Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Pechay Production Guide
Загружено:
Julie Anne Uy AutenticoИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Pechay Production Guide
Загружено:
Julie Anne Uy AutenticoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Pechay Production Guide
Introduction
Pechay (Brassica rapa L. cv group Pak Choi) is an erect, biennial herb, cultivated as an annual about 15-30 cm tall in vegetative stage. Ovate leaves are arranged spirally and spreading. The petioles are enlarged and grow upright forming a subcylindrical bundle. Inflorescence is a raceme with pale yellow flowers. Seeds are 1 mm in diameter and are reddish to blackish brown in color. Uses and Nutritional Value Pechay is used mainly for its immature, but fully expanded tender leaves. The succulent petioles are often the preferred part. It is used as main ingredient for soup and stir-fried dishes. In Chinese cuisine, its green petioles and leaves are also used as garnish.
Each 100 g fresh edible portion contains:
________________________________________ Nutrient Amount ________________________________________ Water 93.0 g Protein 1.7 g Fat 0.2 g Carbohydrates 3.1 g Fiber 0.7 g Ash 0.8 g B-carotene 2.3 g Vitamin C 53.0 mg Calcium 102.0 mg Phosphorus 46.0 mg Iron 2.6 mg Energy Value 86.0 kJ Production Management Varieties Black Behi; Hari Digma; Shin Kang Gengis Khan; Shanhai No. 2 Climatic and Soil Requirements
Pechay can be grown from low to mid elevations throughout the year. Production is best, however, during the dry season in sandy to clay loam soil, with a pH of 5.5-6.5. Planting A1-ha production area requires kg seeds. Pechay can either be sown directly in soil or transplanted. Direct seeding is carried out by broadcasting or by sowing in rows. Cover seeds to a depth of about 1 cm by raking or spreading additional topsoil. Water immediately after sowing. Plant spacing should be 10 cm between plants and 20 cm between rows. If transplanted, sow seeds initially in seedbeds. Transplant seedlings 2-3 weeks after sowing at a distance of 10 cm between plants and 20 cm between rows. Transplant preferably in the afternoon and water immediately. Mulch with grass clippings or rice straw. Fertilization Apply seedlings with starter solution using urea (46-0-0) at the rate of 2 tbsp/gal of water. Side-dress along the rows at the rate of 1 tbsp/plant one week after transplanting. Pest and Disease Management Damping-off, soft rot and clubroot are the most important diseases of pechay, while diamondback moth and aphids are the major insect pests. Spraying hot pepper extract can control these pests. When seedlings begin to wilt, reduce watering immediately. Uproot and burn disease-infected plants to prevent spread of diseases. Cultivation is also necessary to minimize weeds. Harvesting Harvest as early as three weeks after planting or between 30-40 days after sowing. Harvest preferably in the afternoon to minimize postharvest losses. Upon harvesting, wash the plants, trim old leaves and remove roots. Grade according to size and quality, and pack in strong rigid containers with holes at the sides to allow aeration. Pack with the base of the plant to the sides of the baskets. Maintain turgidity by lining the basket with paper.
Costs and Return Analysis Per Hectare ITEMS I. VARIABLE COSTS A. Labor (P150/MD) Plowing AMOUNT (P) P 36,635 1,500
Harrowing Bedding Manure application (10 MD) Planting (10 MD) Fertilization (2x) (4MD) Irrigation (16 MD) Weeding (2X) (20 MD) Spraying (8 MD) Harvesting (8 MD) Postharvest operations(8MD) Sub-total Materials Seeds (3 kg/ha) Animal manure (10 t) Fertilizer (46-0-0) (4 bags) Fuel & Oil Miscellaneous Sub-total
1,000 1,500 1,500 1,500 600 2,400 3,000 1,200 1,200 1,200 16,600 675 10,000 1,860 2,500 5,000 20,035
II. FIXED COSTS 5,423 Land rental 3,000 Depreciation 5 pcs. Scythe (1 yr) 38 2 pcs. Hoe ( 3 yrs) 50 2 pcs. Shovel (3 yrs) 85 2 knapsack sprayers (5 yrs) 250 Interest on Loans at 20% int. p.a. 2,000 TOTAL COSTS 42,058 GROSS INCOME a 50 ,000-75,000 NET INCOME 7,942 32,942
Вам также может понравиться
- Better Homes and Gardens Recipes For EntertainingДокумент132 страницыBetter Homes and Gardens Recipes For EntertainingKenneth100% (4)
- BulbДокумент4 страницыBulbAdrian MausigОценок пока нет
- Quiz ScienceДокумент3 страницыQuiz ScienceKristine May Doydora100% (3)
- Growth and Yield of Bell Pepper Using Organic ManureДокумент9 страницGrowth and Yield of Bell Pepper Using Organic ManureSubic AutoОценок пока нет
- ThesisДокумент62 страницыThesisAlmae Delos Santos Borromeo100% (3)
- IGeography - Map Study - Interpretation and Topographical Map PDFДокумент24 страницыIGeography - Map Study - Interpretation and Topographical Map PDFSurajit DasОценок пока нет
- New Research Reedit by Ms - Gomez in Feb 8,2016Документ37 страницNew Research Reedit by Ms - Gomez in Feb 8,2016Christine Berunio70% (10)
- Growth and yield of pechay applied with different levels of compost fertilizerДокумент4 страницыGrowth and yield of pechay applied with different levels of compost fertilizerSannie Ong MonoyОценок пока нет
- Growth and Yield Performance of Container - Grown Radish (Rhapanus Sativus L.) Applied With FFJ and FPJ CombinationsДокумент20 страницGrowth and Yield Performance of Container - Grown Radish (Rhapanus Sativus L.) Applied With FFJ and FPJ CombinationsRoselyn BritanicoОценок пока нет
- Minus One Element Technique 1Документ16 страницMinus One Element Technique 1Maria Ric50% (2)
- Mien Ruys' 70-year legacy of extraordinary Dutch garden designДокумент4 страницыMien Ruys' 70-year legacy of extraordinary Dutch garden designLucia IfranОценок пока нет
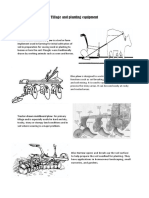
- Tillage and Planting EquipmentДокумент2 страницыTillage and Planting EquipmentJonalyn Manangan100% (2)
- Production of PechayДокумент7 страницProduction of PechayBrunno Cals100% (1)
- Biodynamic AgricultureДокумент3 страницыBiodynamic AgricultureEliane MasonОценок пока нет
- Growth and Yield of Okra 2nd DraftДокумент17 страницGrowth and Yield of Okra 2nd DraftSaheden SalilawanОценок пока нет
- THESIS JUNE 24 EditedДокумент86 страницTHESIS JUNE 24 EditedEdcel John Minglana LamanilaoОценок пока нет
- Banana Peel Extract As A Foliar FertilizerДокумент27 страницBanana Peel Extract As A Foliar FertilizerChing Itim-Isidro0% (1)
- Mondejar, Jr. Arturo BДокумент25 страницMondejar, Jr. Arturo BJulius PrimaОценок пока нет
- Hugas BigasДокумент4 страницыHugas BigasEvan Jordan67% (12)
- Dobi PDFДокумент8 страницDobi PDFRozi AndriansyahОценок пока нет
- PhilRice - Fertilizer CalculationДокумент21 страницаPhilRice - Fertilizer CalculationMichelle Ann SoledadОценок пока нет
- Growth and Yield Perpormance of Pechay FinalДокумент25 страницGrowth and Yield Perpormance of Pechay FinalJaimeh Annabelle100% (2)
- MOET TechnologiesДокумент10 страницMOET TechnologiesPhilRice Field Office CMUОценок пока нет
- Aldrin ResearchДокумент17 страницAldrin ResearchJaimie Del MundoОценок пока нет
- Orca Share Media1488715190585Документ16 страницOrca Share Media1488715190585Edi Wow100% (7)
- 2nd Year Commercial GeographyДокумент2 страницы2nd Year Commercial GeographyFarrukh Saleem17% (6)
- Baby Thesis7Документ38 страницBaby Thesis7jay ar canieteОценок пока нет
- PechayДокумент1 страницаPechayLugabaluga60% (5)
- Banana peels as plant fertilizerДокумент4 страницыBanana peels as plant fertilizerLynlyn BagacinaОценок пока нет
- Growing Pechay (Brassica Napus L.) in Different Organic MulchesДокумент4 страницыGrowing Pechay (Brassica Napus L.) in Different Organic MulchesAdizHares100% (1)
- Effects of Fermented Plant Juice and Fruit Juice On Growth and Yield of Tomato For Sustainable PracticesДокумент1 страницаEffects of Fermented Plant Juice and Fruit Juice On Growth and Yield of Tomato For Sustainable PracticesMitch Angela Claire Villena100% (1)
- Descritive Analysis of Leech Compost Tea and Vermi TeaДокумент49 страницDescritive Analysis of Leech Compost Tea and Vermi TeaPaolo AlcoleaОценок пока нет
- Performance of Zucchini Applied With Fish Amino Acid ConcoctionДокумент50 страницPerformance of Zucchini Applied With Fish Amino Acid ConcoctionVon Carlo Tabuan Lpt100% (1)
- ThesisДокумент60 страницThesisDaisy EgotОценок пока нет
- Review of Related Literature and StudiesДокумент7 страницReview of Related Literature and Studiesjirppy Esparaguera0% (1)
- Chapter 1 DoneДокумент9 страницChapter 1 DoneLemuel L. Madridejos0% (2)
- Effect of Soil, Seaweed and Cow Manure Tea Foliar Fertilizer on Pechay GrowthДокумент18 страницEffect of Soil, Seaweed and Cow Manure Tea Foliar Fertilizer on Pechay GrowthCastor Jr JavierОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 1 IntroductionДокумент4 страницыCHAPTER 1 IntroductionMARK DEVEN LEAL100% (3)
- Application of Vermicast and Fermented Plant Juice On The Growth and Yield Performance of RadishДокумент16 страницApplication of Vermicast and Fermented Plant Juice On The Growth and Yield Performance of RadishJevelyn Mendoza FarroОценок пока нет
- Utilization of Golden Snail As Alternative Liquid Organic Fertilizer Lof On Paddy Farmers in Dairi IndonesiaДокумент5 страницUtilization of Golden Snail As Alternative Liquid Organic Fertilizer Lof On Paddy Farmers in Dairi IndonesiaAlyssa AsuncionОценок пока нет
- Narrative ReportДокумент1 страницаNarrative ReportMariquel FurioОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 LettuceДокумент6 страницChapter 2 LettuceAquilino PagaduanОценок пока нет
- String Bean Performance with Animal ManureДокумент17 страницString Bean Performance with Animal ManureJericho Basmayor SajulanОценок пока нет
- Growth and Yield Performance of Radish Under Fertilizer ApplicationДокумент21 страницаGrowth and Yield Performance of Radish Under Fertilizer ApplicationJanmark Ahig80% (5)
- Paper in Research.... (Rip)Документ58 страницPaper in Research.... (Rip)Mar Jerome Tomas100% (1)
- Bottle Gourd Peel Extract (Lagenaria Siceraria) As An Alternative Liquid Fertilizer For Spring Onion (Allium Fistulosum)Документ14 страницBottle Gourd Peel Extract (Lagenaria Siceraria) As An Alternative Liquid Fertilizer For Spring Onion (Allium Fistulosum)Jenie SoncioОценок пока нет
- Background of The StudyДокумент9 страницBackground of The StudyLuz Anne de GuzmanОценок пока нет
- Production Performance of Native ChickenДокумент6 страницProduction Performance of Native ChickenAileen BaldecasaОценок пока нет
- Republic of The Philippines Western Mindanao State University College of Agriculture Agricultural Sciences Department San Ramon, Zamboanga CityДокумент112 страницRepublic of The Philippines Western Mindanao State University College of Agriculture Agricultural Sciences Department San Ramon, Zamboanga CityJaryll Vhasti P LagumbayОценок пока нет
- Effents of Organic Manure On The Growth and Yield Performance of EggplantДокумент2 страницыEffents of Organic Manure On The Growth and Yield Performance of EggplantMichael GaanoОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER I 1newДокумент35 страницCHAPTER I 1newsabel sardilla100% (1)
- Jessac RepublicaДокумент21 страницаJessac Republicajessa republicaОценок пока нет
- Marketing Losses of Pechay Sold in Public Markets in Davao City - Docx 1Документ6 страницMarketing Losses of Pechay Sold in Public Markets in Davao City - Docx 1Ralph Justin II100% (1)
- Light and Seed Germination ExperimentДокумент21 страницаLight and Seed Germination ExperimentVincent Felix A. Hernandez50% (2)
- Group 1 Chapter 1PDFДокумент24 страницыGroup 1 Chapter 1PDFRai-Dale Lorence L. ArrofoОценок пока нет
- Bottle Gourd: Site Selection and Soil TypeДокумент2 страницыBottle Gourd: Site Selection and Soil TypeJessielito P. AmadorОценок пока нет
- Cucumber Introduction With PageДокумент28 страницCucumber Introduction With PageRandy Pacquiao100% (1)
- Aesa Based Pechay Production - AbdulwahidДокумент17 страницAesa Based Pechay Production - AbdulwahidAnne Xx100% (1)
- Growing Ampalaya (Bitter Gourd) in The Philippines 2Документ29 страницGrowing Ampalaya (Bitter Gourd) in The Philippines 2kishore_hemlani86% (7)
- RRLДокумент19 страницRRLMary Mae Saligan CortezОценок пока нет
- Growth and Yield of Radish Using Fish Amino AcidДокумент28 страницGrowth and Yield of Radish Using Fish Amino AcidPrincess Jhobie Celin DivinagraciaОценок пока нет
- Carbonized Rice Hull (CRH) Silica Extract Efficiency For Yield and Nutrient Uptake of Cucumber - IJB JournalДокумент7 страницCarbonized Rice Hull (CRH) Silica Extract Efficiency For Yield and Nutrient Uptake of Cucumber - IJB JournalInternational Network For Natural SciencesОценок пока нет
- Exer 8 Scientific ReportДокумент8 страницExer 8 Scientific ReportMatthew DenusОценок пока нет
- Pechay Production GuideДокумент23 страницыPechay Production GuideMajorineОценок пока нет
- Crop Descriptio N: CRSC 2 (AB-5L)Документ7 страницCrop Descriptio N: CRSC 2 (AB-5L)Fatima Pontiga LucidoОценок пока нет
- Crop Protection 102.terminal ReportДокумент8 страницCrop Protection 102.terminal ReportRoseJeanAbingosaPernito100% (2)
- Agri Science Form 5 Term 1 2020-2021 Handout 5 Week 3 and 4Документ13 страницAgri Science Form 5 Term 1 2020-2021 Handout 5 Week 3 and 4Ishmael Samuel 4Y ABCCОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Postharvest Handling of Table Eggs Produced in San Jose, Batangas, PhilippinesДокумент13 страницAnalysis of Postharvest Handling of Table Eggs Produced in San Jose, Batangas, PhilippinesJulieta Delos ReyesОценок пока нет
- 823 (August, 2019)Документ830 страниц823 (August, 2019)SalikОценок пока нет
- Agriculturalscience Year09Документ190 страницAgriculturalscience Year09Tom Sun100% (1)
- AKPAKPANДокумент7 страницAKPAKPANErwin SugiartoeОценок пока нет
- Exam Natural ResourceДокумент25 страницExam Natural ResourceZul HMОценок пока нет
- OsirisДокумент5 страницOsirischrisОценок пока нет
- FLAXДокумент13 страницFLAXkavi RAJ SenОценок пока нет
- The PedosphereДокумент21 страницаThe PedosphereDominador MasiragОценок пока нет
- CBLM Oap Detailed CBLMДокумент37 страницCBLM Oap Detailed CBLMReynole DulaganОценок пока нет
- Problems and Solutions for Poultry Farming in a Tropical ClimateДокумент4 страницыProblems and Solutions for Poultry Farming in a Tropical ClimateNeverSad Ej Nadabar100% (2)
- Detailed Lesson Plan Grade 2 English II I. ObjectivesДокумент4 страницыDetailed Lesson Plan Grade 2 English II I. ObjectivesBernard Dayot100% (1)
- Global Wine War 2009: Old vs New Country StrategiesДокумент8 страницGlobal Wine War 2009: Old vs New Country StrategiesserapОценок пока нет
- Tackling The Thesis StatementДокумент4 страницыTackling The Thesis Statementapi-293700871Оценок пока нет
- Undac Disaster Assessment (Chapter e of Undac Manual)Документ36 страницUndac Disaster Assessment (Chapter e of Undac Manual)api-3731030Оценок пока нет
- Ayub Khan Solved QuestionsДокумент11 страницAyub Khan Solved QuestionsSayan Rashdi33% (3)
- What Is This Zero Budget Spiritual FarmingДокумент58 страницWhat Is This Zero Budget Spiritual FarmingUmeshОценок пока нет
- A Spatio - Temporal Analysis of Selected Rainfall Characteristics - A Case Study of Vannathangarai Watershed, Tamil NaduДокумент8 страницA Spatio - Temporal Analysis of Selected Rainfall Characteristics - A Case Study of Vannathangarai Watershed, Tamil NadurameshОценок пока нет
- Report on Land AcquisitionДокумент2 страницыReport on Land AcquisitionJames Adam ZozobradoОценок пока нет
- Load ScheduleДокумент8 страницLoad Schedulezafrikhan875Оценок пока нет
- CuisineДокумент28 страницCuisineGio FabianОценок пока нет
- Asynchronous Activity, RPHДокумент5 страницAsynchronous Activity, RPHBea Bianca Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Cases in Nat ResДокумент57 страницCases in Nat ResDenver Dela Cruz PadrigoОценок пока нет
- Module 6 - Agriculture - BДокумент38 страницModule 6 - Agriculture - BAlyssa AlejandroОценок пока нет