет
- Che Ekserimen 3CДокумент3 страницыChe Ekserimen 3CHEYYMANATHAPILLAY A/L VARATHA RAJU MoeОценок пока нет
- Std.8 Module.7 Semester.2Документ56 страницStd.8 Module.7 Semester.2Md ZayedОценок пока нет
- List of Chemical Reactions: A) Combination ReactionДокумент5 страницList of Chemical Reactions: A) Combination Reactionaditya khuntiaОценок пока нет
- Experiment SadurДокумент4 страницыExperiment SadurApik Suhimi100% (1)
- Chem F5 Chapter 3 (2020)Документ39 страницChem F5 Chapter 3 (2020)JΞτΗασ0% (1)
- Esis 2Документ35 страницEsis 2Amir Abd KadirОценок пока нет
- Chap 5Документ11 страницChap 5Tun Lin AungОценок пока нет
- Electrolysis: Electrolysis of Molten SaltsДокумент2 страницыElectrolysis: Electrolysis of Molten SaltsSunnyОценок пока нет
- Thermal Decomposition ReactionsДокумент3 страницыThermal Decomposition ReactionspreethaОценок пока нет
- Extraction 2Документ1 страницаExtraction 2meganekokun kawaiiОценок пока нет
- 4.4 ElectrochemistryДокумент20 страниц4.4 Electrochemistrygabrielsiema4Оценок пока нет
- La Chatelaine Junior College 2021-2022 Science (Chemistry) Grade: X Chapter 1: Chemical Reactions and Equations NOTES (2) - Decomposition ReactionДокумент5 страницLa Chatelaine Junior College 2021-2022 Science (Chemistry) Grade: X Chapter 1: Chemical Reactions and Equations NOTES (2) - Decomposition ReactionSantha KumarОценок пока нет
- OxidationДокумент2 страницыOxidationMariaОценок пока нет
- D-& F Block ElementsДокумент46 страницD-& F Block ElementsdetectionisimpressionОценок пока нет
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-985613Документ7 страницCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-985613abiniveshofficial4708Оценок пока нет
- Metals and Non MetalsДокумент15 страницMetals and Non Metals2erwr100% (2)
- Ch-3 Sc-1 Kitabcd MSBSHSE Class 10 SolutionsДокумент15 страницCh-3 Sc-1 Kitabcd MSBSHSE Class 10 Solutionsankushsune1999Оценок пока нет
- Investigation Into The Copper Content of Penny CoinsДокумент31 страницаInvestigation Into The Copper Content of Penny CoinsOctavianLars50% (6)
- CHM 114 Exp 10Документ6 страницCHM 114 Exp 10João Antonio BassettoОценок пока нет
- Metals and Non Metals - Shobhit NirwanДокумент17 страницMetals and Non Metals - Shobhit NirwanBhaskar 8287Оценок пока нет
- Chemistry NotesДокумент3 страницыChemistry NotesIngrid ChanОценок пока нет
- Chem F5-3.2Документ3 страницыChem F5-3.2Rienellene Joyce FieldadОценок пока нет
- Chemical Arithmetic and Reactions: ObjectivesДокумент24 страницыChemical Arithmetic and Reactions: Objectivesgoputs6386Оценок пока нет
- Getting Copper Fom It So Rev 4Документ8 страницGetting Copper Fom It So Rev 4Giancarlo Zegarra TorresОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Oxidation and ReductionДокумент0 страницIntroduction To Oxidation and ReductionAdnan ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- ElectrochemistryДокумент16 страницElectrochemistryitsshaunboteОценок пока нет
- Adobe Scan Aug 17, 2023Документ5 страницAdobe Scan Aug 17, 2023gulatisrishti15Оценок пока нет
- Chap 9Документ17 страницChap 9Tun Lin AungОценок пока нет
- 01 Ra 81321Документ20 страниц01 Ra 81321Amrit KumarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7-9Документ68 страницChapter 7-9captain20119Оценок пока нет
- Oxidation & Reduction - Redox Reactions - Oxidation: Oxygen Atoms From The Oxygen Molecules in Air E.GДокумент4 страницыOxidation & Reduction - Redox Reactions - Oxidation: Oxygen Atoms From The Oxygen Molecules in Air E.Ghussein hajiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13, 14 - Metals PDFДокумент9 страницChapter 13, 14 - Metals PDFAarush SharmaОценок пока нет
- Assignment Zinc ChemicalДокумент5 страницAssignment Zinc ChemicalNaveed SDОценок пока нет
- Oxidation-Reduction p5Документ11 страницOxidation-Reduction p5maramalhaj404Оценок пока нет
- OxidationreductionДокумент40 страницOxidationreductionMohamad HanifОценок пока нет
- R2 6lA5NCДокумент7 страницR2 6lA5NCIsa ShahidОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Chemistry - Redox, Reactivity Series and AnalysisДокумент20 страницIGCSE Chemistry - Redox, Reactivity Series and AnalysisChemistryKlipz93% (14)
- Types of Reversible CellsДокумент16 страницTypes of Reversible CellsKaran RavalОценок пока нет
- Reactivity Series of Metals: Reactions of Metals Effect of Heat On Metal CarbonatesДокумент24 страницыReactivity Series of Metals: Reactions of Metals Effect of Heat On Metal CarbonatesCarl Agape DavisОценок пока нет
- Experiment 2 Reaction Between Iron and Copper SulphateДокумент4 страницыExperiment 2 Reaction Between Iron and Copper SulphateKartik PillayОценок пока нет
- Thermochemistry TeacherДокумент20 страницThermochemistry TeacherjiaОценок пока нет
- EM - 10th Science Notes 2018-19-1Документ153 страницыEM - 10th Science Notes 2018-19-1Nagesh EinsteinОценок пока нет
- Chemical Reactions and Equations: Chapter - 1Документ8 страницChemical Reactions and Equations: Chapter - 1Samradh Singh 9-H DPSKОценок пока нет
- 10 Science Notes 01 Chemical Reactions and Equations 1Документ8 страниц10 Science Notes 01 Chemical Reactions and Equations 1aarushiranjan0802Оценок пока нет
- ScienceДокумент322 страницыScienceIssmeh FatimaОценок пока нет
- Extraction of IRON FROM ORE - Putligarh (G) - AmritsarДокумент6 страницExtraction of IRON FROM ORE - Putligarh (G) - Amritsarapi-3731257Оценок пока нет
- Skema Jawapan Mid Sem 2019 t5Документ10 страницSkema Jawapan Mid Sem 2019 t5lhmooОценок пока нет
- Ncert Solution Cbse Class 10 Sci Chap 3Документ12 страницNcert Solution Cbse Class 10 Sci Chap 3Asdak kalimОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry: All High School Revision Materials Are Available OnДокумент50 страницElectrochemistry: All High School Revision Materials Are Available OnAhmad AlShahrourОценок пока нет
- Metals and Non Metals - NotesДокумент13 страницMetals and Non Metals - NotesmittalshivamОценок пока нет
- NCERT Solutions For CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non MetalsДокумент10 страницNCERT Solutions For CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non MetalsHari PrasadОценок пока нет
- Oxidation ReductionДокумент7 страницOxidation ReductionZul Abror Bin Ya'akopОценок пока нет
- CopperДокумент16 страницCopperPrerit PandeyОценок пока нет
- Electrochemsitry NotesДокумент9 страницElectrochemsitry NotesAhmad Shafiq ZiaОценок пока нет
- Acid and MetalДокумент2 страницыAcid and MetalMariaОценок пока нет