Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Integrating MM with Key SAP Modules
Загружено:
emily668Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Integrating MM with Key SAP Modules
Загружено:
emily668Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
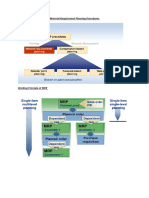
MM Integration with SD-PM-PS-FI-WM-QM modules
Material Management (MM) module is one of the core modules of SAP ERP (formerly known as SAP R/3). MM is highly integrated with other modules such as FICO (Financial Accounting & Controlling), Sales & Distribution (SD), Production Planning (PP), Plant Maintenance (PM), Project System (PS), Warehouse Management (WM), Quality Management (QM), etc. The main areas covered by MM are: Enterprise structure Master Data (vendor and material) Purchasing /procurement Materials planning (MRP and CBP) Inventory Management and Physical Inventory Management Material valuation and Account determination Invoice verification
The sales order (SO) or demand forecast of a finished product from SD module can be considered as a requirement in SAP MM. I have explained the SD business processes at previous article.
If the finished product is available, then it can be delivered to the customer by converting SO to outbound delivery, then perform Goods Issue (GI) transaction based on outbound delivery in inventory management. If the finished product is not available, this requirement can trigger materials planning process in MM. Materials planning in SAP can automatically create procurement proposals, such as planned order. Planned order can be converted into:
Purchase Requisition (PR), if the finished product is procured externally. Production order in PP, if the finished product is produced internally. The production order will be considered as dependent requirement for their components or raw materials. SAP will determine these dependent requirements by using the information from Bill of Materials (BOM) of finished product. These dependent requirements will also trigger materials planning for the components that will create planned order of the components.
In addition, materials planning can also create purchase requisition directly as a procurement proposal (no planned order). The maintenance order (from PM) or network activity (from PS) can also create:
PR of material/service that is procured externally, or Reservation of the stock material. If the stock of material is available then the reservation item can be issued with GI transaction in Inventory Management. If its not available, the reservation (which can be considered as requirement) can be processed by materials planning to create procurement proposals, such as planned order that can be converted to PR or production order.
The PR will be processed by purchasing/procurement department with MM module to be a purchase order (PO). Based on the PO, the vendor will deliver the material/service. Then it will be received in Inventory Management with Goods Receipt (GR) transaction.
If the material received is finished product, we can deliver it to the customer by converting SO to outbound delivery, then perform GI transaction in inventory management. If the material is component or raw material, we can use it in production order to produce the finished product with GI to production order transaction. When the finished product has been produced, we can perform the GR to production order transaction in inventory management. Then, we can deliver it to the customer by converting SO to outbound delivery, and then perform GI transaction in inventory management.
The vendor that delivered the material/service based on PO, will send their invoice to the responsible person in the company. Then, he/she will perform the Invoice Receipt (IR) transaction in MM. Based on the IR transaction; the finance department will process the payment in FI module.
The GR, GI, and other transactions in Inventory Management can be linked in details to the WM module. In WM module, we can maintain material stock at a level that more detail (which is storage bin) than MM module (which is storage location). We can store the same materials at several storage bins in a storage location. With QM, we can copy quality master data, such as certificate required, of a material that ordered in a PO, so the vendor will provide it. When we post GR transaction, we can post it to quality inspection stock. We can give a score/quality level to the material that delivered by vendor. The GR and GI transactions in inventory management also trigger the accounting journals in FI module that in a real-time basis update the company financial reports such as Balance Sheet and Profit & Loss Statement. The budgeting in PS can also be linked to the PR and PO in MM to keep that the total value (price) in PR and PO does not exceed the budget. SAP MM Process Flow The typical procurement cycle for a service or material consists of the following phases: 1. Determination of Requirements Materials requirements are identified either in the user departments or via materials planning and control. (This can cover both MRP proper and the demand-based approach to inventory control. The regular checking of stock levels of materials defined by master records, use of the order-point method, and forecasting on the basis of past usage are important aspects of the latter.) You can enter purchase requisitions yourself, or they can be generated automatically by the materials planning and control system. 2. Source Determination The Purchasing component helps you identify potential sources of supply based on past orders and existing longer-term purchase agreements. This speeds the process of creating requests for quotation (RFQs), which can be sent to vendors electronically via SAP EDI, if desired. 3. Vendor Selection and Comparison of Quotations The system is capable of simulating pricing scenarios, allowing you to compare a number of different quotations. Rejection letters can be sent automatically. 4. Purchase Order Processing The Purchasing system adopts information from the requisition and the quotation to help you create a purchase order. As with purchase requisitions, you can generate Pos yourself or have the system generate them automatically. Vendor scheduling agreements and contracts (in the SAP System, types of longer-term purchase agreement) are also supported. 5. Purchase Order Follow-Up The system checks the reminder periods you have specified and - if necessary - automatically prints
reminders or expediters at the predefined intervals. It also provides you with an up-to-date status of all purchase requisitions, quotations, and purchase orders. 6. Goods Receiving and Inventory Management Goods Receiving personnel can confirm the receipt of goods simply by entering the Po number. By specifying permissible tolerances, buyers can limit over- and under deliveries of ordered goods. 7. Invoice Verification The system supports the checking and matching of invoices. The accounts payable clerk is notified of quantity and price variances because the system has access to PO and goods receipt data. This speeds the process of auditing and clearing invoices for payment SAP SD business process In the previous article we have explained about the relationship between SAP SD module with SAP FICO, MM, PP, and WM modules. In this article we will explain more about the general business processes covered by SD and other related modules, which are:
Pre-sales activities When a client (existing customer or new customer) asks or requests information (can be through a phone call, an email, or a Request For Quotation (RFQ) document) about the products or services he needs, the sales personnel can input that request into SAP SD module by creating an Inquiry document.
In SD module, an Inquiry is an internal document that records the information about request from prospective customer for internal use only. In an inquiry, we record some information such as: which customer that request information, what products or services customer needs, how many products or services customer needs, etc. By creating inquiry, we can reduce the sales opportunity lost, especially when we need some extra time or procedures before we can reply the customer request. If we can immediately reply the customer request (if we have a standard products or services that the price and other condition are fixed), we dont need the inquiry document, we can just create a Quotation document to reply the customers request. But if we cant, we should create an Inquiry document, so when we have determined the price and other condition to be offered to the customer, we can create a Quotation document that refers to the inquiry document. We can create Inquiry with VA11 t-code. In SD module, a Quotation is a document that legally attached for us who issued it, that contains information about the offering to the customer, such as: which customer that been offered, what and how many products or services that been offered to the customer, how much the price of the
products or services, when the delivery date of the products or services, how the term of payment that been offered to the customer, the validity date of the offering, etc. A Quotation can be created by referring to the Inquiry document (if any) or not, depends on the business scenario defined. We can create Quotation with VA21 t-code. From the above explanation, it is clear what the differences between Inquiry and Quotation in SD module are. Both of them are SD document in pre-sales activities. Sales Order processing After we send the quotation to the customers, they will do their own purchasing procedure to determine from where they will purchase the products or services. If needed, they may negotiate with us about our quotation in terms of price, terms of payment, delivery date, or something else. We may send an updated quotation based on the negotiation. If they decide to purchase the material or service from us, they will send us a Purchase Order (PO). Then we create a Sales Order (SO) that refers to the Quotation sent to the customers before. We can put the customers PO number in our SO. Depends on business scenario and configuration, in SAP R/3 system we can also create an SO without referring to a Quotation. For example if we have a products or services catalog that can be used by customers as reference for their PO. An SO must contain the information of: Customer Materials or services sold to the customer Quantity of materials or services Pricing condition of materials or services Delivery dates Shipping processing, such as the incoterms, etc. Billing processing, such as terms of payment, etc. We can create Sales Order with VA01 t-code.
Inventory Sourcing To fulfill the products requirement from an SO at the required date, we can obtain them by one of these options:
o o o
Taking from Available stock at warehouse, if needed triggering a stock transfer between warehouses. Triggering a production order to produce the products in-house. Triggering a purchasing order to purchase the products from vendor (in case of third-party business transaction).
There is no sales document in these activities. They are done on other modules such as Production Planning (PP) and Material Management (MM).
Shipping Once the products are available at warehouse, the sales personnel can start shipping activities by creating an outbound delivery document (Delivery Order/DO). A DO can be created by referring to an SO. A DO will trigger warehouse personnel to prepare the products. We can create Delivery Order with VL01N t-code. If we use Warehouse Management (WM) module, a DO can trigger a Transfer Order. When the products are ready to be sent, the warehouse personnel posts the Goods Issue (GI) transaction that refers to the DO. The GI transaction will reduce the inventory level of products. We can post the Goods Issue that refers to a DO with VL02N t-code. Then the warehouse personnel sends the products to the customer by transportation mode that has been determined in SO document.
Billing The customer will receive the products at the delivery date promised in SO document. The finance department will generate a billing document and send an invoice form to the customer. The invoice will request the customer to pay the products we have sent at the price condition and terms of payment we have agreed in SO document. We can create Billing document with VF01 t-code.
Вам также может понравиться
- SAP PR Release Strategy Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyОт EverandSAP PR Release Strategy Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- Sap Integration Between MM+SD+PPДокумент17 страницSap Integration Between MM+SD+PPSrikanth MОценок пока нет
- Standard Business Processes in SAP MMДокумент71 страницаStandard Business Processes in SAP MMrole67% (3)
- SAP IS-Retail Interview Questions, Answers, and ExplanationsОт EverandSAP IS-Retail Interview Questions, Answers, and ExplanationsРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (11)
- Sap Integration Between MMДокумент17 страницSap Integration Between MMMuhammad Shakeel Khan100% (1)
- Release Process in SAP MMДокумент9 страницRelease Process in SAP MMsumitjain_25Оценок пока нет
- SAP Enterprise Structure Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyОт EverandSAP Enterprise Structure Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Sap MM SampleДокумент26 страницSap MM SampleJoy VeluОценок пока нет
- Configure Stock Transport OrdersДокумент12 страницConfigure Stock Transport OrdersTasneem Molla100% (3)
- MM WM NotesДокумент37 страницMM WM Notesalwin_sunnyОценок пока нет
- Sap MM Interview QuestionsДокумент3 страницыSap MM Interview QuestionsSrinu Kakollu100% (1)
- Delivery Types in SAP SDДокумент8 страницDelivery Types in SAP SDBalaji_SAPОценок пока нет
- Implementing Integrated Business Planning: A Guide Exemplified With Process Context and SAP IBP Use CasesОт EverandImplementing Integrated Business Planning: A Guide Exemplified With Process Context and SAP IBP Use CasesОценок пока нет
- SAP MM Third Party OrderДокумент25 страницSAP MM Third Party Orderparamjeet588100% (1)
- Influence Factors Account Determination SAP MMДокумент28 страницInfluence Factors Account Determination SAP MMMd Saif100% (1)
- SAP ECC 6.0 Service Order Processing ManualДокумент22 страницыSAP ECC 6.0 Service Order Processing ManualDayanandamurthy100% (2)
- Subcontracting in Purchasing SAP MMДокумент6 страницSubcontracting in Purchasing SAP MMJothi Anandharaman100% (1)
- SAP QM: Quality Management Module OverviewДокумент34 страницыSAP QM: Quality Management Module OverviewAna Luque100% (1)
- RICEFWДокумент10 страницRICEFWBraian ManaguelodОценок пока нет
- SAP Query - User Group Creation: SQ03Документ21 страницаSAP Query - User Group Creation: SQ03Rahul pawadeОценок пока нет
- Sap MM - ASAPДокумент7 страницSap MM - ASAPraoraj78100% (1)
- Enterprise Structure SAP MMДокумент3 страницыEnterprise Structure SAP MMvivekchokshiОценок пока нет
- SAP InterfacingДокумент19 страницSAP InterfacingSharan MathapatiОценок пока нет
- Stock Transfer Plant To PlantДокумент36 страницStock Transfer Plant To Plantbalu4indians100% (1)
- Sap SD Pricing ConditionsДокумент3 страницыSap SD Pricing ConditionsAnand PattedОценок пока нет
- Split ValuationДокумент11 страницSplit ValuationSubbu Reddy100% (1)
- MTS & MtoДокумент4 страницыMTS & MtokalidasmОценок пока нет
- Scrap Sales Order Cycle - SAP SDДокумент2 страницыScrap Sales Order Cycle - SAP SDAnand50% (2)
- Material Requirement Planning ProceduresДокумент15 страницMaterial Requirement Planning Proceduresonlinelearn sapОценок пока нет
- SAP Good Movement Types in SAP MM and SAP WM (With Tables)Документ5 страницSAP Good Movement Types in SAP MM and SAP WM (With Tables)sanjanasingh29100% (1)
- Sap MM Im WM Slides Class EightДокумент124 страницыSap MM Im WM Slides Class EightMd Saif100% (2)
- Sap SD Master Data Training DocumentДокумент39 страницSap SD Master Data Training DocumentSreeram Sreeram100% (2)
- Status Profile Functionality For Sap SD ProfessionalsДокумент7 страницStatus Profile Functionality For Sap SD Professionalskumar_gnb100% (1)
- Sap Sto PDFДокумент4 страницыSap Sto PDFSunny SongОценок пока нет
- MRP PROCEDURESДокумент21 страницаMRP PROCEDURESKrishna Penjarla100% (1)
- ATP PresentationДокумент15 страницATP PresentationHussain MulthazimОценок пока нет
- (An ERP Implementation Company) : (A Brand of Day Orpsol Rivate Imited)Документ8 страниц(An ERP Implementation Company) : (A Brand of Day Orpsol Rivate Imited)mvmbbbОценок пока нет
- s4270-SAP Advanced ATP (aATP) - 2020-4Документ10 страницs4270-SAP Advanced ATP (aATP) - 2020-4董董董Оценок пока нет
- SAP MM Interview Question 1. What Is Valuation Grouping Code in Sap MMДокумент2 страницыSAP MM Interview Question 1. What Is Valuation Grouping Code in Sap MMsachinОценок пока нет
- Sap MM Interview QuestionaireДокумент34 страницыSap MM Interview QuestionaireGadigota Suresh ReddyОценок пока нет
- SAP Logistics Execution (LE) OverviewДокумент2 страницыSAP Logistics Execution (LE) Overviewbiltex100% (1)
- Differences Between IM - WM and EWM - LinkedInДокумент5 страницDifferences Between IM - WM and EWM - LinkedInolivier laroche100% (1)
- Session: Credit Management:: SAP SD - My NotesДокумент25 страницSession: Credit Management:: SAP SD - My Notesiammahi2511100% (1)
- Partner Determination in SAP Sales and DistributionДокумент4 страницыPartner Determination in SAP Sales and DistributionRamesh BalajiОценок пока нет
- Sample Sap PP Business Blueprint Document For Textile CompanyДокумент17 страницSample Sap PP Business Blueprint Document For Textile CompanyKumar Ajit100% (1)
- Sample SD BBPДокумент30 страницSample SD BBProlsonlewisОценок пока нет
- Define Pricing Procedure StepsДокумент3 страницыDefine Pricing Procedure Stepsashokkumar1979Оценок пока нет
- Vendor Return Process in SapДокумент3 страницыVendor Return Process in SapDipak BanerjeeОценок пока нет
- Key data structures for procurementДокумент78 страницKey data structures for procurementPawanDubeyОценок пока нет
- SAP SD Notes & ConfigurationsДокумент20 страницSAP SD Notes & Configurationsvivek singhОценок пока нет
- 101 Examples of How Things Post Pre-Configured ClientДокумент94 страницы101 Examples of How Things Post Pre-Configured Clientrajendrakumarsahu88% (8)
- Sap MM TicketsДокумент9 страницSap MM TicketsSatyajit Sahoo100% (1)
- Project Proposal TemplateДокумент12 страницProject Proposal Templateemily668100% (2)
- ProductCosting Workshop1Документ150 страницProductCosting Workshop1sam100% (3)
- SAP New GL Configuration DocumentsДокумент17 страницSAP New GL Configuration DocumentsansulgoyalОценок пока нет
- Line Item Level Data Extraction For Financial Accounting and ControllingДокумент17 страницLine Item Level Data Extraction For Financial Accounting and Controllingvijayam_44Оценок пока нет
- Quick Response LogisticsДокумент18 страницQuick Response LogisticsPrasad Chandran100% (7)
- Concepts On Oracle SCM PDFДокумент31 страницаConcepts On Oracle SCM PDFAravindAllamОценок пока нет
- VF Corporation Gains Nearly 100% Inventory Accuracy Outfitted With Manhattan SolutionsДокумент2 страницыVF Corporation Gains Nearly 100% Inventory Accuracy Outfitted With Manhattan SolutionsArchana Mahesh MalveОценок пока нет
- Training Template ISO 9001 Ver.2015 Bahasa IndonesiaДокумент29 страницTraining Template ISO 9001 Ver.2015 Bahasa IndonesiaWin Salamsyah LinggaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Solutions - Matching Supply With DemandДокумент13 страницChapter 2 Solutions - Matching Supply With Demanddonutshop100% (1)
- FOB Definition and Shipping Terms of SaleДокумент2 страницыFOB Definition and Shipping Terms of Salepfdr101Оценок пока нет
- Mumbai DabbawalaДокумент22 страницыMumbai DabbawalaPrachiJainОценок пока нет
- Repitive Man-Sap LibraryДокумент15 страницRepitive Man-Sap LibraryPrateek SehgalОценок пока нет
- Iteb G621 256Документ2 страницыIteb G621 256saket reddyОценок пока нет
- Iit Kanpur: MBA 601: Accounting For Management, 3-0-0-4Документ11 страницIit Kanpur: MBA 601: Accounting For Management, 3-0-0-4Anand VamsiОценок пока нет
- Notice: Ocean Transportation Intermediary Licenses: Fastpak Express Corp., Et Al.Документ1 страницаNotice: Ocean Transportation Intermediary Licenses: Fastpak Express Corp., Et Al.Justia.comОценок пока нет
- Case DescriptionДокумент12 страницCase DescriptionAYAN GHOSHОценок пока нет
- Akash Singh Report On Buying Behaviour of Consumer at Big BazaarДокумент117 страницAkash Singh Report On Buying Behaviour of Consumer at Big BazaarAkash SinghОценок пока нет
- Penjelasan Expenditure CycleДокумент22 страницыPenjelasan Expenditure CycleMuhammad Teguh PratiknoОценок пока нет
- Productivity Improvement of Excavator Assembly LineДокумент8 страницProductivity Improvement of Excavator Assembly LineIJRASETPublicationsОценок пока нет
- Material Handling Equipment Selection - New ClassificationДокумент8 страницMaterial Handling Equipment Selection - New ClassificationReda MokhtatarОценок пока нет
- SCM Drivers Ndi Word NdiДокумент5 страницSCM Drivers Ndi Word Ndiernest ngieОценок пока нет
- Evaly's unique ecommerce business model drives rapid growth in BangladeshДокумент3 страницыEvaly's unique ecommerce business model drives rapid growth in BangladeshAli Akand AsifОценок пока нет
- CIF vs FOB DifferencesДокумент9 страницCIF vs FOB DifferencesSadia AfrinОценок пока нет
- Resume S4 HANA UAEДокумент4 страницыResume S4 HANA UAERULER KINGSОценок пока нет
- Apparel Merchandising - 2017 PDFДокумент397 страницApparel Merchandising - 2017 PDFalexandraherepean83% (18)
- MMS - A - BATCH 2019-21-GROUP 3 (SDC - Marico)Документ18 страницMMS - A - BATCH 2019-21-GROUP 3 (SDC - Marico)Zoya KhanОценок пока нет
- Complaints and Claims: Parts of A ComplaintДокумент20 страницComplaints and Claims: Parts of A ComplaintBảo TrúcОценок пока нет
- Distribution ChannelsДокумент15 страницDistribution ChannelsZybel RosalesОценок пока нет
- Review: Midterm I Financial Accounting (2) Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент40 страницReview: Midterm I Financial Accounting (2) Multiple Choice QuestionsC14041159王莫堯Оценок пока нет
- 5 Ijlemr 77730Документ6 страниц5 Ijlemr 77730Rorim PandayОценок пока нет
- XLRI ClockspeedДокумент15 страницXLRI ClockspeedSneha KhaitanОценок пока нет
- Sap MM Role MatrixДокумент12 страницSap MM Role MatrixBijay Agarwal100% (1)
- The Effectiveness of Collaboration Within Supply Chain Management: A Case Study of Adidas GroupДокумент40 страницThe Effectiveness of Collaboration Within Supply Chain Management: A Case Study of Adidas GroupAlhamza AhmedОценок пока нет
- Logistics and Competitive StrategyДокумент63 страницыLogistics and Competitive StrategyChetan ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- A Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsОт EverandA Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (241)
- An Architect's Guide to Construction: Tales from the Trenches Book 1От EverandAn Architect's Guide to Construction: Tales from the Trenches Book 1Оценок пока нет
- Building Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 1От EverandBuilding Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 1Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (3)
- Building Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 2От EverandBuilding Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 2Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsОт EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedОт EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationОт EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (18)
- Civil Engineer's Handbook of Professional PracticeОт EverandCivil Engineer's Handbook of Professional PracticeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- The Complete Guide to Alternative Home Building Materials & Methods: Including Sod, Compressed Earth, Plaster, Straw, Beer Cans, Bottles, Cordwood, and Many Other Low Cost MaterialsОт EverandThe Complete Guide to Alternative Home Building Materials & Methods: Including Sod, Compressed Earth, Plaster, Straw, Beer Cans, Bottles, Cordwood, and Many Other Low Cost MaterialsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialОт EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialОценок пока нет
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressОт EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- The Complete Guide to Building Your Own Home and Saving Thousands on Your New HouseОт EverandThe Complete Guide to Building Your Own Home and Saving Thousands on Your New HouseРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- How to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionОт EverandHow to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Engineering Critical Assessment (ECA) for Offshore Pipeline SystemsОт EverandEngineering Critical Assessment (ECA) for Offshore Pipeline SystemsОценок пока нет
- Field Guide for Construction Management: Management by Walking AroundОт EverandField Guide for Construction Management: Management by Walking AroundРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Woodworking: 25 Unique Woodworking Projects For Making Your Own Wood Furniture and Modern Kitchen CabinetsОт EverandWoodworking: 25 Unique Woodworking Projects For Making Your Own Wood Furniture and Modern Kitchen CabinetsРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (4)
- 1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideОт Everand1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (7)
- Markup & Profit: A Contractor's Guide, RevisitedОт EverandMarkup & Profit: A Contractor's Guide, RevisitedРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (11)
- The E-Myth Contractor: Why Most Contractors' Businesses Don't Work and What to Do About ItОт EverandThe E-Myth Contractor: Why Most Contractors' Businesses Don't Work and What to Do About ItРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (16)
- Estimator's General Construction Manhour ManualОт EverandEstimator's General Construction Manhour ManualРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (20)