Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Patho 2
Загружено:
David DueñasИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Patho 2
Загружено:
David DueñasАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
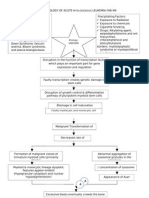
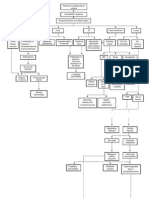
VII.
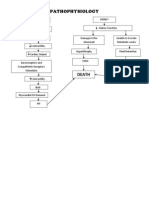
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
ETIOLOGY >Idiopathic
PREDISPOSING FACTORS >Age (60-74 y/o) >Sex (Male) >Family history >Diabetes mellitus
PRECIPITATING FACTORS >Smoking >Alcoholism >Obesity >Sedentary life style >High-fat diet >Hypertension > LDL >HDL >Drug abuse
LDL deposit in the arterial blood vessel wall Inflammation WBC attacks LDL
Development of foam cells Atheroma plaques develops increase growth of plaque Bleeding 28
Formation of thick fibrous cap on the bleeding site blood flow to the brain Anaerobic respirations
Production of lactic acid
Insufficient ATP production Depolarization Electrolyte imbalance
Acidosis Potassium level Manifestation M Muscle weakness U Urine, oliguria, anuria R Respiratory distress D Decrease cardiac contractility E ECG changes R Reflexes, hyperreflexia, or areflexia (flaccid)
Intracellular calcium and glutamate release
Damaging pathways activation >Destruction of the cell membrane >More calcium and glutamate are release >Vasoconstriction >Generation of free radicals Cell ceased to function Penumbra region develop (Ischemic brain tissue)
28
Induction of inflammatory reaction
Accumulation of leukocytes to begin phagocytosis of cell debris Lacunar infarction in the right thalamus
Hemiplegia (L extremities)
Decrease function of the thalamus like sending their axons to the cerebral cortex Failure to generate action impulses potential in the cerebral cortex Cerebral atrophy Decrease response of the cerebrum to bodily function >Motor functions (teary left eye) >Perception of most sensory information (numbness) >Reception and perception of visual input >Olfactory and auditory sensations >Memory
28
Вам также может понравиться
- Pathophysiology: Precipitating FactorДокумент6 страницPathophysiology: Precipitating FactorMark Anthony YabresОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of StrokeДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAy100% (2)
- CKDДокумент3 страницыCKDMarc Lawrence Balderas CAra100% (2)
- Lab Values Chart That Includes What Each Abnormal Might Indicate (Nursing)Документ9 страницLab Values Chart That Includes What Each Abnormal Might Indicate (Nursing)Linsey Bowen75% (8)
- HELLP Concept Map RevisedДокумент1 страницаHELLP Concept Map RevisedwandaОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Fab m4Документ3 страницыPathophysiology of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Fab m4KristaMaeC.Lazo100% (2)
- Process Recording ExampleДокумент7 страницProcess Recording ExampleCheska ت HortelanoОценок пока нет
- Pa Tho PhysiologyДокумент11 страницPa Tho PhysiologyJonathan CuaОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsErrol B. TiozonОценок пока нет
- Client-Based Pathophysiology CVAДокумент1 страницаClient-Based Pathophysiology CVAJeffrey Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Pa Tho Physiology of Diabetes MellitusДокумент3 страницыPa Tho Physiology of Diabetes MellitusPong's Teodoro SalvadorОценок пока нет
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramДокумент3 страницыMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramAbi Habiling100% (3)
- Pathophysilogy Acute Myocardial InfarctionДокумент3 страницыPathophysilogy Acute Myocardial InfarctionronvhadzОценок пока нет
- Atherosclerosis: Kathryn Rennie Bms 1 QEH GatesheadДокумент17 страницAtherosclerosis: Kathryn Rennie Bms 1 QEH Gatesheadkatren29Оценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of StrokeДокумент4 страницыPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyОценок пока нет
- PatoДокумент3 страницыPatoJohn BisnarОценок пока нет
- Diseases and Disorders of The Human Circulatory SystemДокумент18 страницDiseases and Disorders of The Human Circulatory SystemvvОценок пока нет
- Schematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesДокумент3 страницыSchematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesJosett RomanoОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Cardiovascular SystemДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Cardiovascular SystemMon GabrielОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology ASCVDДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology ASCVDAlvheen JoaquinОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Acute Coronary SyndromeДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Acute Coronary SyndromeHarvey MatbaganОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular PathologyДокумент182 страницыCardiovascular PathologyPavan chowdaryОценок пока нет
- PathophysiologyДокумент3 страницыPathophysiologyJosh LazoОценок пока нет
- Pa Tho Physiology of AtherosclerosisДокумент1 страницаPa Tho Physiology of Atherosclerosisjl03Оценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusJerene67% (3)
- Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram and NarrativeДокумент15 страницPathophysiology Schematic Diagram and NarrativeKathrina CraveОценок пока нет
- Diagnostic TestsДокумент3 страницыDiagnostic Testsapi-251516913100% (1)
- NSG 210 Study GuideДокумент25 страницNSG 210 Study GuideyasserОценок пока нет
- Copd Cad Pathophysiology (Revised)Документ3 страницыCopd Cad Pathophysiology (Revised)Israel Soria EsperoОценок пока нет
- CADword - Mam Jelu NogoyДокумент15 страницCADword - Mam Jelu Nogoyhan_angelaОценок пока нет
- Hemolytic AnemiaДокумент6 страницHemolytic AnemiaLupita Yessica Tarigan0% (1)
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureLeng Royo BrionesОценок пока нет
- Hematologymnemonics 151002194222 Lva1 App6891Документ8 страницHematologymnemonics 151002194222 Lva1 App6891padmaОценок пока нет
- Hematologymnemonics 151002194222 Lva1 App6891 PDFДокумент8 страницHematologymnemonics 151002194222 Lva1 App6891 PDFpadmaОценок пока нет
- Myocardial Infarction: Nonmodifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsДокумент4 страницыMyocardial Infarction: Nonmodifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsHearty ArriolaОценок пока нет
- III. Modul 6 - SyokДокумент81 страницаIII. Modul 6 - SyokGrace Noviyanthi SinambelaОценок пока нет
- AtherosclerosisДокумент19 страницAtherosclerosissanjivdasОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of StrokeДокумент7 страницPathophysiology of StrokeCHANDAN RAIОценок пока нет
- ESRD PathophysiologyДокумент2 страницыESRD PathophysiologyMark Ronhel Gallardo PerenalОценок пока нет
- Modifiable Factors: Ix. Pathophysiology (Client-Based)Документ3 страницыModifiable Factors: Ix. Pathophysiology (Client-Based)Charlayne AnneОценок пока нет
- 3 PathophysiologyДокумент4 страницы3 PathophysiologySherlyn KirisakiОценок пока нет
- PathophysiologyДокумент10 страницPathophysiologyAneeza RanaОценок пока нет
- Atherosclerosis and Myocardial InfractionДокумент26 страницAtherosclerosis and Myocardial InfractionElina GОценок пока нет
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyДокумент3 страницыCoronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyElmer Balgos Alinsog50% (4)
- Cirrhosis of LiverДокумент35 страницCirrhosis of LiverShazia Parveen100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of CVA D/T DMДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of CVA D/T DMDanielle Marie SamblacenoОценок пока нет
- KMU Blood DisorderДокумент43 страницыKMU Blood DisorderSHAFIQОценок пока нет
- Path o Physiology Yy YyyДокумент4 страницыPath o Physiology Yy YyyLouisse TadiqueОценок пока нет
- Atherosclerosis & Trombosis Dr. FaturochmanДокумент50 страницAtherosclerosis & Trombosis Dr. FaturochmanPutry RizqiaОценок пока нет
- Types Heart Failure PDFДокумент10 страницTypes Heart Failure PDFHannaОценок пока нет
- Liver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorДокумент22 страницыLiver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorJorie RocoОценок пока нет
- Patofisiologi Jantung: Fika EkayantiДокумент59 страницPatofisiologi Jantung: Fika EkayantiMaytaravikaHasan100% (1)
- Alternative NamesДокумент67 страницAlternative NamespashaОценок пока нет
- Fast Facts: Deficiencia de piruvato quinasa para pacientes y familiares: Una enfermedad genética rara que afecta a los glóbulos rojos Información + Asumir el control = El mejor resultadoОт EverandFast Facts: Deficiencia de piruvato quinasa para pacientes y familiares: Una enfermedad genética rara que afecta a los glóbulos rojos Información + Asumir el control = El mejor resultadoОценок пока нет
- Clinical Signs in Humans and Animals Associated with Minerals, Trace Elements and Rare Earth ElementsОт EverandClinical Signs in Humans and Animals Associated with Minerals, Trace Elements and Rare Earth ElementsОценок пока нет
- Atherosclerosis, (Vascular Thickening) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandAtherosclerosis, (Vascular Thickening) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Reverse and Prevent Heart Disease: Natural Ways to Stop and Prevent Heart Disease, Using Plant-Based Oil-Free Diets (Cure Congestive Heart Failure)От EverandReverse and Prevent Heart Disease: Natural Ways to Stop and Prevent Heart Disease, Using Plant-Based Oil-Free Diets (Cure Congestive Heart Failure)Оценок пока нет
- Quino CaseДокумент9 страницQuino CaseDavid DueñasОценок пока нет
- Position Paper On The 4psДокумент7 страницPosition Paper On The 4psDavid Dueñas100% (5)
- Position Paper On The RH BillДокумент10 страницPosition Paper On The RH BillDavid DueñasОценок пока нет
- Position Paper New Rh971Документ2 страницыPosition Paper New Rh971David DueñasОценок пока нет
- Abscess Case Pre FinalДокумент41 страницаAbscess Case Pre FinalDavid DueñasОценок пока нет
- Sample of Process Recording #2Документ6 страницSample of Process Recording #2David DueñasОценок пока нет