Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Metronidazole Drug Study
Загружено:
Jessica Christine Datuin GustiloИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Metronidazole Drug Study
Загружено:
Jessica Christine Datuin GustiloАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
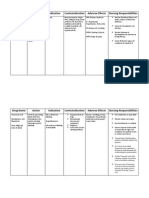
VIII.
DRUG STUDY
Metronidazole Classification: antiinfective; antitrichomonal; amebicide; antibiotic
Indication: Metronidazole is an antibiotic effective against anaerobic bacteria and certain parasites. Anaerobic bacteria are singlecelled, living organisms that thrive in environments in which there is little oxygen (anaerobic environments) and can cause disease in the abdomen (bacterial peritonitis), liver (liver abscess), and pelvis (abscess of the ovaries and the Fallopian tubes). Metronidazole selectively blocks some of the functions within the bacterial cells and the parasites resulting in their death. Adverse effects: Common adverse drug reactions (1% of patients) associated with systemic metronidazole therapy include: nausea, diarrhea, and/or metallic taste in the mouth. Intravenous administration is commonly associated with thrombophlebitis. Infrequent adverse effects include:hypersensitivity reactions (rash, itch, flushing, fever), headache, dizziness, vomiting, glossitis, stomatitis, dark urine, and/or paraesthesia. High doses and/or long-term systemic treatment with metronidazole is associated with the development of leukopenia, neutropenia, increased risk of peripheral neuropathy and/or CNS toxicity.
Mechanism of action: Metronidazole, taken up by diffusion, is selectively absorbed by anaerobic bacteria and sensitive protozoa. Once taken up by anaerobes, it is non-enzymatically reduced by reacting with reduced ferredoxin, which is generated by pyruvate oxido-reductase. This reduction causes the production of toxic products to anaerobic cells, and allows for selective accumulation in anaerobes. The metronidazole metabolites are taken up into bacterial DNA, and form unstable molecules. This function only occurs when metronidazole is partially reduced, and because this reduction
usually happens only in anaerobic cells, it has relatively little effect upon human cells or aerobic bacteria.
Nursing Implications: Assessment & Drug Effects Discontinue therapy immediately if symptoms of CNS toxicity develop. Monitor especially for seizures and peripheral neuropathy (e.g., numbness and paresthesia of extremities). Lab tests: Obtain total and differential WBC counts before, during, and after therapy, especially if a second course is necessary. Monitor for S&S of sodium retention, especially in patients on corticosteroid therapy or with a history of CHF. Monitor patients on lithium for elevated lithium levels. Report appearance of candidiasis or its becoming more prominent with therapy to physician promptly. Repeat feces examinations, usually up to 3 mo, to ensure that amebae have been eliminated. Patient & Family Education Adhere closely to the established regimen without schedule interruption or changing the dose. Refrain from intercourse during therapy for trichomoniasis unless male partner wears a condom to prevent reinfection. Have sexual partners receive concurrent treatment. Asymptomatic trichomoniasis in the male is a frequent source of reinfection of the female. Do not drink alcohol during therapy; may induce a disulfiramtype reaction. Avoid alcohol or alcohol-containing medications for at least 48 h after treatment is completed. Urine may appear dark or reddish brown (especially with higher than recommended doses). This appears to have no clinical significance. Report symptoms of candidal overgrowth: Furry tongue, color changes of tongue, glossitis, stomatitis; vaginitis, curdlike, milky vaginal discharge; proctitis. Treatment with a candidacidal agent may be indicated. Do not breast feed while taking this drug.
Вам также может понравиться
- Generic NameДокумент2 страницыGeneric NameMichael PalmaОценок пока нет
- Sbi Afi 2012Документ48 страницSbi Afi 2012Moneylife FoundationОценок пока нет
- A Drug Study On Evening Primrose OilДокумент5 страницA Drug Study On Evening Primrose OilAlexis Khalyl Y. MontejoОценок пока нет
- Diphenhydramine HydrochlorideДокумент1 страницаDiphenhydramine Hydrochloridegita24203965100% (1)
- Drill Bit Classifier 2004 PDFДокумент15 страницDrill Bit Classifier 2004 PDFgustavoemir0% (2)
- HeparinДокумент4 страницыHeparinapi-3797941100% (2)
- Cebu Normal University College of Nursing: Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыCebu Normal University College of Nursing: Drug StudyNiño Naryana Luke PanchoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study MetronidazoleДокумент1 страницаDrug Study MetronidazoleSarah Benjamin33% (3)
- Volleyball Unit PlanДокумент4 страницыVolleyball Unit Planapi-214597204Оценок пока нет
- Drug - Study VENTOLINДокумент1 страницаDrug - Study VENTOLINahrhicxОценок пока нет
- PiperacillinДокумент3 страницыPiperacillinmyer pasandalanОценок пока нет
- Writing Short StoriesДокумент10 страницWriting Short StoriesRodiatun YooОценок пока нет
- DiphenhydramineДокумент1 страницаDiphenhydramineYanejoulce SacanleОценок пока нет
- Czarina Drug Study JuneДокумент20 страницCzarina Drug Study JuneNicoh AvilaОценок пока нет
- CONZACEДокумент2 страницыCONZACEDanielle Desiree RamasОценок пока нет
- Vastarel MRДокумент1 страницаVastarel MRianecunar100% (2)
- Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыDrug StudyJames Michael BalicocoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentДокумент1 страницаDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloe100% (1)
- Fe SO4Документ3 страницыFe SO4CarmellaDawnОценок пока нет
- Definition Nature and Scope of Urban GeographyДокумент4 страницыDefinition Nature and Scope of Urban Geographysamim akhtarОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - Zinc DropsДокумент3 страницыDrug Study - Zinc DropsAlexa Lexington Rae ZagadoОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент6 страницDrug StudyJenivic Empig PuedanОценок пока нет
- Penicillin G Benzathine-Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыPenicillin G Benzathine-Drug StudyDaisy Palisoc50% (4)
- HydroxyureaДокумент2 страницыHydroxyureaBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Welding and Heat Treatment Requirements For Equipment and PipingДокумент34 страницыWelding and Heat Treatment Requirements For Equipment and Pipingonur gunesОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент7 страницDrug StudyRowland PascuaОценок пока нет
- MultivitaminsДокумент2 страницыMultivitaminsOrpheus Francisco100% (2)
- CefepimeДокумент2 страницыCefepimeMae Ann Bueno CastillonОценок пока нет
- Drug Study CloxacillinДокумент2 страницыDrug Study CloxacillinKen Ancheta Lagayada33% (3)
- Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыDrug Studymike_steven12Оценок пока нет
- Tetracycline HCL Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыTetracycline HCL Drug StudyCheezy BreadОценок пока нет
- The Challenge of Managing Tendinopathy in Competing AthletesДокумент7 страницThe Challenge of Managing Tendinopathy in Competing AthletesMichele MarengoОценок пока нет
- MetronidazoleДокумент2 страницыMetronidazolehauteanicoleОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент7 страницDrug StudyJoseph Angelo Fortuna CarmonaОценок пока нет
- MultivitaminДокумент1 страницаMultivitaminKatie McPeek88% (8)
- Paracetamol Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыParacetamol Drug StudyDennis Nyambane MomanyiОценок пока нет
- Senna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeДокумент2 страницыSenna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeTempoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study of ChloramphenicolДокумент3 страницыDrug Study of Chloramphenicolcasimir1128Оценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыDrug StudyFloribelle SamaniegoОценок пока нет
- Silvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)Документ1 страницаSilvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)EОценок пока нет
- Sucralfate PDFДокумент2 страницыSucralfate PDFJoshua Christian Penggele100% (1)
- Drug Study in PneumoniaДокумент17 страницDrug Study in PneumoniaKara Kathrina FuentesОценок пока нет
- MultivitaminДокумент1 страницаMultivitaminJesrel DelotaОценок пока нет
- Drug Study Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing InterventionsДокумент5 страницDrug Study Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing InterventionsYvonne AgathaОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolДокумент1 страницаDrug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolmikErlh100% (2)
- PnssДокумент2 страницыPnssFrances Oscar GaviolaОценок пока нет
- Drug Study CefuroximeДокумент2 страницыDrug Study CefuroximeDave Michael GeliОценок пока нет
- SilgramДокумент6 страницSilgramJacqueline SweetОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - HYDROCORTISONE, DIAZEPAM, DIGOXIN EtcДокумент6 страницDrug Study - HYDROCORTISONE, DIAZEPAM, DIGOXIN Etc'jmark FranciaОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыDrug StudySunshine Jaranilla0% (1)
- MetoclopramideДокумент3 страницыMetoclopramideapi-3797941100% (1)
- CiticolineДокумент1 страницаCiticolineHarvey BanagОценок пока нет
- Tramadol HCLДокумент4 страницыTramadol HCLCherrylyn FerrerОценок пока нет
- Acetaminophen ParacetamolДокумент1 страницаAcetaminophen ParacetamolAyeОценок пока нет
- DiphenhydramineДокумент6 страницDiphenhydramineAndrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- LevofloxacinДокумент2 страницыLevofloxacinMuhammad ArsalanОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыDrug StudyDanica AbayaОценок пока нет
- Ketorolac Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыKetorolac Drug StudyRic VelascoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study MetronidazoleДокумент2 страницыDrug Study MetronidazoleJha NetОценок пока нет
- Levothyroxine SodiumДокумент3 страницыLevothyroxine Sodiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- NitrofurantoinДокумент3 страницыNitrofurantoinapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- DemerolДокумент1 страницаDemerolCassie100% (1)
- AlgesiaДокумент1 страницаAlgesiaSaf DicamОценок пока нет
- Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesДокумент5 страницDrug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengОценок пока нет
- Patient-Centered Drug Study/ AnalysisДокумент2 страницыPatient-Centered Drug Study/ AnalysisNiksОценок пока нет
- Pharmaco 1Документ10 страницPharmaco 1Joyce Blancaflor LoganОценок пока нет
- Principles in UTIДокумент36 страницPrinciples in UTIMaydhista PoetriОценок пока нет
- 5s Lean ToolДокумент4 страницы5s Lean ToolJessica Christine Datuin GustiloОценок пока нет
- ISMP List of Confused Drugs NamesДокумент0 страницISMP List of Confused Drugs NamesFlorentina Endah WellingОценок пока нет
- Treatment Mod Ali TiesДокумент5 страницTreatment Mod Ali TiesJessica Christine Datuin GustiloОценок пока нет
- Appendectomy O.R. Write UpДокумент11 страницAppendectomy O.R. Write UpJessica Christine Datuin GustiloОценок пока нет
- Loch ChildrenДокумент4 страницыLoch ChildrenLauro De Jesus FernandesОценок пока нет
- NCP81205Документ1 страницаNCP81205Tom TomОценок пока нет
- Piezoelectric-Material Based Energy Harvesting Device.Документ29 страницPiezoelectric-Material Based Energy Harvesting Device.jobert100% (1)
- WHITE TOWN GROUP-4 FinalДокумент112 страницWHITE TOWN GROUP-4 Finalaswath manojОценок пока нет
- Module 1Документ64 страницыModule 1Jackyson RajkumarОценок пока нет
- Hotel Voucher: Itinerary ID Hotel Santika Taman Mini Indonesia IndahДокумент2 страницыHotel Voucher: Itinerary ID Hotel Santika Taman Mini Indonesia IndahSyukron PribadiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7odeДокумент29 страницChapter 7odeRoberto NascimentoОценок пока нет
- FO - Course Transition Info - Acknowledgement - SIT50422 - Dip Hospitality Management - V1Документ2 страницыFO - Course Transition Info - Acknowledgement - SIT50422 - Dip Hospitality Management - V1nitesh.kc06Оценок пока нет
- AC MachinesДокумент32 страницыAC Machinesjoeney guardiarioОценок пока нет
- A Review On Different Yogas Used in The Management of Mandali Damsa Vrana W.S.R. To KriyakaumudiДокумент11 страницA Review On Different Yogas Used in The Management of Mandali Damsa Vrana W.S.R. To KriyakaumudiTiya TiwariОценок пока нет
- Sample Spec For AWWA HDPE Pipe Fittings 6.02revДокумент6 страницSample Spec For AWWA HDPE Pipe Fittings 6.02revmg4myОценок пока нет
- In Other Words RE Increased by P250,000 (Income Less Dividends)Документ6 страницIn Other Words RE Increased by P250,000 (Income Less Dividends)Agatha de CastroОценок пока нет
- WebMethods System Requirements 8xДокумент7 страницWebMethods System Requirements 8xmaxprinceОценок пока нет
- Victaulic-FP-FireLock Fire-Pac Series 745 PreactionДокумент9 страницVictaulic-FP-FireLock Fire-Pac Series 745 PreactionTấn ĐạtОценок пока нет
- Introductions and Basic Personal Information (In/Formal Communication)Документ6 страницIntroductions and Basic Personal Information (In/Formal Communication)juan morenoОценок пока нет
- Gel Electrophoresis Worksheet Teacher AnswersДокумент3 страницыGel Electrophoresis Worksheet Teacher AnswersChris FalokunОценок пока нет
- Paper Format IJRDTДокумент3 страницыPaper Format IJRDTrock starОценок пока нет
- Classical Encryption TechniqueДокумент18 страницClassical Encryption TechniquetalebmuhsinОценок пока нет
- Al Multaqaa Presentation v2Документ22 страницыAl Multaqaa Presentation v2Hasaan WaheedОценок пока нет
- Bubble Deck SlabДокумент29 страницBubble Deck SlabJhimy Rusbel Gutierrez YanapaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Mine Ventialtion ProblemДокумент3 страницыChapter 3 Mine Ventialtion ProblemfahimОценок пока нет
- Review Problems On Gas TurbineДокумент9 страницReview Problems On Gas TurbinejehadyamОценок пока нет
- Presentation 1Документ22 страницыPresentation 1AILYN PECASALESОценок пока нет