Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
A Brief History of CALL
Загружено:
Mike BuenoИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
A Brief History of CALL
Загружено:
Mike BuenoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
By: Miguel Bueno Applied Linguistics.
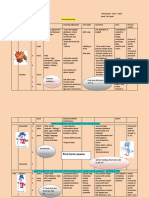
1950s and 1860s
The first computers for language learning wereavailable at
research facilities on universitycampuses. Learners had to leave the classroom and travel to a computer. Students use computers to translate of onelanguage to another. Machine Translation:Application of computers of translating texts. PLATO(1959):system developed by theUniversity of Illinois for the purpose of teachinglanguage. It gave feedback to learners.Grammar translation approach.
1970s and 1980s
Mainframe computers: Room-sizedmachines. Mini computers: like call servers.Microcomputers: like
desktop computers or personal computers Computers were classified into:
Macario: videodisc program for learning Spanish/ Interactive diagram: on-screenvideo provided visual
and listeningoportunities intended to befolloweed up in with in-classconversation. Montevidisco: 1100 branchingchoices allow the learner to pursuedifferent links or lines of enquiry.
ALLP: machines connected to eachother and textual
and visualdatabases through a local areanetwork. Eliza: This program seeks clarification toand simulates a sympathetic listener through series of general comments,requests for explanations andparaphrases of the learnerscomments with additional questiontags.
CALL in the 1990s
Multiplicity of protagonists.
Multiplicity of plot events Knowledge-based choice points
Choice-points based on thetemperament of the
learner Whimisical surprises Multimedia fot presentation Instrinsic rathr than extrinsic rewards
Вам также может понравиться
- A Brief History of Call: Selma Caballero Hernández. Applied LinguisticsДокумент7 страницA Brief History of Call: Selma Caballero Hernández. Applied LinguisticsSelma Caballero HernandezОценок пока нет
- New Learning of Python by Practical Innovation and TechnologyОт EverandNew Learning of Python by Practical Innovation and TechnologyОценок пока нет
- A Brief History of CALLДокумент2 страницыA Brief History of CALLmichelalaОценок пока нет
- A Brief History of CallДокумент10 страницA Brief History of Callmarialex_3Оценок пока нет
- History of Call: (Computer Assisted Language Learning)Документ10 страницHistory of Call: (Computer Assisted Language Learning)Ana Julia ParedesОценок пока нет
- CALL, Technology. Language LearningДокумент18 страницCALL, Technology. Language Learningabdelfattah_moh100% (1)
- Natzyelly BlogДокумент1 страницаNatzyelly Bloglane_1291Оценок пока нет
- Computer Assisted Language Learning: A Brief History of CALLДокумент40 страницComputer Assisted Language Learning: A Brief History of CALLJessie MoronesОценок пока нет
- CALL Through HistoryДокумент2 страницыCALL Through HistoryRodrigo CaballeroОценок пока нет
- A Brief History of CallДокумент10 страницA Brief History of CallPameliiОценок пока нет
- Name of The School: Computer Application ProjectДокумент8 страницName of The School: Computer Application ProjectSabarna DasОценок пока нет
- Computer Generations: ITSC 1401, Intro To ComputersДокумент12 страницComputer Generations: ITSC 1401, Intro To ComputersSahir KhanОценок пока нет
- Generation of ComputerДокумент12 страницGeneration of ComputerJulius Supe-riorОценок пока нет
- Computer GenerationsДокумент15 страницComputer GenerationsSunilОценок пока нет
- Computer Generations: ITSC 1401, Intro To ComputersДокумент12 страницComputer Generations: ITSC 1401, Intro To Computerspooranisrinivasan85Оценок пока нет
- 11computers in Language TeachingДокумент4 страницы11computers in Language TeachingronanjosephdОценок пока нет
- A Brief History of CALLДокумент2 страницыA Brief History of CALLKatjaS21Оценок пока нет
- Sample ThesisДокумент32 страницыSample ThesisbaterbeeОценок пока нет
- GENERATIДокумент12 страницGENERATIAmit Singh RajputОценок пока нет
- Literature Review: A Historical Perspective of CallДокумент12 страницLiterature Review: A Historical Perspective of Calltabassum shafiqОценок пока нет
- What Is CALL ?Документ20 страницWhat Is CALL ?Michelle RangesОценок пока нет
- Lesson 4 Visual Aide SummaryДокумент13 страницLesson 4 Visual Aide SummaryWayneОценок пока нет
- History of Edtech - AbieДокумент40 страницHistory of Edtech - AbieAbegail DfОценок пока нет
- Unit 3. "Technology in The Language Class"Документ2 страницыUnit 3. "Technology in The Language Class"lianata16Оценок пока нет
- Kompüter Tərcümə ProqramlariДокумент65 страницKompüter Tərcümə Proqramlaribagirovanar26Оценок пока нет
- First Generation (1940-1956) Vacuum Tubes: Machine LanguageДокумент2 страницыFirst Generation (1940-1956) Vacuum Tubes: Machine LanguageacciacatauraОценок пока нет
- ProjectДокумент88 страницProjectSivaguru GurusivaОценок пока нет
- Computers GenerationsДокумент7 страницComputers GenerationsBubrikaОценок пока нет
- Generation of Computers and Computers LanguageДокумент11 страницGeneration of Computers and Computers LanguageNidhi Hada JainОценок пока нет
- P - (Operating Systems II)Документ6 страницP - (Operating Systems II)Demal BecirovicОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ7 страницChapter 3Hà PhạmОценок пока нет
- Brief History of CallДокумент5 страницBrief History of CallDoris ViviОценок пока нет
- Call: Overview and History: Prepared By: Dr. Tarfah AlshammariДокумент24 страницыCall: Overview and History: Prepared By: Dr. Tarfah Alshammarinora aliОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Call Electronic PresentationДокумент19 страницFundamentals of Call Electronic Presentationapi-342891415Оценок пока нет
- ICT 9 01 Evolution of Programming LanguagesДокумент33 страницыICT 9 01 Evolution of Programming LanguagesAngela Joy AmparadoОценок пока нет
- CallДокумент12 страницCallapi-387036492Оценок пока нет
- Week 1 DKДокумент18 страницWeek 1 DKDararat KhampusaenОценок пока нет
- K. Anusha 17131A1251Документ13 страницK. Anusha 17131A1251Anusha KandulaОценок пока нет
- The Five Generations of ComputeДокумент11 страницThe Five Generations of Computemuna cliffОценок пока нет
- Structures, System Software, PerformanceДокумент13 страницStructures, System Software, PerformanceHariniОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To MultimediaДокумент6 страницChapter 1 - Introduction To MultimediagcrossnОценок пока нет
- Understanding The ICT On ComputersДокумент54 страницыUnderstanding The ICT On ComputersSync KichiiОценок пока нет
- Infot 1 - Chapter 1Документ12 страницInfot 1 - Chapter 1ArianneОценок пока нет
- Vicmairy Charles Laureano: Politecnico Liliam BayonaДокумент8 страницVicmairy Charles Laureano: Politecnico Liliam BayonaVicky CharlesОценок пока нет
- History of ComputerДокумент10 страницHistory of Computerapi-422166600100% (1)
- Arm Assembly Language ProgrammingДокумент170 страницArm Assembly Language ProgrammingAnup Kumar Yadav100% (4)
- Computer-Assisted Translation ToolsДокумент1 страницаComputer-Assisted Translation ToolsDenisa NeagoeОценок пока нет
- Computer Project Ms PowerpointДокумент8 страницComputer Project Ms PowerpointYashas KumarОценок пока нет
- History of CallДокумент1 страницаHistory of CallItalia GarcíaОценок пока нет
- History of EdTechДокумент42 страницыHistory of EdTechMhariah My-an Manrique100% (2)
- Fundamentals of MultimediaДокумент53 страницыFundamentals of MultimediaBindu Devender Mahajan100% (2)
- The Five Generations of ComputeДокумент11 страницThe Five Generations of ComputeblessaОценок пока нет
- ARM Assembly Language Programming: Peter KnaggsДокумент172 страницыARM Assembly Language Programming: Peter KnaggsbklОценок пока нет
- Machine Translation and Human Translation: in Competition or in Complementation?Документ10 страницMachine Translation and Human Translation: in Competition or in Complementation?lukasinski23Оценок пока нет
- Img 0007Документ24 страницыImg 0007Jayesh ShindeОценок пока нет
- Homework - Week 17Документ3 страницыHomework - Week 17Azucena Ramírez SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Generation of ComputersДокумент4 страницыGeneration of ComputersMohammed Abu ShaibuОценок пока нет
- What Is ComputerДокумент2 страницыWhat Is ComputerDAS INFOTECH WBОценок пока нет
- Personal Best - Upper Intermediate SyllabusДокумент2 страницыPersonal Best - Upper Intermediate Syllabusbaksi100% (1)
- The Study of Fiction and Non FictionДокумент40 страницThe Study of Fiction and Non FictionMaeca Angela SerranoОценок пока нет
- W4 LP Precalculus 11Документ6 страницW4 LP Precalculus 11Jerom B CanayongОценок пока нет
- SMJK Convent Datuk Keramat Pulau Pinang Final Examination 2019 English Paper 2 Form 1 1 Hour Name: - Class: - (20 MARKS)Документ2 страницыSMJK Convent Datuk Keramat Pulau Pinang Final Examination 2019 English Paper 2 Form 1 1 Hour Name: - Class: - (20 MARKS)Noel KlОценок пока нет
- Author's Purpose Blog RubricДокумент2 страницыAuthor's Purpose Blog Rubricleigh_marcischakОценок пока нет
- DYZENHAUS - Hobbes and The Legitimacy of LawДокумент39 страницDYZENHAUS - Hobbes and The Legitimacy of LawmehrbuchОценок пока нет
- Marriage Biodata Format For A Muslim GirlДокумент1 страницаMarriage Biodata Format For A Muslim GirlSrinivas Krishnaswamy41% (29)
- 18 Postcolonialism: Julia LossauДокумент9 страниц18 Postcolonialism: Julia Lossaujuancr3Оценок пока нет
- Civil Code of The Phil. Tolentino Chapter SummaryДокумент3 страницыCivil Code of The Phil. Tolentino Chapter SummaryBrian Balio100% (3)
- Oh The Thinks You Can ThinkДокумент2 страницыOh The Thinks You Can ThinkFady Abulsoud100% (1)
- Simon Leys - Introduction - The Analects of ConfuciusДокумент15 страницSimon Leys - Introduction - The Analects of ConfuciusChester Feng50% (2)
- Nasir Khusraw HunsbergerДокумент10 страницNasir Khusraw Hunsbergerstudnt07Оценок пока нет
- Ateneo de Zamboanga University Telephone Directory: ND RDДокумент2 страницыAteneo de Zamboanga University Telephone Directory: ND RD蔡松柏Оценок пока нет
- 08 Cognitive Behavioral TreatmentДокумент10 страниц08 Cognitive Behavioral TreatmentAnderson GaldinoОценок пока нет
- Korean Honorifics: Important Titles, Words, & PhrasesДокумент11 страницKorean Honorifics: Important Titles, Words, & PhrasesCESH50% (2)
- ENG-116: Branches of Linguistics: Books) .Farmer, A. K Demers, R. A. A Linguistics WorkbookДокумент6 страницENG-116: Branches of Linguistics: Books) .Farmer, A. K Demers, R. A. A Linguistics WorkbookBILAL ZAFARОценок пока нет
- A Report On The Movement To Reconnect Children To The Natural World 2009Документ55 страницA Report On The Movement To Reconnect Children To The Natural World 2009Children & Nature Network Resource LibraryОценок пока нет
- Chapter-2 The Oromo of EthiopiaДокумент46 страницChapter-2 The Oromo of Ethiopiaልጅ እያሱОценок пока нет
- ELLevate Teacher Resource Guide PDFДокумент744 страницыELLevate Teacher Resource Guide PDFnicole4reyes-4301040% (1)
- Levels of FormalityДокумент18 страницLevels of Formalityapi-259573881Оценок пока нет
- Styles and RegistersДокумент4 страницыStyles and RegisterspeterekaОценок пока нет
- What Does It Mean To Be Global CitizenДокумент4 страницыWhat Does It Mean To Be Global Citizenapi-499948660Оценок пока нет
- Art Integration Lesson Plan Template: Know.Документ8 страницArt Integration Lesson Plan Template: Know.api-311755668Оценок пока нет
- Digital Art and Meaning Roberto SimanowskiДокумент24 страницыDigital Art and Meaning Roberto SimanowskirugitusОценок пока нет
- Keiichi 2009 Nishida Kitarō As Philosopher of ScienceДокумент8 страницKeiichi 2009 Nishida Kitarō As Philosopher of ScienceJacqueCheОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - The Principle of Fashion - The NewДокумент15 страницChapter 2 - The Principle of Fashion - The NewyhiОценок пока нет
- Thus at Least Presuppose, and Should Perhaps Make Explicit, A Normative AccountДокумент5 страницThus at Least Presuppose, and Should Perhaps Make Explicit, A Normative AccountPio Guieb AguilarОценок пока нет
- التوزيع السنوي لجميع المستوياتДокумент17 страницالتوزيع السنوي لجميع المستوياتothmaneОценок пока нет
- Roaring 20s PPДокумент11 страницRoaring 20s PPapi-385685813Оценок пока нет