Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Engineering Graphics
Загружено:
vpsraviОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Engineering Graphics
Загружено:
vpsraviАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS UNIT I CONICS 1.
Draw an ellipse when the distance of focus from the directrix is equal t o 40mm and eccentricity is 3/5. 2. Draw a parabola when the distance of focus from the directrix is equal t o 30mm and eccentricity is 1. 3. Draw a hyperbola when the distance of focus from the directrix is equal to 40mm and eccentricity is 5/3. 4. Construct a cycloid given the diameter of the generating circle radius = 36mm. 5. 6. Draw an involute of a square of side 40mm. Draw an involute of a regular hexagon of side 30mm.
7. Construct an involute of a circle of radius 25mm. Also draw tangent and normal from a point on the curve. 8. A string of length 150mm is wound round a pentagon of side 28mm. Draw th e path traced by the end of the string. 9. A string of length 180mm is wound round a circle of radius 20mm. Draw th e path traced by the end of the string.
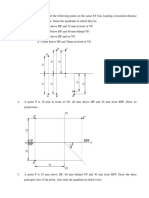
UNIT II PROJECTIONS OF POINTS 1. Draw the projections for the following points: i) ii) Point A, 10mm infront of VP and 45mm above HP. Point B, on HP and 50mm infront of VP.
iii) iv) v) vi) t. vii) viii)
Point Point Point Point
C, D, E, F,
10mm above HP and 25mm behind VP. in VP and 35mm below HP. 35mm below HP and 30mm behind VP. 45mm away from the reference planes and is in the third quadran
Point G, 50mm below HP and 25mm infront of VP. Point H, 20mm in below HP and in VP.
PROJECTIONS OF STRAIGHT LINES 1. A straight line 70mm long has one end 15mm infront of VP and 30mm above HP while the other end is 35mm infront of VP and 20mm above HP. Draw the plan an d elevation of the line. 2. A straight line 85mm long has one end 15mm infront of VP and 25mm above HP while the other end is 30mm infront of VP and 45mm above HP. Draw the plan an d elevation of the line. Determine the inclinations of the line to HP and VP. 3. A line JK is 80mm long. It is making an angle of 30 with HP and 20 with VP . The line is such that its lowermost point J is 15mm above HP and 25mm infront of VP. Draw the projections of the line JK. 4. A point C is 50 above HP and 15 infront of VP. Point D is 10mm above HP and 30mm infront of VP. The distance between end projectors is 40mm. Draw the pr ojections and determine the true length between C and D true inclination of CD w ith HP and VP. 5. A line AB 75mm has its end A 15mm above and 20mm infront of VP. Its top view and elevation measures 65mm and 45mm respectively. Draw the projection of t he line and determine its inclinations with HP and VP. 6. A line AB 70mm long is inclined at an angle of 40 to the HP and 30 to the VP. The end A is 35mm infront of VP and 20mm above HP. Draw the projections of t he line. 7. One end of a line 60mm long is 35mm above HP and 10mm infront of VP. The other end is 20mm above HP and 55mm infront of VP. Draw the projection and find true inclinations. 8. One end of a line 65mm long is 20mm above the HP and 10mm infront of the VP. The line is inclined at 30 to the HP and the top view makes 55 with the VP. D raw the projections of the line and find its true inclination with the VP. 9. A line measuring 60mm long has one of its ends 50mm infront of VP and 10 mm above HP. The top view of the line is 45mm long. The other end is 5mm infront of VP and is above HP. Draw the projection and find true inclination. 10. One end of a line is 60mm above HP and 70mm infront of VP. The other end is 25mm above HP and 10mm infront of VP. The distance between the end projector is 35mm. Draw the projection and find true inclinations and true length. 11. A line 100mm long has one of its ends 50mm infront of VP and 20mm above HP. The other end is 20mm infront of VP and above HP. The length of plan is 80mm. Find t he Inclinations of the line and the traces. 12. The line CD, 75mm long, makes an angle of 30 with the VP and is in a plan
e perpendicular to both the HP and VP. Its end C is in the VP and the end D is in the HP. Draw its projections and locate its traces. 13. A line AB, 65mm long has its end A, 25mm above the HP and 20mm infront o f the VP. The end B is 40mm above the HP and 50mm infront of the VP. Draw its projection a nd find its inclinations with the HP and VP. Determine its trace MID POINT PROBLEMS 14. The mid point of a line 80mm long, is 40mm above HP and 60mm infront of VP. It is inclined at 30 to HP and 55 to VP. Draw the projection. 15. A straight line AB 100mm long is inclined at 30 to HP and 45 to VP. Its mi d point is in the VP and 20mm above HP. The end A is in the first quadrant and t he end B is in the third quadrant. Draw the projection and locate its traces.
PROJECTIONS OF PLANES PLANE TO PARALLEL HP AND PERPENDICULAR TO VP 1. Draw the projections of a square plane of side 30mm parallel to HP and p erpendicular to VP. 2. Draw the projections of a pentagonal plane of side 25mm, in HP and perpe ndicular to VP with one of its edges parallel to VP. PLANE TO PARALLEL VP AND PERPENDICULAR TO HP 3. Draw the projections of a square plane of side 25mm parallel to VP and p erpendicular to HP. 4. An equilateral triangle of 40mm side is parallel to and 25mm in front of VP. Draw the projection when one of its sides is inclined at 50 to the HP. PLANE PERPENDICULAR TO BOTH HP AND VP. 5. Draw the projections of a triangle of side 45mm perpendicular to both HP & VP with an edge on HP. Also draw the side view. 6. Draw the projections of a rectangular plane of size 70mm X 30mm perpendi cular to both HP & VP. 7. A hexagon of side 30mm is perpendicular to both HP & VP, such that one e dge is on the ground. Draw its front view and top view. PLANE PERPENDICULAR TO VP AND INCLINED TO HP 8. A regular hexagonal plane of side 25mm is resting on HP on one of the si de edges with the plane making 30 with HP and perpendicular to VP. Draw its proje ctions. 9. A regular pentagonal plane of 30mm side has one edge in the HP and incli ned at an angle of 35 to the HP. Draw the projections of the plane. 10. A rectangle of size 60mm X 30mm is seen as square in the plan. Draw the
projection and find the true inclination with HP. PLANE PERPENDICULAR TO HP AND INCLINED TO VP 11. Draw the projections of a square plane of side 40mm inclined at 45 to VP and perpendicular to HP. 12. A circular lamina diameter 50mm lies in a plane inclined at 40 to VP and perpendicular to HP. Draw its plan and elevation. 13. A 45 set-square of longest side of 60mm is kept such that the longest sid e is in HP and making an angle of 30 with XY line. Draw the projection. 14. A circular lamina of diameter 70mm lies in a plane inclined at 60 to HP a nd perpendicular to VP. Draw its plan and elevation. PLANE INCLINED TO BOTH HP AND VP 15. A pentagonal plane of side 25mm is resting on one of its edges in the HP with that edge making 45 with the VP. The edge is again inclined at 35 to HP. Dra w the projections. 16. Draw the projections of a circular plate of diameter 60mm resting on the ground on a point A on the circumference, it is inclined at 30 to HP and plan of the diameter AB making 45 with VP. 17. A rectangular lamina of size 40mm X 60mm rests on HP on one of its short er edges. The lamina is rotated about the edge on which it rests till it appears as square in the top view. the edge on which the lamina rests being parallel to both HP and VP. Draw its projection and find the inclinations with HP and VP. 18. A circular lamina of diameter 60mm is perpendicular to HP and inclined t o VP so that its front view is an ellipse of major diameter 60mm and minor diame ter 20mm. Draw the projections and find true inclination. 19. A pentagonal lamina of side 30mm is perpendicular to HP and inclined to VP, such that one edge is in VP and the corner opposite to the resting edge is 20mm above HP. Draw its projections and find its true inclination. 20. Draw the projections of a regular hexagon of side 25mm, having one of it s sides on the ground and inclined at 60 to the VP and its surface making an angl e of 45 with the ground.
UNIT III PROJECTIONS OF SOLIDS AXIS PARALLEL TO BOTH HP & VP Cube 1. A hexahedron of side 40mm rests on HP on one of its edges such that the face contained that edge makes an angle of 35 to VP & any one of the faces is per pendicular to VP. Draw its projections. Prism
2. A pentagonal prism of base side 25mm and axis 65mm long is lying on grou nd on one of its rectangular faces with its axis parallel to both HP & VP. Draw the projections of the solid. Pyramid 3. A triangular pyramid of base side 30mm & height 40mm rests on HP on its base corner such that the base is perpendicular to both the planes & the nearest shorter edge is parallel to VP. Draw the elevation, plan & right side view of t he pyramid. 4. A triangular pyramid of base side 30mm and height 60mm is resting on the ground on one of its base edges with the axis parallel to both HP and VP. Draw the projection. Cylinder 5. Draw the projections of a cylinder of 40mm diameter & height 70mm, when it lies on HP on its generator which is parallel to VP. AXIS INCLILNED TO HP & PARALLEL TO VP Cube 6. Draw the projections of a cube of 35mm rests on HP on its corner, such t hat the edge contained that corner is inclined 45 to HP & all vertical faces are equally inclined to VP. Prism 7. A right regular pentagonal prism, edge of base 25mm & height 55mm rests on HP with an edge of its base such that its axis is parallel to VP & inclined t o the HP at 45. Draw the projections of the solid 8. A hexagonal prism of side of base 25mm and axis 60mm rests on a corner o f its base in HP with the axis of the prism inclined at 40 to HP & parallel to VP . Draw the projections. 9. A triangular prism of base side 35mm, axis height 60mm is lying on the g round on one of its base edges such that the axis is parallel to VP and inclined at 45 to HP. Draw the projection. Pyramid 10. Draw the projections of a pentagonal pyramid 70mm high & side base 30mm with one triangular face of the pyramid is vertical. 11. A square pyramid of base side 40mm & 70mm high rests on HP on its slant face such that the base is perpendicular to VP. Draw its plan. 12. Draw the projections of a hexagonal pyramid 70mm high & side base 30mm, when it lies on HP on one of its slant edges which is parallel to VP. Also, the two base edges are parallel to VP. 13. A pentagonal pyramid side of base 25mm & axis 50mm long lies with one of its triangular faces on HP & its axis is parallel to VP. Draw its projections. 14. Draw the projections of a pentagonal pyramid of base 25mm side and axis 70mm long when it lies on the HP on one of its longer edges with its axis parall el to VP. 15. Draw the projections of a hexagonal pyramid of base side 20mm and axis h
eight 60mm with a lateral edge perpendicular to HP and parallel to VP. Cylinder 16. A cylinder of diameter 50mm & altitude 70mm tilted, the axis makes an an gle of 60 with the HP. Draw the projections of the cylinder. 17. A cylinder of diameter 50mm, height 70mm is resting on the ground on its base. It is then tilted such that a solid diagonal is vertical. Draw the projec tion. Cone 18. Draw the projections of a cone of diameter 50mm & axis length 70mm when it lies on one of its generators with the axis parallel to VP 19. A cone 50mm base & axis 70mm long touches the HP on a point of its base circle. The axis is parallel to VP & inclined at 30 to HP. Draw its projections 20. Draw the projection of a cone diameter 40mm and height 60mm is on HP on one of its base circle point and the opposite base point is lifted up 30mm above HP with the axis parallel to VP. AXIS INCLINED TO VP & PARALLEL TO HP Cube 21. A cube of base side 50mm rests on HP on its edge such that the face cont ained that edge is inclined 50 to HP & that edge is then tilted 45 to VP. Draw its projections. Prism 22. A hexagonal prism of base side 20mm & altitude 70mm lies on HP on one of its longer edges such that the face contained that edge is inclined 15 to HP & t he base is inclined 60 to VP. Draw its projections. 23. A square prism of 25mm side, 60mm height lies with one of its faces on H P and the axis is inclined at 40 to VP. Draw the top and front views of the prism . 24. A triangular prism of base side 30mm, axis height 70mm is kept on HP on one of its longer edges such that a base edge is inclined at 25 to HP. The object is then tilted 60 to VP. Draw the projection.
Pyramid 25. Draw the projections of the square pyramid of base side 40mm & altitude 70mm, when it stands on the HP on its base corner such that the shorter edges ar e equally inclined to HP & the base is inclined 50 to VP and perpendicular to HP, vertex is towards the VP. 26. A hexagonal pyramid of base side 30mm and 70mm high rests on its base co rner on HP such that the axis is parallel to HP & 45 inclined to VP & the base ed ge contained that resting corner makes 45 to HP. The vertex is towards the Observ er. Draw its projections. Cylinder
27. Draw the projections of a cylinder of 75mm diameter & 100mm long, lying on HP on one of its generators with its axis inclined at 30 to VP & parallel to H P. 28. Draw the projections of a cylinder of 30mm diameter & 60mm long, lying o n HP on its generator such that the nearest base circle point is 20mm infront of VP & the other end nearest base circle point is 40mm infront of VP. Cone 29. A cone of base diameter 40mm & height 80mm rests on HP on a point of its base circle such that the contour generator makes 30 to VP & base is perpendicul ar to HP. Draw the elevation of the cone.
UNIT IV SECTIONS OF SOLIDS CUTTING PLANE PERPENDICULAR TO VP & INCLINED TO HP Cube 1. A cube of side 40mm is resting on the ground on one of its faces with it s vertical faces inclined at 20 to the VP. It is cut by a plane perpendicular to VP and inclined at 45 to the HP and bisecting the axis. Draw the sectional plan a nd true shape of the section. 2. A cube of 60mm sides has its base edges equally inclined to VP. It is cu t by a section plane perpendicular to VP, so that the true shape of the cut sect ion is a regular hexagon. Locate the plane & determine the angle of inclination of VT with the reference line XY. Draw the sectional top view. Prism
3. A pentagonal prism axis vertical and base edge 30mm is 65mm high. A plan e cuts it perpendicular to VP, inclined at 60 to HP bisecting the axis. Draw the true shape. 4. A square prism, base 45mm side, axis 90mm long, stands on the HP with it s axis vertical such that its faces are equally inclined to VP. It is cut by a p lane inclined at 60 to the HP and passing through a point on the axis of the pris m 65mm above the HP. Draw its projections and the true shape of the section. 5. A hexagonal prism of base 20mm side and altitude 60mm rests on HP with i ts axis vertical and one edge of its base inclined at 15 to VP. The solid is cut by a plane which is perpendicular to VP and inclined at 40 to HP and bisecting th e axis of the prism. Draw the projections of the prism and the true shape of the section. (Madras Oct97) Pyramid 6. A regular hexagonal pyramid, base 35mm side and axis 80mm long is restin g on its base on the ground with two edges parallel to VP. It is cuy by a sectio n plane perpendicular to VP and inclined at 45 to HP and intersecting the axis at a point 30mm above the base. Draw its front view, sectional top view and true s hape of the section. 7. A pentagonal pyramid base side 25mm and axis 65mm is resting on the grou nd on its base with a base edge parallel to VP. It is cut by two cutting planes starting from a point on the axis 35mm above the base, one is perpendicular to V P and parallel to HP and the other is perpendicular to VP and 30 to the HP. Draw sectional plan and true shape of the section. 8. A hexagonal pyramid of base side 30 and axis 70 is resting on its base o n HP with two base sides parallel to VP. A cutting plane perpendicular to VP and 45 to HP cuts the pyramid passing through a point on the axis 40 above base. Dra w the sectional view and true shape of section. Cylinder 9. A cylinder of 48mm diameter and axis 60mm height is resting on the groun d on its base. It is cut by a plane perpendicular to VP and inclined at 35 to the HP and meets the axis at a point 25mm from the top. Draw the sectional plan and true shape. 10. A cylinder of diameter 40mm and height 65mm rests on its base on the HP. It is cut by a plane perpendicular to the VP and inclined at 60 to HP. The cutti ng plane meets the axis at a distance of 40mm from the base. Draw the sectional plan and true shape of section. Cone 11. A cone of 40mm diameter and axis 55mm is resting on the ground. It is cu t by a plane perpendicular to VP and inclined at 50 to the HP and meets the axis at a point 30mm above the base. Draw the sectional plan and true shape. 12. A cone of diameter 50mm and axis 60mm rests on its base on HP. An auxili ary inclined plane inclined at 45 to HP cuts the cone and passes through a point on axis which is 20mm below the apex. Draw the sectional plan and elevation and draw the true shape of the section. CUTTING PLANE PERPENDICULAR TO HP & INCLINED TO VP.
Cube 13. A Cube of 30mm side rests on HP on one of its faces such that all the ve rtical faces are equally inclined to VP. It is cut by a vertical plane passing t hrough the axis of the cube such that the true shape of the section is square in shape. Prism 14. A hexagonal prism of edge of base 30mm and altitude 70mm lying with a fa ce on HP. It is cut into two halves by a vertical plane inclined at 60 to the axi s. Draw the sectional elevation and the true shape of one of the halves. 15. A pentagonal prism, base edge 25mm and altitude 70mm, lies on the ground on one of its lateral edges. It is cut into two halves by a vertical plane incl ined at 45 to the axis. Draw the sectional elevation and the true shape of one of the halves. Pyramid 16. A pentagonal pyramid of 20mm edge of base and 40mm high stands verticall y with its base on HP and an edge of the base perpendicular to VP. A sectional p lane perpendicular to HP and inclined at 30 to VP cuts the pyramid at a distance of 5mm from its axis and infront of it. Draw its sectional front view and projec t the auxiliary view showing the true shape of the section. 17. A hexagonal pyramid of base 25mm side and axis 65mm height is lying on t he ground on its base with a base edge parallel to the VP. It is cut by a plane perpendicular to the HP and inclined at 35 to the VP and passes through a point 8 mm away from the axis. Draw sectional elevation and add an auxiliary sectional v iew on a plane parallel to the section plane. Cylinder 18. A cylinder 40mm diameter and 70mm long lies on a base point on HP with i ts axis making 40 to HP. A plane inclined at 30 to VP bisecting the axis cuts the solid. Draw the true shape of the section. Cone 19. A cone, 60mm diameter and axis 70mm long is lying on the HP on one of it s generators with the axis parallel to VP. A vertical section plane which is tan gent to the ellipse (for the base) in the plan, cuts the cone and bisecting the axis and removing a portion containing the apex. Draw its sectional elevation an d true shape of the section. DEVELOPMENT OF SURFACES CUBE 1. Draw the development of the cube of side 35mm resting on the ground on a face with an edge 45 to VP, which is cut by a plane inclined at 30 to the base at 10mm from the left top corner of the cube. PRISM 2. A pentagonal prism of base side 30mm and height 70mm stands on one of it s ends on the HP with the rectangular face perpendicular to VP. A hole of diamet er 22mm is drilled centrally to the prism in such a way that the axis of the hol e bisects the axis of the prism at right angles. The axis of the hole is perpend icular to the VP. Draw the development of the lateral surfaces of the prism. 3. A hexagonal prism of base side 20mm and height 60mm is resting on the gr
ound with one of its base edges parallel to VP. Find graphically the shortest di stance of a string that connects one end of the lateral edge with the other end of the same edge, covering all the lateral surfaces of the solid. Also trace the points on to the development. PYRAMID 4. A plane cuts it a hexagonal pyramid, of edge of base 25mm and altitude 6 5mm stands on HP with a base edge parallel to HP, perpendicular to VP and inclin ed at 45 to HP and bisecting the axis. Draw the development of the frustum of the pyramid. 5. A hexagonal pyramid of base side 20mm, axis height 65mm is resting on th e ground with one of its base edge perpendicular to HP. It is cut by two planes one is parallel to HP and the other is inclined at 45 to HP intersecting the axis at 30mm from the base. Draw the development of lateral surface of the solid. 6. A right regular pentagonal pyramid, edge of base 25mm, and height 60mm, is lying on one of its triangular faces on HP, with its axis parallel to VP. An auxiliary vertical section plane, perpendicular to HP, inclined to the VP at 30 a nd bisecting the axis cuts the pyramid, removing the part containing the vertex. Draw the top view, sectional front view and development of the surface of the r emaining portion of the pyramid. 7. A hexagonal pyramid of base side 20mm and height 70mm rests vertically o n HP with one of the base sides making 30 to VP. A string is wound round the surf aces of the prism from the left extreme point on the base and ending at the same point. Find graphically the shortest length of the string required. Also trace the path of the string in the front and top views. CYLINDER 8. A cylinder of diameter 50mm and height 70mm is resting vertically on one of its ends on the HP. It is cut by a plane perpendicular to VP and inclined at 45 to the HP. The plane meets the axis at a point 40mm from the base. Draw the d evelopment of the lateral surface of the lower portion of the truncated cylinder . 9. A vertical chimney of circular section of 500mm diameter joints the roof of a room sloping at 40 to the horizontal. The shortest portion of the chimney i s 200mm high. Determine the shape of the sheet metal from which the chimney can be made. Use 1:10 scale. 10. A cylinder of diameter 50mm, height 70mm rests on its base on the ground . A square hole of side 25mm is drilled horizontally, centrally, with its faces equally inclined to HP. Draw the lateral surface development of the solid. CONE . 11. A right circular cone of diameter 50mm and height 65mm is cut by an incl ined plane passing through the axis at a point 30mm above the base inclined at 3 0 to HP. Draw the development of lateral surface. 12. A cone of diameter 60mm and height 70mm is resting on its base on the gr ound. It is cut by a plane perpendicular to VP and parallel to the HP at a dista nce 20mm from the vertex. It is also cut by a plane inclined at 40 to the base an d meeting the axis at a point 20mm above base. Draw the development of the later al surface of the cut cone.
13. A cone of diameter 70mm and axis 75mm when resting on its base on HP, is cut by a sectional plane parallel to and 50mm above base. Two more sectional pl anes perpendicular to VP and 30 to HP cut the cone passing through the base centr e on either sides. Draw the development of the surface of mid portion of the cut cone. DEVELOPMENT OF LATERAL SURFACES OF SOLIDS WITH SQUARE CUTOUTS 14. A square prism of base side 42mm and axis height 68mm is resting on the ground on its base with all bases edge equally inclined to VP. A square hole of side 32mm is drilled centrally with the axis perpendicular to VP, bisecting and intersecting the axis of the prism at right angles with all its rectangular face s are equally inclined to HP. Draw the development of the lateral surfaces of th e prism. 15. A pentagonal prism of base side 24mm and axis height 56mm is resting on the ground on its base with a base edge parallel to VP. A square hole of side 22 mm is drilled centrally with the axis perpendicular to VP, bisecting and interse cting the axis of the prism at right angles with all its rectangular faces are e qually inclined to HP. Draw the development of the lateral surfaces of the prism . 16. A cylinder of diameter 50mm, height 70mm rests on its base on the ground . A square hole of side 24mm is drilled horizontally, centrally, with its faces equally inclined to HP. Draw the lateral surface development of the solid. DEVELOPMENT OF LATERAL SURFACES OF SOLIDS WITH CYLINDRICAL CUTOUT 17. Draw the lateral development of a hexagonal prism of base side 32mm, par allel to VP, and height 72mm is having a hole of radius 16mm with the axis of th e hole is parallel to HP and perpendicular to VP intersecting the axis of the pr ism at the height of 22mm from the base. 18. A vertical Triangular Pyramid of 40mm side and height 62mm has a circula r hole of diameter 22mm. Their axes intersect at right angles. The axis of the h orizontal hole is perpendicular to VP and 18mm above HP. The base edge of the ve rtical prism parallel to VP. Develop the surface of the vertical prism.
UNIT V ISOMETRIC PROJECTIONS SINGLE FULL SOLIDS 1. Draw the isometric views of a pentagonal prism of base side 20mm & heigh t 60mm, resting on HP on (i) one of its ends, (ii) one of its longer edges and ( iii) one of its rectangular faces. 2. Draw the isometric view of a hexagonal pyramid of edge of base 20mm and axis 65mm long when it lies on one of its rectangular faces in HP. 3. Draw the isometric view of a rectangular pyramid of base 30 X 50mm and a xis height 60mm . When it rests on the ground vertically. FRUSTUMS 4. A pentagonal pyramid base side 20mm and height 65mm stands with its base on HP. An edge of the base is parallel to VP and nearer to it. A horizontal sec tion plane cuts the pyramid and passes through a point on the axis at a distance
of 25mm from the apex. Draw the isometric view of the frustum of the pyramid. 5. The frustum of a hexagonal pyramid base side 20mm side and top face 10mm side has a height of 50mm. Draw its isometric view, when one of the base edges is perpendicular to VP. 6. The frustum of a pentagonal pyramid base 30mm side and top 15mm side has a height of 40mm. Draw its isometric view. 7. Draw the isometric view of a frustum of a hexagonal pyramid when it is r esting on its base on the HP with two sides of the base parallel to VP. The side of base is 20mm and top 8mm. The height of the frustum is 55mm. TRUNCATED SOLIDS 8. A cone 50mm diameter and height 70mm stands on HP with its base. It is c ut by a cutting plane inclined at 30 to HP cutting the axis of the cone at a heig ht of 40mm from its base. Draw the isometric view of the remaining part of the c one. 9. A triangular prism of base side 30mm axis height 60mm is resting on the ground on its base with one base edge is perpendicular to VP. It is cut by a pla ne perpendicular to VP, inclined at 45 to HP. & meets the axis at 25mm from the t op. Draw the isometric view of the prism. 10. A hexagonal prism of base side 25mm, axis 60mm height rests on its base on the ground with one vertical face parallel to VP. A cutting plane cuts it per pendicular to VP, inclined at 45 to the HP & bisecting the axis. Draw the isometr ic view of the truncated prism. 11. ground dicular ic view A pentagonal pyramid of base 20mm side and axis 60mm height rests on the on its base with a base edge parallel to VP. It is cut by a plane perpen to the VP and inclined at 45 to the VP bisects the axis. Draw the isometr of the truncated solid.
SETUP OF TWO SOLIDS 12. A Cone of diameter 40mm and axis length 70mm lies centrally on the top o f a rectangular slab 60 X 90mm and 10mm thick. Draw the isometric view of the co mbination. 13. A sphere of radius 20mm is kept centrally over a frustum of a square pyr amid of side 30mm at the bottom and 15mm at the top and height 40mm. Draw the is ometric projection of the solids. 14. A cone of diameter 40mm and axis 60mm is mounted centrally on the top of a square slab of side 60mm and thickness 15mm. Draw the isometric projection of the solids. 15. Draw the isometric view of a pentagonal prism of side of base 25mm and a ltitude 60mm surmounting a tetrahedron of side of 20mm such that the axes of the two solids are collinear and that at least one of the edges of the two solids a re parallel. 16. A cone of diameter 30mm and height 40mm rests centrally over a frustum o f a hexagonal pyramid of base side 30mm, top side 20mm and height 30mm. Draw the isometric view of the solids. 17. A cylinder diameter 60mm and length 75mm lies centrally on the top of a
rectangular slab 50mm x 80mm and 20mm thick. Draw the isometric view of the comb ination. 18. A cone 50mm diameter and 40mm axis is placed centrally over a cylindrica l slab (50mm diameter and 35mm axis). The axis of the solid coincide and vertica lly positioned. Draw the isometric projection of the solids. 19. A square pyramid of base side 30mm and axis 50mm is placed centrally on top of a cylindrical slab of 60mm diameter and 35mm thick. Draw the isometric pr ojection 20. A sphere of 50mm diameter is placed centrally on top of a frustum of a s quare pyramid when it rests on its base on HP with two base sides parallel to VP . The base side is 50mm, top side 25mm and height is 50mm. Draw isometric projec tion. PERSPECTIVE PROJECTIONS PERSPECTIVE OF PLANAR FIGURE 21. A point A is 20mm behind PP and 5mm above GP. The central plane is 30mm to the left of the point. The station point is 50mm infront of PP and 65mm above GL. Draw the perspective view of the point. 22. The end A of a straight line AB, 50mm long is 10mm behind the PP. The st raight line is inclined at 60 to the PP, parallel to and 20mm above the GP. The s tation point is 50mm above the ground plane and 60mm infront of PP lies on a cen tral plane that passes through a point on AB, 25mm from one end. Draw the perspe ctive view of the line. 23. A square lamina of size 40mm rests on the ground with one edge on PP and the remaining portion behind PP. The station point is 50mm above GP and 40mm in front of PP and lies on a central plane 45mm to the left of the nearest edge of the lamina. Draw the perspective view of the lamina. 24. A pentagonal plane of side 30mm is resting on the ground such that the n earest corner of the plane is 5mm behind PP with an edge containing that corner is inclined at 25 to PP. The station point is 50mm infront of PP, 65mm above GP a nd lies on a central plane 40mm to the left of the corner. Draw the perspective projection. PROBLEMS FOR VISUAL RAY METHOD 25. A cube of side 50mm is resting on the ground on a face such that one ver tical face is parallel to and 15mm behind PP. The central plane is located 10mm to the left of the nearest corner of the cube. The station point is 50mm infront of PP and 80mm above GP. Draw the perspective view of the solid. 26. A cube of side 40mm is resting on the ground such the one of its faces i s parallel to and mid of the solid is on the PP. The central plane is located 20 mm to the left of the nearest corner of the cube. The station point is 60mm infr ont of PP and 70mm above GP. Draw the perspective view of the solid. 27. A rectangular prism of base size 25mm X 50mm and height 75mm rests with its base on the ground such that the longer base edge recedes 45 to the right of PP, with one end of it is 5mm behind PP. The station point is 65mm infront of PP , 90mm above GP and lying on a central plane 50mm from the nearest vertical edge . Draw the perspective view.
28. A pentagonal pyramid of base side 30mm and height 60mm rests on the GP o n its base with an edge in PP. The station point is 65mm infront of PP, 90mm abo ve GP and lying on a central plane 15mm to the left of nearest corner. Draw the perspective view. 29. A square prism of base side 30mm and height 60mm rests on its base with the nearest edge of the base is parallel to and 5mm behind PP. The station point is 60mm infront of PP, 50mm above GP and lying on a central plane 25mm to the l eft of the mid of the solid. Draw the perspective projection. 30. A rectangular pyramid of sides of base 60mm X 30mm and height 80mm rests with its base on the ground such that one of the longer base edges is in PP and the rest behind it. The station point is 50mm infront of PP, 100mm above GP and on a central plane 15mm to the left of the nearest base corner of the pyramid. Draw the perspective projection.
CONVERTION OF PICTORIAL TO ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION Draw the Front View, Top View & one Side View for the figures shown below:
Вам также может понравиться
- Diamond Traditions: 11 Multifaceted Quilts • Easy Piecing • Fat-Quarter FriendlyОт EverandDiamond Traditions: 11 Multifaceted Quilts • Easy Piecing • Fat-Quarter FriendlyРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- The Way To Geometry: [Being Necessary and Usefull for Astronomers, Enginees, Geographers,. Architects, Land-meaters, Carpenters, Sea-men & Etc.]От EverandThe Way To Geometry: [Being Necessary and Usefull for Astronomers, Enginees, Geographers,. Architects, Land-meaters, Carpenters, Sea-men & Etc.]Оценок пока нет
- EG Question BankДокумент9 страницEG Question BankdiduthegreatОценок пока нет
- Eg QBДокумент13 страницEg QBHarini RameshОценок пока нет
- Question Bank Engineering Graphics (GE6152) : Unit-I Plane Curves & Free Hand SketchingДокумент14 страницQuestion Bank Engineering Graphics (GE6152) : Unit-I Plane Curves & Free Hand Sketchingnandhu20Оценок пока нет
- GE6152-Engineering Graphics PDFДокумент8 страницGE6152-Engineering Graphics PDFSivakumar LОценок пока нет
- GE6152-Engineering Graphics PDFДокумент8 страницGE6152-Engineering Graphics PDFSivakumar LОценок пока нет
- Engineering Graphics - Question Bank Unit - I A) Ellipse, Parabola & HyperbolaДокумент6 страницEngineering Graphics - Question Bank Unit - I A) Ellipse, Parabola & HyperbolaDamo Daran GОценок пока нет
- Anna University Engineering Graphics Question BankДокумент8 страницAnna University Engineering Graphics Question BankflorenceprasadОценок пока нет
- GE6152 Engineering GraphicsДокумент13 страницGE6152 Engineering GraphicspsvnccОценок пока нет
- First Sem Engineering Graphics Question BankДокумент11 страницFirst Sem Engineering Graphics Question BankPRIYA RAJIОценок пока нет
- Engineering Graphics - Question BankДокумент15 страницEngineering Graphics - Question BankimamuddeenОценок пока нет
- Engineering Graphics Question BankДокумент8 страницEngineering Graphics Question BankSriram JОценок пока нет
- Anna University Question Bank For Engineering GraphicsДокумент11 страницAnna University Question Bank For Engineering GraphicsRajkumarОценок пока нет
- GE6152 / Engineering Graphics / Unit-2 Assignment-2Документ1 страницаGE6152 / Engineering Graphics / Unit-2 Assignment-2kumar kmОценок пока нет
- GE6152 EngineeringGraphicsquestionbankДокумент11 страницGE6152 EngineeringGraphicsquestionbankNatarajan AgoramОценок пока нет
- Projection of LinesДокумент2 страницыProjection of LinesanandandmeenaОценок пока нет
- Engineering Graphics QB PDFДокумент8 страницEngineering Graphics QB PDFKarthi SanОценок пока нет
- Engg. Drawing QuestionsДокумент9 страницEngg. Drawing QuestionsdearsaswatОценок пока нет
- Kings: Department of Mechanical EngineeringДокумент11 страницKings: Department of Mechanical Engineeringrammit2007Оценок пока нет
- Qus PaperДокумент6 страницQus PaperBalamurugan KarnanОценок пока нет
- Question BankДокумент12 страницQuestion BankBalaChandarОценок пока нет
- Caed Manual-Apr2823Документ45 страницCaed Manual-Apr2823Aditya KulkarniОценок пока нет
- Anna University Engineering Graphics Question Bank Unit1 Unit5Документ7 страницAnna University Engineering Graphics Question Bank Unit1 Unit5florenceprasadОценок пока нет
- EG Important QuestionДокумент1 страницаEG Important QuestionsenthurrОценок пока нет
- Projection of PlanesДокумент2 страницыProjection of PlanesanandandmeenaОценок пока нет
- Caed QB1Документ11 страницCaed QB1nandukushi100% (1)
- GE8152 EG Consolidated Question BankДокумент13 страницGE8152 EG Consolidated Question BankGnaneswaran NarayananОценок пока нет
- EG TutorialДокумент20 страницEG TutorialSubramanian ManivelОценок пока нет
- Questions of Projection of PlanesДокумент2 страницыQuestions of Projection of PlanesSubhajyoti DasОценок пока нет
- Drawing Class 2Документ1 страницаDrawing Class 2Kiran MОценок пока нет
- Engineering Graphics QuestionsДокумент13 страницEngineering Graphics QuestionsRichard S DavidsonОценок пока нет
- Caed QB-2022Документ9 страницCaed QB-2022kalyanivishal777Оценок пока нет
- Development of Surfaces 240416Документ7 страницDevelopment of Surfaces 240416Nagaraj MuniyandiОценок пока нет
- Solids HWДокумент2 страницыSolids HWnavneet patilОценок пока нет
- Eg QPДокумент5 страницEg QPSurulivelrajantОценок пока нет
- Ed Assignments 2021Документ9 страницEd Assignments 2021avscoolguy123Оценок пока нет
- Projection of SolidsДокумент2 страницыProjection of SolidsanandandmeenaОценок пока нет
- Projection of SolidsДокумент1 страницаProjection of SolidsKHUSHBOO KHUSHBOOОценок пока нет
- Engineering Graphics ProblemsДокумент3 страницыEngineering Graphics ProblemsBALAMUGUNDAN50% (2)
- Section of SolidsДокумент4 страницыSection of Solidsanandandmeena100% (1)
- Unit IV Questions (Iae III)Документ5 страницUnit IV Questions (Iae III)Anonymous 4p20nXgWDZОценок пока нет
- GE2111 QB Unit 1 To 5Документ7 страницGE2111 QB Unit 1 To 5meckup123Оценок пока нет
- GE2111 Engineering Graphics Notes 2013Документ271 страницаGE2111 Engineering Graphics Notes 2013Mahesh KannanОценок пока нет
- Aux Projection 240416Документ2 страницыAux Projection 240416Nagaraj MuniyandiОценок пока нет
- Projection of Planes (CAED)Документ5 страницProjection of Planes (CAED)Akarsh manОценок пока нет
- Eg Question Bank - 2013Документ18 страницEg Question Bank - 2013kgmaheswaranОценок пока нет
- Ge 6152 Engineering Graphics Anna University Question Bank - I Plane Curves & Freehand SketchingДокумент14 страницGe 6152 Engineering Graphics Anna University Question Bank - I Plane Curves & Freehand SketchingArul JothiОценок пока нет
- Eg 2 TutorialДокумент10 страницEg 2 TutorialGanni GowthamОценок пока нет
- Engineering GraphicsДокумент18 страницEngineering GraphicsPraveen MathiОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент10 страницUntitledSuyog ChaudhariОценок пока нет
- EGДокумент4 страницыEGbalajimeieОценок пока нет
- Engineering GraphicsДокумент32 страницыEngineering GraphicsL1-36 Abhisaranya koyyalamudiОценок пока нет
- 21EVN15 25 Cirl QBДокумент11 страниц21EVN15 25 Cirl QBprajwal ursОценок пока нет
- Question Bank Engg Graphics 1Документ15 страницQuestion Bank Engg Graphics 1yuvashreesharmiОценок пока нет
- Question Plate For EgДокумент4 страницыQuestion Plate For EgNagaraj Muniyandi0% (1)
- GEC 1101 - Engineering Graphics: Tutorial-Module - 3 Projection of Straight Lines and PlanesДокумент3 страницыGEC 1101 - Engineering Graphics: Tutorial-Module - 3 Projection of Straight Lines and PlanesG. RajeshОценок пока нет
- Model Exam Eg 06.07.2022 ImportantДокумент1 страницаModel Exam Eg 06.07.2022 ImportantculvertsОценок пока нет
- V.question BankДокумент20 страницV.question Bankhnafiul97Оценок пока нет
- IV Mech - Students CGPAДокумент3 страницыIV Mech - Students CGPAvpsraviОценок пока нет
- Machinery Inspection ChecklistДокумент3 страницыMachinery Inspection Checklistfahadfadi48Оценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan: LP - ME2402 LP Rev. No: 00 Date: 25/06/14 Page: 1 of 6 Unit I Computer Aided DesignДокумент6 страницLesson Plan: LP - ME2402 LP Rev. No: 00 Date: 25/06/14 Page: 1 of 6 Unit I Computer Aided DesignvpsraviОценок пока нет
- What Is The Communication MatrixДокумент1 страницаWhat Is The Communication MatrixvpsraviОценок пока нет
- Total Quality Management Question PaperДокумент4 страницыTotal Quality Management Question Papervpsravi67% (3)
- Multi Response Optimization of EDM Parameters by Using Grey Relational Analysis and Tagauchi MethodДокумент12 страницMulti Response Optimization of EDM Parameters by Using Grey Relational Analysis and Tagauchi MethodvpsraviОценок пока нет
- Index NotationДокумент2 страницыIndex NotationShanza RehmanОценок пока нет
- Vector CalculusДокумент21 страницаVector CalculustetojogoldenboyОценок пока нет
- 45+ Questions (1) 45-90Документ2 страницы45+ Questions (1) 45-90shrinidhirajshetty 1Оценок пока нет
- Differentiation Summary Exam QuestionsДокумент11 страницDifferentiation Summary Exam QuestionsAОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Connections On Principal Fibre Bundles: by Rupert WayДокумент12 страницIntroduction To Connections On Principal Fibre Bundles: by Rupert WayMike AlexОценок пока нет
- 2020微积分II期末考试 (A卷) - 出题人刘刚 - 20200702102946Документ6 страниц2020微积分II期末考试 (A卷) - 出题人刘刚 - 20200702102946Luisa SóniaОценок пока нет
- Geometry Four Ordered PairsДокумент2 страницыGeometry Four Ordered Pairsapi-3148096000% (1)
- r05221801 Mathematics IIIДокумент7 страницr05221801 Mathematics IIISRINIVASA RAO GANTAОценок пока нет
- QuaternionДокумент31 страницаQuaternionsairam poosarlaОценок пока нет
- Geometric Modeling of SurfacesДокумент14 страницGeometric Modeling of SurfacessauravОценок пока нет
- MRCTC Analytic GeometryДокумент6 страницMRCTC Analytic GeometryJunnar Jay AbañoОценок пока нет
- ParabolaДокумент29 страницParabolaSayantan Chatterjee80% (5)
- MI1026 Calculus IIДокумент3 страницыMI1026 Calculus IIDương Cá ThuОценок пока нет
- Pre-Calculus: Quarter 1 Week 2 Module 2Документ23 страницыPre-Calculus: Quarter 1 Week 2 Module 2Nherwin Ostia100% (1)
- N 4 n+5 N N 6 N: Lim (n+4) Lim 2n 3n 1 Lim 2 N 7 N 4 Lim 3n 2 Lim (2n 1) Lim 0.4 Lim 36 Lim 8 Lim 12n+7 11 8nДокумент11 страницN 4 n+5 N N 6 N: Lim (n+4) Lim 2n 3n 1 Lim 2 N 7 N 4 Lim 3n 2 Lim (2n 1) Lim 0.4 Lim 36 Lim 8 Lim 12n+7 11 8nkitty helloОценок пока нет
- 2 - Matrices and TensorsДокумент8 страниц2 - Matrices and Tensorsamd mhmОценок пока нет
- Bum2123 Applied Calculus S2 0818Документ6 страницBum2123 Applied Calculus S2 0818Deisigan ManiОценок пока нет
- Example of Cambridge Lectures CatalogueДокумент11 страницExample of Cambridge Lectures CataloguesiddhantОценок пока нет
- Course Syllabus T1 2021 MATH 206 enДокумент3 страницыCourse Syllabus T1 2021 MATH 206 enAmal Al-attasОценок пока нет
- C3 Integration PDFДокумент5 страницC3 Integration PDFRokonuddin AhmedОценок пока нет
- Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces YamadaДокумент327 страницDifferential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces Yamadaagui100% (2)
- Thesis PDFДокумент76 страницThesis PDFAnthonny Gabryell LimaОценок пока нет
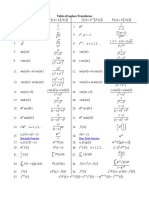
- Laplace Table CompletaДокумент2 страницыLaplace Table CompletaAlexis Gianlvca Rodrigvez PereaОценок пока нет
- Advanced CAD-SurfacesДокумент186 страницAdvanced CAD-SurfacesBarış ÇayОценок пока нет
- 3 1BasicMathДокумент43 страницы3 1BasicMathAliОценок пока нет
- Cylindrical ProjectionДокумент7 страницCylindrical ProjectionJuanapol ManaladОценок пока нет
- Ogievetsky - Karpacz Nonlinear Realization LecturesДокумент12 страницOgievetsky - Karpacz Nonlinear Realization LecturesIrvin MartinezОценок пока нет
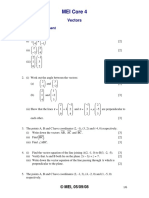
- Vectors CHP Assessment C4 PDFДокумент6 страницVectors CHP Assessment C4 PDFTianlu WangОценок пока нет
- S Nand: Sum To N TermsДокумент35 страницS Nand: Sum To N TermsMahi QuaziОценок пока нет

![The Way To Geometry: [Being Necessary and Usefull for Astronomers, Enginees, Geographers,. Architects, Land-meaters, Carpenters, Sea-men & Etc.]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/297553103/149x198/1b5dac0300/1617233367?v=1)