Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
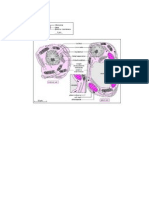
Cell Division
Загружено:
Hanumat SinghИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cell Division
Загружено:
Hanumat SinghАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1
CLLL DIVISICN
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus
into two identical sets in two separate nuclei. It is generally Iollowed immediately by
cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells
containing roughly equal shares oI these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together
deIine the mitotic (M) phase oI the cell cyclethe division oI the mother cell into two daughter
cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell. This accounts Ior approximately
10 oI the cell cycle.
Meiosis is a special type oI cell division necessary Ior sexual reproduction. The cells produced
by meiosis are called gametes. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells.
Whilst the process oI meiosis bears a number oI similarities with the 'liIe-cycle' cell division
process oI mitosis, it diIIers in two important respects:
O The chromosomes in meiosis undergo a recombination which shuIIles the genes producing a
diIIerent genetic combination in each gamete, compared with the co-existence oI each oI the two
separate pairs oI each chromosome (one received Irom each parent) in each cell which results
Irom mitosis.
O The outcome oI meiosis is Iour (genetically unique) haploid cells, compared with the two
(genetically identical) diploid cells produced Irom mitosis.
10
11
1
1
Ml1CSlS CLLL ulvlSlCn
1
1
Ml1CSlS CLLL ulvlSlCn
1
MLlCSlS CLLL ulvlSlCn
1
1
1
0
1
Вам также может понравиться
- Transport PhenomenaДокумент7 страницTransport PhenomenaDolly PriyaОценок пока нет
- Transport Phenomena TP O6Документ4 страницыTransport Phenomena TP O6Hanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- Transport Phenomena TP 06-07Документ7 страницTransport Phenomena TP 06-07Hanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- Structure and Function of Bio MoleculesДокумент79 страницStructure and Function of Bio MoleculesHanumat Singh50% (2)
- Ast Paper 6-7Документ3 страницыAst Paper 6-7Hanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- Regulation of Gene ExpressionДокумент5 страницRegulation of Gene ExpressionHanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- Question Bank Ncer1Документ8 страницQuestion Bank Ncer1Hanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- Ncer Question PaperДокумент3 страницыNcer Question PaperHanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- MitochondriaДокумент10 страницMitochondriaHanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- Stem CellДокумент8 страницStem CellHanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentДокумент3 страницыNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentHanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- Endoplasmic ReticulumДокумент3 страницыEndoplasmic ReticulumHanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- Introduction To DNA StructureДокумент13 страницIntroduction To DNA StructureHanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- Safety of Biotechnology FoodДокумент5 страницSafety of Biotechnology FoodHanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- Gregor MendelДокумент5 страницGregor MendelHanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- Introduction of Genetic EngineeringДокумент6 страницIntroduction of Genetic EngineeringHanumat Singh100% (1)
- ETHICAL ISSUE in BiotechnologyДокумент4 страницыETHICAL ISSUE in BiotechnologyHanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- DNA and Genomic LibraryДокумент2 страницыDNA and Genomic LibraryHanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- Enzyme TechnologyДокумент3 страницыEnzyme TechnologyHanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Technology: Proteins Catalyze Increase The Rates Chemical Reactions Molecules Substrates Products Biological CellДокумент20 страницEnzyme Technology: Proteins Catalyze Increase The Rates Chemical Reactions Molecules Substrates Products Biological CellHanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyДокумент5 страницCentral Dogma of Molecular BiologyHanumat Singh100% (1)
- Diagram of CellДокумент1 страницаDiagram of CellHanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- DNA FingerprintingДокумент8 страницDNA FingerprintingHanumat SinghОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)