Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
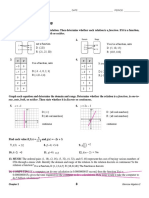
YMS Ch7: Random Variables AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. Molesky
Загружено:
InTerp0olАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
YMS Ch7: Random Variables AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. Molesky
Загружено:
InTerp0olАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
YMS Ch7: Random Variables
AP Statistics at LSHS
Mr. Molesky
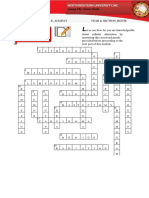
1
D
2
C O N T I N U O U S
3
U O S
4 5 6
N H M C S D
7 8
D E N S I T Y I B B E R N O U L L I
F S I E M S
9 10
E O T N T N T
11 12 13
V X R A N D O M A Z E R O R
A P M G T R I
R E R I M B
14
I C O R R E L A T I O N A U
A T M N L T
15
N U M B E R S I
C D O
16
E D E V I A T I O N
Across Down
2. Random variable that takes on all values in an 1. Random variable that has a countable number of
interval [continuous] possible values [discrete]
7. Type of curve that describes the probability 2. Any linear _ of independent normal random
distribution of a continuous random variable [density] variables is also normally distributed [combination]
8. Swiss family of mathematicians. Jakob made 3. This distribution's density curve looks like a
significant contributions to probability [Bernoulli] rectangle [uniform]
12. A variable whose value is a numerical outcome of 4. Probability distributions of discrete random
a random phenomenon [random] variables can be pictured using a _ [histogram]
13. Probability of an individual outcome in a 5. If X and Y are independent random variables, the
continuous probability distribution [zero] variance of X±Y is the _ of the variances of X and Y
14. When random variables are not independent, the [sum]
variance of their sum depends on the _ between 6. The probability _ of a random variable tells us the
them. [correlation] possible values of X and how probabilities are
15. Law of large _: As the number of observations assigned to those values [distribution]
increases, the mean of the observations approaches 9. The mean of a random variable is called its _ value
the true mean of the population. [numbers] [expected]
16. Square root of the variance: standard _ [deviation] 10. Name for a distribution described by N(mu, sigma)
[normal]
11. A measure of variability around the mean
[variance]
Вам также может понравиться
- Learning Activity Sheets: Quarter 3, Week 5 and 6Документ11 страницLearning Activity Sheets: Quarter 3, Week 5 and 6Jhude JosephОценок пока нет
- Measure of DispersionДокумент24 страницыMeasure of DispersionJaya PrakashОценок пока нет
- Unit 1: Review On FunctionsДокумент50 страницUnit 1: Review On FunctionsNaBi MinОценок пока нет
- Chapter1 Electrostatic 2016 ReviewedДокумент98 страницChapter1 Electrostatic 2016 ReviewedSyaza IzzatyОценок пока нет
- Conditional ProbabilityДокумент3 страницыConditional ProbabilityMelaiitotx DonОценок пока нет
- MATH01 CO1 Lesson 2 Inverse FunctionsДокумент16 страницMATH01 CO1 Lesson 2 Inverse FunctionsMitzie LorraineОценок пока нет
- GenMath Week 1 - 051343Документ61 страницаGenMath Week 1 - 051343Reymark VelascoОценок пока нет
- Final - Copy.2022 2023 Grade 8 Third Periodical ExamДокумент6 страницFinal - Copy.2022 2023 Grade 8 Third Periodical ExamJessalyn De VillaОценок пока нет
- Normal Random VariableДокумент8 страницNormal Random VariableLoraine Buen FranciscoОценок пока нет
- 2.1 PracticeДокумент1 страница2.1 PracticeCatalinaОценок пока нет
- Circle and Related Terms 1Документ15 страницCircle and Related Terms 1John Angel Baring100% (1)
- Gen Math Q1 W2 D1&2Документ8 страницGen Math Q1 W2 D1&2Baems AmborОценок пока нет
- Module 1 Review On FunctionsДокумент50 страницModule 1 Review On FunctionsRonald DalidaОценок пока нет
- Karaoke CodesДокумент9 страницKaraoke CodesDahLinBlazaОценок пока нет
- Math 9 Lesson 1 Quadratic EquationДокумент15 страницMath 9 Lesson 1 Quadratic EquationJosielyn ValladolidОценок пока нет
- 3.3 Measures of Skew and OutliersДокумент42 страницы3.3 Measures of Skew and OutliersVincent WongОценок пока нет
- Test of Hypothesis FinalДокумент7 страницTest of Hypothesis Finalaliyah regacho100% (1)
- Statistics and Probability Act. WorksheetsДокумент21 страницаStatistics and Probability Act. WorksheetsAnne RaveloОценок пока нет
- Mann KendallДокумент4 страницыMann KendallOm Prakash SahuОценок пока нет
- Euler HamДокумент29 страницEuler HamAnonymous ZGIK4H5KОценок пока нет
- Grade 10 LwsonnДокумент18 страницGrade 10 LwsonnReynaldo Jr. SaliotОценок пока нет
- G10 ARithmetic SeriesДокумент17 страницG10 ARithmetic SeriesSalve SerranoОценок пока нет
- Learning Module: Sequences and SeriesДокумент89 страницLearning Module: Sequences and SeriesMaria Martina Delos Santos100% (1)
- The Circle Third EditionДокумент20 страницThe Circle Third EditionBaraka LoibangutiОценок пока нет
- PEA 303 Unit2 - ProbabilityДокумент49 страницPEA 303 Unit2 - ProbabilityVinay Prakash100% (1)
- Collinear Coplanar PointsДокумент9 страницCollinear Coplanar PointsDelgado, Ritchel Ann D.Оценок пока нет
- Packet 0 A - Are You Ready For CalculusДокумент3 страницыPacket 0 A - Are You Ready For CalculusteachopensourceОценок пока нет
- Mathematics: Illustrations of Quadratic EquationsДокумент16 страницMathematics: Illustrations of Quadratic EquationsABIGAIL ROSACEÑAОценок пока нет
- Mathematics: Quarter 4 - Module 35 Analyzing and Interpreting Research DataДокумент26 страницMathematics: Quarter 4 - Module 35 Analyzing and Interpreting Research DataZT EstreraОценок пока нет
- Antiderivatives of Polynomial Functions and Antidifferentiation TheoremsДокумент19 страницAntiderivatives of Polynomial Functions and Antidifferentiation TheoremsAngel Ranel PeñarandaОценок пока нет
- Activity 2.2 Atomic Orbitals - S2-2015Документ10 страницActivity 2.2 Atomic Orbitals - S2-2015Devandra Eko RadityoОценок пока нет
- The Derivative As The Slope of The Tangent Line: (At A Point)Документ20 страницThe Derivative As The Slope of The Tangent Line: (At A Point)Levi LeuckОценок пока нет
- Math 30perm Restrictions ShortДокумент4 страницыMath 30perm Restrictions ShortJanineОценок пока нет
- Inverse FunctionsДокумент23 страницыInverse FunctionsL AlcosabaОценок пока нет
- Mathematics 8, Quarter 4 Week 8: Activity 1 Response All You Can!Документ8 страницMathematics 8, Quarter 4 Week 8: Activity 1 Response All You Can!NylinamОценок пока нет
- Differential Equations 1Документ273 страницыDifferential Equations 1Clarence Sulit QuijanoОценок пока нет
- EstimationДокумент32 страницыEstimationJester RubiteОценок пока нет
- YMS Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyДокумент2 страницыYMS Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyInTerp0ol100% (2)
- YMS Ch7: Random Variables AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyДокумент2 страницыYMS Ch7: Random Variables AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyInTerp0ol100% (2)
- YMS Ch4: More On Two-Variable Data AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyДокумент2 страницыYMS Ch4: More On Two-Variable Data AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyInTerp0ol100% (1)
- YMS Ch6: Probability AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyДокумент2 страницыYMS Ch6: Probability AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyInTerp0olОценок пока нет
- YMS Ch3: Examining Relationships AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyДокумент2 страницыYMS Ch3: Examining Relationships AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyInTerp0ol100% (2)
- YMS Ch9: Sampling Distributions AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyДокумент1 страницаYMS Ch9: Sampling Distributions AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyInTerp0ol100% (1)
- HIVAIDS Answer KeyДокумент1 страницаHIVAIDS Answer KeyKadesha ManswellОценок пока нет
- Movies Television: AcrossДокумент3 страницыMovies Television: Acrossvo phan nghiemОценок пока нет
- POLYNOMIALS Puzzle 1Документ1 страницаPOLYNOMIALS Puzzle 1Sekhar Reddy100% (1)
- Neurology Crossword Puzzle Answer KeyДокумент1 страницаNeurology Crossword Puzzle Answer KeyRavinaAhujaОценок пока нет
- Career CrosswordДокумент2 страницыCareer CrosswordTran MaiОценок пока нет
- M Set TheoryДокумент1 страницаM Set TheoryMarriel Palle TahilОценок пока нет
- Financial Terms Crossword Puzzle Answer Key PDFДокумент1 страницаFinancial Terms Crossword Puzzle Answer Key PDFKilman AguilarОценок пока нет
- Crossword Electricity Answers 1Документ1 страницаCrossword Electricity Answers 1Ralph brian VillarОценок пока нет
- Naming of Inorganic Compounds: Across DownДокумент1 страницаNaming of Inorganic Compounds: Across DownArebeeJayBelloОценок пока нет
- Phase ChangesStates of Matter Answer KeyДокумент1 страницаPhase ChangesStates of Matter Answer KeyKristyne OliciaОценок пока нет
- 21MID0051 SustainableДокумент2 страницы21MID0051 SustainableՏᎡᏆᎠᎬᏙ ՏОценок пока нет
- Epithelium Assignment - Lorenzo, B.Документ2 страницыEpithelium Assignment - Lorenzo, B.Bianca Isabel LorenzoОценок пока нет
- Nervous System Lecture Assignment - Lorenzo, B.Документ1 страницаNervous System Lecture Assignment - Lorenzo, B.Bianca Isabel LorenzoОценок пока нет
- Name: Kristel Faye E. Aglipay Year & Section: Bsn3B: Northwestern University, IncДокумент2 страницыName: Kristel Faye E. Aglipay Year & Section: Bsn3B: Northwestern University, IncKristel FayeОценок пока нет
- Crossword Puzzle Form 3 AnswersДокумент6 страницCrossword Puzzle Form 3 AnswersNur Irdhina AkhtariОценок пока нет
- The Nervous System Answer KeyДокумент1 страницаThe Nervous System Answer KeymichelleОценок пока нет
- Worksheet AnswerkeyДокумент1 страницаWorksheet Answerkeyrik rikОценок пока нет
- YMS Ch7: Random Variables AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyДокумент2 страницыYMS Ch7: Random Variables AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyInTerp0ol100% (2)
- YMS Ch5: Producing Data AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyДокумент2 страницыYMS Ch5: Producing Data AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyInTerp0ol100% (2)
- YMS Ch6: Probability AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyДокумент2 страницыYMS Ch6: Probability AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyInTerp0olОценок пока нет
- YMS Ch4: More On Two-Variable Data AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyДокумент2 страницыYMS Ch4: More On Two-Variable Data AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyInTerp0ol100% (1)
- YMS Ch3: Examining Relationships AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyДокумент2 страницыYMS Ch3: Examining Relationships AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyInTerp0ol100% (2)
- YMS Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyДокумент2 страницыYMS Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyInTerp0ol100% (2)
- YMS Chapter 1: Exploring Data AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyДокумент2 страницыYMS Chapter 1: Exploring Data AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyInTerp0ol100% (4)
- YMS Ch9: Sampling Distributions AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyДокумент1 страницаYMS Ch9: Sampling Distributions AP Statistics at LSHS Mr. MoleskyInTerp0ol100% (1)
- Quantitative Methods or Quantitative All QuizДокумент17 страницQuantitative Methods or Quantitative All QuizHiro GamerОценок пока нет
- Original PDF Statistics For Business Decision Making and Analysis 3rd Edition PDFДокумент41 страницаOriginal PDF Statistics For Business Decision Making and Analysis 3rd Edition PDFalyssa.meiners16297% (33)
- Two-Sample Tests of Hypothesis: ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 2008 Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinДокумент38 страницTwo-Sample Tests of Hypothesis: ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 2008 Mcgraw-Hill/Irwiniracahyaning tyasОценок пока нет
- Lampiran 4: Uji Validitas Dan Reliabilitas: Reliability StatisticsДокумент2 страницыLampiran 4: Uji Validitas Dan Reliabilitas: Reliability StatisticsApril MitchellОценок пока нет
- 2007 Stat Released MC 1 To 20Документ7 страниц2007 Stat Released MC 1 To 20Shelbie ShelderОценок пока нет
- P2 Trial Exam SMK Sacred Heart Sibu (Q )Документ4 страницыP2 Trial Exam SMK Sacred Heart Sibu (Q )Alban HengОценок пока нет
- Psychometric Conversion Table PDFДокумент2 страницыPsychometric Conversion Table PDFMaureen Montanía67% (3)
- Probability-Chapter 1 Random VariablesДокумент92 страницыProbability-Chapter 1 Random VariablesEr Baer80% (5)
- Puc 3103 Fundamentals of Probability and Statistics: Cat IДокумент5 страницPuc 3103 Fundamentals of Probability and Statistics: Cat ImichaelОценок пока нет
- Modern Business Statistics With Microsoft Office Excel 4th Edition Anderson Test BankДокумент26 страницModern Business Statistics With Microsoft Office Excel 4th Edition Anderson Test Bankhebexuyenod8q100% (31)
- Revision Sheet 5 - Stats 1Документ10 страницRevision Sheet 5 - Stats 1Rose WilliamsОценок пока нет
- FitdistrplusДокумент87 страницFitdistrplusPedro Humberto Almeida GonzagaОценок пока нет
- Statistics For Business-IIДокумент3 страницыStatistics For Business-IINagiib Haibe Ibrahim Awale 6107Оценок пока нет
- SHS Statistics and Probability Q3 Mod4 Estimation of Parameters v4Документ29 страницSHS Statistics and Probability Q3 Mod4 Estimation of Parameters v4Charmian70% (10)
- Linear Stationary ModelsДокумент16 страницLinear Stationary ModelsKaled AbodeОценок пока нет
- Statistics How To: The ANOVA TestДокумент24 страницыStatistics How To: The ANOVA TestDebdeep GhoshОценок пока нет
- BZAN6310 Chapter 2Документ79 страницBZAN6310 Chapter 2Jack AgronОценок пока нет
- T-Tests & Chi2Документ35 страницT-Tests & Chi2JANAОценок пока нет
- Ch. 10 Principal Components Analysis (PCA)Документ17 страницCh. 10 Principal Components Analysis (PCA)José António PereiraОценок пока нет
- Chap 013Документ141 страницаChap 013theluckless77750% (2)
- Univariate StatisticsДокумент4 страницыUnivariate StatisticsDebmalya DuttaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2-Statistics The Normal Distribution and The Central Limit TheoremДокумент73 страницыLecture 2-Statistics The Normal Distribution and The Central Limit TheoremDstormОценок пока нет
- Sta301 Finalterm Mcqs With Reference Solved by ArslanДокумент45 страницSta301 Finalterm Mcqs With Reference Solved by ArslanAbd Ul AahОценок пока нет
- STATISTICS-AND-PROBABILITY ContentДокумент6 страницSTATISTICS-AND-PROBABILITY ContentRalph Michael Err ImperialОценок пока нет
- Stats Semester ProjectДокумент11 страницStats Semester Projectapi-276989071Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3: Data PreprocessingДокумент41 страницаChapter 3: Data Preprocessingjozef jostarОценок пока нет
- CAE 21 - Results and Discussions 01-31Документ9 страницCAE 21 - Results and Discussions 01-31Kiro ParafrostОценок пока нет
- Process CapabilityДокумент20 страницProcess CapabilityKaya Eralp AsanОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент3 страницыUntitledapi-262707463Оценок пока нет
- Traffic Data AnalysisДокумент4 страницыTraffic Data AnalysisRachelle C. AbanesОценок пока нет