Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
PHYANA Chapter1
Загружено:
Christine SimИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
PHYANA Chapter1
Загружено:
Christine SimАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Terms ana tomy anatomy physio logy physiology atoms molecules DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) hemoglobin glucose vitamins
cells cells organelles tissues muscle, nerve, blood epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous organ organ serous membrane smooth muscle tissue layers epithelial tissue layer system organismal level organism chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, system , organismal metabolism, responsiveness, movement, growth, differentiation, reproduction metabolism responsiveness movement growth -size of existing cells -number of cells -amount of material surrounding the cells differentiation - the formation of new cel ls for growth, repair, or replacement -production of a new individual homeostasis homeo stasis interstitial fluid dynamic nervous and endocrine nerve impulses hormones feedback system/feedback loop
Definition up process of cutting the science of structure and the relationships among the structure nature study of the science of body functions the smallest units of matter that participate in chemical reactions two or more atoms joined together the genetic material passed on from one generation to another carrise oxygen in the blood blood sugar needed for a variety of chemical processes the basic structural and functional units of an organism smallest living units in the body specialized structures inside the cell groups of cells and the materials surrounding them that work together to perform a specific function examples of types of cells 4 types of tissues different kinds of tissues join together to form body structures have a recognizable shape layer around the outside of the stomach that protects it and reduces friction when the stomach contract to churn and mix food and push it to the small interstine contributes fluids and chemicals that aid digestion related organs that have a common function largest level of organization one human being levels of organization life processes the sum of all the chemical proceses that occur in the body body's ability to detect and respond to changes in its inter/external environment motion of the whole body increase in body size 3 possible "growths"
the process whereby unspecialized cells become specialized cells two possible meanings of reproduction
controlled condition stimulus receptor, control center, effector receptor input input
maintenance of relatively stable conditions sameness standing still a large part of the internal environment consisting the fluid surrounding body cells homeostasis can change over a narrow range that is compatible with maintaining cellular life proceses 2 systems that contribute a lot in homeostasis nervous system- homeostasis endocrine system- homeostasis a cycle of events in which a condition in the body is continually monitored, evaluated, changed, remonitored,... a monitored condition any disruption that causes a change in a controlled condition three basic components that make up a feedback system a body structure that monitors changes in a controlled condition information sent by a receptor a form of nerve impulses or chemical signals
control center control center output effector
response negative feedback system blood pressure baroreceptors positive feedback system disorder disease symptoms signs diagnosis symptoms, signs, medical history, physical examination, lab tests ispection palpation auscultation percussion vital signs aging anatomical position upright prone supine head, neck, trunk,upper and lower limb head skull face neck trunk chest, abdomen, pelvis upper limb shoulder, armpit, arm, forearm, wrist, hand arm forearm lower limb thigh leg groin directional terms anterior posterior superior cephalic/cranial superior inferior inferior anterior anterior posterior posterior medial lateral proximal distal
sets the range of values within which a controlled condition should be maintined; evaluates the input it receives from receptors and generates an output information that is relayed from the control center to an effector a body structure that receives output from the control center and produces a response that changes the controlled condition changes the controlled condition reverses a change in a controlled condition the force exerted by blod as it presses against the walls of blood vessesls pressure-sensitive nerve cells located in the walls of certain blood vessels strengthens a change in a controlled condition any abnormality of structure and/or function an illness characterized by a recognizable set of symptoms and signs subjective changes in body functions that are not apparent to an observer objective changes that can be observed and measured identification of a disease or disorder evaluations needed for a diagnosis observing the body for any changes that deviate from normal feeling body surfaces with hands listening to body sounds often using a stethoscope tapping on body surfaces and listening to the resulting echo temperatire, pulse, respiratory rate and blood pressure a normal process characterized by a progressive decline in the body's ability to restore homeostasis specific stance anatomical position face down face up body regions skull and face part of the head that encloses and protects the brain front portion of the head that includes the eyes, nose, mouth, forehead, cheeks, and chin supports the head and attaches it to the trunk chest, abdomen, pelvis trunk shoulder, armpit, arm, forearm, wrist, hand upper lumb portion of the limb from the shoulder to the elbow portion of the limb from the elbow to the wrist buttock, thigh, leg, ankle, and foot portion of the limb from the hip to the kneel portion of the limb from the knee to the ankle marked by a crease on each side, where the trnk attaches to the thighs words that describe the position of one body part relative to another front back cephalic/cranial superior toward the head/upper part of the structure caudal away from the head/ lower part of the structure ventral nearer to/front of the body dorsal back of the body nearer the midline/midsagittal plane farther the midline/midsagittal plane near the attachment of limb to trunk/ origin/ beginning far the attachment of limb to trunk/ origin/ beginning
superficial deep sagittal, frontal, transverse, oblique sagitt planes sagittal plane midsagittal plane parasagittal frontal plane frontal plan transverse plane transverse plane sagittal, frontal, transverse oblique plane section cranial, vertebral, thoracic, pleural, pericardial, mediastinum, abdominopelvic, abdominal, pelvic body cavities cranial cavity vertebral cavity thoracic cavity thoracic cavity pleural cavity pleura pericardial cavity pericardium mediastinum mediastinum mediastinum abdominal cavity peritineum right hypochondriac, epigastric, left hypochondriac, right lumbar, left lumbar, umbilical, right inguinal/iliac, hypogastric (pubic), left inguinal/iliac media stinum diafram diaphragm diaphragm abdomin viscera serous membrane parietal and visceral parietal layer visceral later oral cavity nasal cavity orbital cavities middle ear cavities synovial cavities nine-region division quadrants left upper, left lower, right upper, right lower
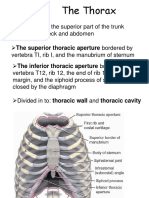
toward or on the surface of the body away from the surface of the body 4 major planes arrow imaginary flat surfaces that pass through the body parts a vertical plane that divides the body/organ into right and left sides equal left and right sides unequal left and right sides coronal plane anterior and posterior portions superior and inferior portion cross-sectionsal/horizontal plane all at right angles to one another angle between transverse and sagittal/frontal cut of the body or an organ made alng one of the planes body cavities spaces within the body that contain, protect, separate, and support internal organs cranial bones and contains the brain vertebral column, spinal cord, beginnings of spinal nerves chest cavity contains pleural and pericardial cavities and mediastinum each surrounds a lung serous membrane of pleural cavity surrounds the heart serous membrane of pericardial cavity central portion of thoracic cavity between the lungs sternum to vertevral column/ neck to diaphragm contains the heart, thymus, esophagus, trachea, blood vessels stomach, spleen, liver, gallbladder, small and large intestine serous membrane of the abdominal cavity 9 regions
middle partition partion/wall a dome shaped muscle that powers breathing separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity belly organs in the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities covers the viscera layers that compose the serous membrane lines the walls of the cavities covers and adheres to the viscera within the cavities tongue teeth nose eyeballs small bones of the middle ear freely movable joints and contain synovial fluid anatomical studies clinicians quadrants
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
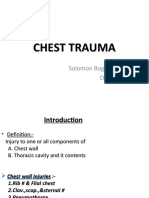
- Chest TraumaДокумент62 страницыChest TraumaayouОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Pericardial DiseaseДокумент36 страницPathophysiology of Pericardial DiseaseivaniОценок пока нет
- 1 - Dr. Dr. Sri Endah Rahayuningsih, SpA (K)Документ19 страниц1 - Dr. Dr. Sri Endah Rahayuningsih, SpA (K)nudhakoОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Human Anatomy and Physiology 2nd Edition by AmermanДокумент19 страницTest Bank For Human Anatomy and Physiology 2nd Edition by AmermanGuadalupe Panek100% (40)
- (Harsh Mohan) Textbook of Pathology (6th Ed.) - 433-476Документ44 страницы(Harsh Mohan) Textbook of Pathology (6th Ed.) - 433-476Ananta DasОценок пока нет
- Electrical Alternans: - Prof.M.K.Sudhakar's UnitДокумент19 страницElectrical Alternans: - Prof.M.K.Sudhakar's UnitVivek AnandanОценок пока нет
- 2015 ESC Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Management of Pericardial Diseases European Heart Journal Oxford AcademicДокумент1 страница2015 ESC Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Management of Pericardial Diseases European Heart Journal Oxford AcademicM Yusuf Arief AkbarОценок пока нет
- Jurnal Pakai 6 (Patofisiologi, Diagnosis, Gejala)Документ13 страницJurnal Pakai 6 (Patofisiologi, Diagnosis, Gejala)Satrya DitaОценок пока нет
- Thoracic ESДокумент237 страницThoracic ESAbel Belete100% (1)
- Violencia Familiar y El Síndrome de Kluver-Bucy SMJ 1987Документ5 страницViolencia Familiar y El Síndrome de Kluver-Bucy SMJ 1987Jose MuñozОценок пока нет
- A&P - 1. Heart Anatomy (9p)Документ9 страницA&P - 1. Heart Anatomy (9p)mr. fakeОценок пока нет
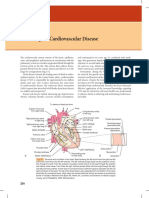
- Cardiovascular System - 4th EdДокумент33 страницыCardiovascular System - 4th EdLeah ArabesОценок пока нет
- Contorno de Órgão de Risco Thoracic Radiation TherapyДокумент106 страницContorno de Órgão de Risco Thoracic Radiation TherapyLEONARDO CORDEIRO PEREIRAОценок пока нет
- Chest TraumaДокумент122 страницыChest TraumaMarina Maleș100% (1)
- Unit 4 Circulatory SystemДокумент157 страницUnit 4 Circulatory SystemChandan ShahОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology Ii-Dm Cardiovascular Sys-1Документ64 страницыAnatomy and Physiology Ii-Dm Cardiovascular Sys-1Mathews showsОценок пока нет
- Heart Dissection WorksheetДокумент5 страницHeart Dissection Worksheetapi-237875296100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular System Functions of The HeartДокумент3 страницыAnatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular System Functions of The HeartPeej ReyesОценок пока нет
- HemopericardiumДокумент1 страницаHemopericardiumlourdesfercab_at_msnОценок пока нет
- PericarditisДокумент45 страницPericarditisJorge Luis Ibarra NaranjoОценок пока нет
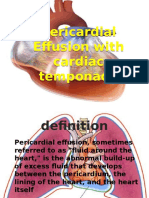
- Pericardial Effusion With Cardiac TemponadeДокумент12 страницPericardial Effusion With Cardiac Temponademeli tswОценок пока нет
- Exam 1 Practice Questions Part 2Документ109 страницExam 1 Practice Questions Part 2NeoGellinОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 3rd Edition EllisДокумент8 страницTest Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 3rd Edition Elliscanebrutalfniy66Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - The Human OrganismДокумент7 страницChapter 1 - The Human Organismllena llenaОценок пока нет
- Veterinary Internal MedicineДокумент233 страницыVeterinary Internal MedicineSulove KoiralaОценок пока нет
- 06章(224 271)Документ48 страниц06章(224 271)zhangpengОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 - Transudates and Exudates IIIДокумент17 страницUnit 3 - Transudates and Exudates IIIRubina KhatunОценок пока нет
- Dr. Madaan Anatomy MCQ 2-2 (Muhadharaty)Документ46 страницDr. Madaan Anatomy MCQ 2-2 (Muhadharaty)Joseph Brima SambaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Chapter 1Документ6 страницAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Chapter 1Cza Mae ArsenalОценок пока нет
- SeminarskiДокумент17 страницSeminarskiKadric Nagla UtokaОценок пока нет