Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Final Economics
Загружено:
Faizan FiziИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Final Economics
Загружено:
Faizan FiziАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Q#1. What is production function? Define in terms of short run & long run.
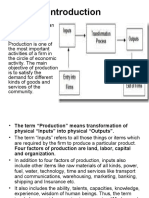
Production Function: The production function relates the output of a firm to the amount of inputs, typically capital and labor. It is important to keep in mind that the production function describes technology, not economic behavior. A firm may maximize its profits given its production function, but generally takes the production function as a given element of that problem. (In specialized long-run models, the firm may choose its capital investments to choose among production technologies). The Econ Model application The Demand for Labor emphasize the role of the production function and marginal product in determining the profit-maximizing demand for labor. Short Run Production: A short-run production represents a specific period in time in which input and output levels are defined in specific ways. The goal of a short-run production is to create an upwardsloping supply curve. When defining a short-run production, you should consider the entirety of the production and identify the main components of this type of production. The short run is a period of time in which only one input (say labor) is allowed to vary while other inputs land and capital are held fixed. In the short run, therefore, production can be increased with one variable factor and other factors remaining constant. In the short run, the law of variable proportion governs the production behavior of a firm. The law of variable proportion shows the direction and rate of change in the output of firm when the amount of only one factor of production is varied while other factors of production are held constant.
Long Run Production: The long run is the lengthy period of time during with all inputs can be varied. There is no fixed output in the long run. All factors of production are variable inputs. We now analyze production function by allowing two factors say labor and capital to very while all others are held constant. With both factors are variable, a firm can produce a given level of output by using more labor and less capital or a greater amount of capital and less labor or moderate amounts of both. A firm continues to substitute one input for another while continuing to produce the same level of output.
Вам также может понравиться
- Activity 6 - Theory of Production and CostДокумент5 страницActivity 6 - Theory of Production and CostJelo DavidОценок пока нет
- Unit - 2Документ20 страницUnit - 2naveennanni988Оценок пока нет
- The Production FunctionДокумент9 страницThe Production FunctionPankaj TirkeyОценок пока нет
- Aec 001-Bacc 001 (Econ) - Week 10 ModuleДокумент4 страницыAec 001-Bacc 001 (Econ) - Week 10 ModuleNicole ValentinoОценок пока нет
- Unit 05 - Production AnalysisДокумент40 страницUnit 05 - Production AnalysisPulakith NagarwalОценок пока нет
- Material No. 8 - Production AnalysisДокумент9 страницMaterial No. 8 - Production AnalysisrhbqztqbzyОценок пока нет
- Production and Cost FunctionДокумент85 страницProduction and Cost FunctionrosaliebalhagcpaОценок пока нет
- Unit 3Документ25 страницUnit 3Tejas ArgulewarОценок пока нет
- Econ ScriptДокумент4 страницыEcon ScriptnanaОценок пока нет
- Production Function: Law of Variable Proportions and Returns To ScaleДокумент23 страницыProduction Function: Law of Variable Proportions and Returns To Scalehiteshgarg2004Оценок пока нет
- Long Run Production FunctionДокумент19 страницLong Run Production FunctionTony KumarОценок пока нет
- PBD - M3Документ20 страницPBD - M3m2fta2311Оценок пока нет
- Unit 7Документ22 страницыUnit 7Sandhya ChimmiliОценок пока нет
- Production FunctionДокумент49 страницProduction FunctionAnuj SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Definition of Short Run Production FunctionДокумент5 страницDefinition of Short Run Production FunctionBrijesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Production - CBSE Notes For Class 12 Micro EconomicsДокумент6 страницProduction - CBSE Notes For Class 12 Micro EconomicsmadhavanramuduОценок пока нет
- Production and Business Organization PDFДокумент12 страницProduction and Business Organization PDFUmerSaeedОценок пока нет
- Production and Cost Notes 1Документ3 страницыProduction and Cost Notes 1tamalbanikcuОценок пока нет
- Ebenstein Ebesntein CHAPTER 6Документ3 страницыEbenstein Ebesntein CHAPTER 6David Bryan Tan OngОценок пока нет
- CH 7 EcoДокумент4 страницыCH 7 Ecosanchita kapoorОценок пока нет
- Topic-2-Production AnalysisДокумент34 страницыTopic-2-Production Analysisreuben kawonga100% (1)
- Managerial Economics: Activity # 7Документ9 страницManagerial Economics: Activity # 7Vienna MamarilОценок пока нет
- Economics Project Production FunctionДокумент13 страницEconomics Project Production FunctionApurva Gupta100% (2)
- 6 Production and Business OrganizationДокумент4 страницы6 Production and Business OrganizationHalimaОценок пока нет
- Topic 5 - Production TheoryДокумент29 страницTopic 5 - Production TheoryPatricia Ann TamposОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 - Production TheoryДокумент10 страницChapter 4 - Production TheorypkashyОценок пока нет
- Production: Questions For ReviewДокумент10 страницProduction: Questions For ReviewTonoy Peter CorrayaОценок пока нет
- Unit 3: Managerial EconomicsДокумент29 страницUnit 3: Managerial Economicsarjun singh100% (1)
- Production FunctionДокумент46 страницProduction FunctionabdanОценок пока нет
- Production Function: Module - 7Документ13 страницProduction Function: Module - 7Kathiresan Mathavi's SonОценок пока нет
- Micro Economics UNIT 2 BBAДокумент6 страницMicro Economics UNIT 2 BBAkunjapОценок пока нет
- Managerial Economic Note For 3 4 5 ChaptersДокумент20 страницManagerial Economic Note For 3 4 5 ChapterseconoОценок пока нет
- 06Документ7 страниц06Bipin Bansal AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Ch06 PRДокумент11 страницCh06 PRGreigh TenОценок пока нет
- Short Run Production FunctionДокумент6 страницShort Run Production FunctionHema Harshitha100% (2)
- BA IT Lecture Theory of ProductionДокумент62 страницыBA IT Lecture Theory of ProductionMirajii OlomiiОценок пока нет
- Production TheoryДокумент7 страницProduction TheoryMila Casandra CastañedaОценок пока нет
- Ch06 PRДокумент10 страницCh06 PRAlexandra SolanoОценок пока нет
- Law of Returns: Production FunctionДокумент5 страницLaw of Returns: Production FunctionriyaОценок пока нет
- Production Analysis: E5 Managerial EconomicsДокумент27 страницProduction Analysis: E5 Managerial EconomicsTharshiОценок пока нет
- Production Analysis - 2nd UnitДокумент18 страницProduction Analysis - 2nd UnitDr VIRUPAKSHA GOUD GОценок пока нет
- Production FunctionДокумент10 страницProduction FunctionAman MeherОценок пока нет
- Managerial Economics Reading Material UNIT 3Документ7 страницManagerial Economics Reading Material UNIT 3kunal kashyapОценок пока нет
- Managerial Economics Unit 2Документ25 страницManagerial Economics Unit 2Raunak KumarОценок пока нет
- Production Function & Cost FunctionДокумент85 страницProduction Function & Cost Functionayushshrimal000_2201Оценок пока нет
- Production AnalysisДокумент23 страницыProduction AnalysisMj RodriguesОценок пока нет
- Organization of ProductionДокумент4 страницыOrganization of ProductionClauie BarsОценок пока нет
- Production FunctionДокумент33 страницыProduction FunctionRence MarcoОценок пока нет
- Microeconomics Chapter 06Документ5 страницMicroeconomics Chapter 06Hasimuddin TafadarОценок пока нет
- Industrial EconomicsДокумент26 страницIndustrial Economicsnishanthreddy89Оценок пока нет
- Managerial EconomicsДокумент15 страницManagerial EconomicsSurya PanwarОценок пока нет
- Economics NotesДокумент2 страницыEconomics NotesMohammed Layik75% (4)
- Production To SendДокумент9 страницProduction To SendThomas Thankachan PakalomuttamОценок пока нет
- Industrial EconomicsДокумент26 страницIndustrial Economicskissaraj0% (1)
- Chap 06Документ12 страницChap 06Syed Hamdan50% (2)
- Module 3 QBДокумент11 страницModule 3 QBKevin V bijuОценок пока нет
- Activity 4 QuestionsДокумент5 страницActivity 4 QuestionsReginald ValenciaОценок пока нет
- Assignment On Production AnalysisДокумент2 страницыAssignment On Production AnalysisShaira Mae Delos ReyesОценок пока нет
- Unit 7 Production Function: ObjectivesДокумент22 страницыUnit 7 Production Function: ObjectivesHelen AkowОценок пока нет
- University of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingОт EverandUniversity of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (98)
- A History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationОт EverandA History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (11)
- Financial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassОт EverandFinancial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassОценок пока нет
- The Meth Lunches: Food and Longing in an American CityОт EverandThe Meth Lunches: Food and Longing in an American CityРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Principles for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailОт EverandPrinciples for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (238)
- Narrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsОт EverandNarrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (94)
- The War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesОт EverandThe War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (8)
- Look Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereОт EverandLook Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- The Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaОт EverandThe Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaОценок пока нет
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationОт EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (46)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyОт EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (229)
- Economics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsОт EverandEconomics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Second Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenОт EverandSecond Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenОценок пока нет
- Decolonial Marxism: Essays from the Pan-African RevolutionОт EverandDecolonial Marxism: Essays from the Pan-African RevolutionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (6)
- This Changes Everything: Capitalism vs. The ClimateОт EverandThis Changes Everything: Capitalism vs. The ClimateРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (349)
- These are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaОт EverandThese are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (14)
- Vulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomОт EverandVulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomОценок пока нет
- The New Elite: Inside the Minds of the Truly WealthyОт EverandThe New Elite: Inside the Minds of the Truly WealthyРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (10)