Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
19 Solutions
Загружено:
RainierGoИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
19 Solutions
Загружено:
RainierGoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
rozner (jsr958) 019 Ghosh (99438) 1
This print-out should have 22 questions.
Multiple-choice questions may continue on
the next column or page nd all choices
before answering.
Students,
This is your last UTHW (19)for the year
unless you want me to post a couple for the
summer vacation! Your brain may stay active
that way. Anyway, please go over the related
materials from your book and work accord-
ingly. It is due on Wednesday night (9:00
PM) this time due to your fast approaching
tests and AP exams. Good Luck! Mrs. Ghosh
001 10.0 points
Quantities that are conserved in all nuclear
reactions include which of the following?
I. electric charge
II. number of nuclei
III. number of protons
1. II only
2. I, II and III
3. I and III only
4. I only correct
5. II and III only
Explanation:
In nuclear reactions, electric charge is con-
served; in fact, electric charge is conserved in
all 4 known basic interactions in nature.
On the other hand, neither number of nu-
clei nor number of protons is conserved. For
example, in nuclear ssion, a uranium nucleus
is split into two or more nuclei of other ele-
ments. And in decay, the number of protons
in the nucleus is changed also.
Thus, I is the correct statement.
keywords:
002 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points
Complete the following nuclear reactions:
27
13
Al +
4
2
He ? +
30
15
P
1.
1
0
n correct
2.
1
1
H
3.
4
2
He
4.
2
4
Be
5.
10
4
Be
Explanation:
The charge is conserved and the nucleon
number is conserved.
A = 27 + 4 30 = 1
Z = 13 + 2 15 = 0
1
0
? is a neutron:
27
13
Al +
4
2
He
1
0
n +
30
15
P
003 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points
1
0
n + ?
4
2
He +
7
3
Li
1.
2
1
H
2.
10
4
Be
3.
11
5
B
4.
10
5
B correct
5.
12
6
C
Explanation:
A = 4 + 7 1 = 10
Z = 2 + 3 0 = 5
10
5
? is boron:
1
0
n +
10
5
B
4
2
He +
7
3
Li
004 10.0 points
rozner (jsr958) 019 Ghosh (99438) 2
Cobalt 60 is a radioactive source with a half-
life of about 5 years.
After how many years will the activity of a
new sample of cobalt 60 be decreased to
1
8
its
original value?
1. T = 10 years
2. T = 2.5 years
3. It depends on the original amount of
cobalt 60
4. T = 15 years correct
5. T = 5 years
Explanation:
After 5 years, the activity would be reduced
to
1
2
its original value; after 10 years,
1
4
; after
15 years,
1
8
.
005 10.0 points
A muon with a lifetime of 2 10
6
s in its
frame of reference is created in the upper
atmosphere with a velocity of 0.984 c toward
the Earth (where c is the speed of light in
vacuum).
What is the lifetime of the muon, as mea-
sured by an observer on the Earth?
Correct answer: 1.12253 10
5
s.
Explanation:
Let : v = 0.984 c and
t
0
= 2 10
6
s .
The lifetime of the muon as seen by the
earthbound observer will seem greater than
the lifetime seen by an observer moving with
the muon. Using the time dilation equation,
t =
t
0
_
1
v
2
c
2
=
1.12253 10
5
s
_
1 (0.984)
2
= 1.12253 10
5
s .
006 10.0 points
At noon a radioactive sample decays at a
rate of 4,000 counts per minute. At 12:30 p.m.
the decay rate has decreased to 2,000 counts
per minute.
What is the decay rate
d N
dt
at 1:30 p.m.?
1.
d N
dt
= 500 counts per minute correct
2.
d N
dt
= 1, 333 counts per minute
3.
d N
dt
= 1, 000 counts per minute
4.
d N
dt
= 0 counts per minute
5.
d N
dt
= 667 counts per minute
Explanation:
The rate of decay decreased by half from
12:00 p.m. to 12:30 p.m. (dening a half-life
of 30 minutes), so the decay is
1
2
from 12:00 to 12:30 p.m.
1
4
from 12:30 to 1:00 p.m.
1
8
from 1:00 to 1:30 p.m.
and the decay rate is
1
8
(4000 counts/min) = 500 counts/min .
007 10.0 points
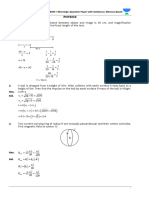
The graph below shows the decay of a sam-
ple of
14
C that initially contained N
0
atoms.
rozner (jsr958) 019 Ghosh (99438) 3
N
0
A B C D E F G H J
N
u
m
b
e
r
o
f
U
n
d
e
c
a
y
e
d
A
t
o
m
s
Time
Decay Plot
Which of the lettered points on the time
axis could represent the half-life of
14
C?
1. C
2. B correct
3. D
4. A
5. E
Explanation:
The half-life of an radioactive sample is the
time it takes for half of the material to decay
into something else. Initially, there were N
0
carbon 14 atoms. At time B, only
N
0
2
atoms
remained. The other half atoms had decayed.
Therefore, the half-life of
14
C is represented
by point B on the time axis.
N
0
N
0
2
A B C D E F G H J
N
u
m
b
e
r
o
f
U
n
d
e
c
a
y
e
d
A
t
o
m
s
Time
Decay Plot
008 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points
A sample of radioactive material is initially
found to have an activity of 132 decays/min.
After 6 d, 1 h, its activity is measured to be
79.5 decays/min.
Calculate the half-life of the material.
Correct answer: 198.22 h.
Explanation:
Let : t
1
= 6 d, 1 h ,
R
0
= 132 decays/min and
R
1
= 79.5 decays/min .
t
1
= (6 d)
24 h
1 d
+ 1 h = 145 h .
R
1
= R
0
e
t
R
1
R
0
= e
t
R
0
R
1
= e
t
=
ln
_
R
0
R
1
_
t
1
,
so the half-life is
1/2
=
ln 2
=
ln 2 T
1
ln
_
R
0
R
1
_
rozner (jsr958) 019 Ghosh (99438) 4
=
(145 h) ln2
ln
_
132 decays/min
79.5 decays/min
_
= 198.22 h .
009 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points
How long (from the initial time) will it take
for the sample to reach an activity level of
15.5 decays/min?
Correct answer: 25.5224 d.
Explanation:
Let : R
2
= 15.5 decays/min .
The time is
t
2
=
1/2
ln2
ln
_
R
0
R
2
_
=
198.22 h
ln 2
ln
_
132 decays/min
15.5 decays/min
_
_
1 d
24 h
_
= 25.5224 d .
010 10.0 points
What is the energy released in the alpha
decay of
238
92
U? The mass of
234
90
Th is 234.044 u,
of
238
92
U 238.051 u, of
4
2
He 4.0026 u and 1 u =
931.5 Mev.
1. 10.5628 Mev
2. 4.0986 Mev correct
3. 2.98764 Mev
4. 1.56298 Mev
5. 0.78109 Mev
6. 7.89735 Mev
Explanation:
Let : m
Th
= 234.044 u ,
m
U
= 238.051 u ,
m
He
= 4.0026 u .
The energy released in the decay
238
92
U
4
2
He +
234
90
Th
is
Q = mc
2
=
_
m
U
(m
He
+m
Th
)
_
c
2
=
_
238.051 u (4.0026 u + 234.044 u)
_
(931.5 Mev/u)
= 4.0986 Mev .
011 10.0 points
What is needed for controlled thermonuclear
reactions to work?
1. All of these correct
2. high density
3. high temperature
4. None of these
5. long time
Explanation:
012 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points
The atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima on
August 6, 1945, released 5 10
13
J of energy
(equivalent to that from 12000 tons of TNT).
Determine the number of
235
92
U nuclei s-
sioned if each
235
U ssion releases 208 MeV of
energy.
Correct answer: 1.5024 10
24
.
Explanation:
Let : E = 5 10
13
J and
ssion energy = 208 MeV.
rozner (jsr958) 019 Ghosh (99438) 5
Suppose each
235
U ssion releases 208 MeV
of energy. Then, the number of nuclei that
must have undergone ssion is
N =
total release
energy per ssion
=
5 10
13
J
(208 MeV)(1.6 10
13
J/MeV)
= 1.5024 10
24
nuclei .
013 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points
Estimate the mass of this atomic bomb.
Correct answer: 0.586197 kg.
Explanation:
Let : m235
U
= 235.044 u
The mass of this number of
235
U atoms is
m =
_
1.5024 10
24
_
(235.044 u) (1.66 10
27
kg/u)
= 0.586197 kg .
keywords:
014 10.0 points
An all-electric home uses approximately
1942 kWh of electric energy per month.
How much uranium-235 would be required
to provide this house with its energy needs for
9 year? (Assume 100% conversion eciency
and 208 MeV released per ssion.)
Correct answer: 8.85216 g.
Explanation:
Let : p = 1942 kWh/month ,
t = 9 year ,
E
fission
= 208 MeV 1.60 10
13
J/Mev
= 3.328 10
11
J , and
m
U
= 235.044 u .
The total energy required for one year is
E =
1942 kWh
1 month
(3.6 10
6
J/kWh)
(12 months/year)
= 8.38944 10
10
J/yr .
The number of ssion events needed will be
N =
E
E
event
=
8.38944 10
10
J/yr
3.328 10
11
J
= 2.52087 10
21
/yr .
So the mass of this number of
235
U atoms is
m = N m
atom
= (2.52087 10
21
/yr) (235.044 u)
(1.66 10
27
kg/u)
1000 g
1 kg
= 0.983574 g/yr .
Therefore, the energy needs for 9 year is
(0.983574 g/yr) (9 year) = 8.85216 g .
keywords:
015 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points
Determine the product of the reaction
7
3
Li +
4
2
He ? + n .
1.
12
6
C
2.
8
4
Be
3.
10
5
B correct
4.
10
4
Be
5.
10
6
C
6.
12
5
B
Explanation:
7
3
C +
4
2
He
10
5
B +
1
0
n
016 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points
Find the Q value of the reaction. The mass of
7
3
Li is 7.016 u, the mass of
4
2
He is 4.0026 u and
the mass of the neutron is 1.00866 u.
rozner (jsr958) 019 Ghosh (99438) 6
1. 5.09873 Mev
2. 32.0987 Mev
3. 123.099 Mev
4. 28.0977 Mev
5. 2.79077 Mev correct
6. 3.09877 Mev
Explanation:
Q = (m) c
2
= (m7
Li
+m4
He
m10
B
m
n
) c
2
= [7.016 u + 4.0026 u 10.0129 u
1.00866 u](931.5 Mev/u)
= 2.79077 Mev .
keywords:
017 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points
The rst known reaction in which the product
nucleus was radioactive (achieved in 1934)
was one in which
27
13
Al was bombarded with
alpha particles. Produced in the reaction were
a neutron and a product nucleus.
What was the product nucleus?
1.
27
14
Si
2.
30
15
P correct
3.
30
13
Al
4.
31
15
P
5.
28
14
Si
6.
26
12
Mg
Explanation:
27
13
Al +
4
2
He n +
30
15
P
018 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points
What was the Q value of reaction?
1. 10.9873 Mev
2. 1.7845 Mev
3. 2.6734 Mev correct
4. 3.5678 Mev
5. 2.0987 Mev
6. 5.0987 Mev
Explanation:
Let : m27
Al
= 26.9815 u ,
m4
2
He
= 4.0026 u ,
m
n
= 1.00866 u , and
m30
P
= 29.9783 u .
Q = mc
2
= (m27
Al
+m4
He
m
n
m30
P
) c
2
= (26.9815 u + 4.0026 u
1.00866 u 29.9783 u)(931.5 Mev/u)
= 2.6734 Mev .
019 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points
Consider nuclear ssion for which the reac-
tion
235
92
U+
1
0
n
138
56
Ba +
95
36
Kr + neutrons + energy
is a good example.
How many free neutrons are in the products
of this reaction?
1. 3 correct
2. 4
3. 2
4. 6
rozner (jsr958) 019 Ghosh (99438) 7
5. 5
Explanation:
In such nuclear reactions, the total baryon
number (the sum of the protons and the neu-
trons) is conserved, as is the total charge.
(235 92) +1 = 144 is the neutron number
before the reaction. In the product, Ba and
Kr have a total neutron number of (138
56) + (95 36) = 141, so the total number of
free neutrons in the product is 144 141 = 3.
020 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points
Which statement is always true for neutron-
induced ssion reactions involving
235
92
U?
I. The end products always include Ba and
Kr.
II. The rest mass of the end products is less
than that of
235
92
U +
1
0
n.
III. The total number of nucleons (protons
plus neutrons) in the end products is less
than that in
235
92
U +
1
0
n.
1. I, II, and III
2. III only
3. II only correct
4. I and III only
5. I and II only
Explanation:
The kinetic energy of the initial (thermal)
neutron is negligible.
Nuclear reactions have many channels (dif-
ferent products), so statement I is false.
The nucleon number is conserved, so state-
ment III is false.
Because of conservation of energy and the
fact that the end products carry kinetic en-
ergy and/or additional energy in terms of
rays (electrons, etc.) and rays (photons),
the rest energy of the product must be less
than that of the initial particles.
021 10.0 points
If an all-electric home uses approximately
1541 kWh of electric energy per month, how
many fusion events described by the reaction
2
1
H +
3
1
H
4
2
He +
1
0
n
would be required to keep this house running
for one year?
Correct answer: 2.36532 10
22
events.
Explanation:
Let : p = 1541 kWh/month ,
t = 1 year ,
m
H2
= 2.0141 u ,
m
H3
= 3.01605 u ,
m
H4
= 4.0026 u , and
m
n
= 1.00866 u .
The energy released in the reaction
2
1
H +
3
1
H
4
2
He +
1
0
n
is
Q = (m) c
2
= [m
H2
+m
H3
m
He4
m
n
] c
2
=
_
2.0141 u + 3.01605 u 4.0026 u
1.00866 u
_
c
2
931.5 MeV/u
c
2
(1.6 10
13
J/MeV)
= 2.81447 10
12
J .
The total energy required for one year is
E =
1541 kWh
1 month
(3.6 10
6
J/kWh)
(12 months/year)
= 6.65712 10
10
J/yr ,
so the number of fusion events needed for one
year is
N =
E
Q
=
6.65712 10
10
J/yr
2.81447 10
12
J
= 2.36532 10
22
/yr .
022 10.0 points
Find the energy released in the fusion reaction
1
1
H +
3
2
He
4
2
He +e
+
+
rozner (jsr958) 019 Ghosh (99438) 8
1. 14.3 MeV
2. 8.5 MeV
3. 20.6 MeV
4. 18.8 MeV correct
5. 10.7 MeV
Explanation:
Let : m1
H
= 1.00782 u/c
2
,
m3
He
= 3.01603 u/c
2
,
m4
He
= 4.0026 u/c
2
, and
m
e
= 0.000549 u/c
2
.
To the reaction for nuclei,
1
1
H +
3
2
He
4
2
He +
0
+1
e +
e
,
we add three electrons to both sides to obtain
1
1
H atom+
3
2
He atom
4
2
He atom+
0
+1
e+
e
.
Then we use the masses of the neutral atoms
to compute
Q = (m)
2
= [m1
H
+m3
He
m4
He
2 m
e
] c
2
=
_
1.00782 u/c
2
+ 3.01603 u/c
2
+4.0026 u/c
2
2 (0.000549 u/c
2
)
c
2
= (0.020154 u) (931.5 MeV/u)
= 18.7735 MeV .
keywords:
Вам также может понравиться
- Multiple choice questions on mechanics, heat and thermodynamicsДокумент21 страницаMultiple choice questions on mechanics, heat and thermodynamicsGodwinОценок пока нет
- Radioactivity - PDFДокумент8 страницRadioactivity - PDFWhite Heart100% (2)
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsОт EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsОценок пока нет
- Physics Stage 3 Exam 2014Документ40 страницPhysics Stage 3 Exam 2014gragon.07Оценок пока нет
- 04Документ25 страниц04Sushil KoiralaОценок пока нет
- 2010 Theoretical Problems IChO42 Official English With AnswersДокумент33 страницы2010 Theoretical Problems IChO42 Official English With AnswersRSLОценок пока нет
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresОт EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- International Chemistry Olympiad 2014 (Problems)Документ80 страницInternational Chemistry Olympiad 2014 (Problems)Science Olympiad Blog100% (7)
- X-Ray Diffraction Modern Experimental Techniques, Seeck, Murphy, 2015 PDFДокумент438 страницX-Ray Diffraction Modern Experimental Techniques, Seeck, Murphy, 2015 PDFAlejandro PuceiroОценок пока нет
- Chemical Kinetics MCQДокумент21 страницаChemical Kinetics MCQParas Thakur67% (3)
- 15 Radio ActivityДокумент7 страниц15 Radio ActivityHasmukh ShahОценок пока нет
- 25 Petrucci10e CSMДокумент25 страниц25 Petrucci10e CSMAlexОценок пока нет
- Homework 1 solutions and nuclear physics problemsДокумент5 страницHomework 1 solutions and nuclear physics problemsIvan SantosОценок пока нет
- Engr-2500u Midterm SolutionsДокумент6 страницEngr-2500u Midterm SolutionsAbdullah AlshihriОценок пока нет
- SEC14 KineticsДокумент16 страницSEC14 KineticsphanthanhhungОценок пока нет
- Olved Xamples: Chapter # 46 The NucleusДокумент18 страницOlved Xamples: Chapter # 46 The NucleusthinkiitОценок пока нет
- Chemical KineticsДокумент8 страницChemical KineticsSnehashis BoseОценок пока нет
- Student Solutions ch00 PDFДокумент7 страницStudent Solutions ch00 PDFSergio Magalhaes FerreiraОценок пока нет
- Jee Main 2017 Question Paper Solutions Physics 2nd AprilДокумент22 страницыJee Main 2017 Question Paper Solutions Physics 2nd AprilAmit SharmaОценок пока нет
- Problem Sheet-Atomic and Nuclear PhysДокумент3 страницыProblem Sheet-Atomic and Nuclear PhysTanjina AkterОценок пока нет
- Nuclear Chemistry Practice ProblemsДокумент16 страницNuclear Chemistry Practice Problemskennethleo69Оценок пока нет
- NCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 13 NucleiДокумент16 страницNCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 13 NucleiVidyakulОценок пока нет
- Numerical AtomsДокумент6 страницNumerical Atomsvishal_kalraОценок пока нет
- Nuclear Energy and Elementary Particles Quick QuizzesДокумент17 страницNuclear Energy and Elementary Particles Quick Quizzesedlover9000Оценок пока нет
- Answers: TEST - 2 (Paper-I)Документ12 страницAnswers: TEST - 2 (Paper-I)ABHIJEET SHARMAОценок пока нет
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 2Документ24 страницыImportant Questions For CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 2PriyanshuОценок пока нет
- Calculate Wave Number for Longest Wavelength Transition in Balmer SeriesДокумент33 страницыCalculate Wave Number for Longest Wavelength Transition in Balmer SeriesKalai VananОценок пока нет
- Chemical KineticsДокумент7 страницChemical Kineticsthinkiit100% (1)
- Co-2 Material MfeДокумент26 страницCo-2 Material MfeAswith ReddyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Structure of Atom: Page No 65Документ48 страницChapter 2 - Structure of Atom: Page No 65BEAST王VIPER GamingОценок пока нет
- Contoh Soal Kenukliran Dan PenyelesaianДокумент9 страницContoh Soal Kenukliran Dan PenyelesaianSiti HannaОценок пока нет
- Radioactive Decay MathematicalДокумент3 страницыRadioactive Decay MathematicalJono WojciechowskiОценок пока нет
- Physics 303K Test 3 SolutionsДокумент11 страницPhysics 303K Test 3 SolutionsbrunosipodОценок пока нет
- JEE-Main-Radioactivity-Previous-Year-Questions-with-Solutions-PDF.docxДокумент6 страницJEE-Main-Radioactivity-Previous-Year-Questions-with-Solutions-PDF.docxJanakiraman SanthoshОценок пока нет
- IPhO 2000Документ26 страницIPhO 2000Gustavo Oliveira SilvaОценок пока нет
- Class 12 - Physics - NucleiДокумент28 страницClass 12 - Physics - NucleiRohit RОценок пока нет
- Physics Morning Shift-1 (30!01!2024) FacultyДокумент7 страницPhysics Morning Shift-1 (30!01!2024) FacultychennareddyvarshithreddyОценок пока нет
- Practice Exam #1Документ9 страницPractice Exam #1Jordan Matias YamsonОценок пока нет
- Nuclear Physics Quick Quizzes ExplainedДокумент18 страницNuclear Physics Quick Quizzes ExplainedAnonymous 8vZnbz6DEОценок пока нет
- 02 Nuclear Chemistry (Part 2)Документ67 страниц02 Nuclear Chemistry (Part 2)Aladha SorianoОценок пока нет
- Physics of Nuclear MedicineДокумент33 страницыPhysics of Nuclear MedicineEssa AliОценок пока нет
- Atomic Structure Assignment-3Документ20 страницAtomic Structure Assignment-3VARSHITHОценок пока нет
- Atomic Structure Type 1Документ28 страницAtomic Structure Type 1kaushik247Оценок пока нет
- 03 - Radioactivity and Nuclear Transformation - Page No. 167Документ6 страниц03 - Radioactivity and Nuclear Transformation - Page No. 167Arvind TiwariОценок пока нет
- PHY 332 Atomic and Nuclear Energy Tutorial QuestionsДокумент3 страницыPHY 332 Atomic and Nuclear Energy Tutorial Questionsemmanuel waekaneОценок пока нет
- 4700 A1 SolutionsДокумент11 страниц4700 A1 SolutionsMaruf MorshedОценок пока нет
- M.sc. - ChemistryДокумент129 страницM.sc. - ChemistryAsim AliОценок пока нет
- Chem Principles 7e ISM Focus 01 Even FINALДокумент26 страницChem Principles 7e ISM Focus 01 Even FINALSelma MeloОценок пока нет
- Exam 3 SolutionsДокумент9 страницExam 3 SolutionsemlfemОценок пока нет
- Material Science and Engineering Ch. 10 SolДокумент72 страницыMaterial Science and Engineering Ch. 10 SolPatrick GibsonОценок пока нет
- Physics M. PalanichamyДокумент3 страницыPhysics M. PalanichamyphysicspalanichamyОценок пока нет
- 12-Ph 19908Документ26 страниц12-Ph 19908Surendra SinghОценок пока нет
- Tutorial Session 3 2010 AnswersДокумент8 страницTutorial Session 3 2010 AnswersNatKrОценок пока нет
- University of London: For Internal Students of Royal HollowayДокумент8 страницUniversity of London: For Internal Students of Royal HollowayPhyo ThihaОценок пока нет
- Page No 462:: (A) Mass of Lithium IsotopeДокумент35 страницPage No 462:: (A) Mass of Lithium Isotopenabil soukОценок пока нет
- Chapter 01Документ19 страницChapter 013112705770Оценок пока нет
- Optics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyОт EverandOptics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Neet 16 - Class XiiДокумент3 страницыNeet 16 - Class XiiSoumya Ranjan NaikОценок пока нет
- Kcet 2016 Answer Key Physics PDFДокумент7 страницKcet 2016 Answer Key Physics PDFLagan TgОценок пока нет
- Goebel AppF ElectronДокумент4 страницыGoebel AppF Electronmdurna2000Оценок пока нет
- PHYS 122 Lecture 4 (Revised)Документ18 страницPHYS 122 Lecture 4 (Revised)BENJAMIN MALUWAZIОценок пока нет
- Interaction of RadiationДокумент54 страницыInteraction of RadiationWayel AmanОценок пока нет
- Math Hiset Ga Sept 2020Документ51 страницаMath Hiset Ga Sept 2020V-academy Maths100% (1)
- New mathematical connections between various solutions of Ramanujan's equations and some parameters of Particle Physics and Cosmology (value of Cosmological Constant). XIII - Michele Nardelli, Antonio NardelliДокумент97 страницNew mathematical connections between various solutions of Ramanujan's equations and some parameters of Particle Physics and Cosmology (value of Cosmological Constant). XIII - Michele Nardelli, Antonio NardelliMichele NardelliОценок пока нет
- FIITJEE Students Excel in JEE Advanced 2016Документ17 страницFIITJEE Students Excel in JEE Advanced 2016AbhijeetОценок пока нет
- Assignment Electricity and Mag.Документ3 страницыAssignment Electricity and Mag.Hafiz IkramaОценок пока нет
- +2 PHYSICS 200 MCQ EM Test WITH Answer Key and Problems Key PDFДокумент25 страниц+2 PHYSICS 200 MCQ EM Test WITH Answer Key and Problems Key PDFRAJA100% (1)
- Rpp2018 Rev KinematicsДокумент11 страницRpp2018 Rev Kinematicsaleacunia87Оценок пока нет
- Kinetic Energy of PhotoelectronsДокумент5 страницKinetic Energy of PhotoelectronsPrajwol ShresthaОценок пока нет
- NUST Computer Science 4Документ42 страницыNUST Computer Science 4ehtashamОценок пока нет
- Photoelectric EffectДокумент8 страницPhotoelectric EffectAshОценок пока нет
- 2nd PUC Question Papers Physics 2006-2010Документ21 страница2nd PUC Question Papers Physics 2006-2010Mohan Kumar P100% (1)
- General Physics 2 4Q Week 9.pubДокумент13 страницGeneral Physics 2 4Q Week 9.pubShane June DemetrialОценок пока нет
- PhysicsДокумент126 страницPhysicsKishanJhaОценок пока нет
- NPL HistoryДокумент24 страницыNPL HistoryMauroОценок пока нет
- 14Документ6 страниц14MEOW41Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Quantum Physics StudentДокумент3 страницыChapter 6 Quantum Physics StudentKhairul AznizamОценок пока нет
- 1.atomic StructureДокумент25 страниц1.atomic StructureP. E. I. AcademicsОценок пока нет
- FSRG1 Term Exam Test 1 Physics QuestionsДокумент12 страницFSRG1 Term Exam Test 1 Physics QuestionsDEADSHOT GAMINGОценок пока нет
- Allen: Test Paper of Jee (Main) Examination - 2019Документ4 страницыAllen: Test Paper of Jee (Main) Examination - 2019AKОценок пока нет
- Moving Charge in A Magnetic FieldДокумент3 страницыMoving Charge in A Magnetic FieldEntertainmentОценок пока нет
- Basic Nuclear CBRДокумент9 страницBasic Nuclear CBRAris JuliantoОценок пока нет
- Basic Radiation Physics: This Set of 194 Slides Is Based On Chapter 1 Authored by E.B. Podgorsak of The IAEA PublicationДокумент97 страницBasic Radiation Physics: This Set of 194 Slides Is Based On Chapter 1 Authored by E.B. Podgorsak of The IAEA PublicationTiti PurwatiОценок пока нет
- Cblephpu 20Документ6 страницCblephpu 20Mahadev SharmaОценок пока нет
- CHEMISTRY-24-12 - 11th (PQRS) Code-A WAДокумент12 страницCHEMISTRY-24-12 - 11th (PQRS) Code-A WARaju SinghОценок пока нет